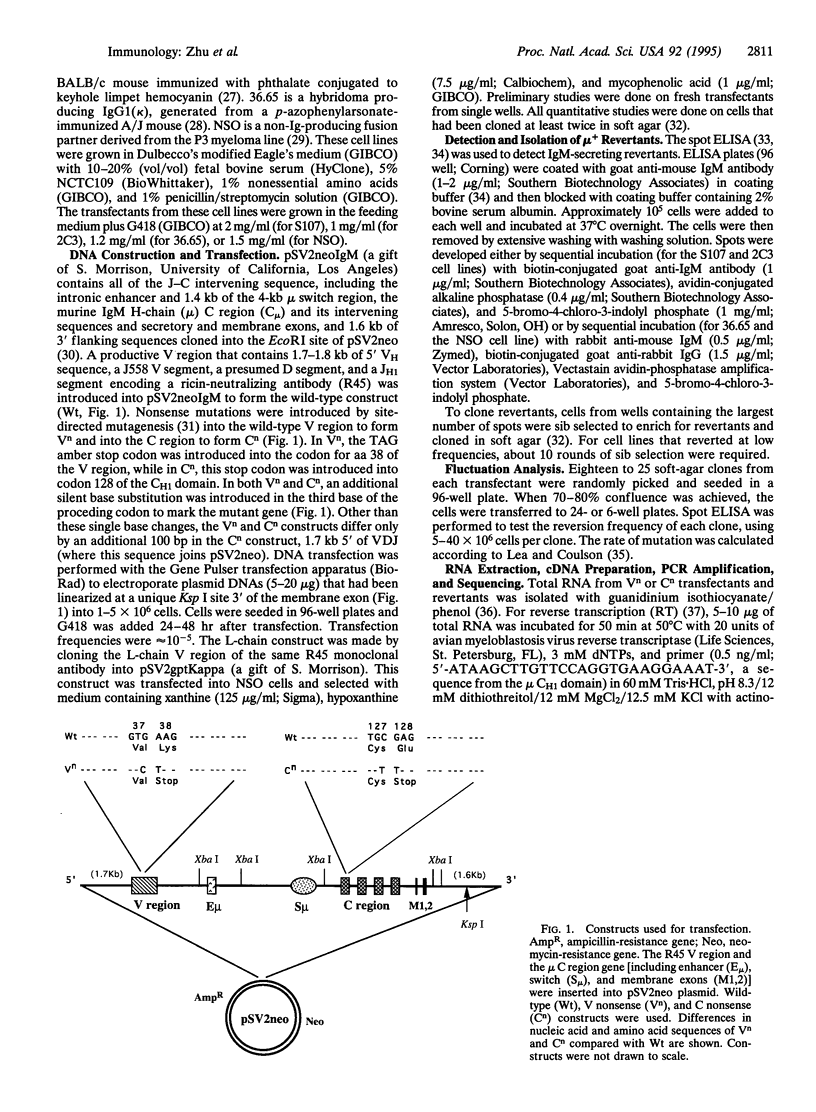
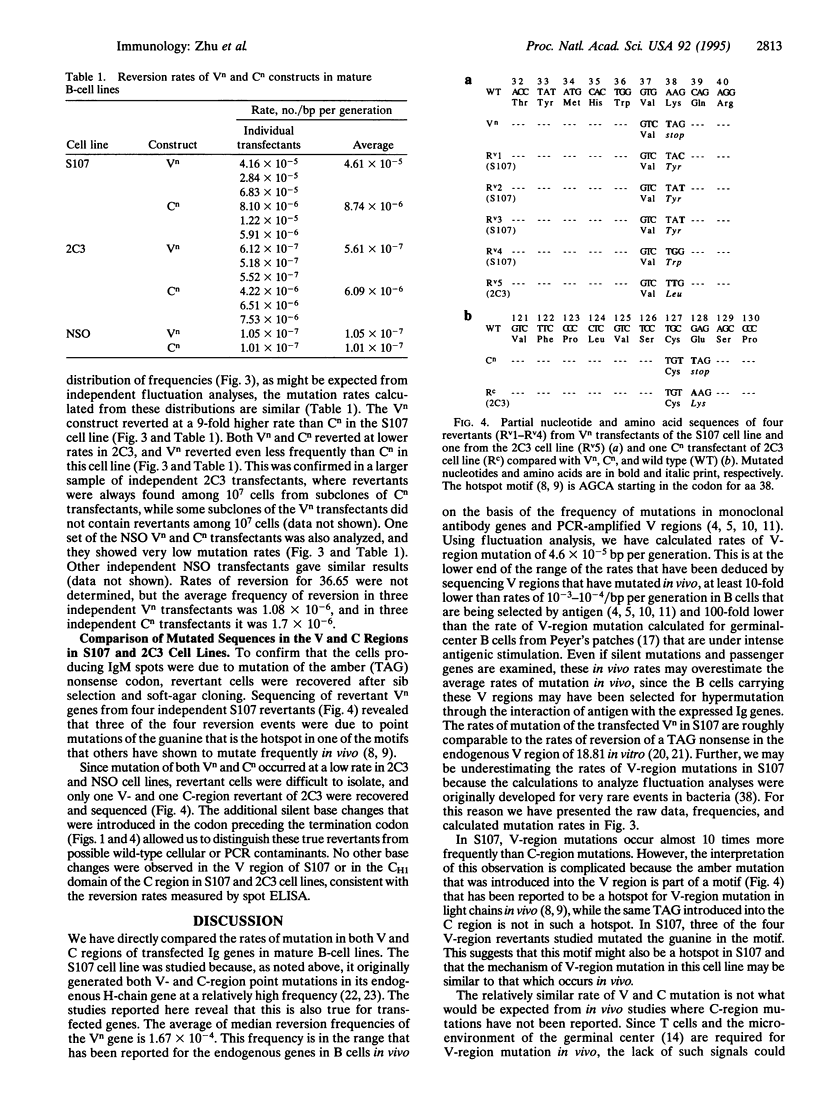
Abstract
pSV2neo plasmids containing an IgM heavy-chain gene with nonsense mutations in either the variable (V) or the constant (C) region were transfected into four differentiated mouse plasma cell lines: S107 and the NSO fusion partner (myeloma cell lines) and 2C3 and 36.65 (hybridoma cell lines). The frequencies of reversion of the nonsense mutations in multiple independent transfectants were determined with the spot ELISA and rates of reversion were calculated by fluctuation analysis. Mutations in both V and C regions were confirmed by sequence analyses. In the S107 cell line, spontaneous point mutations occurred in the V region at a rate of approximately 5 x 10(-5)/bp per cell generation, > 400-fold higher than the rate of V-region mutation in the NSO cell line and considerably higher than the rates in 2C3 and 36.65 hybridoma cell lines. These studies suggest that S107 is a relatively permissive cell line in which V-region mutations can occur constitutively, even though it represents a late stage of B-cell differentiation. Further, the results show that the construct used contains sufficient information in its flanking and coding sequences to allow a relatively high rate of V-region mutation, at least in the S107 cell line.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apel M., Berek C. Somatic mutations in antibodies expressed by germinal centre B cells early after primary immunization. Int Immunol. 1990;2(9):813–819. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.9.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. The role of the kappa enhancer and its binding factor NF-kappa B in the developmental regulation of kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma T., Motoyama N., Fields L. E., Loh D. Y. Mutations of the chloramphenicol acetyl transferase transgene driven by the immunoglobulin promoter and intron enhancer. Int Immunol. 1993 Feb;5(2):121–130. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.2.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berek C., Milstein C. Mutation drift and repertoire shift in the maturation of the immune response. Immunol Rev. 1987 Apr;96:23–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz A. G., Milstein C., González-Fernández A., Pannell R., Larson T., Neuberger M. S. Elements regulating somatic hypermutation of an immunoglobulin kappa gene: critical role for the intron enhancer/matrix attachment region. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz A. G., Neuberger M. S., Milstein C. Discriminating intrinsic and antigen-selected mutational hotspots in immunoglobulin V genes. Immunol Today. 1993 Aug;14(8):405–411. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90144-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Taylor L., Pollard J. W., Steele E. J. Distribution of mutations around rearranged heavy-chain antibody variable-region genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5187–5196. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. D., Rudikoff S., Giusti A. M., Scharff M. D. Somatic mutation in a cultured mouse myeloma cell affects antigen binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1240–1244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. D., Scharff M. D. Antigen-binding mutants of mouse myeloma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5687–5691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durdik J., Gerstein R. M., Rath S., Robbins P. F., Nisonoff A., Selsing E. Isotype switching by a microinjected mu immunoglobulin heavy chain gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2346–2350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French D. L., Laskov R., Scharff M. D. The role of somatic hypermutation in the generation of antibody diversity. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1152–1157. doi: 10.1126/science.2658060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French D., Kelly T., Buhl S., Scharff M. D. Somatic cell genetic analysis of myelomas and hybridomas. Methods Enzymol. 1987;151:50–66. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)51008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geliebter J., Zeff R. A., Melvold R. W., Nathenson S. G. Mitotic recombination in germ cells generated two major histocompatibility complex mutant genes shown to be identical by RNA sequence analysis: Kbm9 and Kbm6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3371–3375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. K., Bankert R. B. Generation of heavy chain-loss mutants in a B cell hybrid mediated by syngeneic idiotype-specific spleen cells. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1677–1682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giusti A. M., Manser T. Somatic generation of hybrid antibody H chain genes in transgenic mice via interchromosomal gene conversion. J Exp Med. 1994 Jan 1;179(1):235–248. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G., Hodous J., Dintzis R. Z., Dintzis H. M. Modification, optimization and simplification of the spot ELISA technique for the enumeration of cells secreting anti-hapten antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1990 May 25;129(2):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90438-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob J., Kelsoe G., Rajewsky K., Weiss U. Intraclonal generation of antibody mutants in germinal centres. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):389–392. doi: 10.1038/354389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob J., Przylepa J., Miller C., Kelsoe G. In situ studies of the primary immune response to (4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)acetyl. III. The kinetics of V region mutation and selection in germinal center B cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Oct 1;178(4):1293–1307. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.4.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Rajewsky K. Stable expression and somatic hypermutation of antibody V regions in B-cell developmental pathways. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:537–559. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leanderson T., Källberg E., Gray D. Expansion, selection and mutation of antigen-specific B cells in germinal centers. Immunol Rev. 1992 Apr;126:47–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb00630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebecque S. G., Gearhart P. J. Boundaries of somatic mutation in rearranged immunoglobulin genes: 5' boundary is near the promoter, and 3' boundary is approximately 1 kb from V(D)J gene. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1717–1727. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. S., Malipiero U. V., Lebecque S. G., Gearhart P. J. Early onset of somatic mutation in immunoglobulin VH genes during the primary immune response. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2007–2019. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies D. H., Kuehl W. M., Scharff M. D. Somatic cell hybridization of mouse myeloma cells. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak-Rothstein A., Siekevitz M., Margolies M. N., Mudgett-Hunter M., Gefter M. L. Hybridoma proteins expressing the predominant idiotype of the antiazophenylarsonate response of A/J mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1120–1124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Jäck H. M., Ellis N., Wabl M. High rate of somatic point mutation in vitro in and near the variable-region segment of an immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6950–6953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogerson B., Hackett J., Jr, Peters A., Haasch D., Storb U. Mutation pattern of immunoglobulin transgenes is compatible with a model of somatic hypermutation in which targeting of the mutator is linked to the direction of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4331–4341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogozin I. B., Kolchanov N. A. Somatic hypermutagenesis in immunoglobulin genes. II. Influence of neighbouring base sequences on mutagenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Nov 15;1171(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90134-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe M. J., Milstein C., Jarvis J. M., Neuberger M. S. Somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin kappa may depend on sequences 3' of C kappa and occurs on passenger transgenes. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2139–2145. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07748.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin S. U., DePinho R., Zack D. J., Rudikoff S., Scharff M. D. Instability of immunoglobulin genes in S107 cell line. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1991 May;17(3):259–276. doi: 10.1007/BF01232821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira G., Scharff M. D. Identification of rare immunoglobulin switch variants using the ELISA spot assay. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Apr 8;148(1-2):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90165-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada S., Saffran D. C., Rawlings D. J., Parolini O., Allen R. C., Klisak I., Sparkes R. S., Kubagawa H., Mohandas T., Quan S. Deficient expression of a B cell cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase in human X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90667-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wabl M., Jäck H. M., Meyer J., Beck-Engeser G., von Borstel R. C., Steinberg C. M. Measurements of mutation rates in B lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1987 Apr;96:91–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M. G., Cesari I. M., Yonkovich S. J., Cohn M. Variability in the lambda light chain sequences of mouse antibody. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1045–1047. doi: 10.1038/2281045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]