Abstract
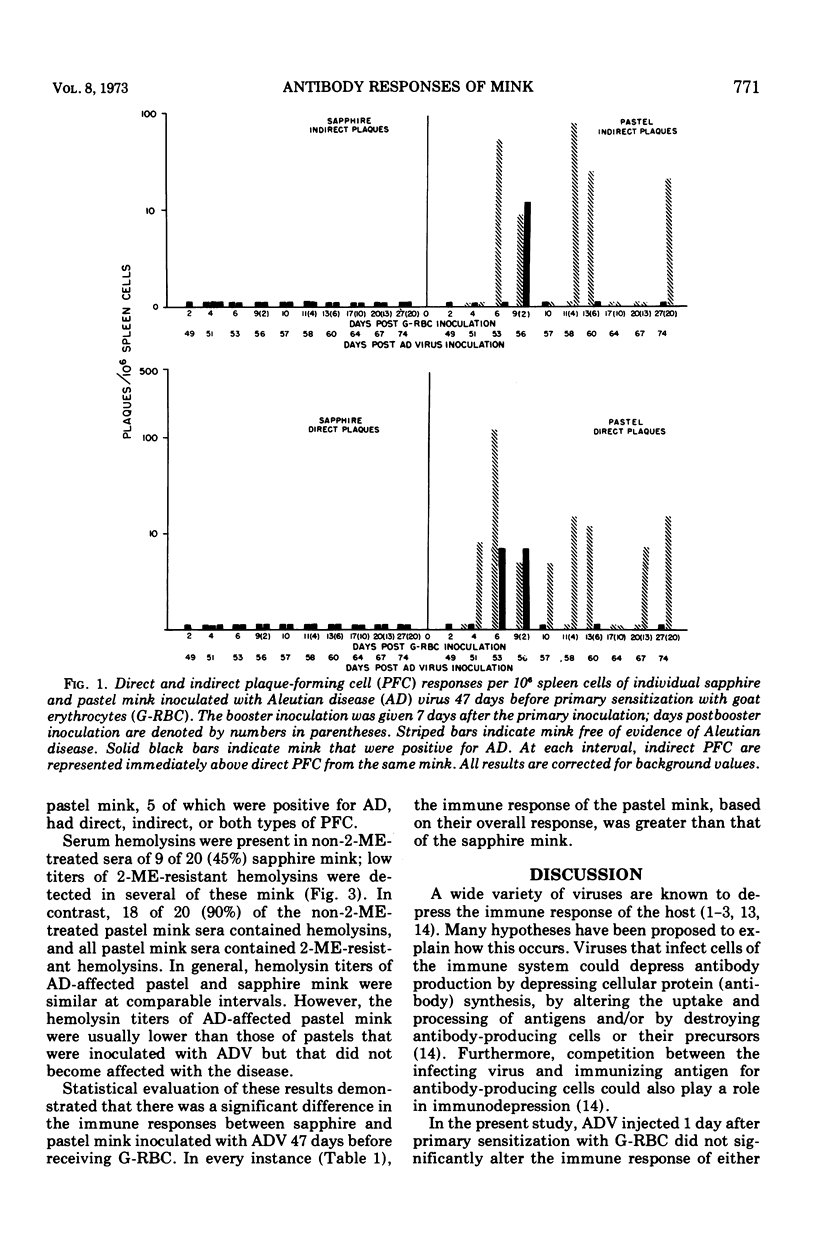
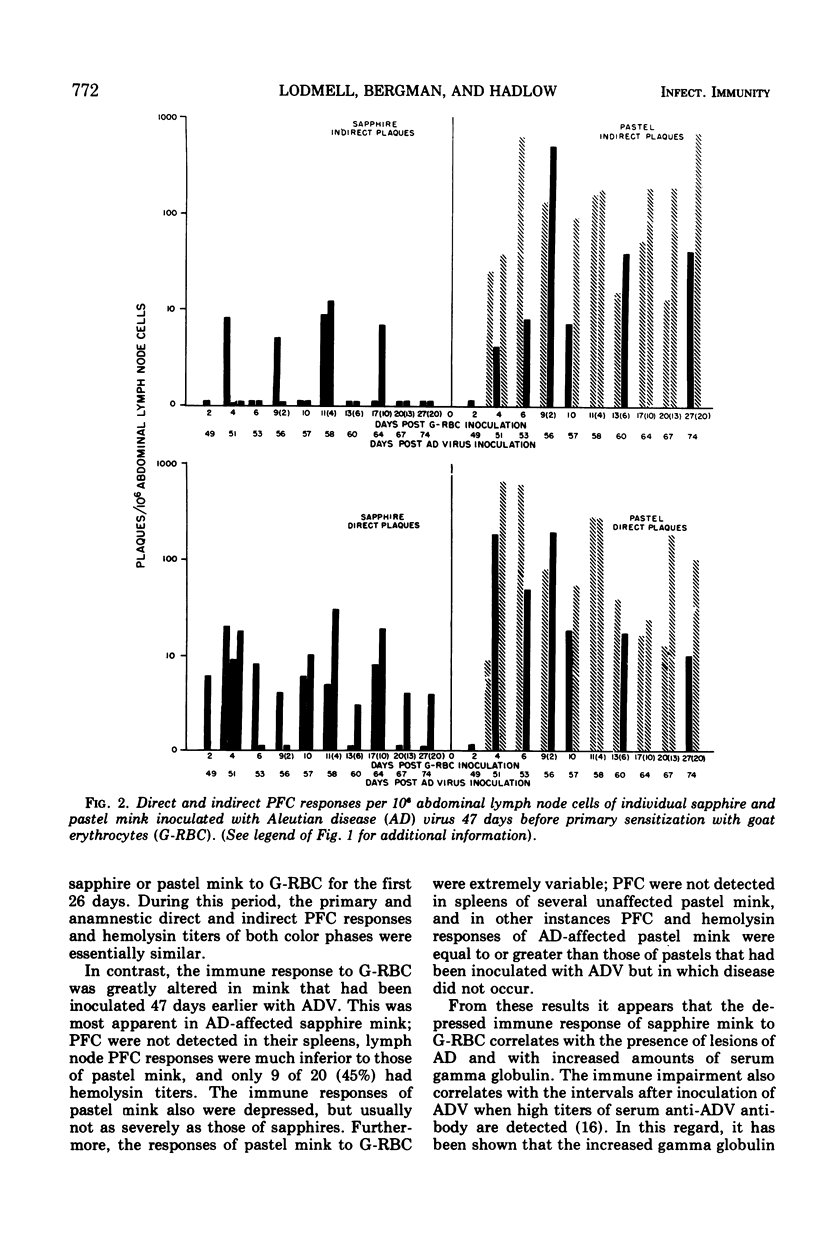
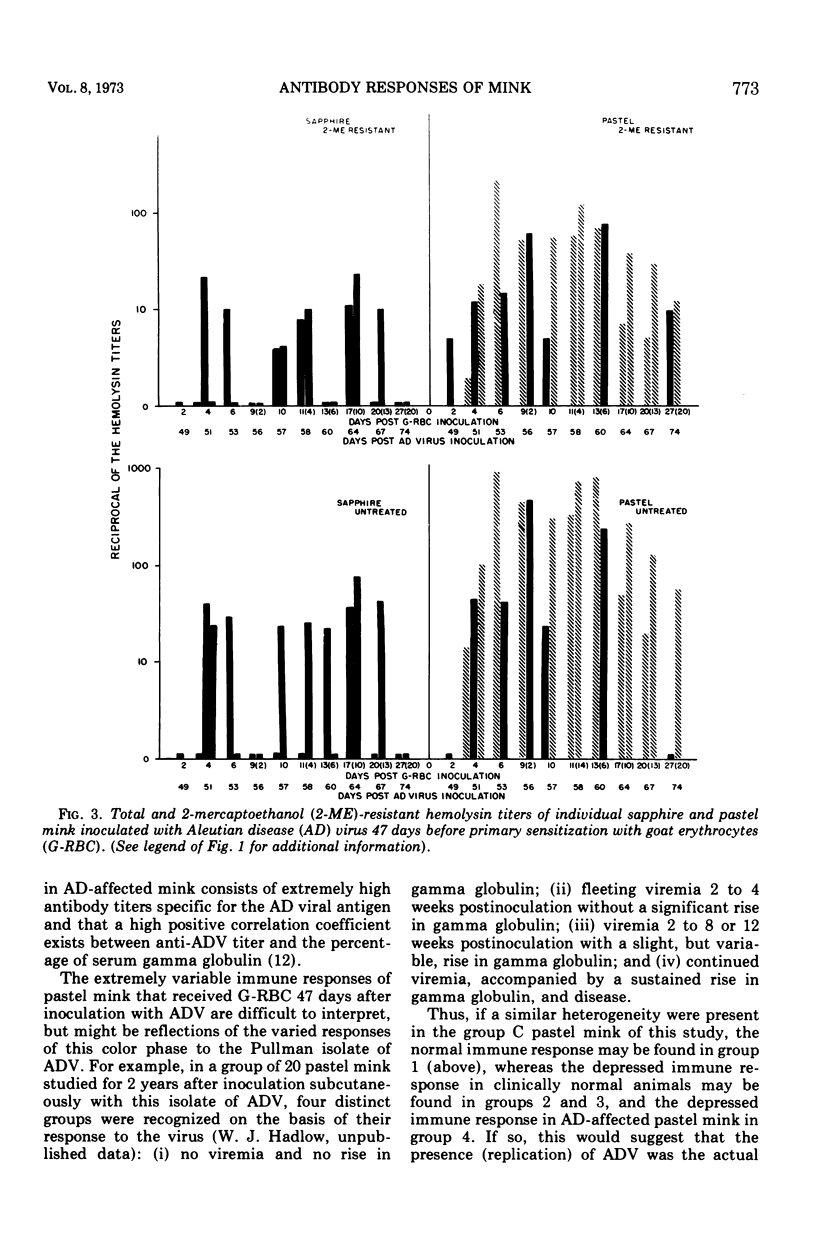
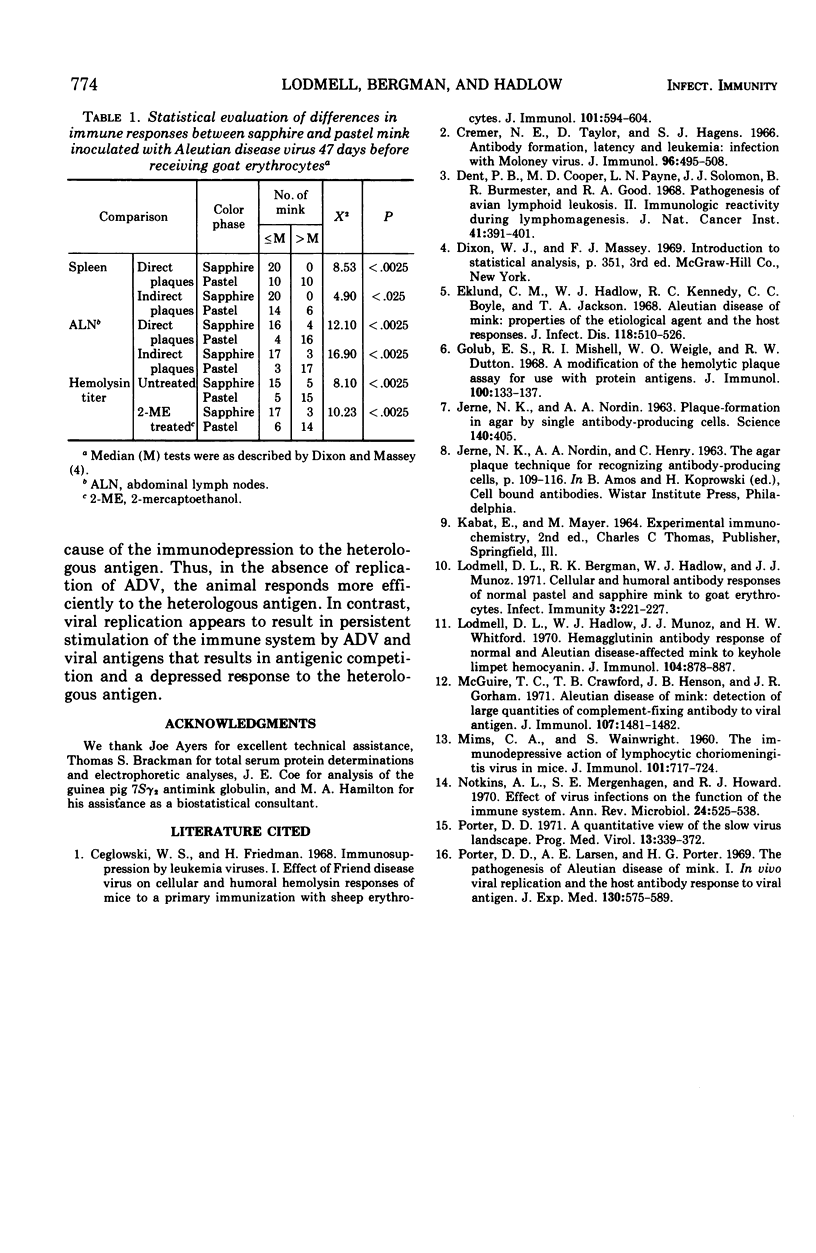
The effect of Aleutian disease virus (ADV) on serum hemolysin titers and antibody-forming cells in lymph nodes and spleens of sapphire and pastel mink inoculated with goat erythrocytes (G-RBC) was investigated. ADV injected 1 day after primary antigenic stimulation with G-RBC did not depress the immune responses of either color phase for a period of 26 days. However, when G-RBC were injected 47 days after ADV, both the number of antibody-forming cells and hemolysin titers were more markedly depressed in sapphire than in pastel mink. The results are discussed in relation to the greater susceptibility of sapphire mink and the variable susceptibility of pastel mink to the Pullman isolate of ADV.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ceglowski W. S., Friedman H. Immunosuppression by leukemia viruses. I. Effect of Friend disease virus on cellular and humoral hemolysin responses of mice to a primary immunization with sheep erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1968 Sep;101(3):594–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer N. E., Taylor D. O., Hagens S. J. Antibody formation, latency and leukemia: infection with Moloney virus. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):495–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P. B., Cooper M. D., Payne L. N., Solomon J. J., Burmester B. R., Good R. A. Pathogenesis of avian lymphoid leukosis. II. Immunologic reactivity during lymphomagenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):391–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund C. M., Hadlow W. J., Kennedy R. C., Boyle C. C., Jackson T. A. Aleutian disease of mink: properties of the etiologic agent and the host responses. J Infect Dis. 1968 Dec;118(5):510–526. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.5.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub E. S., Mishell R. I., Weigle W. O., Dutton R. W. A modification of the hemolytic plaque assay for use with protein antigens. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):133–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodmell D. L., Bergman R. K., Hadlow W. J., Munoz J. J. Cellular and humoral antibody responses of normal pastel and sapphire mink to goat erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):221–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.221-227.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodmell D. L., Hadlow W. J., Munoz J. J., Whitford H. W. Hemagglutinin antibody response of normal and Aleutian disease-affected mink to keyhole limpet hemocyanin. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):878–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Crawford T. B., Henson J. B., Gorham J. R. Aleutian disease of mink: detection of large quantities of complement-fixing antibody to viral antigen. J Immunol. 1971 Nov;107(5):1481–1482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. A., Wainwright S. The immunodepressive action of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in mice. J Immunol. 1968 Oct;101(4):717–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L., Mergenhagen S. E., Howard R. J. Effect of virus infections on the function of the immune system. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:525–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.002521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. I. In vivo viral replication and the host antibody response to viral antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):575–593. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


