Abstract
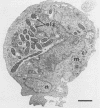
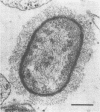
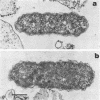
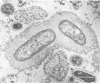
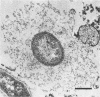
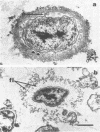
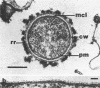
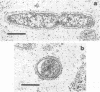
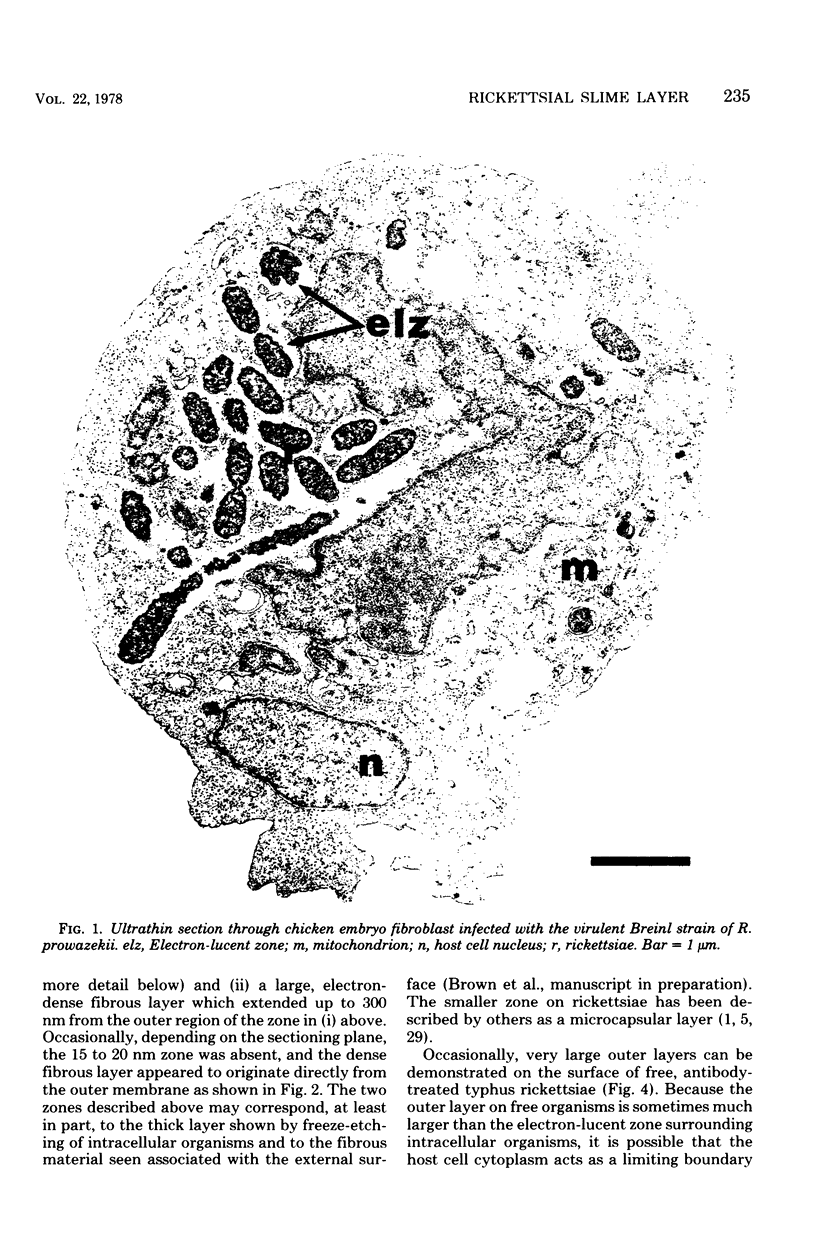
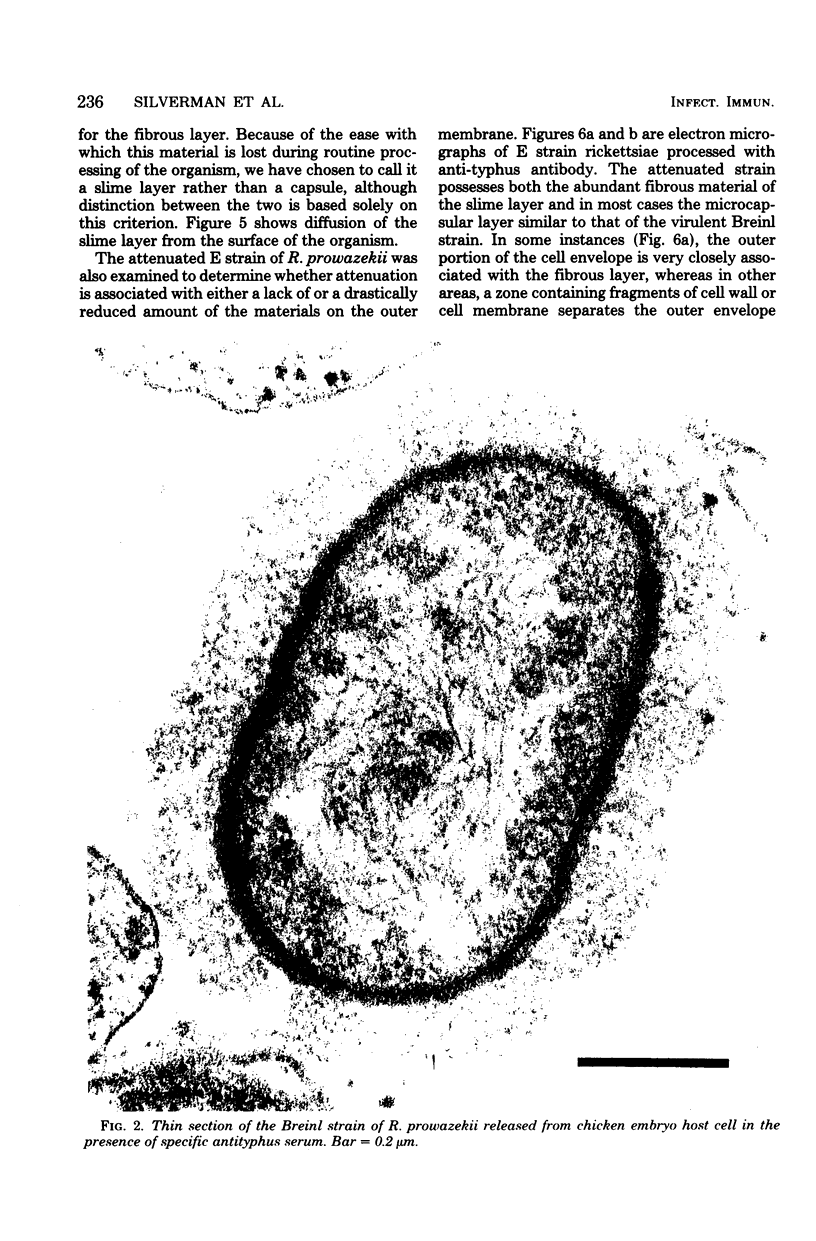
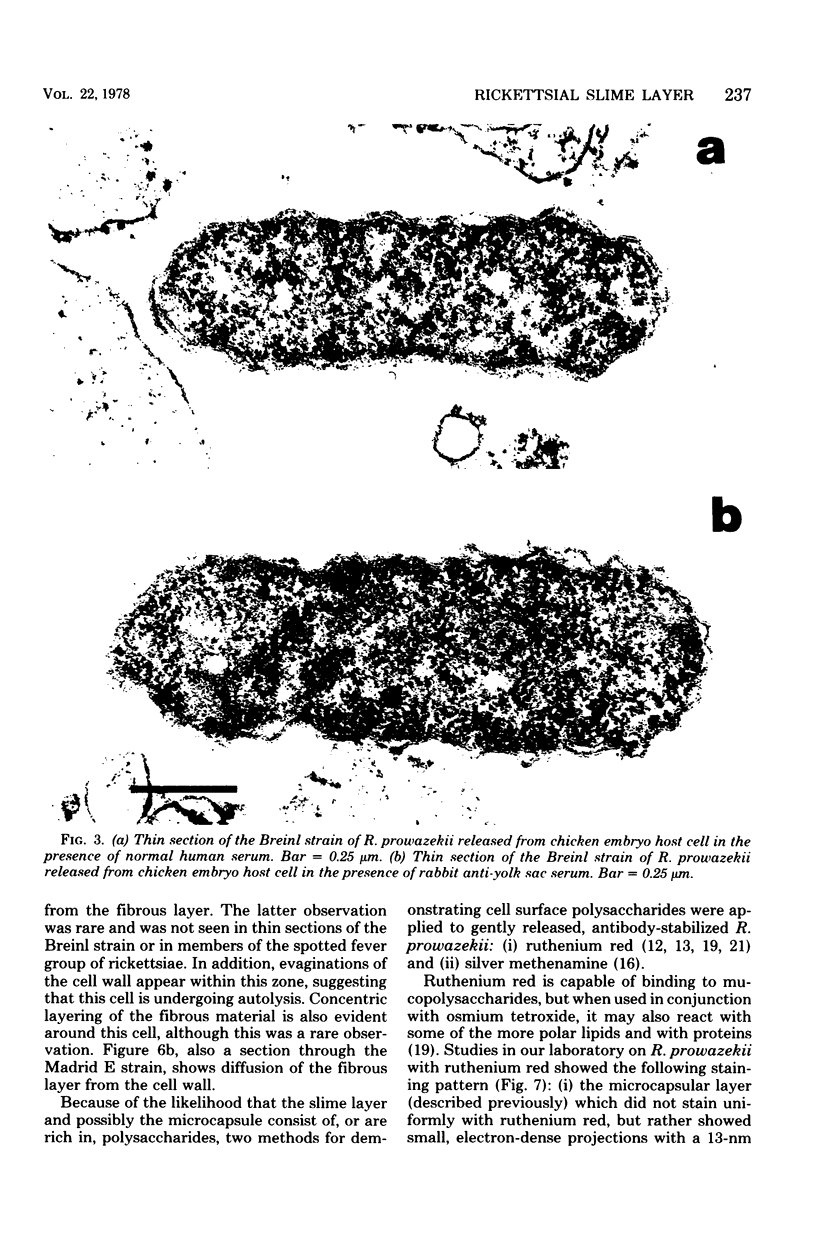
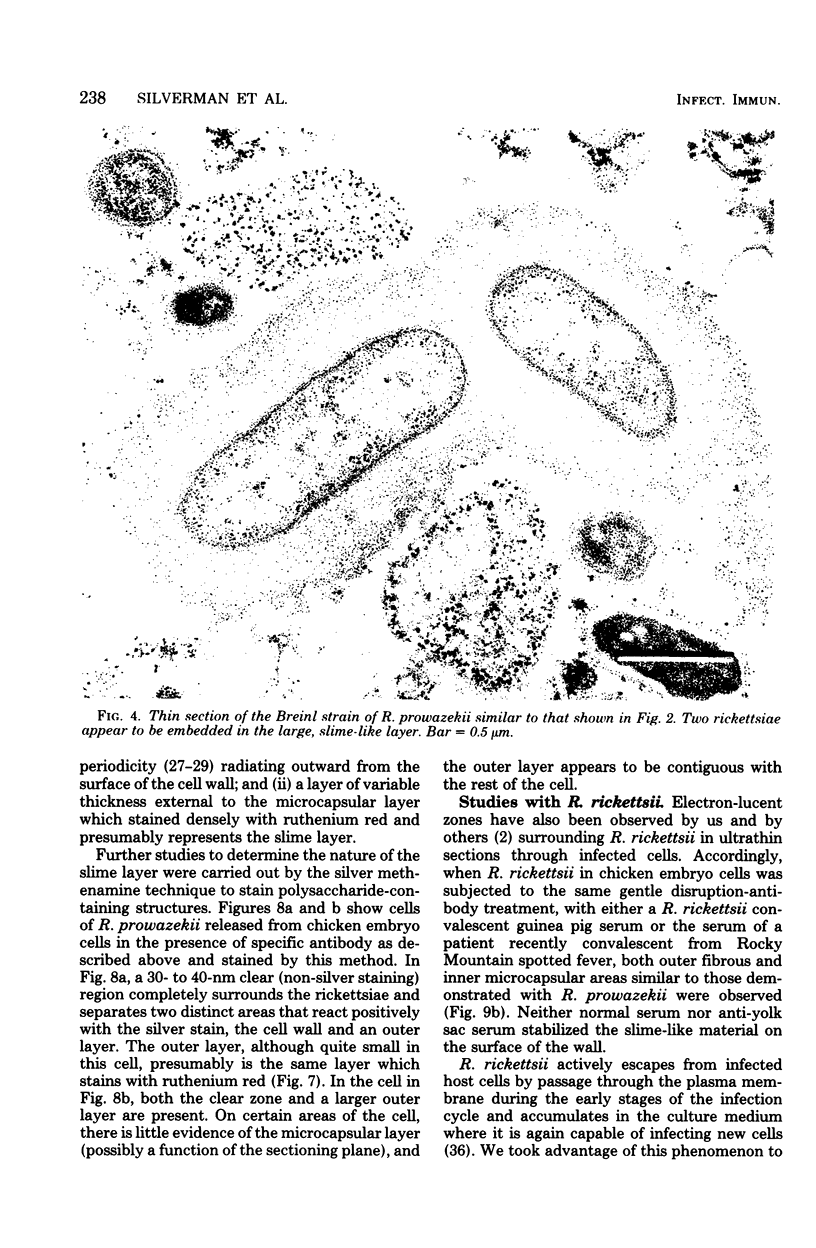
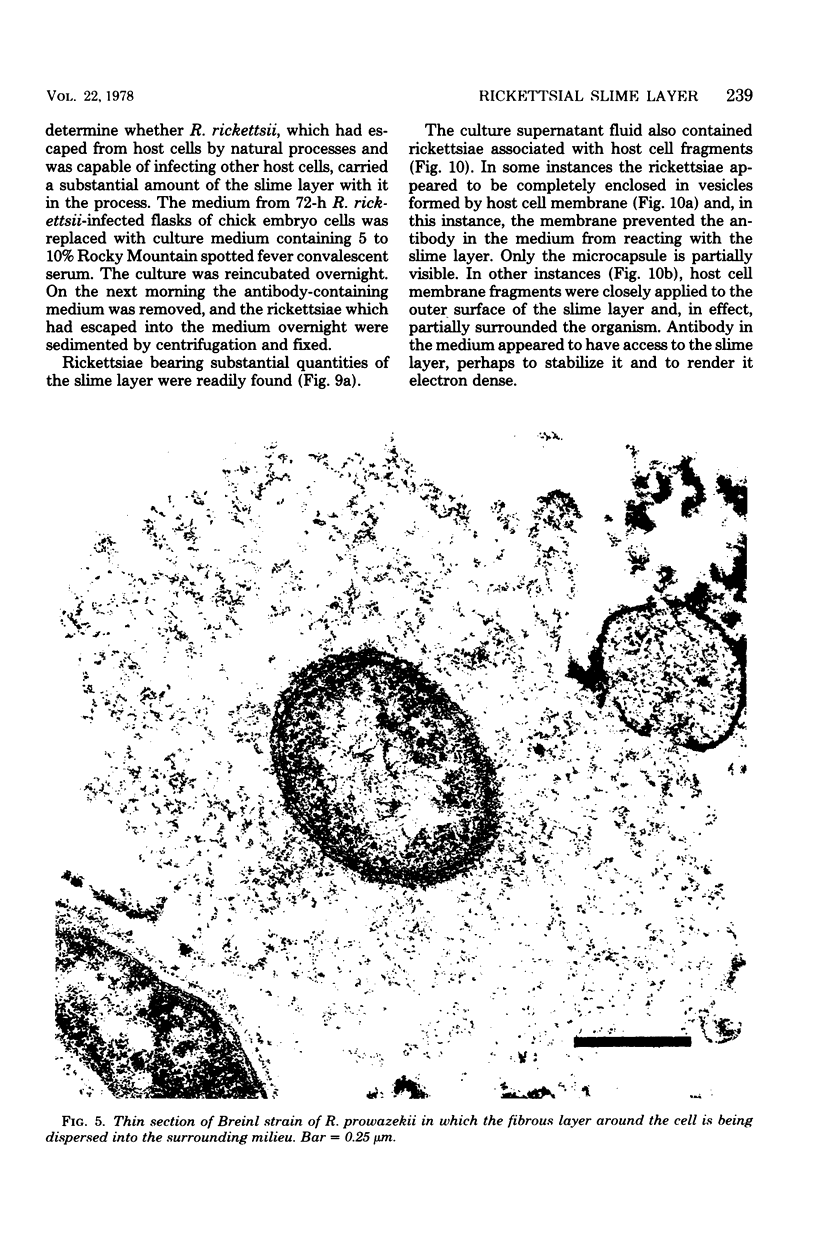
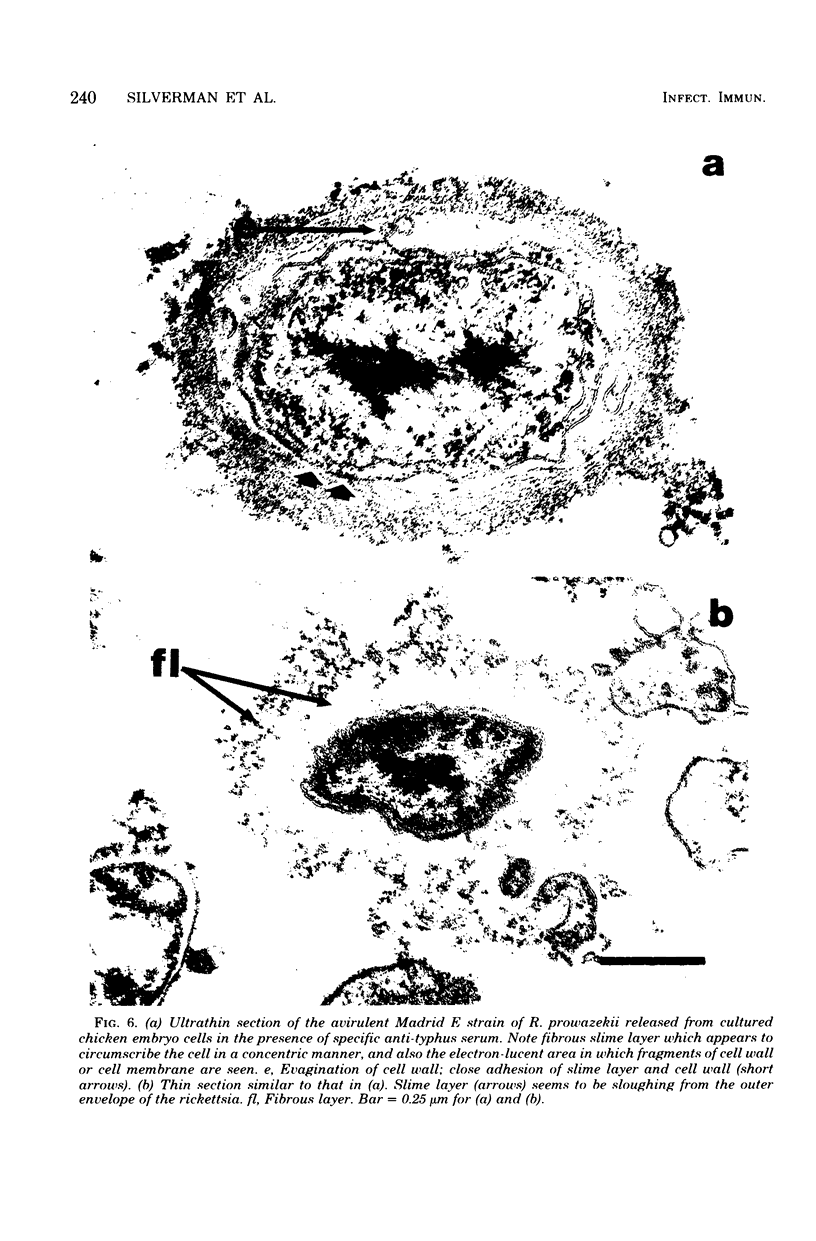
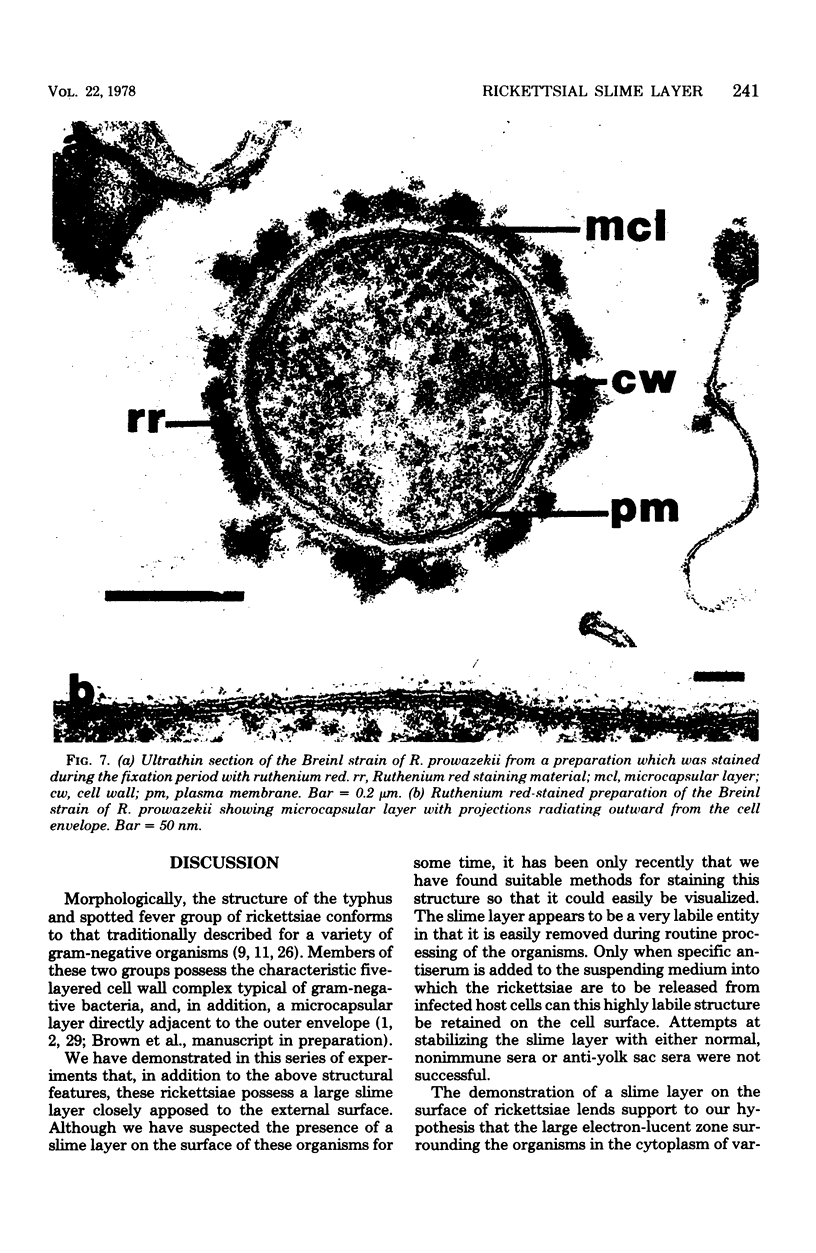
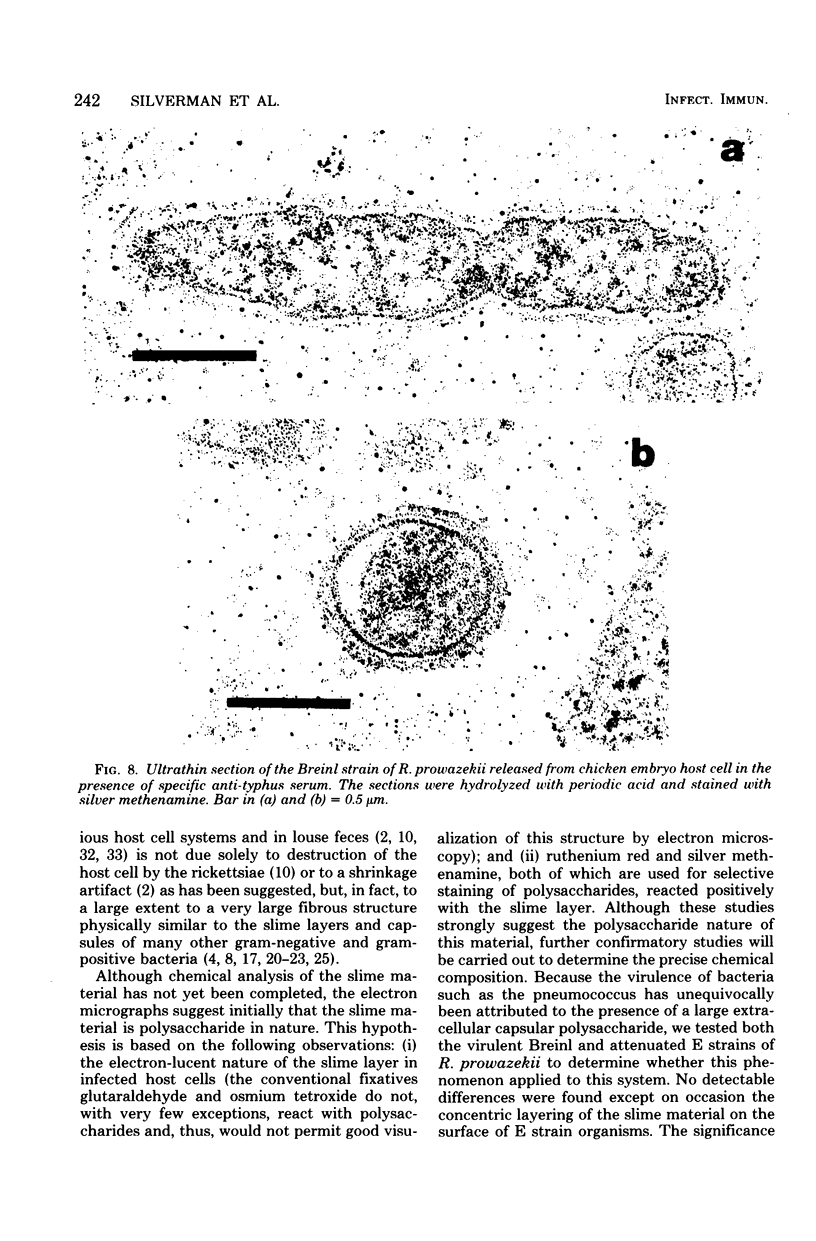
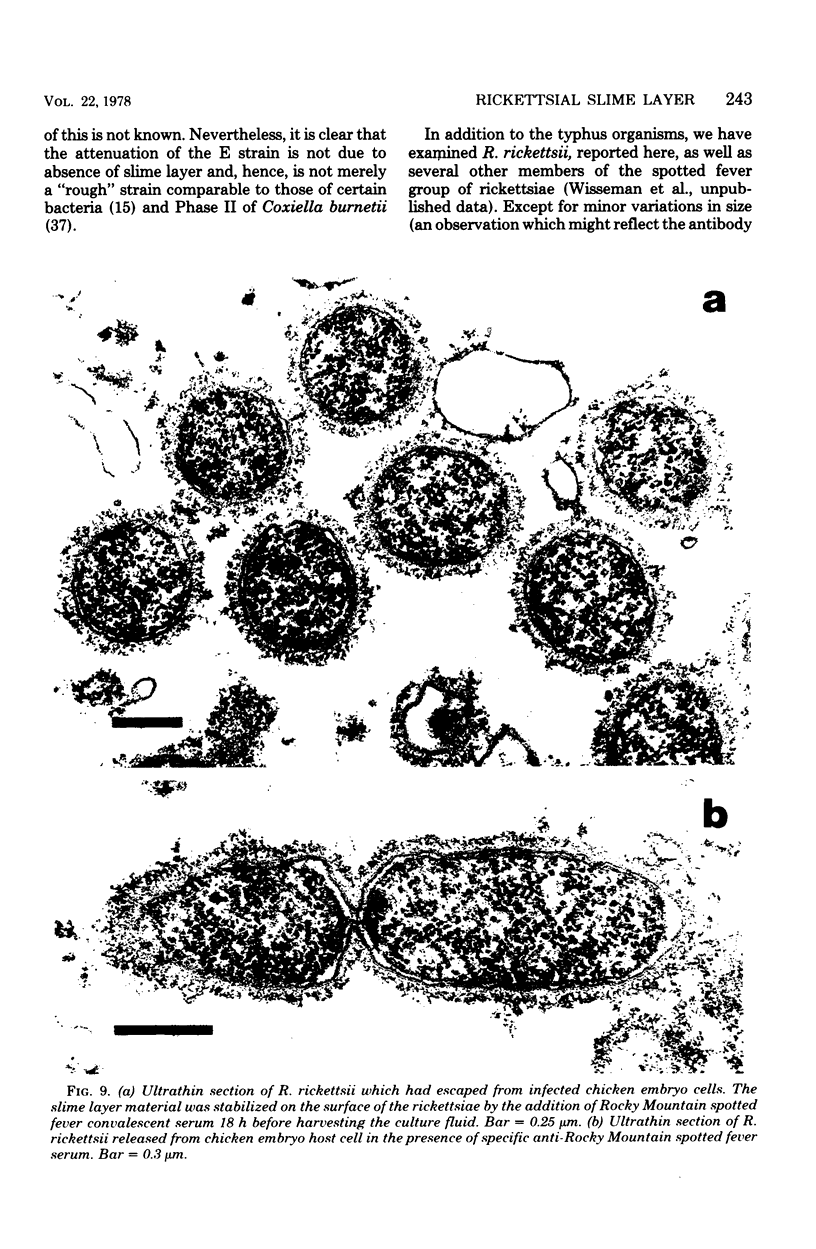
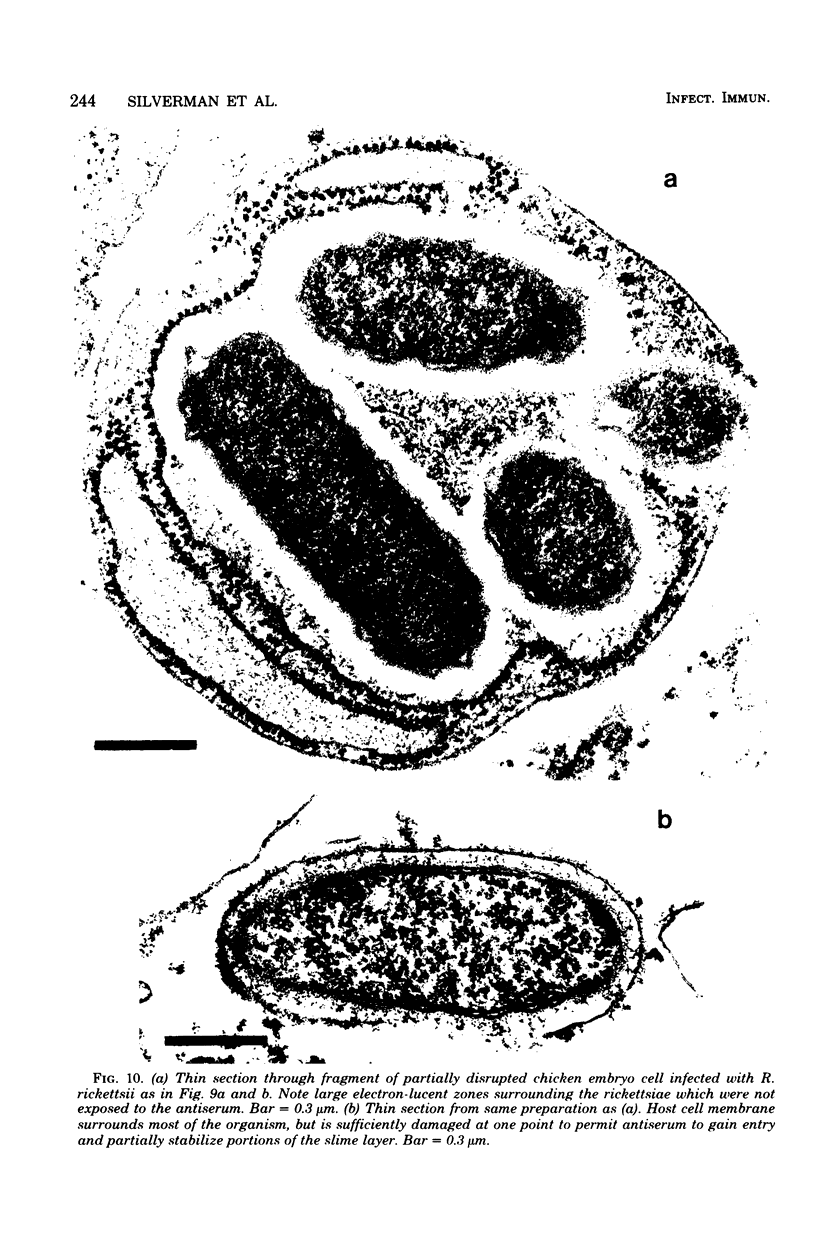
Using a simple specific-antibody stabilization procedure on organisms gently liberated from their host cells, we have demonstrated by electron microscopy that Rickettsia prowazekii and Rickettsia rickettsii possess a coat of variable thickness, external to the outer leaflet of the cell wall and the structure designated by others as a "microcapsule," which corresponds most closely to the slime layer of certain other bacteria. Reactions in the methenamine silver and ruthenium red staining procedures and the failure to be visualized by standard procedures suggest that the slime layer is largely polysaccharide in nature. It is postulated that this slime layer accounts in large part for the large, electron-lucent, halo-like zone which is found by electron microscopy to surround organisms of the typhus and spotted fever groups in the cytoplasm of their host cells, that it may be the locus of some major group-specific antigens, and that it may function as an antiphagocytic mechanism, as an aid for attachment of rickettsiae to potential host cells, or both. Moreover, because the attenuated E strain of R. prowazekii has been shown to possess a substantial slime layer, the basis for attenuation is not likely to be a simple smooth-to-rough variation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., Pickens E. G., Lackman D. B. Details of the ultrastructure of Rickettsia prowazekii grown in the chick yolk sac. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):260–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.260-262.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. R., Hopps H. E., Barile M. F., Bernheim B. C. Comparison of the ultrastructure of several rickettsiae, ornithosis virus, and Mycoplasma in tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1387–1404. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1387-1404.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. F., Loosli C. G. The ultrastructure of encapsulated Diplococcus pneumoniae type 1 before and after exposure to type specific antibody. Lab Invest. 1966 Apr;15(4):716–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balayeva N. M., Gulevskaya S. A. Comparative characteristics of "ether" and "non-ether" soluble ricketssia prowazekii antigens and electron microscopy findings on the morphology of the rickettsiae during isolation of the antigens. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1972;16(1):92–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balayeva N. M., Zubok L. P., Nikolskaya V. N. Soluble antigen of Rickettsia prowazeki. Acta Virol. 1966 Mar;10(2):161–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Thurow H. Polysaccharide capsule of Escherichia coli: microscope study of its size, structure, and sites of synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):911–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.911-936.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Rehn K. Chemical characterization, spatial distribution and function of a lipoprotein (murein-lipoprotein) of the E. coli cell wall. The specific effect of trypsin on the membrane structure. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Oct;10(3):426–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton L. P., Burgdorfer W. Fine structure of Rickettsia canada in tissues of Dermacentor andersoni Stiles. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1149–1159. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1149-1159.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett I. D., Murray R. G. Septum formation in Escherichia coli: characterization of septal structure and the effects of antibiotics on cell division. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):303–324. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.303-324.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. R., Stueckemann J., Paretsky D. Electron microscopy studies of the limiting layers of the rickettsia Coxiella burneti. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):316–324. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.316-324.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciampor F., Schramek S., Brezina R. Electron microscopy of ruthenium red-stained phase I and II Coxiella burneti. Acta Virol. 1972 Nov;16(6):503–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Geesey G. G., Cheng K. J. How bacteria stick. Sci Am. 1978 Jan;238(1):86–95. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0178-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhir S. P., Boatman E. S. Location of polysaccharide on Chlamydia psittaci by silver-methenamine staining and electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):267–271. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.267-271.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doern G. V., Buckmire F. L. Ultrastructural characterization of capsulated Haemophilus influenzae type b and two spontaneous nontypable mutants. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):523–535. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.523-535.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambrill M. R., Wisseman C. L., Jr Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infections. 3. Influence of human immune serum and complement on the fate of Rickettsia mooseri within the human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):631–640. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.631-640.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendley J. W., Powell K. R., Rodewald R., Holzgrefe H. H., Lyles R. Demonstration of a capsule on Neisseria gonorrhoeae. N Engl J Med. 1977 Mar 17;296(11):608–611. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197703172961105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. C., Roth I. L., Sanders W. M., 3rd Electron microscopic study of a slime layer. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):316–325. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.316-325.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L. The polysaccharide capsule of Bacteroides fragilis subspecies fragilis: immunochemical and morphologic definition. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):79–87. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C., Listgarten M., Rosan B. Serology of Streptococcus sanguis: localization of antigens with unlabeled antisera. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):475–481. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.475-481.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., STEED P., ELSON H. E. THE LOCATION OF THE MUCOPEPTIDE IN SECTIONS OF THE CELL WALL OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND OTHER GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Jun;11:547–560. doi: 10.1139/m65-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melly M. A., Duke L. J., Liau D. F., Hash J. H. Biological properties of the encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.389-397.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E. L., Mallavia L. P., Tzianabos T., Obijeski J. F. Electron microscopy of the cell wall of Rickettsia prowazeki. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):1158–1166. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.1158-1166.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E. L., Martin M. L., Mallavia L. Ultrastucture of the surface of Rickettsia prowazeki and Rickettsia akari. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):713–716. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.713-716.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popov V. L., Ignatovich V. F. Electron microscopy of surface structures of Rickettsia prowazeki stained with ruthenium red. Acta Virol. 1976 Oct;20(5):424–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Weekly Reports for May 31, 1946. Public Health Rep. 1946 May 31;61(22):761–800. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W. Localization of Somatic Antigen on Gram-Negative Bacteria by Electron Microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):266–270. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.266-270.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Boese J. L., Wisseman C. L., Jr Ultrastructural studies of Rickettsia prowazeki from louse midgut cells to feces: search for "dormant" forms. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):257–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.257-263.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzianabos T., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F., Martin M. L. Origin and structure of the group-specific, complement-fixing antigen of Rickettsia rickettsii. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Sep;28(3):481–488. doi: 10.1128/am.28.3.481-488.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISSEMAN C. L., Jr, TABOR H. INTERACTION OF RICKETTSIAE AND PHAGOCYTIC HOST CELLS. IV. EARLY CELLULAR RESPONSE OF MAN TO TYPHUS RICKETTSIAE AS REVEALED BY THE SKIN WINDOW TECHNIQUE, WITH OBSERVATIONS ON IN VIVO PHAGOCYTOSIS. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:816–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Edlinger E. A., Waddell A. D., Jones M. R. Infection cycle of Rickettsia rickettsii in chicken embryo and L-929 cells in culture. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1052–1064. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1052-1064.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Fiset P., Ormsbee R. A. Interaction of rickettsiae and phagocytic host cells. V. Phagocytic and opsonic interactions of phase 1 and phase 2 Coxiella burneti with normal and immune human leukocytes and antibodies. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):669–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D. In vitro studies on rickettsia-host cell interactions: intracellular growth cycle of virulent and attenuated Rickettsia prowazeki in chicken embryo cells in slide chamber cultures. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1391–1404. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1391-1401.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D., Silverman D. J. In vitro studies on Rickettsia-host cell interactions: lag phase in intracellular growth cycle as a function of stage of growth of infecting Rickettsia prowazeki, with preliminary observations on inhibition of rickettsial uptake by host cell fragments. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1749–1760. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1749-1760.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]