Abstract
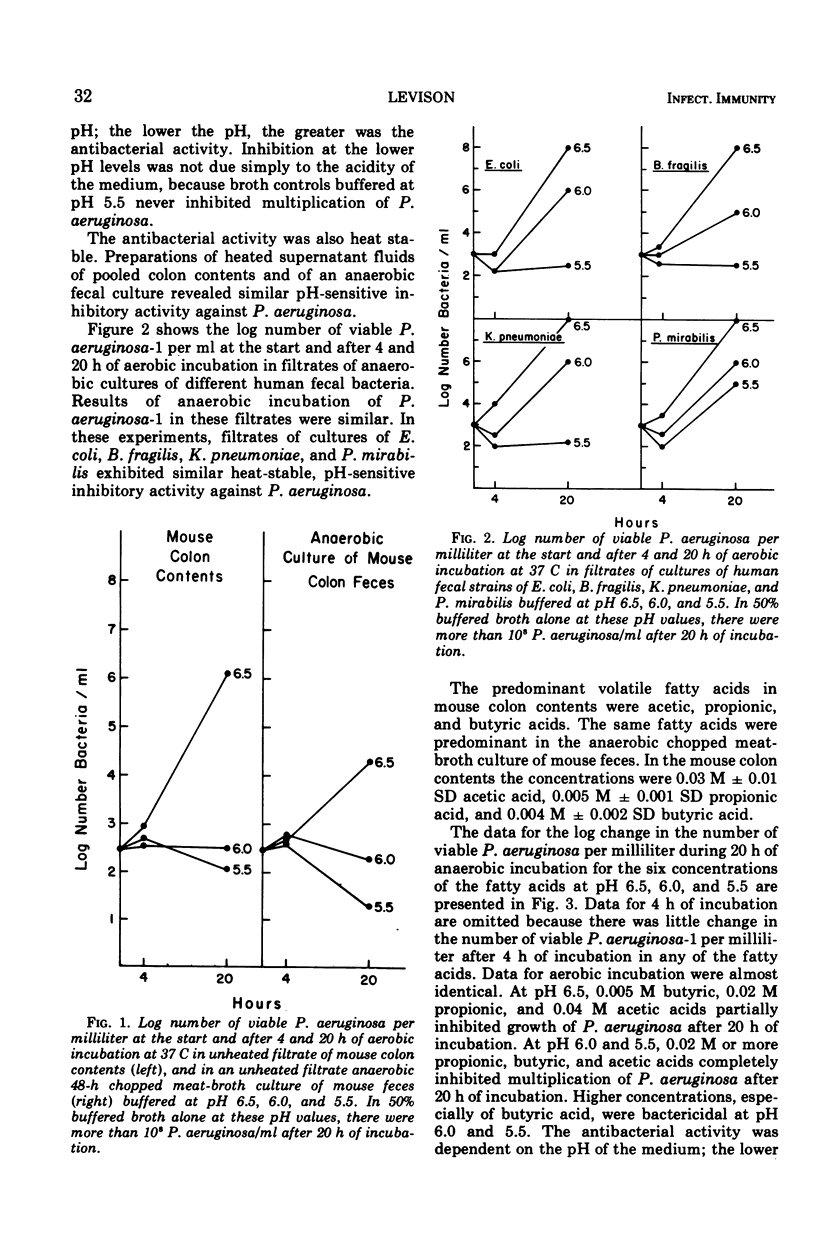
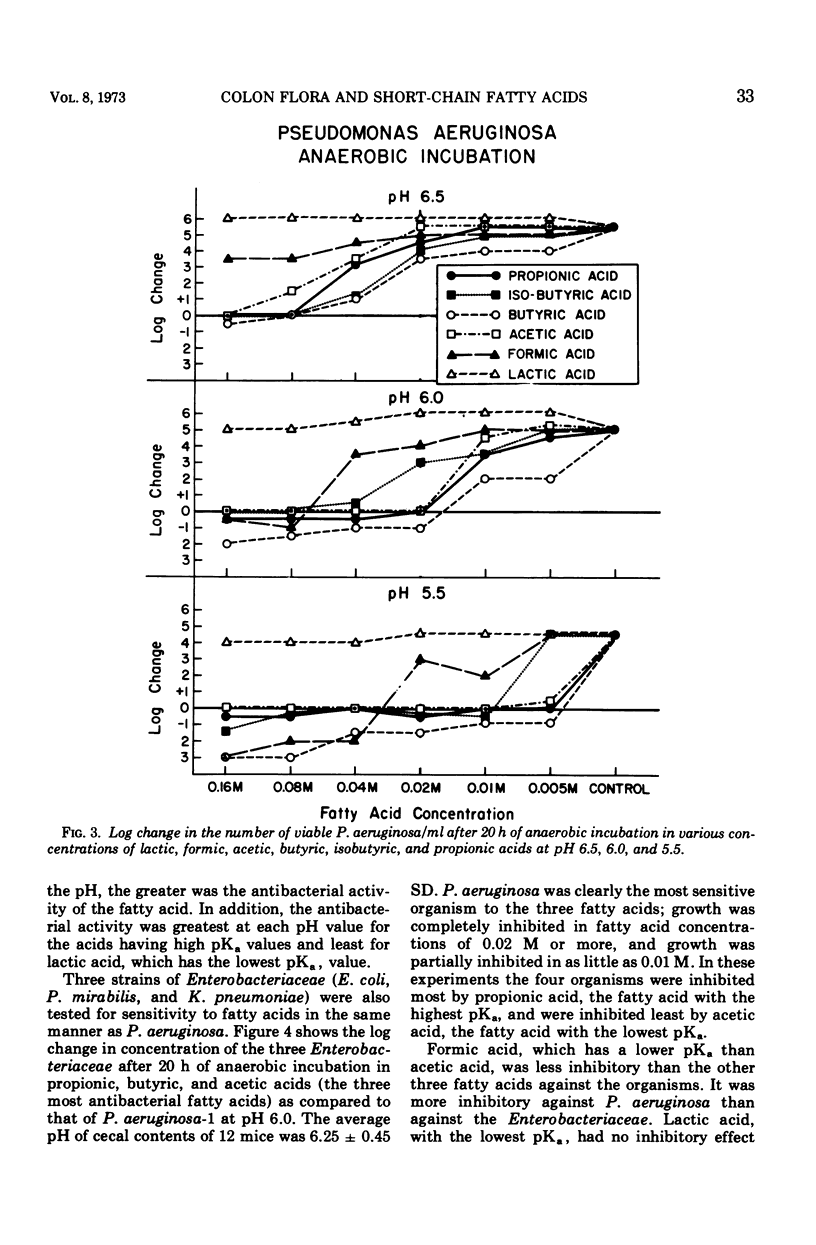
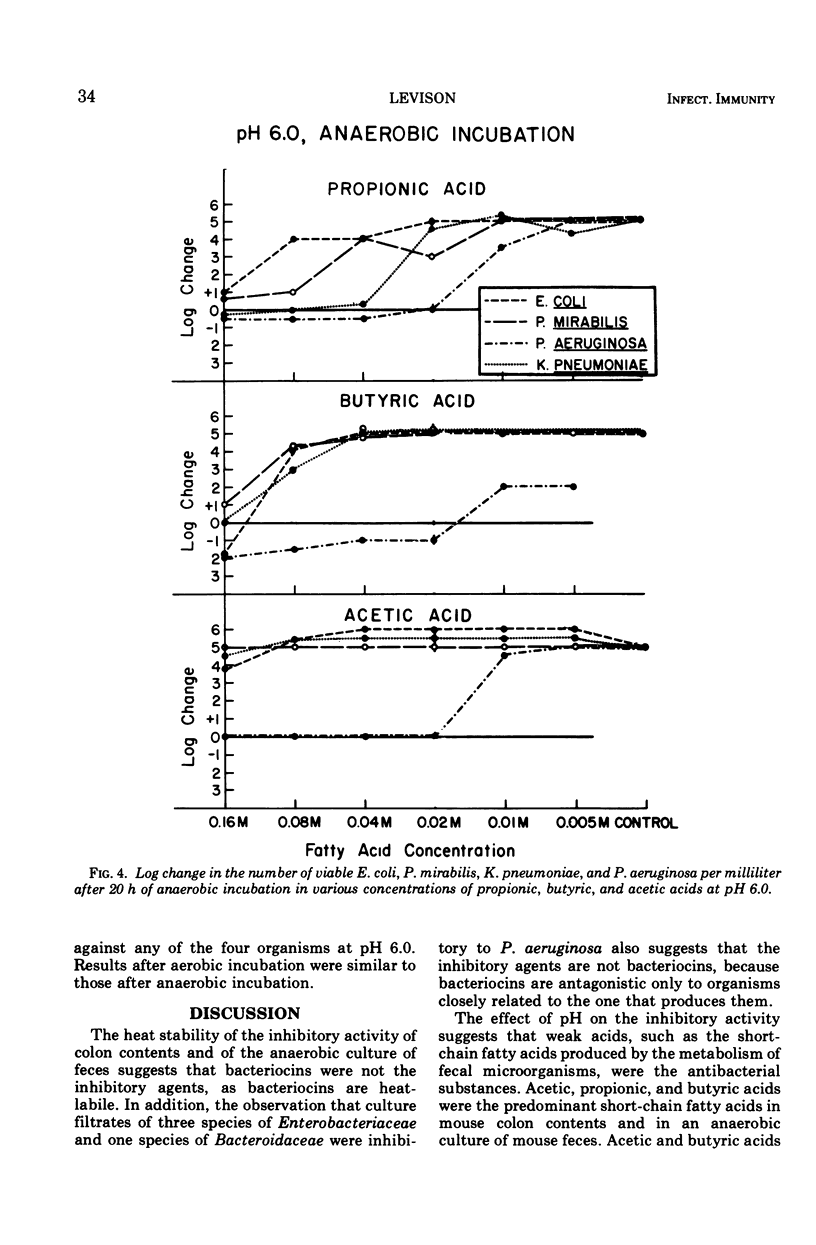
Heat-stable antibacterial activity in the following suspensions was demonstrated against Pseudomonas aeruginosa at pH 6.5, 6.0, and 5.5: (i) pooled colon contents of normal mice; (ii) an anaerobic, 48-h culture of normal mouse feces; and (iii) anaerobic, 48-h cultures of different bacteria from human colon flora (Escherichia coli, Bacteroides fragilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis). The lower the pH of the medium, the greater was the antibacterial activity of these suspensions. The antibacterial activity of five fatty acids (propionic, butyric, isobutyric, acetic, and formic acids) was greater against P. aeruginosa than against three Enterobacteriaceae (E. coli, K. pneumoniae, and P. mirabilis) at all fatty acid concentrations (0.16 M to 0.005 M) and at the 3 pH values studied (5.5, 6.0, and 6.5). As the pH value increased, the antibacterial activity decreased. Antibacterial activity was greater at higher fatty acid concentrations, and at each pH value it was greatest for the fatty acids having high pKa values. Lactic acid, with the lowest pKa, exhibited little or no antibacterial activity. Acetic and butyric acids, two of the three predominant volatile fatty acids determined by gas chromatography in the mouse colon contents and in the anaerobic culture of mouse feces, occurred in vivo in concentrations which inhibited growth of P. aeruginosa in vitro at the pH of the mouse cecum. These results suggest that undissociated short-chain fatty acids produced by the colon flora may be a mechanism of intestinal resistance to colonization by P. aeruginosa.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOHNHOFF M., MILLER C. P., MARTIN W. R. RESISTANCE OF THE MOUSE'S INTESTINAL TRACT TO EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLA INFECTION. I. FACTORS WHICH INTERFERE WITH THE INITIATION OF INFECTION BY ORAL INOCULATION. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:805–816. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck A. C., Cooke E. M. The fate of ingested Pseudomonas aeruginosa in normal persons. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Nov 4;2(4):521–525. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-4-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMOND C. W., RUML D. D., COOPER D. B., MILLER C. P. Studies on susceptibility to infection following ionizing radiation. III. Susceptibility of the intestinal tract to oral inoculation with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Exp Med. 1955 Oct 1;102(4):403–411. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.4.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENTGES D. J., FRETER R. In vivo and in vitro antagonism of intestinal bacteria against Shigella flexneri. I. Correlation between various tests. J Infect Dis. 1962 Jan-Feb;110:30–37. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.1.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentges D. J. Influence of pH on the inhibitory activity of formic and acetic acids for Shigella. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):2029–2030. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.2029-2030.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hird F. J., Weidemann M. J. Oxidative phosphorylation accompanying oxidation of short-chain fatty acids by rat-liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):378–388. doi: 10.1042/bj0980378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A., Gemmell E. Changes in the mouse intestinal microflora during weaning: role of volatile fatty acids. Infect Immun. 1972 Jan;5(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.1.1-7.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levison M. E., Kaye D. Fecal flora in man: effect of cathartic. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jun;119(6):591–596. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.6.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G. Antibacterial mechanisms of the mouse gut. II. The role of Eh and volatile fatty acids in the normal gut. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Apr;44:209–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G., SUBBAIAH T. V. Antibacterial mechanisms of the mouse gut. I. Kinetics of infection by Salmonella typhi-murium in normal and streptomycin-treated mice studied with abortive transductants. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Apr;44:197–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Cato E. P., Holdeman L. V. Anaerobic bacteria of the gastrointestinal flora and their occurrence in clinical infections. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jun;119(6):641–649. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.6.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


