Abstract
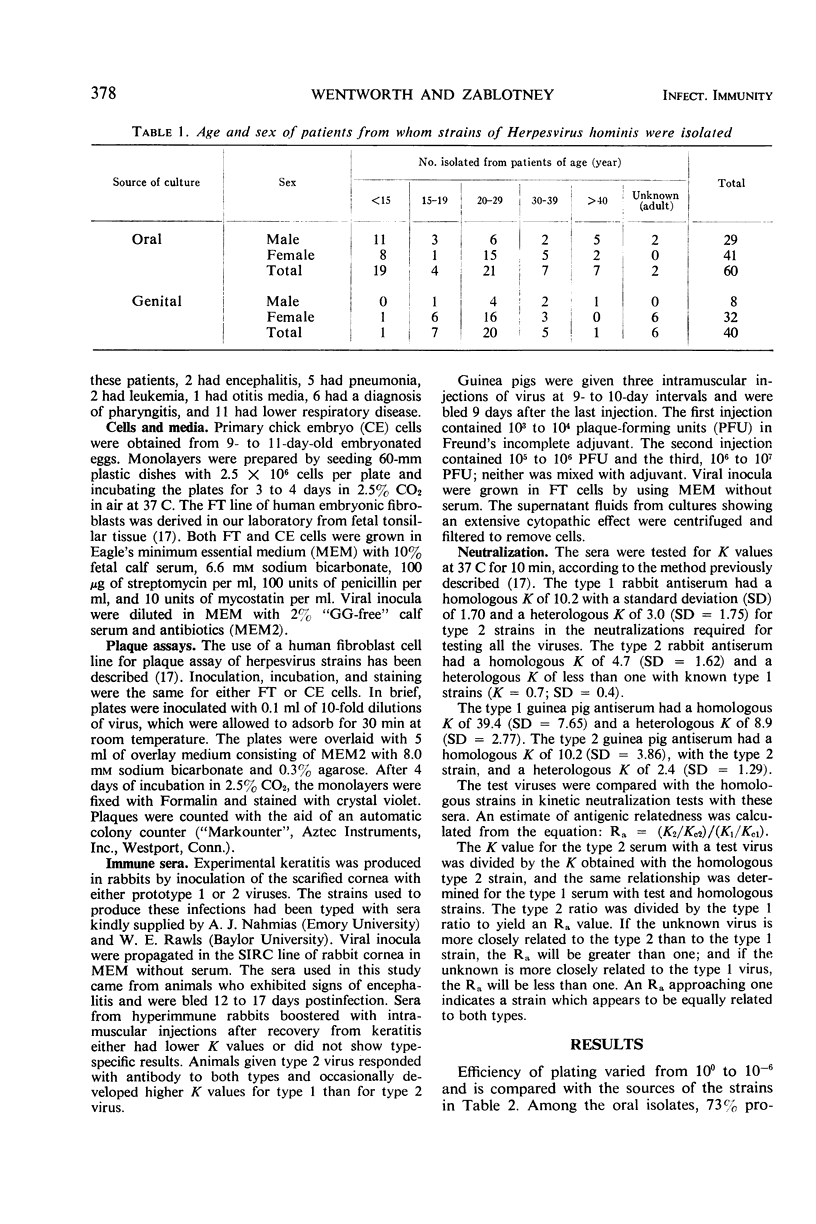
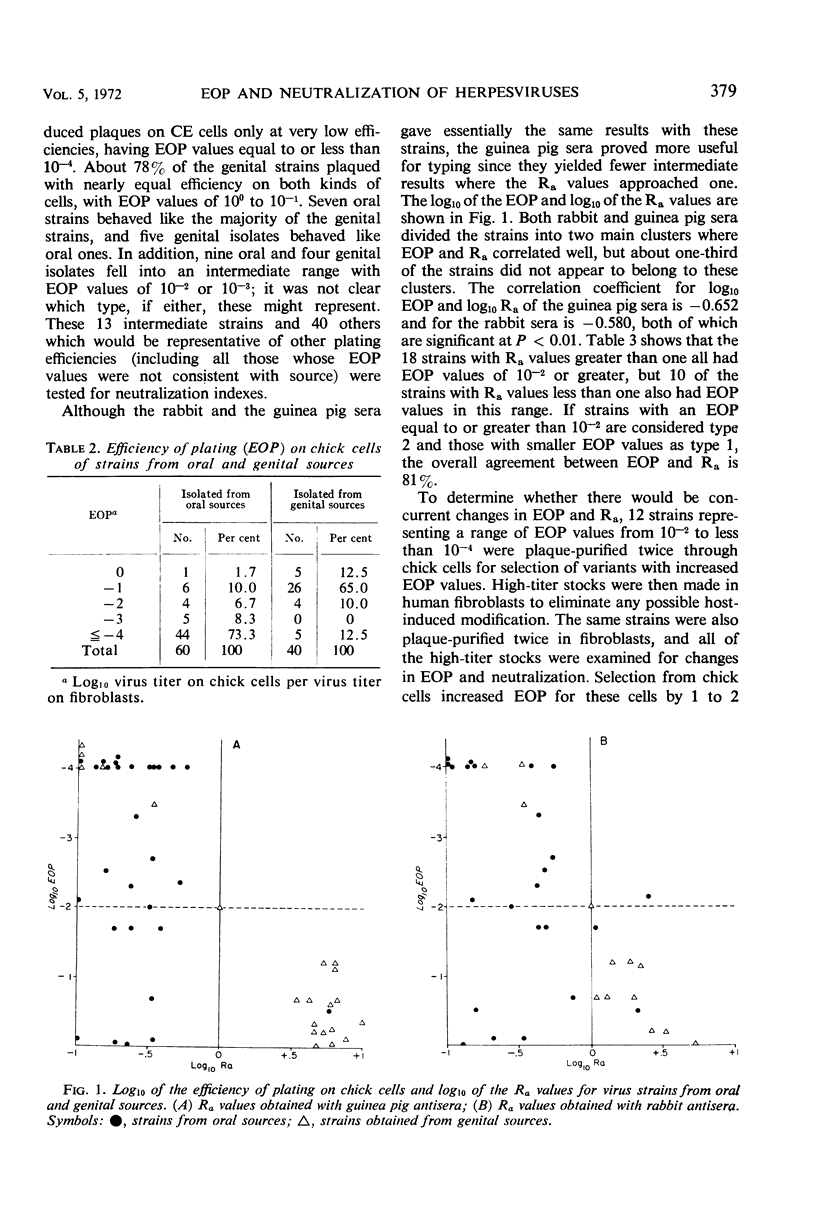
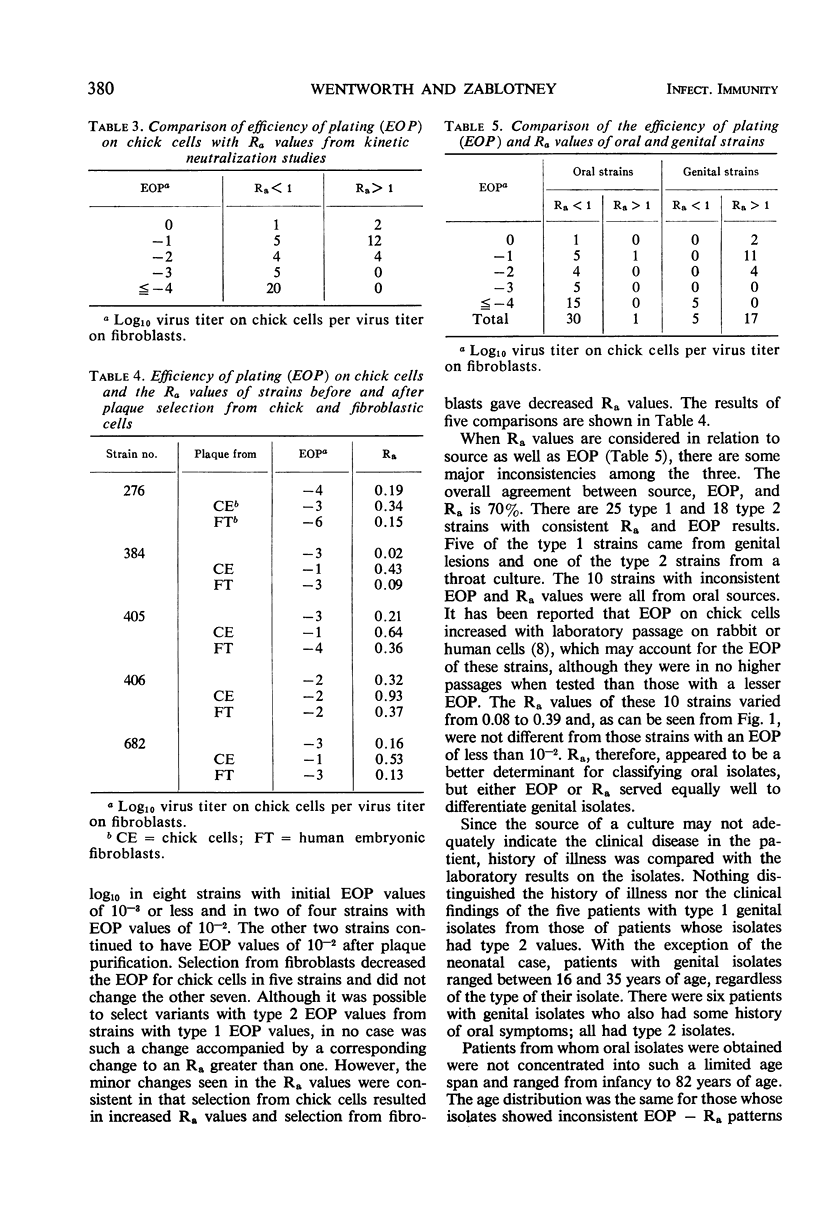
Since it appeared that plaque formation in monolayers of primary chick embryo cells might provide a simple technique for the typing of Herpesvirus hominis strains, 100 isolates were tested for their efficiency of plating (EOP) on chick embryo cells versus plating on human embryonic fibroblasts. EOP values varied from 100 to 10−6: 88% of the strains of genital origin had an EOP equal to or greater than 10−2, and 82% of the oral isolates had an EOP equal to or less than 10−3. Kinetic neutralizations were done with 53 strains, including those 12 with an EOP of 10−2 or 10−3. An estimate of antigenic relatedness (Ra) between strains was calculated from the neutralization results. Although the site of recovery, EOP, and Ra generally correlated, the EOP of some oral strains did not agree with the neutralization results, and some genital strains showed type 1 EOP and Ra values. Selection of variants with increased EOP values did not result in accompanying changes in Ra. Thus, the two markers appeared to vary independently. These data support other findings which suggest that there may be no absolute correlation between biological and antigenic markers in herpesviruses and that a larger number with more diversity of strains should be examined for more markers before a typing system is established.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amstey M. S., Balduzzi P. C. Genital herpesvirus (type II) strain differences. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1970 Mar 15;106(6):924–927. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(70)90491-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdle W. R., Nahmias A. J., Harwell R. W., Pauls F. P. Association of antigenic type of Herpesvirus hominis with site of viral recovery. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):974–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa M. E., Rawls W. E. Biological markers for differentiation of herpes-virus strains of oral and genital origin. J Gen Virol. 1969 Mar;4(2):259–267. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-2-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodheart C. R., Plummer G., Waner J. L. Density difference of DNA of human herpes simplex viruses, types I and II. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):473–475. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90225-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampar B., Miyamoto K., Martos L. M. Serologic classification of Herpes simplex viruses. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):580–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieff E. D., Bachenheimer S. L., Roizman B. Size, composition, and structure of the deoxyribonucleic acid of herpes simplex virus subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):125–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.125-132.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry S. P., Melnick J. L., Rawls W. E. Investigation of plaque formation in chick embryo cells as a biological marker for distinguishing herpes virus type 2 from type 1. J Gen Virol. 1971 Jan;10(1):1–9. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-10-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Dowdle W. R. Antigenic and biologic differences in herpesvirus hominis. Prog Med Virol. 1968;10:110–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Dowdle W. R., Naib Z. M., Highsmith A., Harwell R. W., Josey W. E. Relation of pock size on chorioallantoic membrane to antigenic type of herpesvirus hominis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):1022–1028. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Dowdle W. R., Naib Z. M., Josey W. E., McLone D., Domescik G. Genital infection with type 2 Herpes virus hominis. A commonly occurring venereal disease. Br J Vener Dis. 1969 Dec;45(4):294–298. doi: 10.1136/sti.45.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer G., Waner J. L., Phuangsab A., Goodheart C. R. Type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex viruses: serological and biological differences. J Virol. 1970 Jan;5(1):51–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.1.51-59.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J., Roizman B. Similarities and Differences in the Development of Laboratory Strains and Freshly Isolated Strains of Herpes Simplex Virus in HEp-2 Cells: Electron Microscopy. J Virol. 1969 Dec;4(6):879–889. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.6.879-889.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Rodriguez J. E., McKee A. P. Biological characteristics of cloned populations of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Feb;21(2):350–357. doi: 10.1128/am.21.2.350-357.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs K. G., Snider M. E., Alford C. A., Jr Influence of host cell on biologic markers of types 1 and 2. Herpesvirus hominis. J Infect Dis. 1971 Feb;123(2):169–177. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terni M., Roizman B. Variability of herpes simplex virus: isolation of two variants from simultaneous eruptions at different sites. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):212–216. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., French L. Plaque assay of Herpesvirus hominis on human embryonic fibroblasts. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jun;131(2):588–592. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


