Abstract
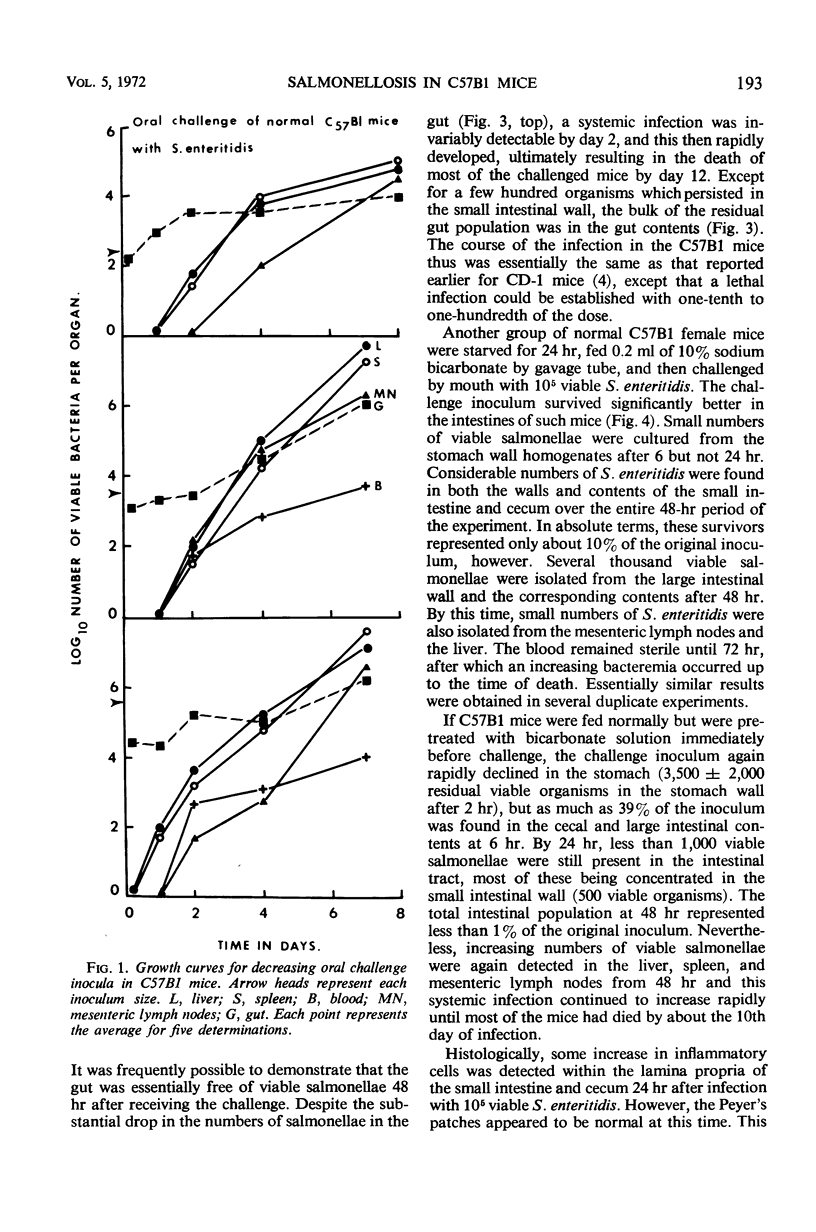
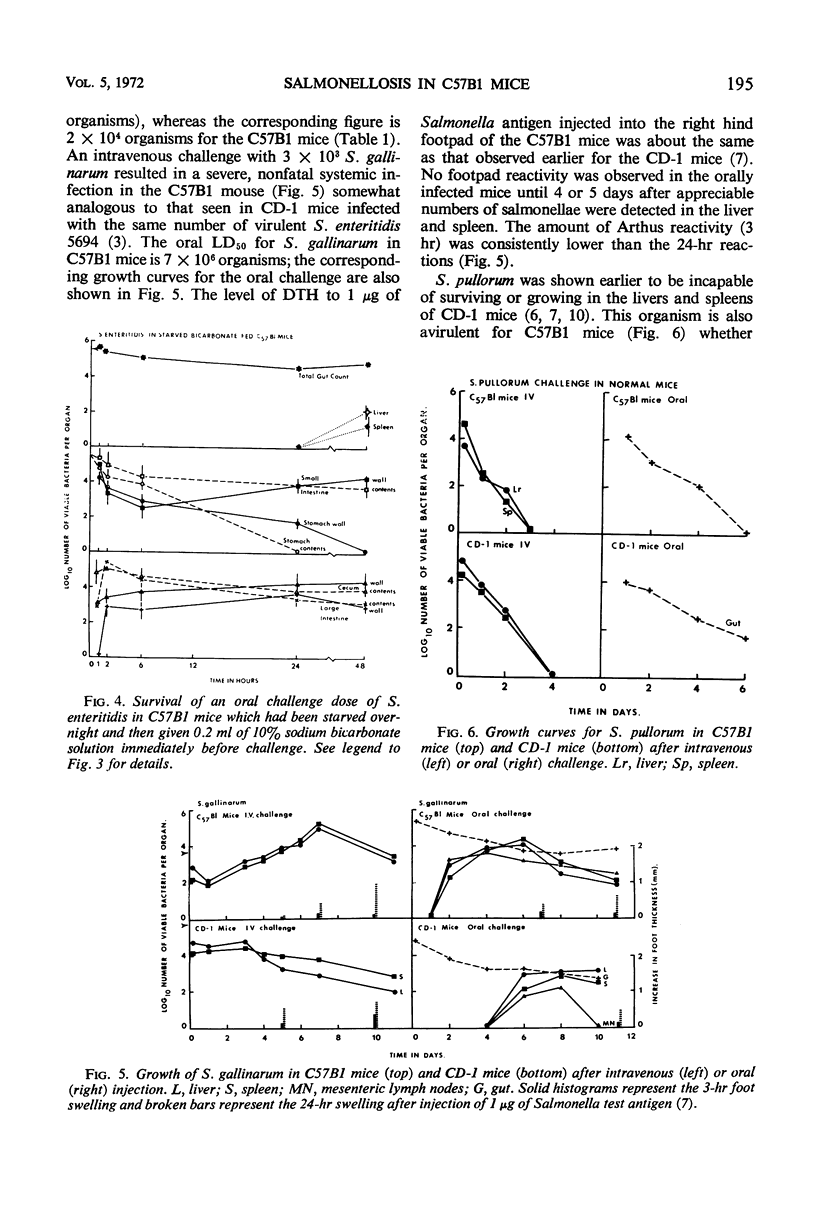
Specific pathogen-free C57B1 mice are 100 to 1,000 times as sensitive as CD-1 mice to intravenous or oral challenge by Salmonella enteritidis or S. gallinarum. Resistance to infection by S. pullorum was unaffected. Growth of Listeria monocytogenes and Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) in intravenously infected C57B1 mice was similar to that seen in CD-1 mice. Quantitative counts of viable S. enteritidis in the walls of the stomach, small intestine, cecum, and large intestine and in the corresponding intestinal contents showed that most of the oral challenge inoculum was rapidly inactivated so that, by 24 hr, less than 1% was still viable. Overnight starvation and pretreatment with bicarbonate solution increased the relative survival of the challenge approximately 10-fold. Despite the rapid and extensive inactivation of the oral inoculum within the normal intestine, significant numbers of salmonellae reached the liver and spleen by 48 hr, and this systemic infection was subsequently responsible for the death of a high proportion of the challenged animals.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams G. D., Bishop J. E. Effect of the normal microbial flora on the resistance of the small intestine to infection. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1604–1608. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1604-1608.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOHNHOFF M., MILLER C. P. Enhanced susceptibility to Salmonella infection in streptomycin-treated mice. J Infect Dis. 1962 Sep-Oct;111:117–127. doi: 10.1093/infdis/111.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehme D. H. Resistance to salmonella infections in inbred mouse strains. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1970 Jul;46(7):499–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in nonvaccinated mice challenged by various routes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):667–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.667-675.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Immunity to enteric infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):243–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.243-250.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Infection-immunity in experimental salmonellosis. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):601–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. Delayed hypersensitivity and arthus reactivity in relation to host resistance in salmonella-infected mice. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):830–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. The relationship of delayed hypersensitivity to acquired antituberculous immunity. I. Tuberculin sensitivity and resistance to reinfection in BCG-vaccinated mice. Cell Immunol. 1970 Sep;1(3):253–265. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Mechanisms in antimicrobial immunity. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1971 Jul;10(1):58–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Miller T. E. Growth of a drug-resistant strain of Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) in normal and immunized mice. J Infect Dis. 1969 Nov;120(5):517–533. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.5.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Milne M. Heat-labile antigens of Salmonella enteritidis. II. Mouse-protection studies. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):549–557. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.549-557.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONOVICK R. The use of the mouse in experimental tuberculosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1949 Dec 14;52(5):671–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1949.tb53956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R. J., PIERCE C. H., SCHAEFER W. B. Differential characteristics in vitro and in vivo of several substrains of BCG. III. Multiplication and survival in vivo. Am Rev Tuberc. 1956 Nov;74(5):683–698. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1956.74.5.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R. J., SCHAEDLER R. W. The effect of diet on the fecal bacterial flora of mice and on their resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Jun 1;115:1161–1172. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.6.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R. J., SCHAEDLER R. W. The effect of the intestinal flora on the growth rate of mice, and on their susceptibility to experimental infections. J Exp Med. 1960 Mar 1;111:407–417. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTTON A. A. The influence of the route of injection on lethal infections in mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Apr;36(2):128–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERICHTER C. B. The dissemination of Salmonella typhi, S. paratyphi A and S. paratyphi B through the organs of the white mouse by oral infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Sep;58:307–319. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY D. F., JENNINGS P. A. Allergy in experimental mouse tuberculosis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1955 Aug;72(2):171–195. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1955.72.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON D. The behaviour of a mutant strain of Salmonella typhimurium in experimental mouse typhoid. J Hyg (Lond) 1957 Sep;55(3):322–333. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawbecker D. E., Carpenter J. A., Hamdy M. K. Translocation and fate of 32P-labeled salmonella in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):546–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER C. P., BOHNHOFF M. CHANGES IN THE MOUSE'S ENTERIC MICROFLORA ASSOCIATED WITH ENHANCED SUSCEPTIBILITY TO SALMONELLA INFECTION FOLLOWING STREPTOMYCIN TREATMENT. J Infect Dis. 1963 Jul-Aug;113:59–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/113.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V., Collins F. M. Host-parasite relations in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):573–583. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushin R., Dubos R. Colonization of the mouse intestine with Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1965 Oct 1;122(4):745–757. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralovich B., Rauss K. Das Schicksal der Maus-avirulenten Salmonellen bei oraler Verabreichung. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1969;211(3):315–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J. Salmonella O antigens and virulence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:443–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L., YOUMANS G. P. Enumeration of viable tubercle bacilli from the organs of nonimmunized and immunized mice. Am Rev Tuberc. 1957 Oct;76(4):616–635. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1957.76.4.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS G. P., YOUMANS A. S., KANAI K. The difference in response of four strains of mice to immunization against tuberculous infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Nov;80:753–756. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.5.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


