Abstract
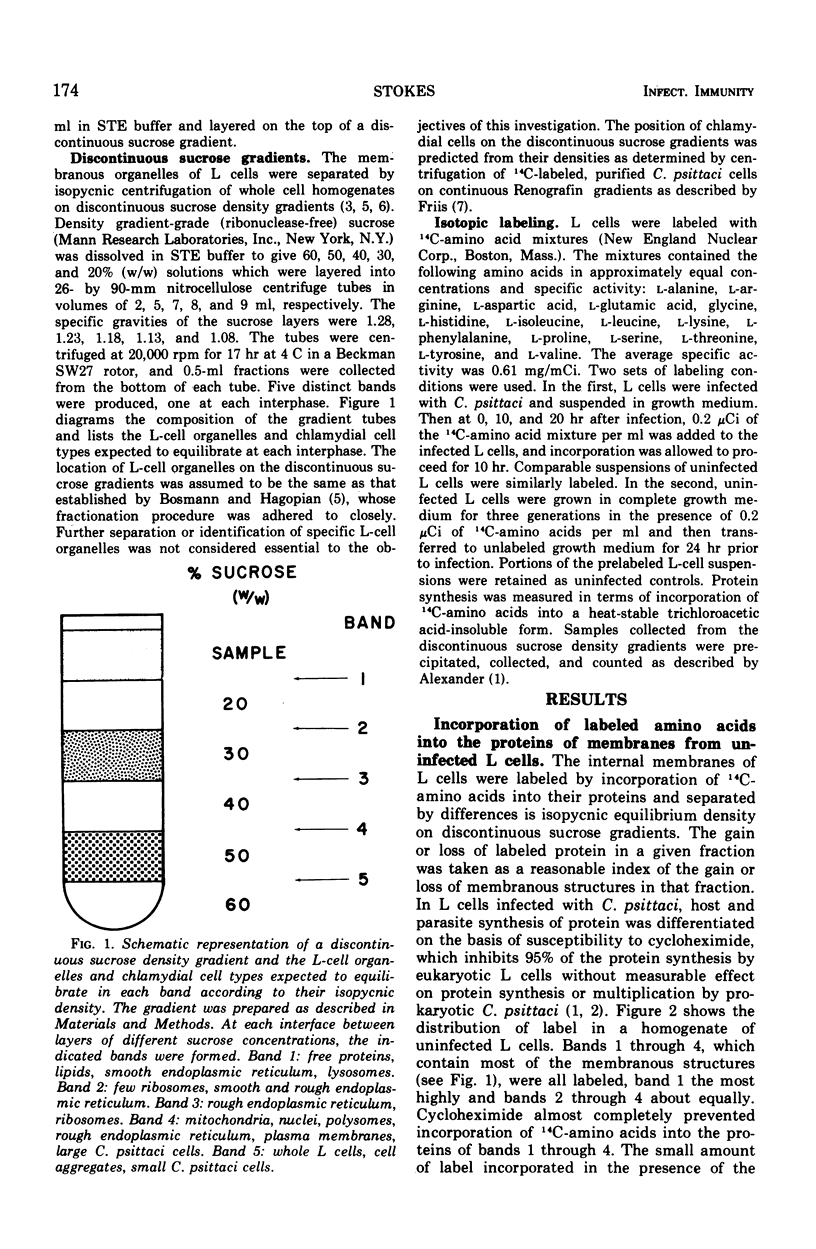
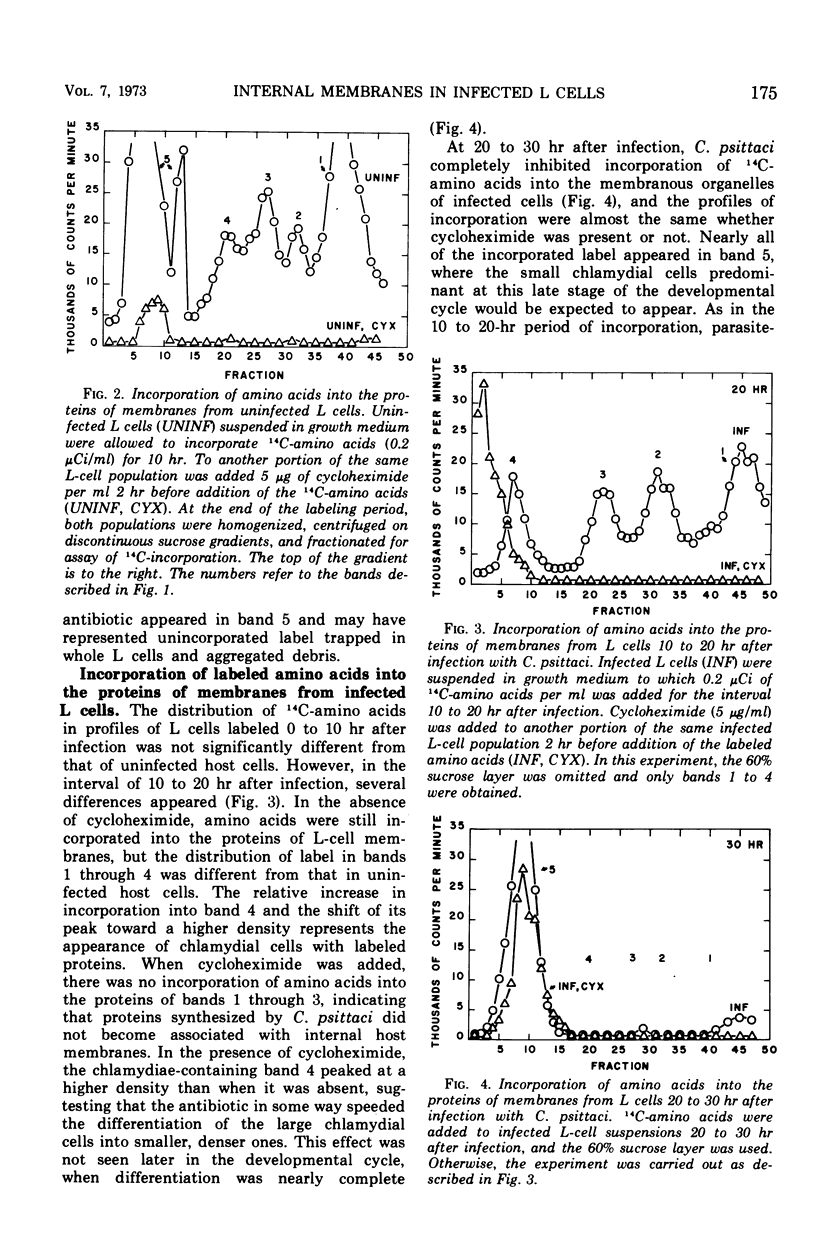
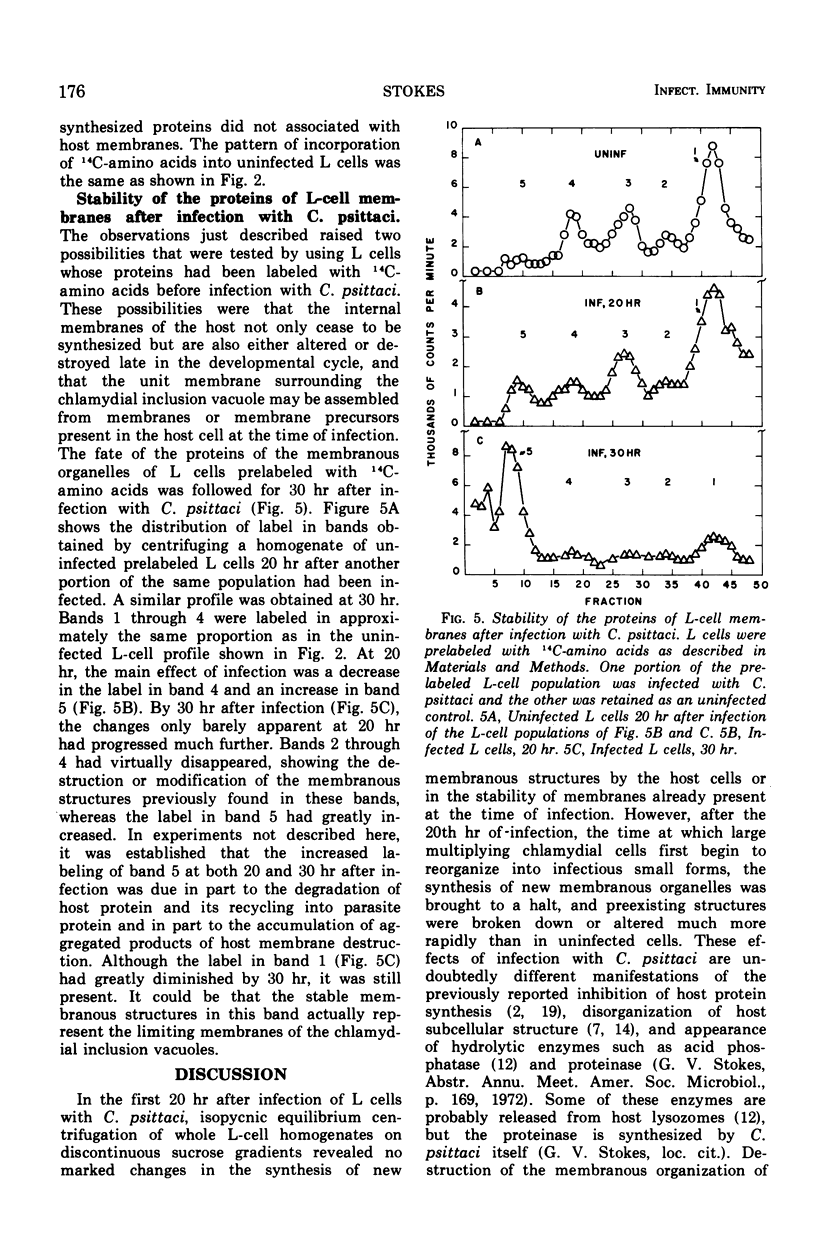
L cells (mouse fibroblasts), uninfected and infected with Chlamydia psittaci (meningopneumonitis strain), were labeled with 14C-amino acids, and their membranous organelles were separated by isopycnic equilibrium centrifugation of whole cell homogenates on discontinuous sucrose density gradients. Incorporation of labeled amino acids into host and parasitic proteins was differentiated on the basis of susceptibility to cycloheximide. Twenty hours after infection with C. psittaci, incorporation of newly synthesized proteins into the internal membranes of L cells was almost completely inhibited, and internal membranes made prior to infection were altered or destroyed. The unit membrane that at all times surrounds the cytoplasmic vacuole containing the multiplying chlamydiae was made by the host from membranes or membrane precursors present before infection. No proteins synthesized by C. psittaci became associated with host cell membranes. Destruction or modification of the internal membranes of the host cell may be an integral part of the chlamydial developmental cycle.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. J. Effect of infection with the meningopneumonitis agent on deoxyribonucleic acid and protein synthesis by its L-cell host. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):653–657. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.653-657.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. J. Separation of protein synthesis in meningopneumonitisgent from that in L cells by differential susceptibility to cycloheximide. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):327–332. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.327-332.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. R., Hopps H. E., Barile M. F., Bernheim B. C. Comparison of the ultrastructure of several rickettsiae, ornithosis virus, and Mycoplasma in tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1387–1404. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1387-1404.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B., Hagopian A., Eylar E. H. Cellular membranes: the isolation and characterization of the plasma and smooth membranes of HeLa cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Oct;128(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R. Interaction of L cells and Chlamydia psittaci: entry of the parasite and host responses to its development. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.706-721.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. D., Stewart R. B. Glucose requirements of L cells infected with Chlamydia psittaci. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Oct;16(10):997–1001. doi: 10.1139/m70-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. D., Stewart R. B. Respiration of L cells infected with Chlamydia psittaci. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Nov;16(11):1033–1039. doi: 10.1139/m70-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGASHI N. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON THE MODE OF REPRODUCTION OF TRACHOMA VIRUS AND PSITTACOSIS VIRUS IN CELL CULTURES. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Feb;76:24–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordová N., Wilt J. C. Lysosomes and the "toxicity" of Rickettsiales. I. Cytochemical studies of macrophages inoculated in vitro with C. psittaci 6BC. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Apr;18(4):457–464. doi: 10.1139/m72-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordová N., Wilt J. C., Sadiq M. Lysosomes in L cells infected with Chlamydia psittaci 6BC strain. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Jul;17(7):955–959. doi: 10.1139/m71-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepinay A., Robineaux R., Orfila J., Moncel C., Coet H., Boutry J. M. Analyse en microcinématographie à contraste de phase du developement intracellulaire de Chlamydia psittaci. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1971;35(2):161–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. S. Inhibition of thymidine kinase activity and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in L cells infected with the meningopneumonitis agent. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2054–2065. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2054-2065.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lépinay A., Orfila J., Anteunis A., Boutry J. M., Orme-Roselli L., Robineaux R. Etude en microscopie électronique du développement et de la morphologie de Chlamydia psittaci dans les macrophages de souris. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1970 Aug;119(2):222–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto A., Manire G. P. Electron microscopic observations on the effects of penicillin on the morphology of Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):278–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.278-285.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Glucose Metabolism of L Cells Before and After Infection with Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1189–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1189-1196.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter E. M. Synthesis of nucleic acid and protein in L cells infected with the agent of meningopneumonitis. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2069–2080. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2069-2080.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribby I. I. Cell Wall Synthesis by Chlamydia psittaci Growing in L Cells. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1176–1188. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1176-1188.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribby I. I., Moulder J. W. Availability of bases and nucleosides as precursors of nucleic acids in L cells and in the agent of meningopneumonitis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2362–2367. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2362-2367.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


