Abstract
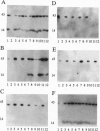
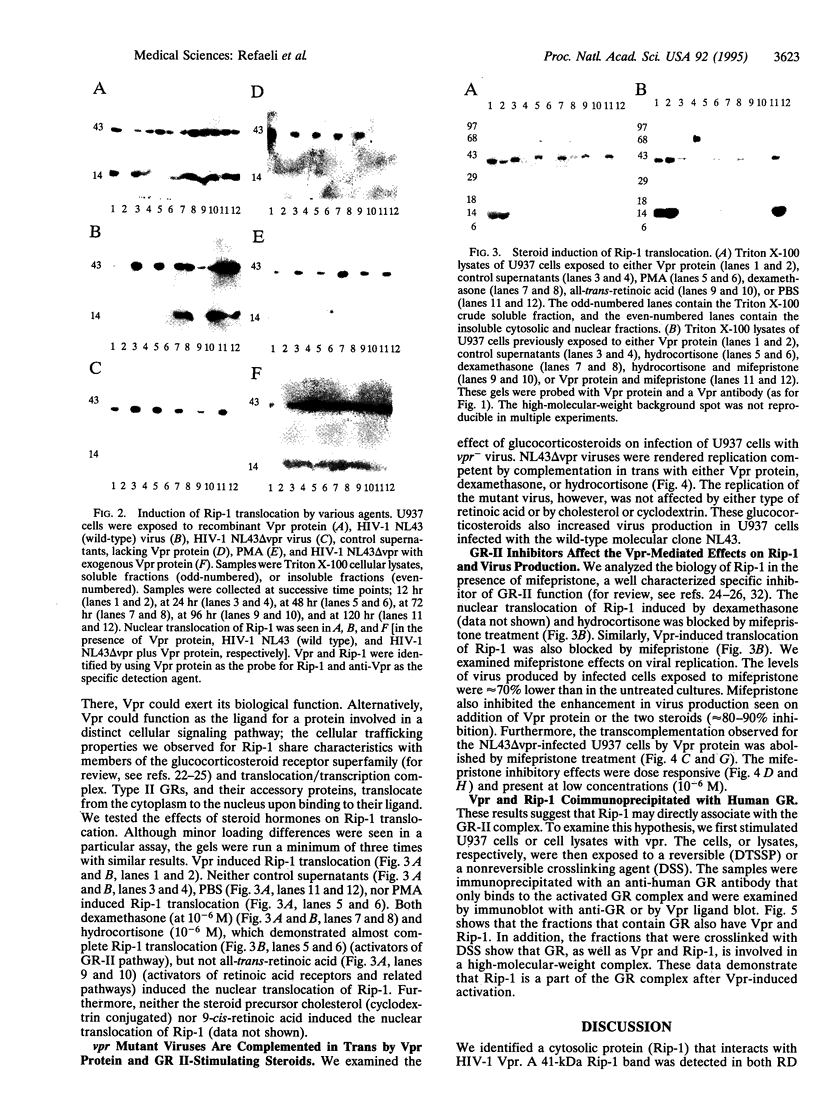
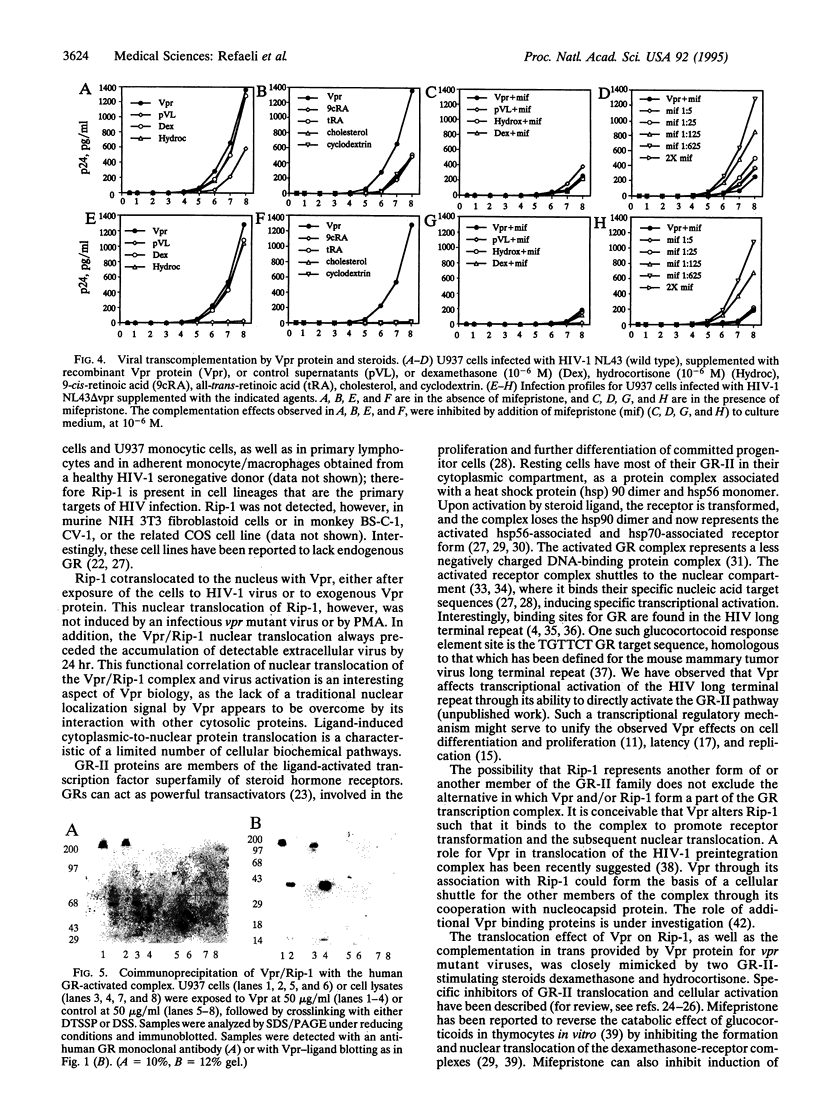
The vpr gene of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) encodes a 15-kDa virion-associated protein that functions as a regulator of cellular processes linked to the HIV life cycle. We report the interaction of a 41-kDa cytosolic viral protein R interacting protein 1 (Rip-1) with Vpr in vitro. Rip-1 displays a wide tissue distribution, including relevant targets of HIV infection. Vpr protein induced nuclear translocation of Rip-1, as did glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-II-stimulating steroids. Importantly, Vpr and Rip-1 coimmunoprecipitated with the human GR as part of an activated receptor complex. Vpr complementation of a vpr mutant virus was also mimicked by GR-II-stimulating steroids. Vpr and GR-II actions were inhibited by mifepristone, a GR-II pathway inhibitor. Together these data directly link the activity of the vpr gene product to the glucocorticoid steroid pathway and provide a biochemical mechanism for the cellular and viral activity of Vpr, as well as suggest that a unique class of antivirals, which includes mifepristone (RU486), may influence HIV-1 replication.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal M. K., Hainque B., Moustaid N., Lazer G. Glucocorticoid antagonists. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 15;217(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80667-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakke O. Antagonistic effect of glucocorticoids on retinoic acid induced growth inhibition and morphological alterations of a human cell line. Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1275–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balotta C., Lusso P., Crowley R., Gallo R. C., Franchini G. Antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides targeted to the vpr gene inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in primary human macrophages. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4409–4414. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4409-4414.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodine P. V., Litwack G. The glucocorticoid receptor and its endogenous regulators. 1990-1991 WinterReceptor. 1(1-2):83–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. A., Dehni G., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Human immunodeficiency virus vpr product is a virion-associated regulatory protein. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3097–3099. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3097-3099.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. A., Terwilliger E. F., Jalinoos Y., Proulx J., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Identification of HIV-1 vpr product and function. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(1):11–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedera D., Hu W., Vander Heyden N., Ratner L. Viral protein R of human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 is dispensable for replication and cytopathogenicity in lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3205–3208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3205-3208.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich J. B., Chasserot-Golaz S., Beck G., Bauer G. Antagonism of glucocorticoid induction of Epstein-Barr virus early antigens by different steroids in Daudi lymphoma cells. J Steroid Biochem. 1986 Jan;24(1):417–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(86)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D. Glucocorticoid receptor-binding site in the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):586–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.586-590.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronemeyer H., Benhamou B., Berry M., Bocquel M. T., Gofflo D., Garcia T., Lerouge T., Metzger D., Meyer M. E., Tora L. Mechanisms of antihormone action. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;41(3-8):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90347-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A. Molecular biology of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2349–2360. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.1829694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori N., Michaels F., Fargnoli K., Marcon L., Gallo R. C., Franchini G. The human immunodeficiency virus type 2 vpr gene is essential for productive infection of human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8080–8084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzinger N. K., Bukrinsky M. I., Haggerty S. A., Ragland A. M., Kewalramani V., Lee M. A., Gendelman H. E., Ratner L., Stevenson M., Emerman M. The Vpr protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 influences nuclear localization of viral nucleic acids in nondividing host cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7311–7315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsanakis C. D., Sekeris C. E., Spandidos D. A. The human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat contains sequences showing partial homology to glucocorticoid responsive elements. Anticancer Res. 1991 Jan-Feb;11(1):381–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnitchenko V., Snart R. S. Regulatory elements in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat LTR (HIV-1) responsive to steroid hormone stimulation. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Dec;8(12):1977–1980. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang S. M., Weeger M., Stahl-Hennig C., Coulibaly C., Hunsmann G., Müller J., Müller-Hermelink H., Fuchs D., Wachter H., Daniel M. M. Importance of vpr for infection of rhesus monkeys with simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):902–912. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.902-912.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavallée C., Yao X. J., Ladha A., Göttlinger H., Haseltine W. A., Cohen E. A. Requirement of the Pr55gag precursor for incorporation of the Vpr product into human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viral particles. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1926–1934. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1926-1934.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar G., Agarwal M. K. Evidence for an antagonist specific receptor that does not bind mineralocorticoid agonists. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90556-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. N., Fernandes L. S., Williams W. V., Weiner D. B. Induction of cell differentiation by human immunodeficiency virus 1 vpr. Cell. 1993 Feb 26;72(4):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90073-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. N., Refaeli Y., MacGregor R. R., Weiner D. B. Serum Vpr regulates productive infection and latency of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10873–10877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):183–289. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.183-289.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindemeyer R. G., Robertson N. M., Litwack G. Glucocorticoid receptor monoclonal antibodies define the biological action of RU 38486 in intact B16 melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 15;50(24):7985–7991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y. L., Spearman P., Ratner L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viral protein R localization in infected cells and virions. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6542–6550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6542-6550.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madan A. P., DeFranco D. B. Bidirectional transport of glucocorticoid receptors across the nuclear envelope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3588–3592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Forbes D. J. Nuclear import can be separated into distinct steps in vitro: nuclear pore binding and translocation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):641–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90402-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K., Shibata R., Kiyomasu T., Higuchi I., Kishida Y., Ishimoto A., Adachi A. Mutational analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus vpr open reading frame. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4110–4114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4110-4114.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paxton W., Connor R. I., Landau N. R. Incorporation of Vpr into human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions: requirement for the p6 region of gag and mutational analysis. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7229–7237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7229-7237.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrot-Applanat M., Guiochon-Mantel A., Milgrom E. Immunolocalization of steroid hormone receptors in normal and tumour cells: mechanisms of their cellular traffic. Cancer Surv. 1992;14:5–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Two signals mediate hormone-dependent nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3333–3340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Prefontaine K. E. Physical association and functional antagonism between the p65 subunit of transcription factor NF-kappa B and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):752–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Mills A. D., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Nuclear protein migration involves two steps: rapid binding at the nuclear envelope followed by slower translocation through nuclear pores. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata R., Miura T., Hayami M., Ogawa K., Sakai H., Kiyomasu T., Ishimoto A., Adachi A. Mutational analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) genome in relation to HIV-1 and simian immunodeficiency virus SIV (AGM). J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):742–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.742-747.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. K., Albers M. W., Chang H., Faber L. E., Schreiber S. L. Association of a 59-kilodalton immunophilin with the glucocorticoid receptor complex. Science. 1992 May 29;256(5061):1315–1318. doi: 10.1126/science.1376003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. B., Liu J., Cohen J. A., Williams W. V., Greene M. I. A point mutation in the neu oncogene mimics ligand induction of receptor aggregation. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):230–231. doi: 10.1038/339230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt P., Henkel T., Trowbridge D. B., Orenstein J., Heuser J., Gendelman H. E., Ratner L. Dual regulation of silent and productive infection in monocytes by distinct human immunodeficiency virus type 1 determinants. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3925–3931. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3925-3931.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan X., Matsuda Z., Matsuda M., Essex M., Lee T. H. Human immunodeficiency virus vpr gene encodes a virion-associated protein. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Nov;6(11):1265–1271. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao L. J., Mukherjee S., Narayan O. Biochemical mechanism of HIV-I Vpr function. Specific interaction with a cellular protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15577–15582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]