Abstract
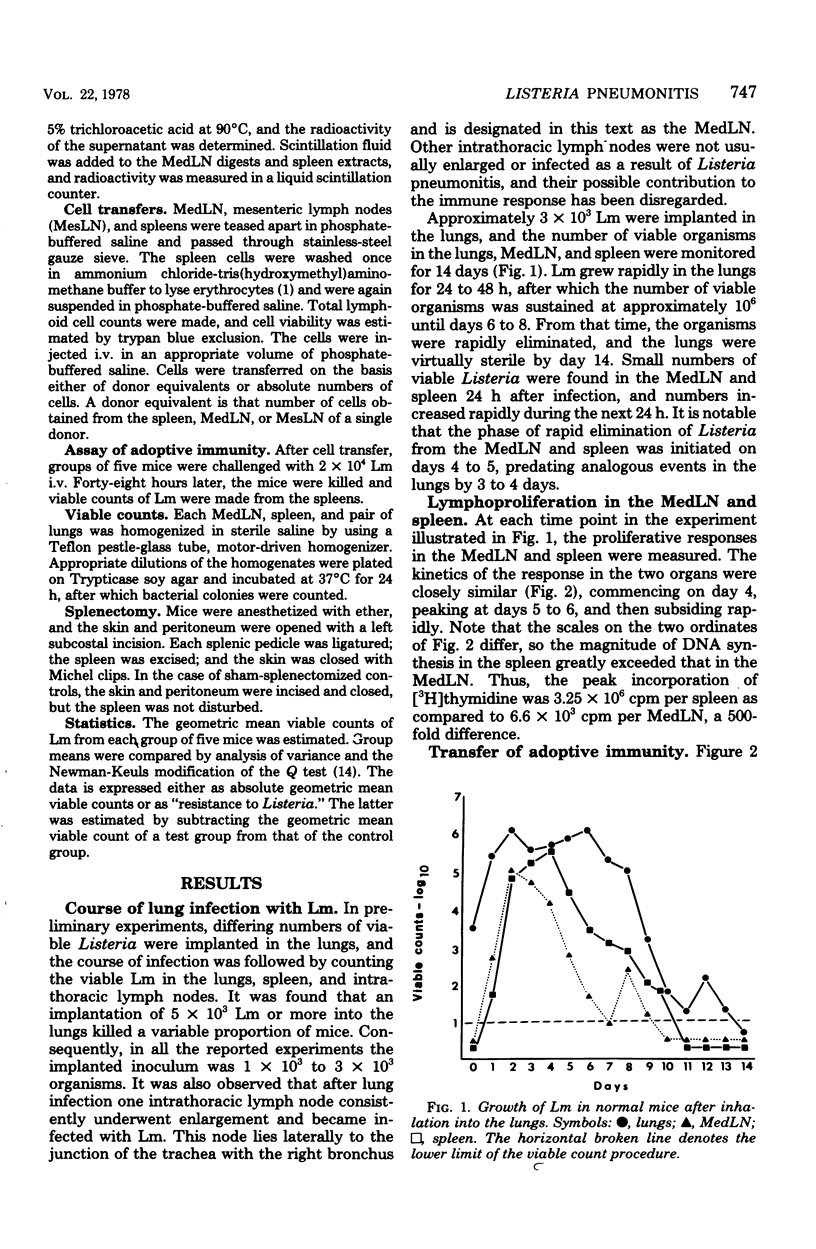
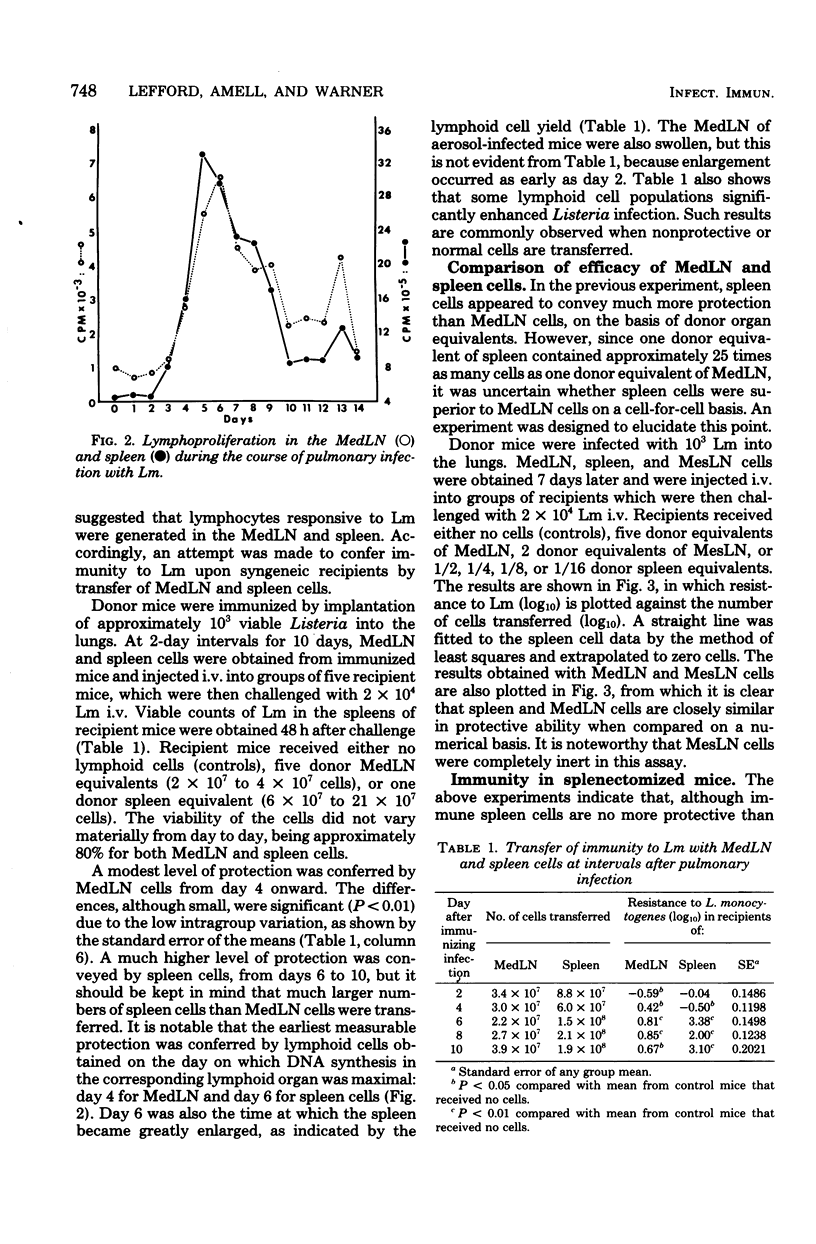
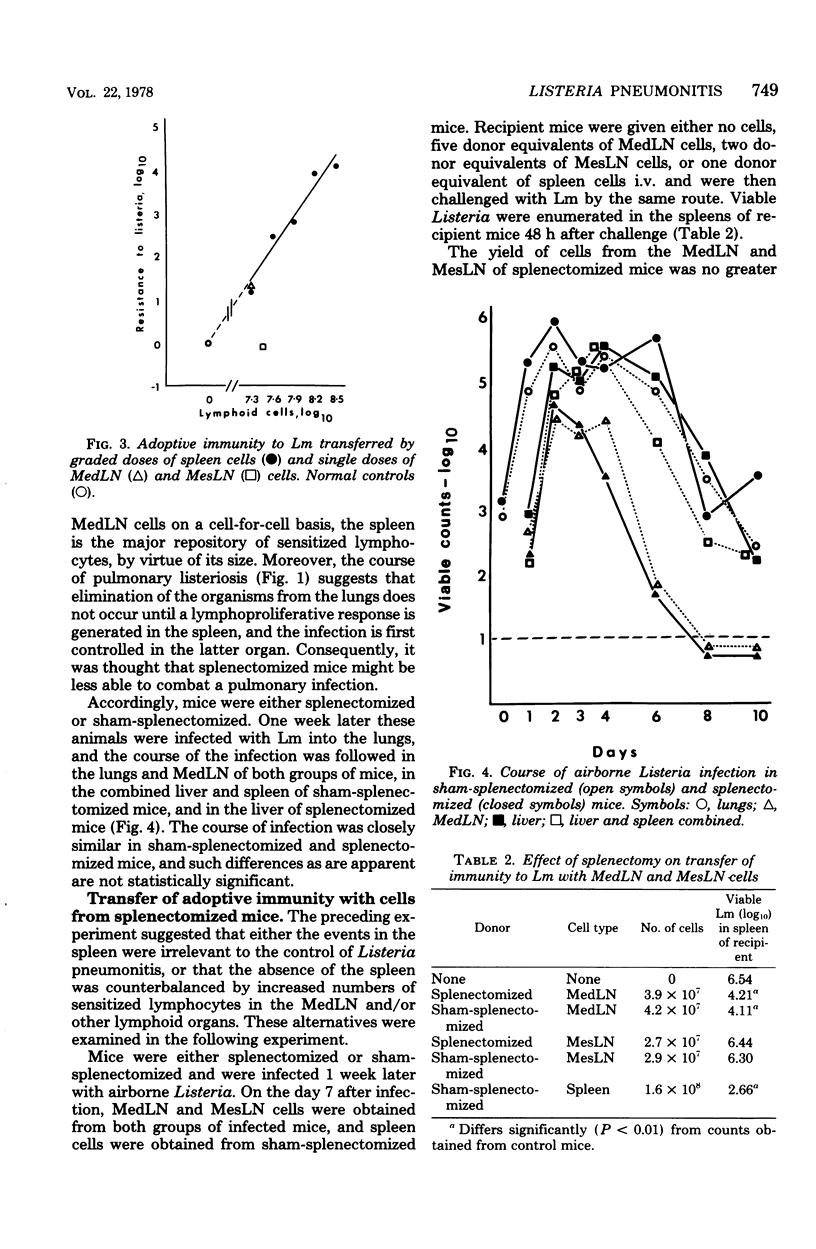
After implantation of approximately 10(3) Listeria monocytogenes organisms into the lungs, mice develop an acute pneumonitis with dissemination of infection to a mediastinal lymph node (MedLN), liver, and spleen. The infections in a MedLN and spleen resolve in approximately 7 days, but the lung infection persists for a few days longer. Pneumonitis is accompanied by a lymphoproliferative response in a MedLN and spleen, and immunity to Listeria is conferred adoptively with MedLN and spleen cells but not with mesenteric lymph node cells. Although the spleen appears to be the major repository of sensitized lymphocytes, splenectomized mice combat Listeria pneumonitis as effectively as normal mice. It is concluded that the induction of immunity to lung infection with L. monocytogenes is efficient and that the cause for the rather protracted pneumonitis is due to a defect in the expression of the cell-mediated immunity effector mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyle W. An extension of the 51Cr-release assay for the estimation of mouse cytotoxins. Transplantation. 1968 Sep;6(6):761–764. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196809000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Hand W. L. Cell-mediated immunity after bacterial infection of the lower respiratory tract. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1125–1134. doi: 10.1172/JCI107856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefford M. J. Induction and expression of immunity after BCG immunization. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):646–653. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.646-653.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The J. Burns Amberson LECTURE The induction and expression of cell-mediated hypersensitivity in the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Dec;104(6):813–828. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.104.6.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor D. D., Koster F. T., Mackaness G. B. The mediator of cellular immunity. I. The life-span and circulation dynamics of the immunologically committed lymphocyte. J Exp Med. 1971 Feb 1;133(2):389–399. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor D. D., Logie P. S. The mediator of cellular immunity. VII. Localization of sensitized lymphocytes in inflammatory exudates. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1415–1430. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash D. R., Holle B. Local and systemic cellular immune responses in guinea-pigs given antigen parenterally or directly into the lower respiratory tract. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Apr;13(4):573–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular kinetics associated with the development of acquired cellular resistance. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):299–314. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular mediators of anti-Listeria immunity as an enlarged population of short lived, replicating T cells. Kinetics of their production. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):342–355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J. C., Waldman R. H., Johnson J. E., 3rd Local and systemic cell-mediated immunity after immunization of guinea pigs with live or killed m. tuberculosis by various routes. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1322–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truitt G. L., Mackaness G. B. Cell-mediated resistance to aerogenic infection of the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Dec;104(6):829–843. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.104.6.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Henney C. S. Cell-mediated immunity and antibody responses in the respiratory tract after local and systemic immunization. J Exp Med. 1971 Aug 1;134(2):482–494. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.2.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


