Abstract
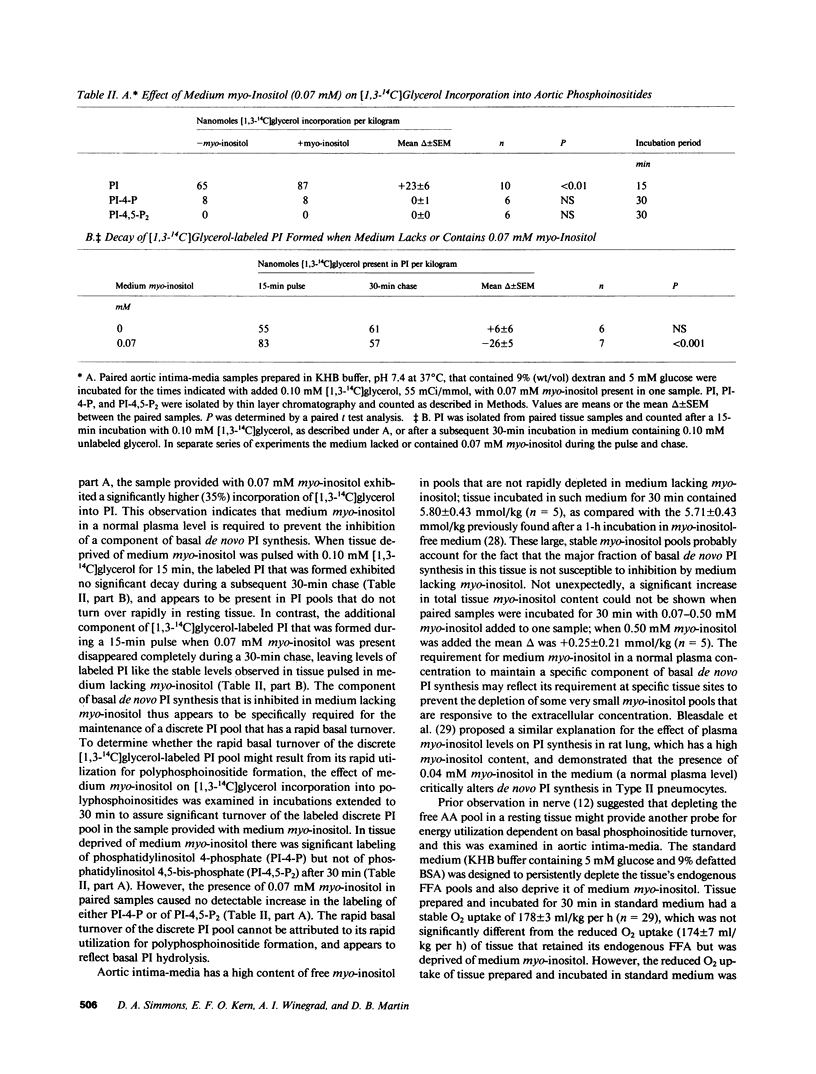
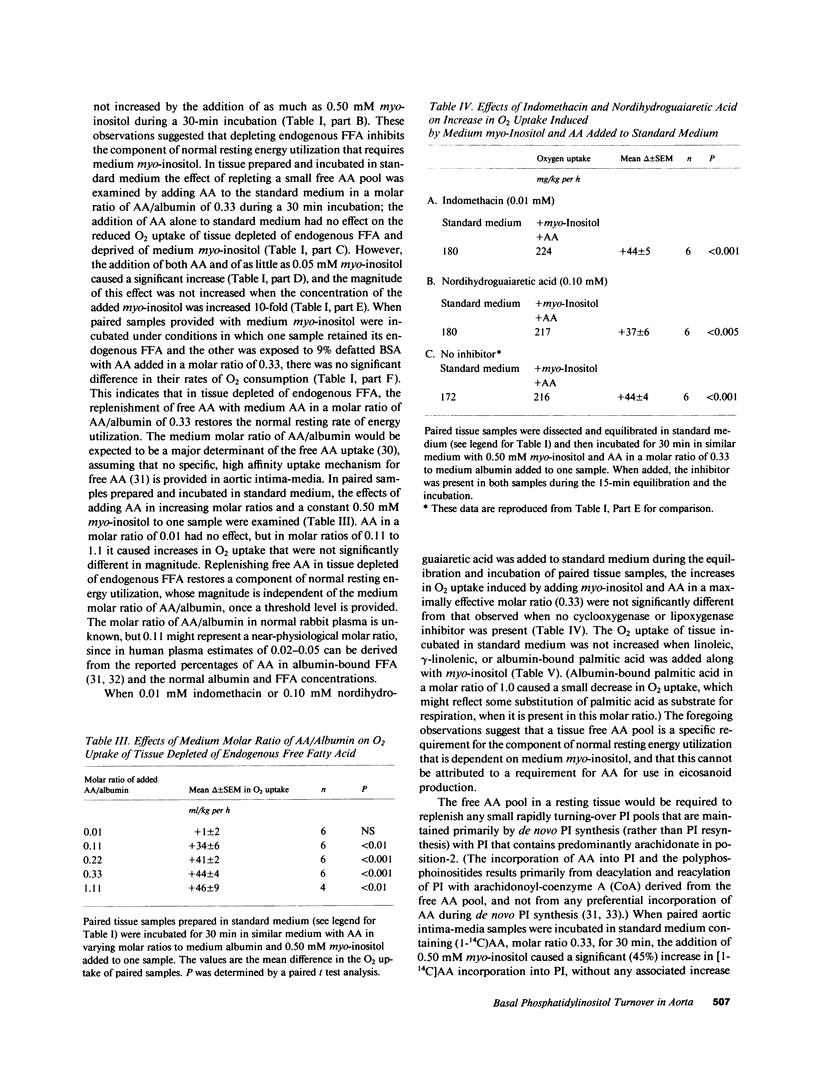
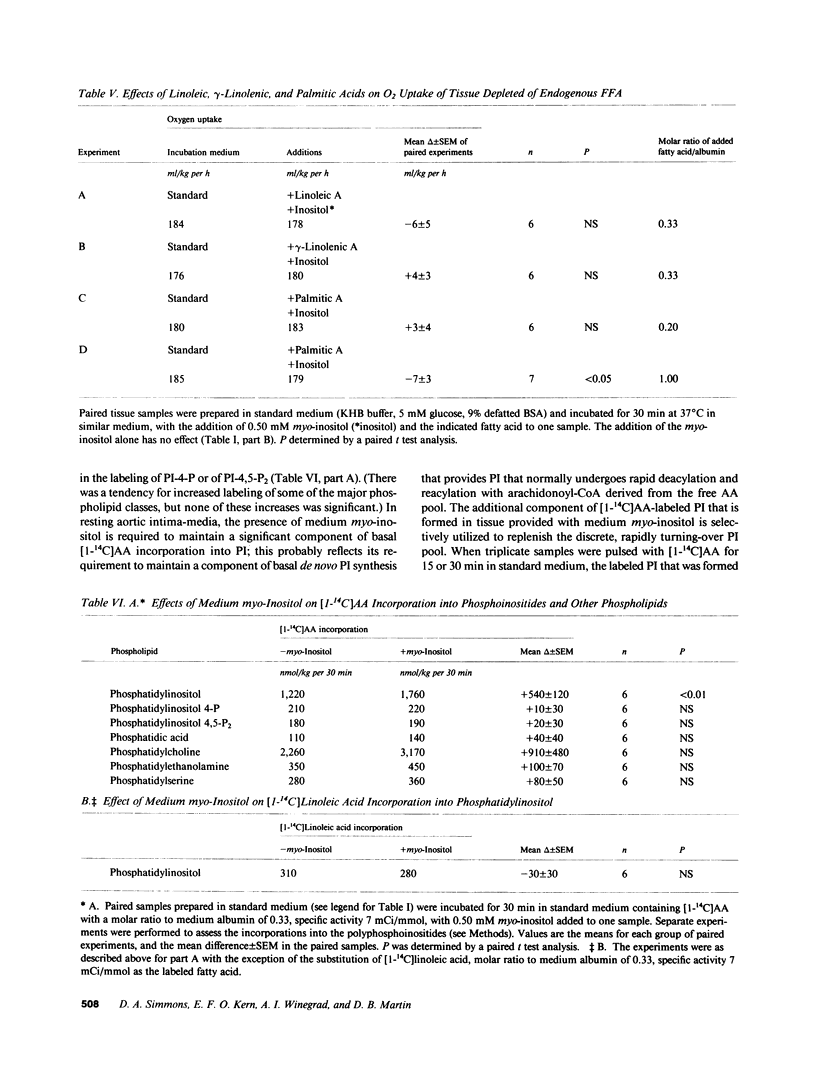
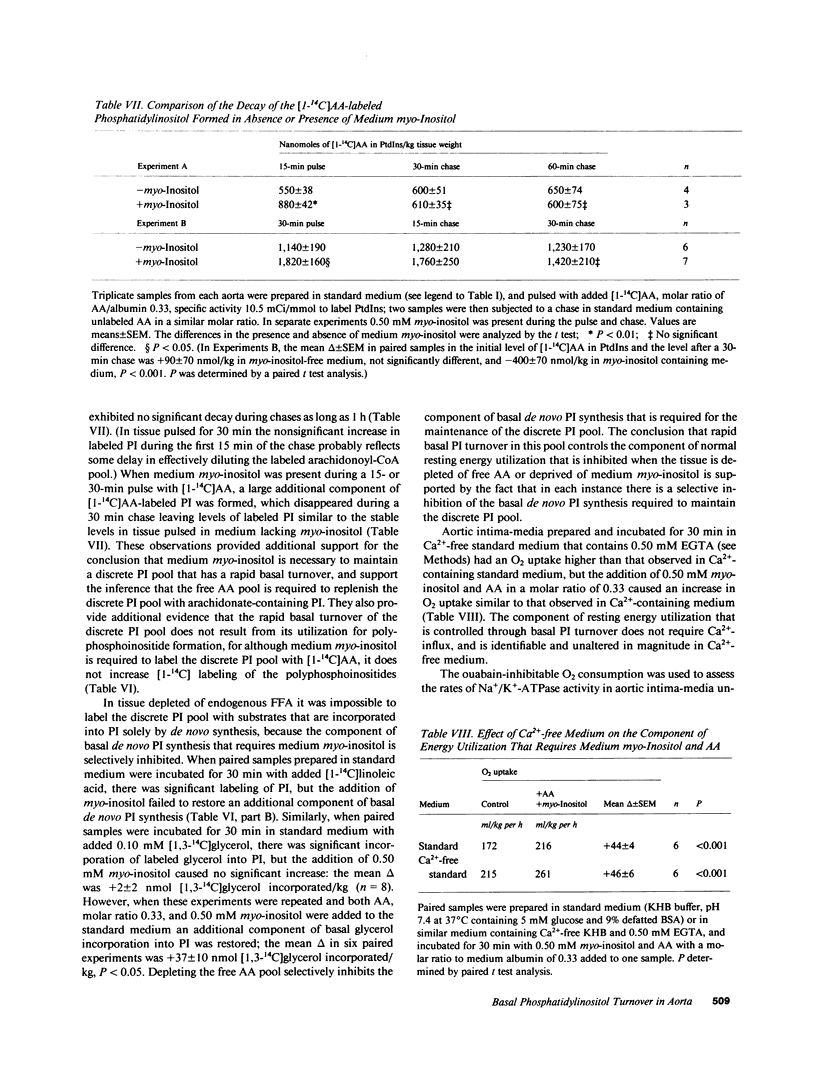
To determine whether basal phosphoinositide turnover plays a role in metabolic regulation in resting rabbit aortic intima-media incubated under steady state conditions, we used deprivation of extracellular myo-inositol as a potential means of inhibiting basal phosphatidylinositol (PI) synthesis at restricted sites and of depleting small phosphoinositide pools with a rapid basal turnover. Medium myo-inositol in a normal plasma level was required to prevent inhibition of a specific component of basal de novo PI synthesis that is necessary to demonstrate a discrete rapidly turning-over [1,3-14C]glycerol-labeled PI pool. Medium myo-inositol was also required to label the discrete PI pool with [1-14C]arachidonic acid (AA). The rapid basal turnover of this PI pool, when labeled with glycerol or AA, was not attributable to its utilization for polyphosphoinositide formation, and it seems to reflect basal PI hydrolysis. Depleting endogenous free AA with medium defatted albumin selectively inhibits the component of basal de novo PI synthesis that replenishes the rapidly turning-over PI pool. A component of normal resting energy utilization in aortic intima-media also specifically requires medium myo-inositol in a normal plasma level and a free AA pool; its magnitude is unaltered by indomethacin, nordihydroguaiaretic acid, or Ca2+-free medium. This energy utilization results primarily from Na+/K+ ATPase activity (ouabain-inhibitable O2 consumption), and in Ca2+-free medium deprivation of medium myo-inositol or of free AA inhibits resting Na+/K+ ATPase activity to a similar degree (60%, 52%). In aortic intima-media basal PI turnover controls a major fraction of resting Na+/K+ ATPase activity.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell R. M., Coleman R. A. Enzymes of glycerolipid synthesis in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:459–487. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamins J. A., Agranoff B. W. Distribution and properties of CDP-diglyceride:inositol transferase from brain. J Neurochem. 1969 Apr;16(4):513–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb06850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C activities of platelets. Differential substrate specificity, Ca2+ requirement, pH dependence, and cellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10227–10231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleasdale J. E., Tyler N. E., Busch F. N., Quirk J. G. The influence of myo-inositol on phosphatidylglycerol synthesis by rat type II pneumonocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):811–818. doi: 10.1042/bj2120811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. Mechanisms of action of transmitters and other substances on smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):606–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borle A. B., Briggs F. N. Microdetermination of calcium in biological material by automatic fluorometric titration. Anal Chem. 1968 Feb;40(2):339–344. doi: 10.1021/ac60258a056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erecińska M., Wilson D. F. Regulation of cellular energy metabolism. J Membr Biol. 1982;70(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01871584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrendelli J. A., Rubin E. H., Orr H. T., Kinscherf D. A., Lowry O. H. Measurement of cyclic nucleotides in histologically defined samples of brain and retina. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):252–259. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., De Jesus P. V., Jr, Winegrad A. I. Effects of insulin and dietary myoinositol on impaired peripheral motor nerve conduction velocity in acute streptozotocin diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1326–1336. doi: 10.1172/JCI108052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN M. R., BENFEY B. G., HOKIN L. E. Phospholipides and adrenaline secretion in guinea pig adrenal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1958 Oct;233(4):814–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin-Neaverson M. Metabolism and role of phosphatidylinositol in acetylcholine-stimulated membrane function. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;83:429–446. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3276-3_40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Receptors and phosphoinositide-generated second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:205–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolles J., Zwiers H., Dekker A., Wirtz K. W., Gispen W. H. Corticotropin-(1--24)-tetracosapeptide affects protein phosphorylation and polyphosphoinositide metabolism in rat brain. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):283–291. doi: 10.1042/bj1940283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling L., Cantley L. The (Na,K)-ATPase of Friend erythroleukemia cells is phosphorylated near the ATP hydrolysis by an endogenous membrane-bound kinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4089–4095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J. Insulin affects the sodium affinity of the rat adipocyte (Na+,K+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10075–10080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco M. E. The phosphatidylinositol cycle in WRK-1 cells. Evidence for a separate, hormone-sensitive phosphatidylinositol pool. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2137–2139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A. D., Berwick L., Orci L., Winegrad A. I. Morphology and metabolism of an aortic intima-media preparation in which an intact endothelium is preserved. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):650–660. doi: 10.1172/JCI108321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A. D., Orci L., Berwick L., Perrelet A., Winegrad A. I. The effects of anoxia on the morphology and composite metabolism of the intact aortic intima-media preparation. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1027–1037. doi: 10.1172/JCI108725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A. D., Orci L., Perrelet A., Winegrad A. I. Studies of the effects of an elevated glucose concentration on the ultrastructure and composite metabolism of the intact rabbit aortic intima-media preparation. Diabetes. 1979 Aug;28(8):720–723. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.8.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVAK M. COLORIMETRIC ULTRAMICRO METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF FREE FATTY ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:431–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. J., Wilson D. B., Sprecher H., Majerus P. W. High affinity esterification of eicosanoid precursor fatty acids by platelets. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):214–220. doi: 10.1172/JCI110959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rana R. S., Mertz R. J., Kowluru A., Dixon J. F., Hokin L. E., MacDonald M. J. Evidence for glucose-responsive and -unresponsive pools of phospholipid in pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7861–7867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Quantitation and characterization of the (Na+,K+)-adenosine triphosphatase in the rat adipocyte plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11946–11952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. A., Winegrad A. I., Martin D. B. Significance of tissue myo-inositol concentrations in metabolic regulation in nerve. Science. 1982 Aug 27;217(4562):848–851. doi: 10.1126/science.6285474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., Hoak J. C. An improved method for the addition of long-chain free fatty acid to protein solutions. Anal Biochem. 1969 Nov;32(2):297–302. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenawa T., Egawa K. CDP-diglyceride:inositol transferase from rat liver. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5419–5423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takhar A. P., Kirk C. J. Stimulation of inorganic-phosphate incorporation into phosphatidylinositol in rat thoracic aorta mediated through V1-vasopressin receptors. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):167–172. doi: 10.1042/bj1940167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Neufeld E. J., Majerus P. W. Phosphoinositide interconversion in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1046–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winegrad A. I., Simmons D. A., Martin D. B. Has one diabetic complication been explained? N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 20;308(3):152–154. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301203080309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yavin E., Zutra A. Separation and analysis of 32P-labeled phospholipids by a simple and rapid thin-layer chromatographic procedure and its application to cultured neuroblastoma cells. Anal Biochem. 1977 Jun;80(2):430–437. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90665-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh L. A., Ling L., English L., Cantley L. Phosphorylation of the (Na,K)-ATPase by a plasma membrane-bound protein kinase in friend erythroleukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6567–6574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


