Abstract
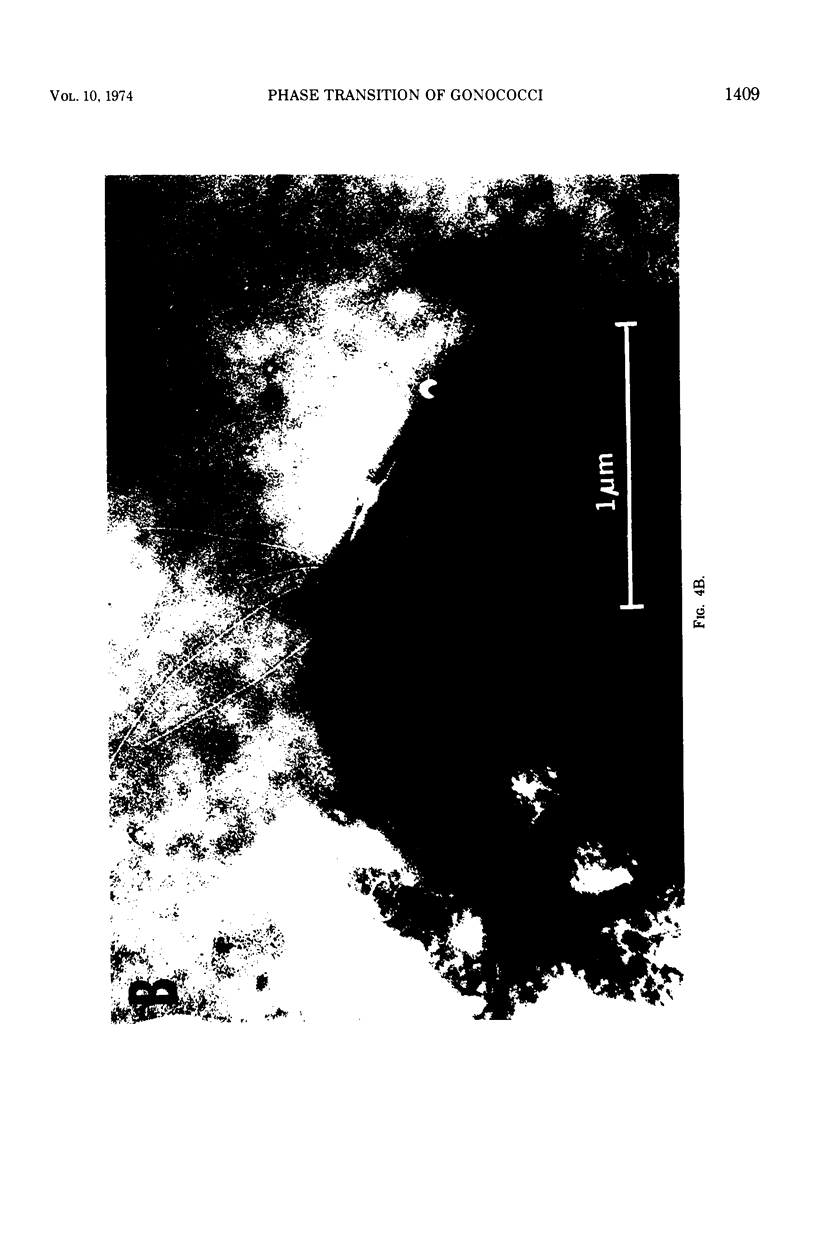
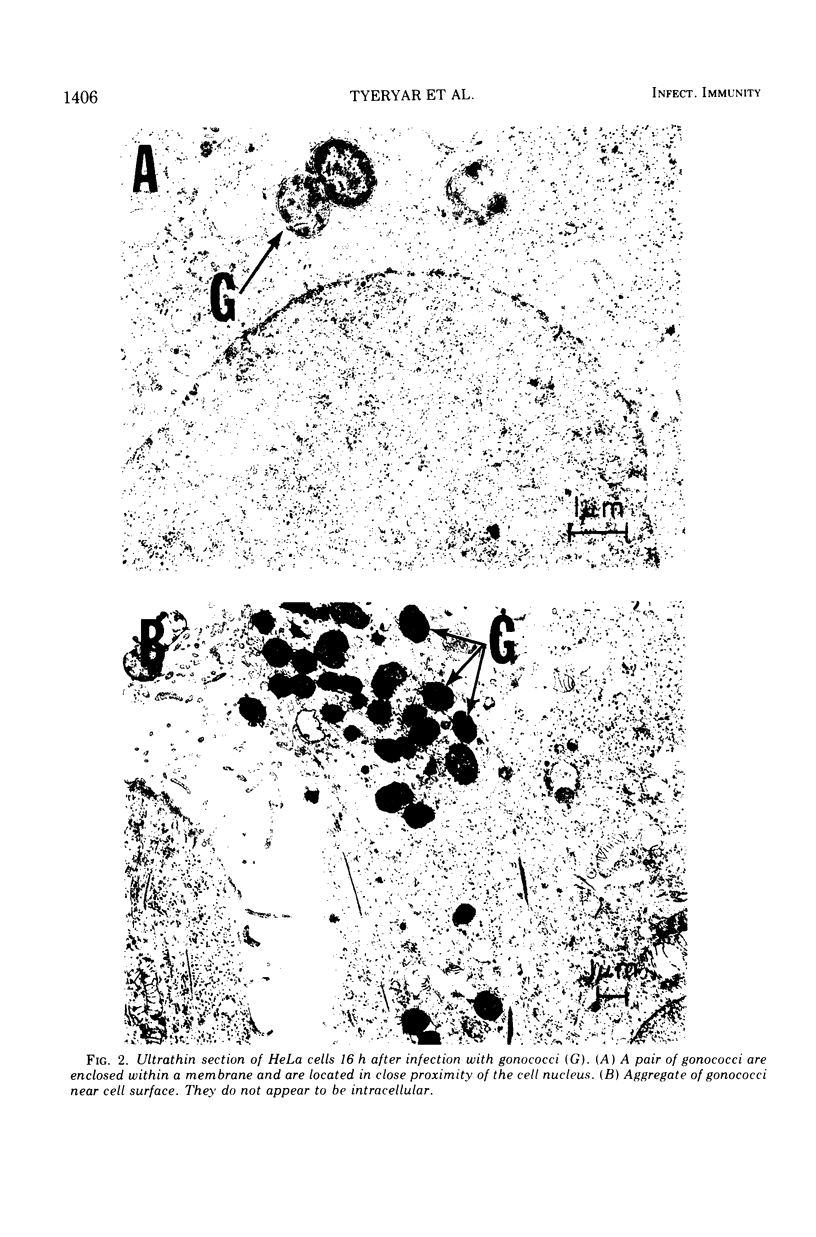
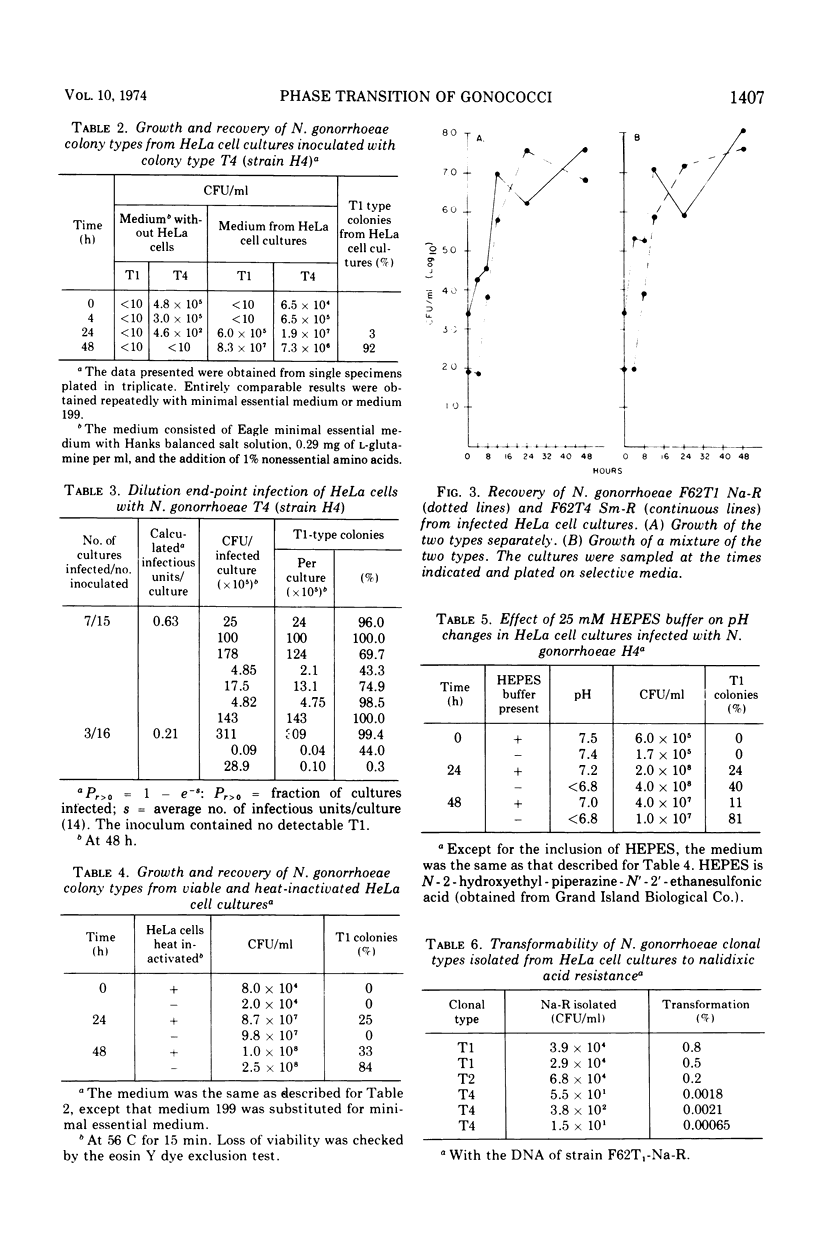
Neisseria gonorrhoeae was cultivated in mammalian cell cultures in an effort to determine if this environment will elicit a T4 → T1 transition. Of four avirulent (T4) isolates tested, only one, H4, yielded T1 colonies. This change was consistently obtained in HeLa, WI-38, and MK2 cells, even when the multiplicity of the gonococcal infection was less than 1 per culture. Growth of the gonococci took place primarily on the surface of the cells, as demonstrated by light and electron microscopy, but occasional bacteria were undoubtedly intracellular. T1 colonies were seen at 24 h and were the major population at 48 h. This shift was favored by the presence of viable cells, since smaller yields of T1 were obtained when the cells were irradiated or heat inactivated. It was also favored by low pH, since T1 recovery was reduced when the buffering capacity of the medium was increased. Although the results suggest that T1 gonococci derived from H4 have a selective advantage over T4 in cell cultures, this is not true of all T1 and T4 colony types. F62 T4, which does not undergo a T4 → T1 shift, propagated as well as T1 in HeLa cell cultures. The change in colony type of strain H4 to T1 was accompanied by formation of pili and by gain in capacity for deoxyribonucleic acid-mediated transformation. It is concluded that gonococci can undergo T4 → T1 phase transition in mammalian cell cultures, but this property is not retained by all strains.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOEVRE K. STUDIES ON TRANSFORMATION IN MORAXELLA AND ORGANISMS ASSUMED TO BE RELATED TO MORAXELLA. 1. A METHOD FOR QUANTITATIVE TRANSFORMATION IN MORAXELLA AND NEISSERIA, WITH STREPLOMYCIN RESISTANCE AS THE GENETIC MARKER. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1964;61:457–473. doi: 10.1111/apm.1964.61.3.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney F. E., Jr, Taylor-Robinson D. Growth and effect of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in organ cultures. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Oct;49(5):435–440. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.5.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. P. A new technique for separation of coverglass substrate from epoxy-embedded specimens for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Nov;37(3):370–377. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilescu M., Lazăr M., Porojan I., Cîrciumărescu T. Long-term cultivation of N. gonorrhoeae in tissue culture. Br J Vener Dis. 1966 Sep;42(3):171–174. doi: 10.1136/sti.42.3.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon F. B., Dressler H. R., Quan A. L., McQuilkin W. T., Thomas J. I. Effect of ionizing irradiation on susceptibility of McCoy cell cultures to Chlamydia trachomatis. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jan;23(1):123–129. doi: 10.1128/am.23.1.123-129.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James-Holmquest A. N., Swanson J., Buchanan T. M., Wende R. D., Williams R. P. Differential attachment by piliated and nonpiliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human sperm. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):897–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.897-902.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny C. P., Sparkes B. G. Inhibitor of bacterial growth released by human cells in culture. Science. 1968 Sep 27;161(3848):1344–1345. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3848.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Bisno A. L. Resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to phagocytosis: relationship to colonial morphology and surface pili. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):310–316. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHBLAT G. H. PPLO contamination in tissue cultures. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:430–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F. Genetic transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to streptomycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1364–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1364-1371.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. IV. Pili: their role in attachment of gonococci to tissue culture cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):571–589. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Hill J. C., Tyeryar F. J., Jr Interaction of gonococci with phagocytic leukocytes from men and mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.98-104.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thongthai C., Sawyer W. D. Studies on the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Relation of colonial morphology and resistance to phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):373–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.373-379.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyeryar F. J., Lawton W. D. Factors Affecting Transformation of Pasteurella novicida. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1312–1317. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1312-1317.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS E., DRESSLER H. R. Centrifugation and Rickettsiae and viruses onto cells and its effect on infection. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Apr;103:691–695. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Watt P. J. Adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to urethral mucosal cells: an electron-microscopic study of human gonorrhea. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):601–605. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]