Abstract
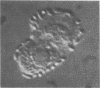
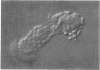
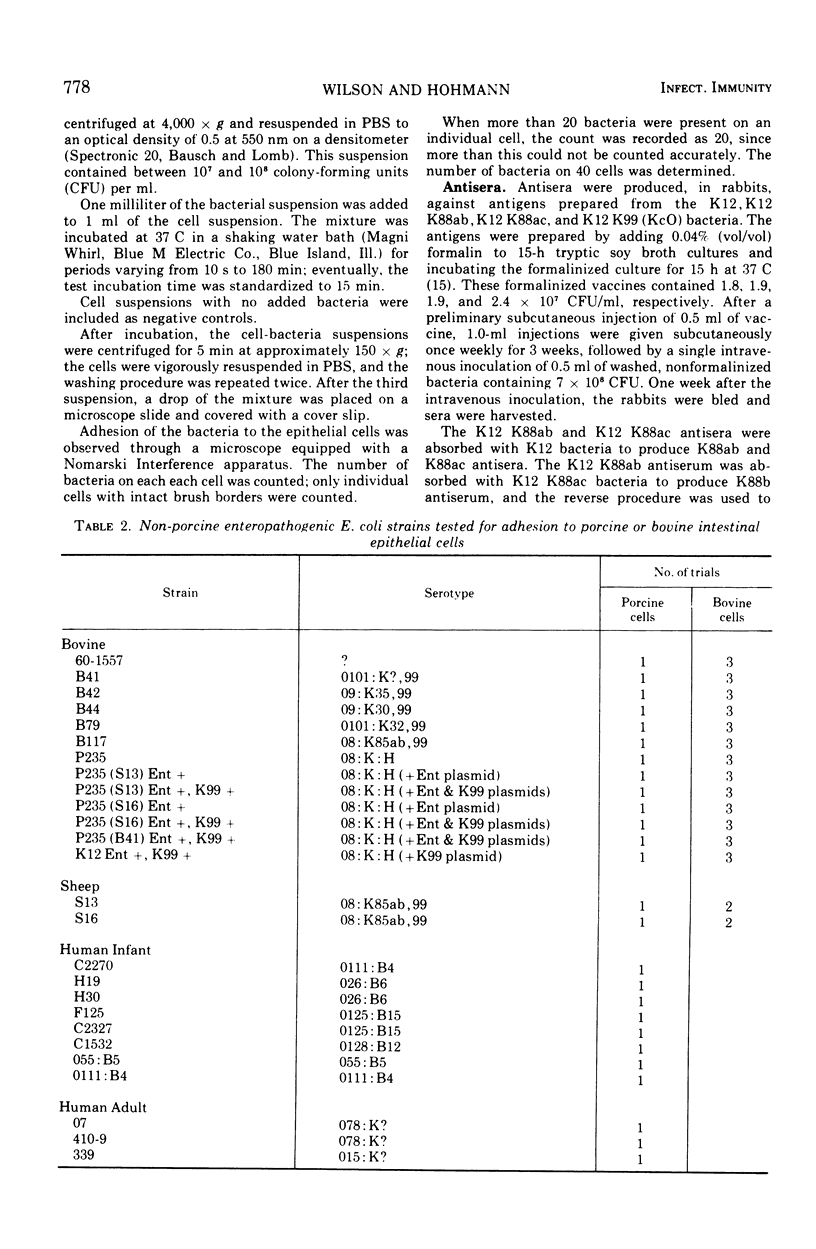
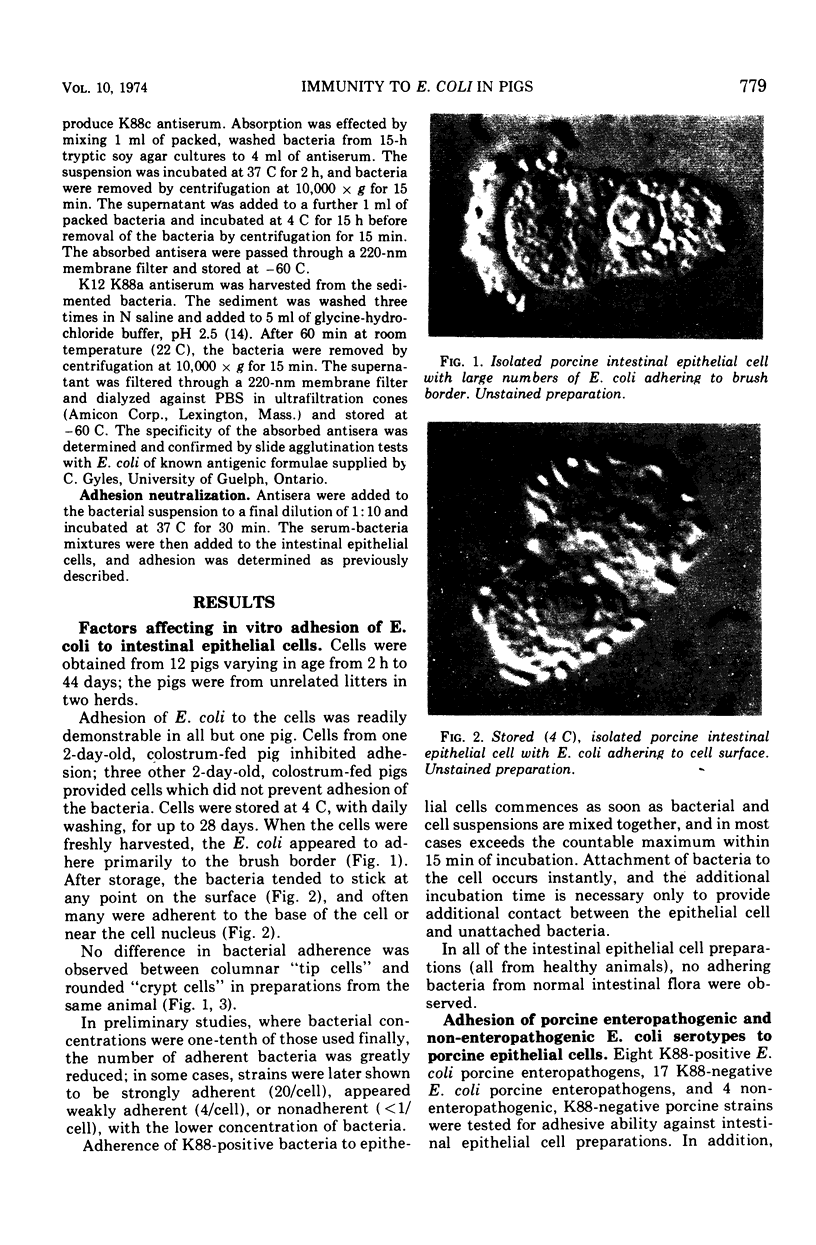
A method was developed to test for the ability of Escherichia coli to adhere to isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Of the E. coli tested, those having either K88ac or K88ab antigens adhered to the cells, and those which did not have these antigens did not. Since some enteropathogenic E. coli did not have the ability to adhere, it is assumed that adherence is not an essential factor of pathogenesis but rather should be considered an enhancement to the pathogenicity of some E. coli. None of the E. coli enteropathogens of cattle tested adhered to either pig or cattle cells. Similarly, human strains did not adhere to pig cells. Although the test system may not have been ideal for human or bovine E. coli, the results reported here suggest that adhesiveness is a property limited to porcine enteropathogenic E. coli carrying one of the K88 antigens. Adhesiveness is associated with the K88c or K88b antigens, and their adhesive ability is only neutralizable by the homologous antisera.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertschinger H. U., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Association of Escherichia coli with the small intestinal epithelium. I. Comparison of enteropathogenic and nonenteropathogenic porcine strains in pigs. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):595–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.595-605.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. A heat-labile enterotoxin from strains of Eschericha coli enteropathogenic for pigs. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):419–426. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Role of the K88 antigen in the pathogenesis of neonatal diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli in piglets. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):918–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.918-927.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine P. H., Weintraub L. R. Preparation of suspensions of small bowel mucosal epithelial cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jun;75(6):1026–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Episome-carried surface antigen K88 of Escherichia coli. I. Transmission of the determinant of the K88 antigen and influence on the transfer of chromosomal markers. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):69–75. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.69-75.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. M., Jones G. W. Protection against enteric disease caused by Escherichia coli--a model for vaccination with a virulence determinant? Nature. 1973 Apr 20;242(5399):531–532. doi: 10.1038/242531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. W., JONES J. E. OBSERVATIONS ON THE ALIMENTARY TRACT AND ITS BACTERIAL FLORA IN HEALTHY AND DISEASED PIGS. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:387–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Observations by the ligated intestinal segment and oral inoculation methods on Escherichia coli infections in pigs, calves, lambs and rabbits. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):499–529. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. The production of oedema disease and diarrhoea in weaned pigs by the oral administration of Escherichia coli: factors that influence the course of the experimental disease. J Med Microbiol. 1968 Aug;1(1):45–59. doi: 10.1099/00222615-1-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Further observations on Escherichia coli enterotoxins with particular regard to those produced by atypical piglet strains and by calf and lamb strains: the transmissible nature of these enterotoxins and of a K antigen possessed by calf and lamb strains. J Med Microbiol. 1972 May;5(2):243–250. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Observations on the pathogenic properties of the K88, Hly and Ent plasmids of Escherichia coli with particular reference to porcine diarrhoea. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Nov;4(4):467–485. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-4-467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. R., Svendsen J. Immunity to Escherichia coli in pigs: serologic response to sows given formalin-treated live Escherichia coli vaccine. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Jun;32(6):891–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]