Abstract
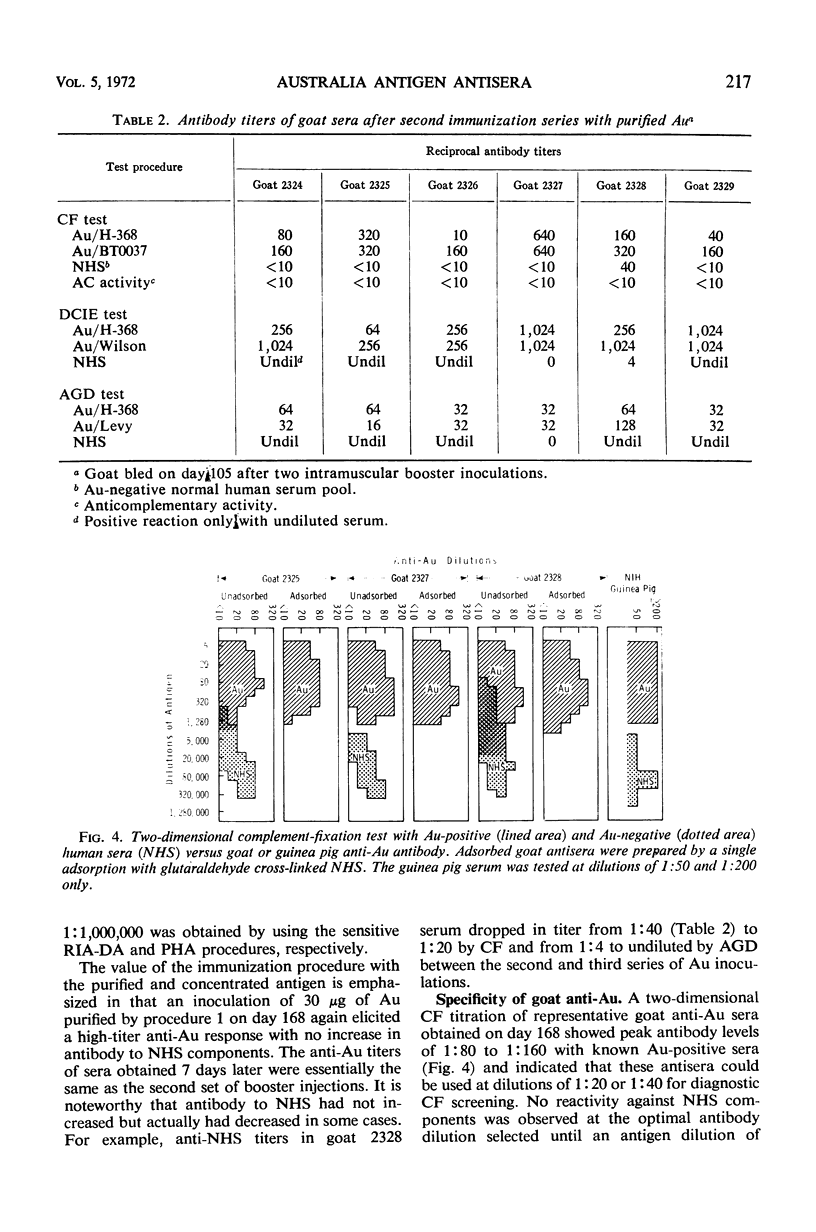
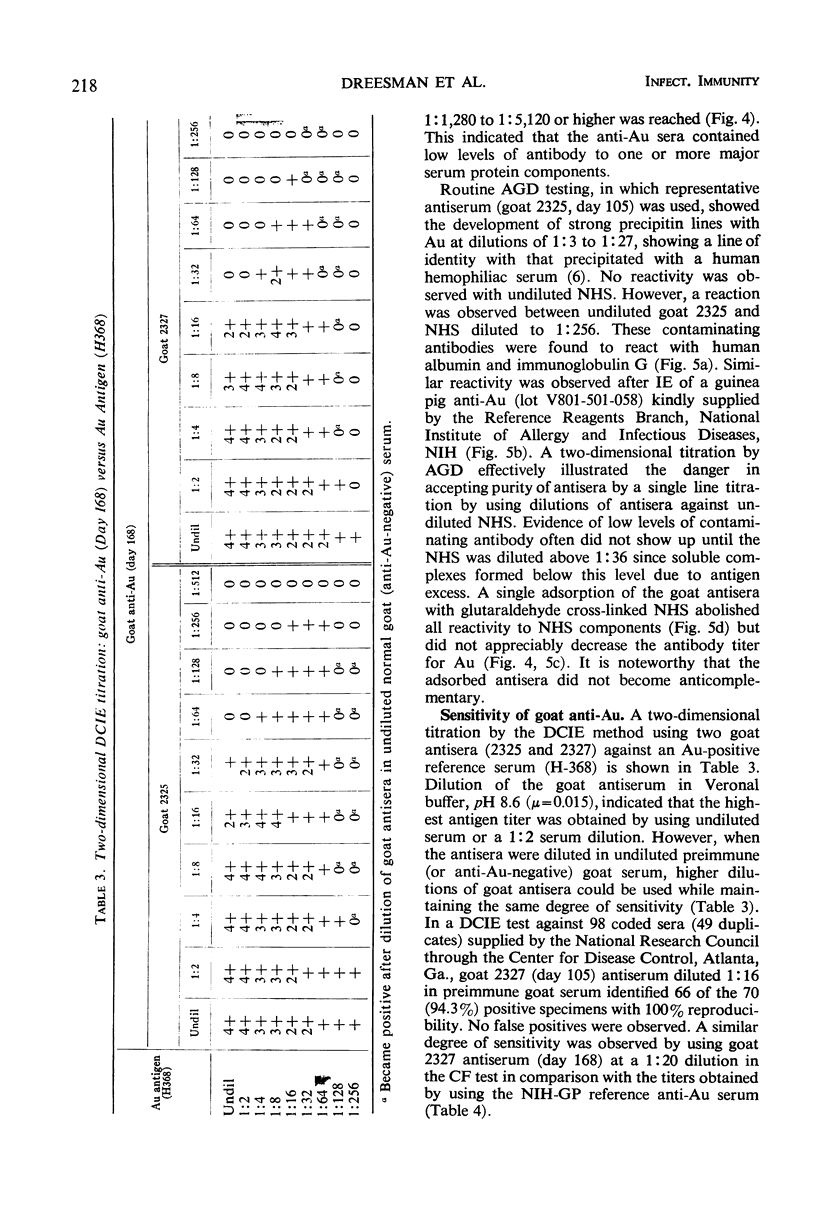
Potent antisera of high specificity and sensitivity were produced, in goats, to purified Australia antigen (Au). The antigen was prepared by one of three methods: (i) pelleting, low pH treatment, isopycnic centrifugation two times in CsCl, and rate zonal centrifugation in sucrose; (ii) same as procedure i, with the exception of the low pH treatment; or (iii) twice banding in CsCl by using a BXIV batch-type zonal centrifuge rotor with subsequent preparative Pevikon electrophoresis. The goat anti-Au sera contained high levels of precipitating antibody as tested by immunodiffusion in agar gel and discontinuous counterimmunoelectrophoresis (DCIE) as well as specific complement-fixing antibody and could be used for routine screening of sera for Au without prior adsorption with Au-negative normal human serum (NHS). Identification of 66 of 70 positive specimens (94.3%) in a panel of 98 coded sera (49 duplicates) with 100% reproducibility was made by using one of the goat anti-Au sera at a dilution of 1:16 in the DCIE method. No false positives were recorded. Low levels of antibody against NHS components were effectively removed by a single adsorption with glutaraldehyde cross-linked NHS.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. S., Gerstley B. J., Hungerford D. A., London W. T., Sutnick A. I. A serum antigen (Australia antigen) in Down's syndrome, leukemia, and hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1967 May;66(5):924–931. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-66-5-924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabasso V. J., Nieman R., Schroeder D. D., Hok K. A., Louie R. E., Mozen M. M. Preparation and standardization of an Australia antigen antibody of equine origin. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jun;21(6):1017–1023. doi: 10.1128/am.21.6.1017-1023.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DREESMAN G., LARSON C., PINCKARD R. N., GROYON R. M., BENEDICT A. A. ANTIBODY ACTIVITY IN DIFFERENT CHICKEN GLOBULINS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jan;118:292–296. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerin J. L., Holland P. V., Purcell R. H. Australia antigen: large-scale purification from human serum and biochemical studies of its proteins. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):569–576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.569-576.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger F. B., Vorndam V., Dreesman G. R. Assay of Australia antigen and antibody employing double-antibody and solid-phase radioimmunoassay techniques and comparison with the passive hemagglutination methods. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1099–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugman S., Giles J. P. Viral hepatitis. New light on an old disease. JAMA. 1970 May 11;212(6):1019–1029. doi: 10.1001/jama.212.6.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouvier G. L., McCollum R. W. Australia (hepatitis-associated) antigen: physicochemical and immunological characteristics. Adv Virus Res. 1970;16:357–396. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60027-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melartin L., Blumberg B. S. Production of antibody against "Australia antigen" in rabbits. Nature. 1966 Jun 25;210(5043):1340–1341. doi: 10.1038/2101340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millman I., Ziegenfuss J. F., Jr, Raunio V., London W. T., Sutnick A. I., Blumberg B. S. The production of antibodies to Australia antigen in mouse ascites fluid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Apr;133(4):1426–1431. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M. An antigen detected in the blood during the incubation period of serum hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):814–821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L., Holland P. V., Cline W. L., Chanock R. M. Preparation and characterization of complement-fixing hepatitis-associated antigen and antiserum. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):222–226. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Complement fixation and immunodiffusion tests for assay of hepatitis-associated "Australia" antigen and antibodies. J Immunol. 1970 Sep;105(3):604–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Shulman N. R. Hemagglutination assay for antigen and antibody associated with viral hepatitis. Science. 1970 Oct 16;170(3955):332–333. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3955.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Enhanced detection of Australia antigen in serum hepatitis patients by discontinuous counter-immunoelectrophoresis. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):867–869. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.867-869.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]