Abstract
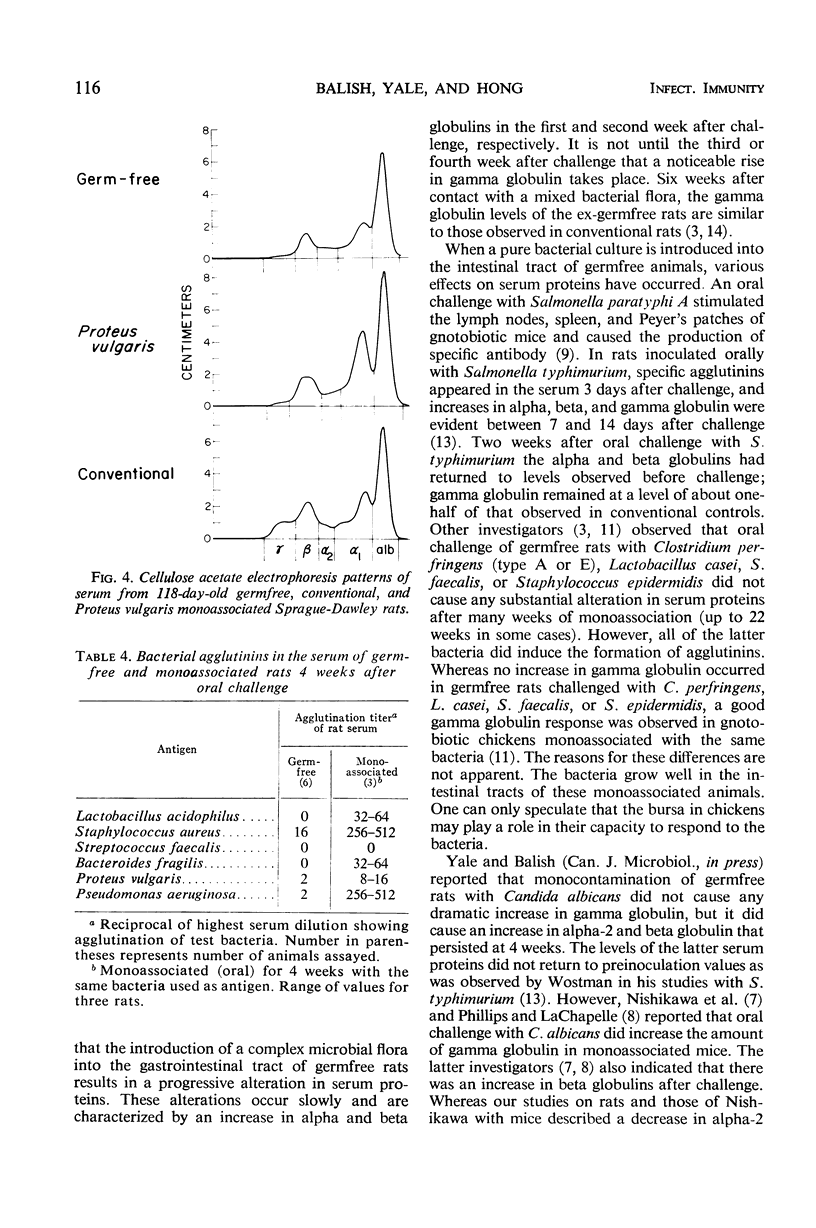
Cellulose-acetate and agar gel immunoelectrophoresis were used to study the serum protein patterns of germfree rats before and after monoassociation with a pure culture of Staphylococcus aureus (phage type 80/81), Streptococcus faecalis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bacteroides fragilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, or Proteus vulgaris. All six bacteria quickly established themselves in the gastrointestinal tract of the germfree rat, and all six increased the animals' total serum proteins. Only S. aureus and P. aeruginosa caused a noticeable rise in gamma globulins. L. acidophilus, S. faecalis, and B. fragilis multiplied readily in the gastrointestinal tract but caused only minimal alterations in the serum proteins. P. vulgaris caused a marked increase in the alpha and beta, but not the gamma globulins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Neuhaus O. W., Balegno H. F., Chandler A. M. Induction of plasma protein synthesis in response to trauma. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):151–156. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa T., Hatano H., Ohnishi N., Sasaki S., Nomura T. Establishment of Candida albicans in the alimentary tract of the germ-free mice and antagonism with Escherichia coli after oral inoculation. Jpn J Microbiol. 1969 Sep;13(3):263–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1969.tb00466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. W., Lachapelle R. C. Serum proteins in the germ-free mouse after oral challenge with Candida albicans. Nature. 1967 Feb 18;213(5077):709–710. doi: 10.1038/213709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard M., Sharon N. Responses of the Peyer's Patches in Germ-Free Mice to Antigenic Stimulation. Infect Immun. 1970 Jul;2(1):96–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.1.96-100.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER M., WOSTMANN B. S. Serum protein fractions and antibody studies in gnotobiotic animals reared germfree or monocontaminated. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Aug 31;94:210–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb35542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOSTMANN B. S., GORDON H. A. Electrophoretic studies on the serum protein pattern of the germfree rat and its changes upon exposure to a conventional bacterial flora. J Immunol. 1960 Jan;84:27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOSTMANN B. S. Recent studies on the serum proteins of germfree animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Aug 31;94:272–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb35547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wostmann B. S. Antimicrobial defense mechanisms in the Salmonella typhimurium associated ex-germfree rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 May;134(1):294–299. doi: 10.3181/00379727-134-34780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wostmann B. S., Olson G. B., Pleasants J. R. Serum proteins of germ-free rats fed water-soluble diets. Nature. 1965 Jun 5;206(988):1056–1057. doi: 10.1038/2061056b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





