Abstract
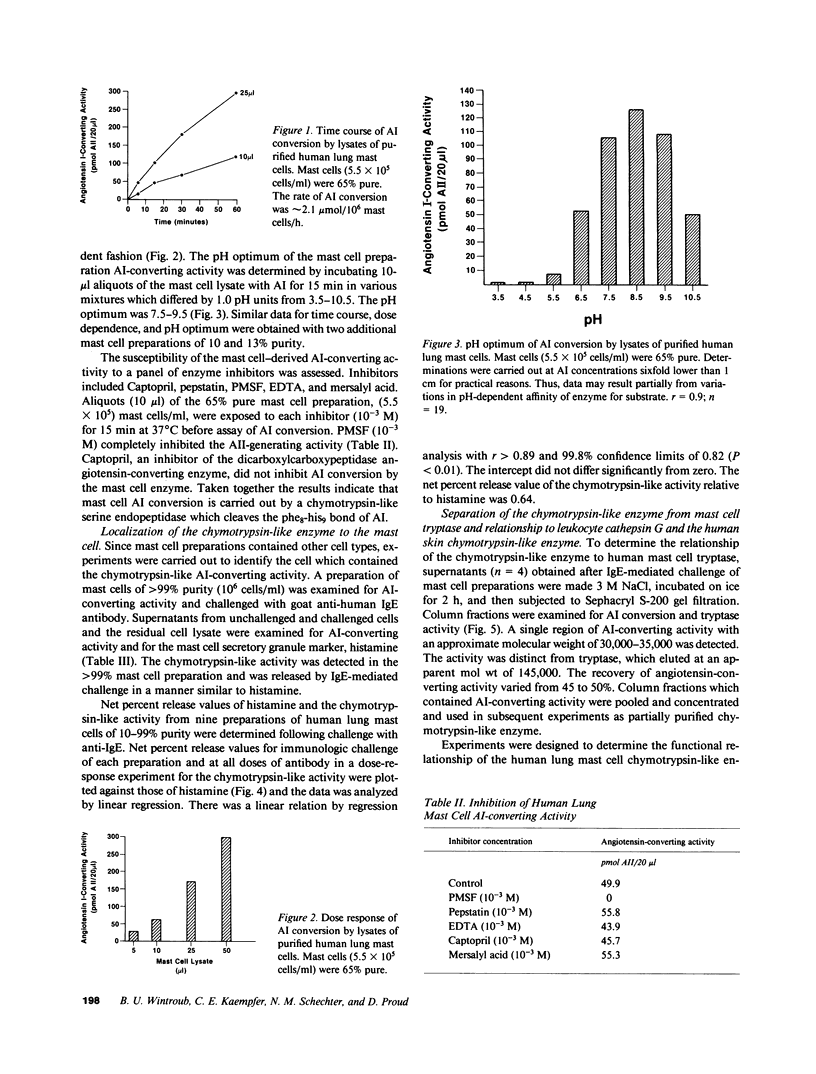
We have used a high performance liquid chromatography assay, which detects chymotryptic cleavage of the phe8-his9 bond of angiotensin I to yield angiotensin II, in order to examine human lung mast cells for the presence of chymotryptic activity. Mast cells, purified from human lung by enzymatic dispersion, countercurrent elutriation, and Percoll gradient centrifugation, were lysed or challenged with goat anti-human IgE. In multiple experiments angiotensin II-converting activity was detected in lysates of 10-99% pure mast cell preparations. Regression analysis of net percent release values of histamine and the angiotensin I-converting activity from dose-response experiments demonstrated a correlation between the two parameters, indicating that the chymotrypsin-like enzyme is a constituent of the mast cell secretory granule. The chymotryptic activity was completely inhibited by 10(-3) M phenylmethylsulfonylfluoride but not by 10(-3) M Captopril, and the pH optimum of activity was 7.5-9.5. Gel filtration of released material separated the activity from tryptase and demonstrated an approximate molecular weight of 30-35,000. The mast cell enzyme, like a human skin chymotrypsin-like proteinase, can be distinguished from leukocyte cathepsin G by lack of susceptibility to inhibition by bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Thus, an enzyme with limited chymotryptic specificity is present in human lung mast cells. The Michaelis constant of the enzyme for angiotensin I of 6.0 X 10(-5) M is similar to that of endothelial cell angiotensin-converting enzyme and is consistent with a reaction of physiologic importance.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMADOR E., DORFMAN L. E., WACKER W. E. SERUM LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITY: AN ANALYTICAL ASSESSMENT OF CURRENT ASSAYS. Clin Chem. 1963 Aug;12:391–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baugh R. J., Travis J. Human leukocyte granule elastase: rapid isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):836–841. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggaman R. A., Schechter N. M., Fraki J., Lazarus G. S. Degradation of the epidermal-dermal junction by proteolytic enzymes from human skin and human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1027–1042. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBuske L., Austen K. F., Czop J., Stevens R. L. Granule-associated serine neutral proteases of the mouse bone marrow-derived mast cell that degrade fibronectin: their increase after sodium butyrate treatment of the cells. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1535–1541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fräki J. E., Hopsu-Havu V. K. Human skin proteases. Differential extraction of proteases and of endogenous protease inhibitors. Arch Dermatol Forsch. 1972;242(4):329–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert H. S., Ornstein L. Basophil counting with a new staining method using alcian blue. Blood. 1975 Aug;46(2):279–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL B. C. A modified spectrophotometric determination of chymotrypsin, trypsin, and thrombin. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Dec;37:1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Conrad D. H., Schulman E. S., Sterk A. R., Ishizaka K. Biochemical analysis of initial triggering events of IgE-mediated histamine release from human lung mast cells. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2357–2362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansén C. T., Hopsu-Havu V. K. Proteolytic enzymes in the skin. II. A comparative study of skin homogenates of five mammalian species. Acta Derm Venereol. 1969;49(5):468–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATAYAMA Y., ENDE N. ESTERASE STUDIES ON DOG MAST-CELL TUMOURS. Nature. 1965 Jan 9;205:190–191. doi: 10.1038/205190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., Auditore J. V., Ende N. Purification and characterization of a mouse mast cell esteroprotease. Exp Mol Pathol. 1971 Apr;14(2):228–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(71)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klickstein L. B., Kaempfer C. E., Wintroub B. U. The granulocyte-angiotensin system. Angiotensin I-converting activity of cathepsin G. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15042–15046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klickstein L. B., Wintroub B. U. Separation of angiotensins and assay of angiotensin-generating enzymes by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Feb;120(1):146–150. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90329-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagunoff D., Pritzl P. Characterization of rat mast cell granule proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Apr;173(2):554–563. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Newball H. H., Schulman E. S., Lichtenstein L. M. Immunoglobulin E-mediated release of a kininogenase from purified human lung mast cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):405–408. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly C. F., Tewksbury D. A., Schechter N. M., Travis J. Rapid conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II by neutrophil and mast cell proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8619–8622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter N. M., Fräki J. E., Geesin J. C., Lazarus G. S. Human skin chymotryptic proteinase. Isolation and relation to cathepsin g and rat mast cell proteinase I. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2973–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman E. S., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Peters S. P., Schleimer R. P., Newball H. H., Lichtenstein L. M. Human lung mast cells: purification and characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2662–2667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Kawahara M. S., Hugli T. E., Vik D., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Generation of C3a anaphylatoxin from human C3 by human mast cell tryptase. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1891–1895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Tryptase from human pulmonary mast cells. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11939–11943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Lewis R. A., Seldin D., Austen K. F. Acid hydrolases and tryptase from secretory granules of dispersed human lung mast cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1290–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Riedel C., Caulfield J. P., Wasserman S. I., Austen K. F. Cell association of complexes of chymase, heparin proteoglycan, and protein after degranulation by rat mast cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2071–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppä H. E., Järvinen M. Rat skin main neutral protease: purification and properties. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Feb;70(2):84–89. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12541221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P. An automated continuous-flow system for the extraction and fluorometric analysis of histamine. Anal Biochem. 1974 Feb;57(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonnesen M. G., Klempner M. S., Austen K. F., Wintroub B. U. Identification of a human neutrophil angiotension II-generating protease as cathepsin G. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):25–30. doi: 10.1172/JCI110437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintroub B. U., Schechter N. B., Lazarus G. S., Kaempfer C. E., Schwartz L. B. Angiotensin I conversion by human and rat chymotryptic proteinases. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Nov;83(5):336–339. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12264144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurt R., Austen K. F. Preparative purification of the rat mast cell chymase: characterization and interaction with granule components. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1405–1419. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


