Abstract
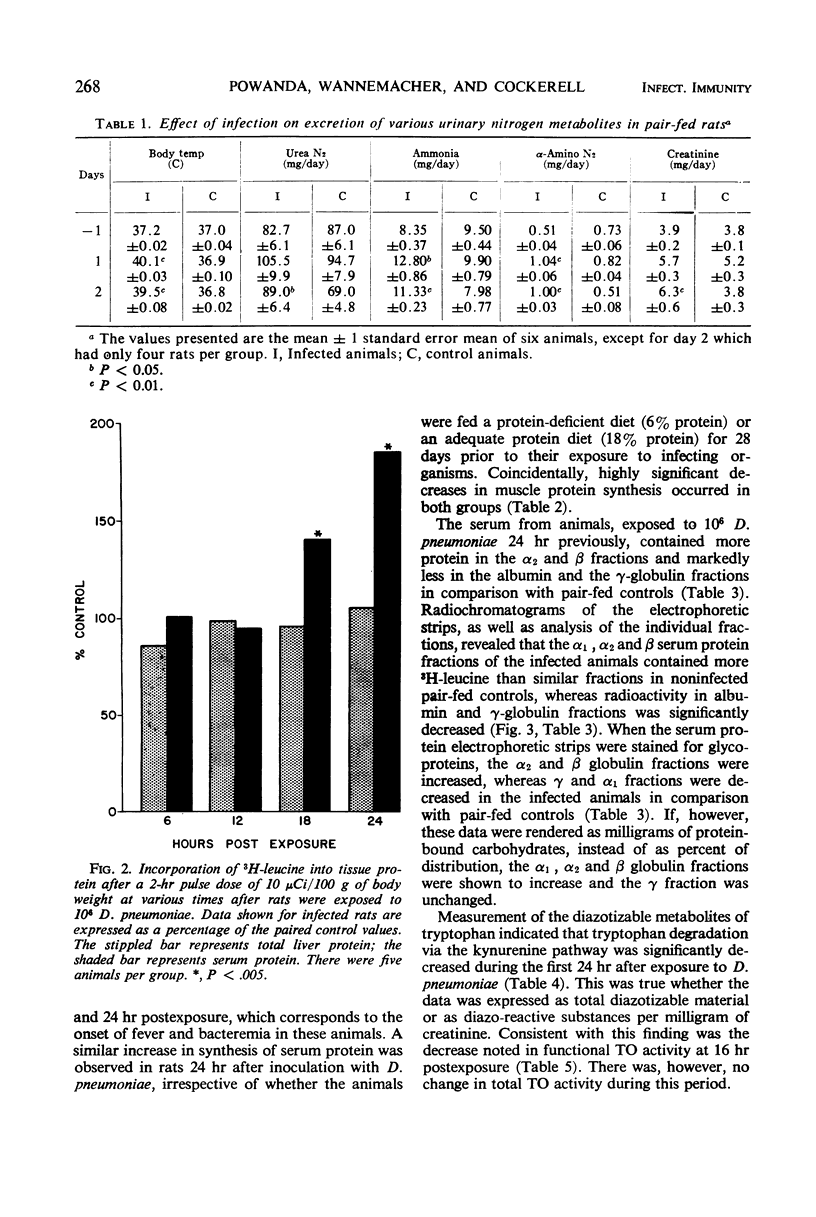
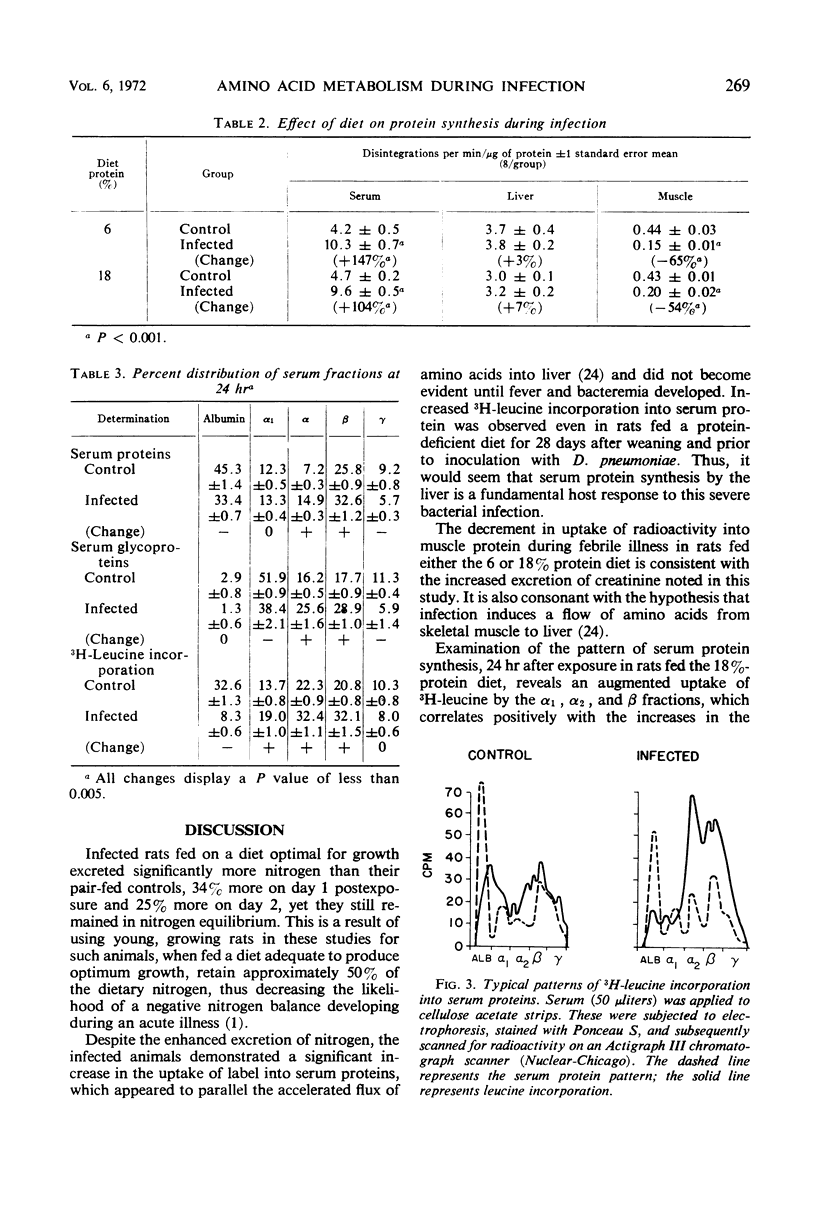
Markedly increased synthesis of α2 and β globulins and α1, α2, and β glycoglobulins occurs during pneumococcal sepsis in the rat simultaneously with decreased albumin formation, diminished tritiated leucine incorporation into muscle protein, and enhanced excretion of nitrogen. This augmented synthesis of specific serum proteins does not become evident until fever and bacteremia develop, and it appears to be a fundamental aspect of host response to a proliferating bacterial infection in that it occurs even in rats fed a protein-deficient (6% protein) diet after weaning and before exposure to Diplococcus pneumoniae.
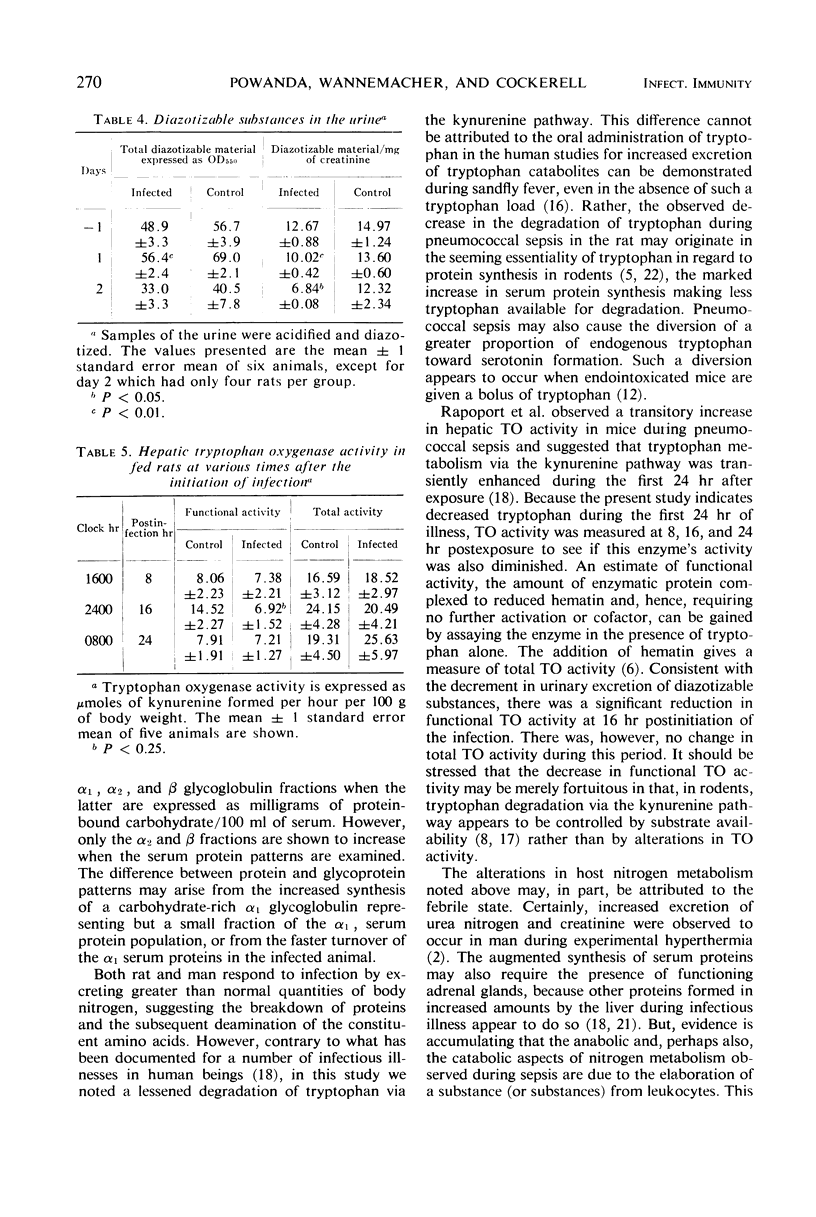
Although amino acid catabolism, in general, appears to be increased during infection, tryptophan degradation via the kynurenine pathway, as assessed by measuring diazotizable urinary metabolites, changes little or is, at times, significantly less than in control animals. Coincidentally, functional tryptophan oxygenase activity decreases at 16 hr after exposure. Total tryptophan oxygenase activity, however, is unchanged.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON J. B., WANNEMACHER R. W., Jr, BANKS W. L., Jr, WUNNER W. H. THE MAGNITUDE AND SIGNIFICANCE OF THE PROTEIN RESERVES IN RATS FED AT VARIOUS LEVELS OF NITROGEN. J Nutr. 1964 Dec;84:383–388. doi: 10.1093/jn/84.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel W. R., Goldman R. F., Joy R. J. Metabolic balance studies during induced hyperthermia in man. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Jan;24(1):1–10. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.24.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel W. R., Sawyer W. D., Ryll E. D., Crozier D. Metabolic effects of intracellular infections in man. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Oct;67(4):744–779. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-4-744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddington C. L., Upchurch H. F., Kampschmidt R. F. Effect of extracts from rabbit leukocytes on levels of acute phase globulins in rat serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Jan;136(1):159–164. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENGARD O., FEIGELSONP The purification and properties of liver tryptophan pyrrolase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1903–1907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman C. M., Sappington T. S., Burrows B. A., Lavietes P. H., Peters J. P. NITROGEN METABOLISM IN ACUTE INFECTIONS. J Clin Invest. 1945 Jul;24(4):523–531. doi: 10.1172/JCI101631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Korner A. Influence of amino acid supply on ribosomes and protein synthesis of perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;111(5):703–712. doi: 10.1042/bj1110703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. H., Miller L. L. The functional significance of changes in activity of the enzymes, tryptophan pyrrolase and tyrosine transaminase, after induction in intact rats and in the isolated, perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 25;244(6):1410–1416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton F., Poole B., Beaufay H., Baudhuin P., Coffey J. W., Fowler S., De Duve C. The large-scale separation of peroxisomes, mitochondria, and lysosomes from the livers of rats injected with triton WR-1339. Improved isolation procedures, automated analysis, biochemical and morphological properties of fractions. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):482–513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitruka B. M. Biochemical aspects of Diplococcus pneumoniae infections in laboratory rats. Yale J Biol Med. 1971 Dec;44(3):253–264. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. J., Berry L. J. Role of tryptophan pyrrolase in endotoxin poisoning. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1247–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1247-1253.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITOT H. C., PERAINO C., BOTTOMLEY R. H., MORRIS H. P. The comparative enzymology and cell origin of rat hepatomas. III. Some enzymes of amino acid metabolism. Cancer Res. 1963 Jan;23:135–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekarek R. S., Beisel W. R. Characterization of the endogenous mediator(s) of serum zinc and iron depression during infection and other stresses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Nov;138(2):728–732. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekarek R. S., Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Beisel W. R. The effect of leukocytic endogenous mediator (LEM) on the tissue distribution of zinc and iron. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jun;140(2):685–688. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powanda M. C., Wannemacher R. W., Jr Tryptophan availability as a control of hepatic pyridine nucleotide concentration in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 12;252(2):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport M. I., Beisel W. R., Hornick R. B. Tryptophan metabolism during infectious illness in man. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):159–169. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport M. I., Lust G., Beisel W. R. Host enzyme induction of bacterial infection. Arch Intern Med. 1968 Jan;121(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNDERMAN F. W., Jr STUDIES ON THE SERUM PROTEINS. VI. RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL INTERPRETATION OF ELECTROPHORETIC FRACTIONATIONS. Am J Clin Pathol. 1964 Jul;42:1–21. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/42.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shambaugh G. E., 3rd, Beisel W. R. Endocrine influences on altered hepatic tyrosine transaminase activity during pneumococcal septicemia in the rat. Endocrinology. 1968 Nov;83(5):965–974. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-5-965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidransky H., Sarma D. S., Bongiorno M., Verney E. Effect of dietary tryptophan on hepatic polyribosomes and protein synthesis in fasted mice. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1123–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS C. A., Jr, WEMYSS C. T., Jr Changes produced in mouse plasma proteins by acute bacterial infections. J Exp Med. 1961 Sep 1;114:311–325. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.3.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Pekarek R. S., Beisel W. R. Mediator of hepatic amino acid flux in infected rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jan;139(1):128–132. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Powanda M. C., Pekarek R. S., Beisel W. R. Tissue amino acid flux after exposure of rats to Diplococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):556–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.556-562.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M. Serum protein changes during the acute phase reaction. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Aug;25(2):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


