Abstract
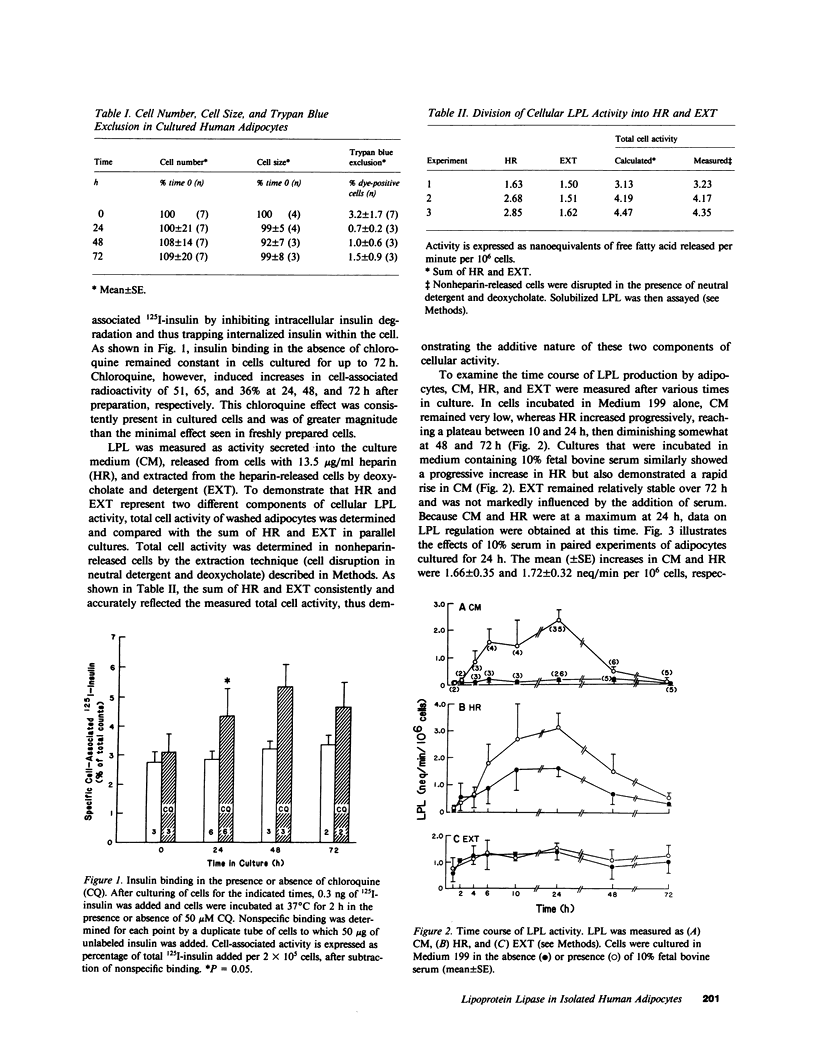
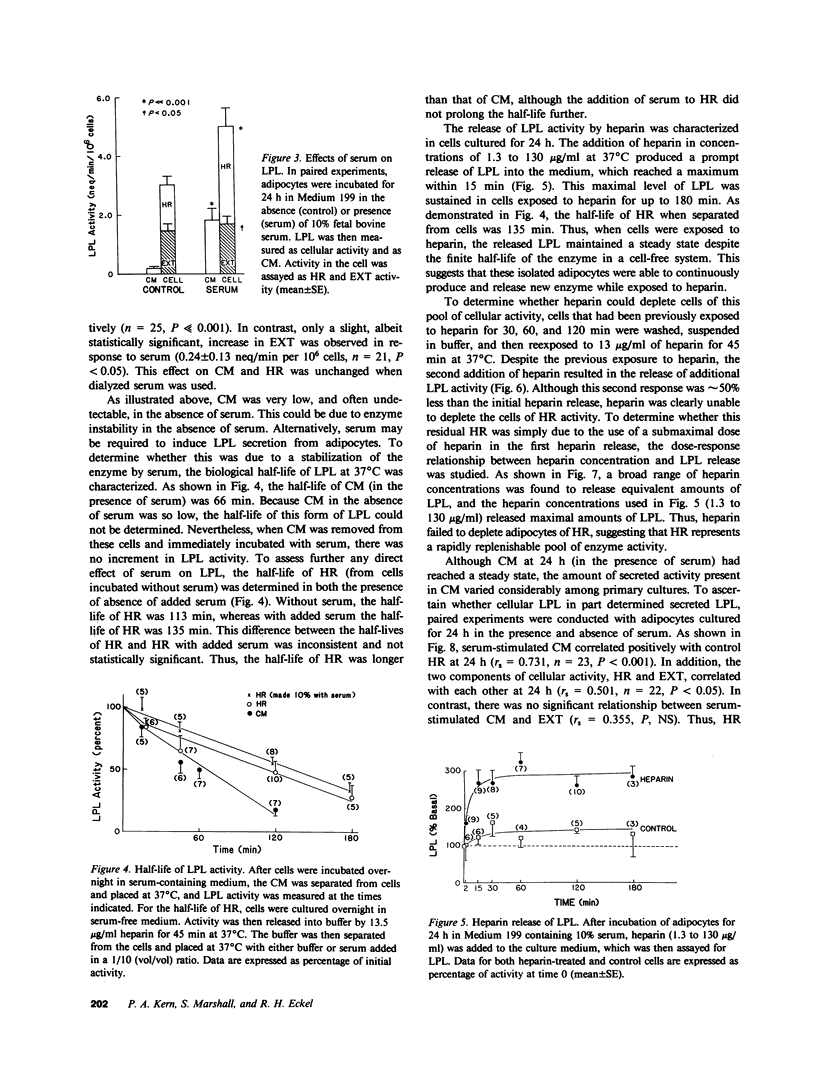
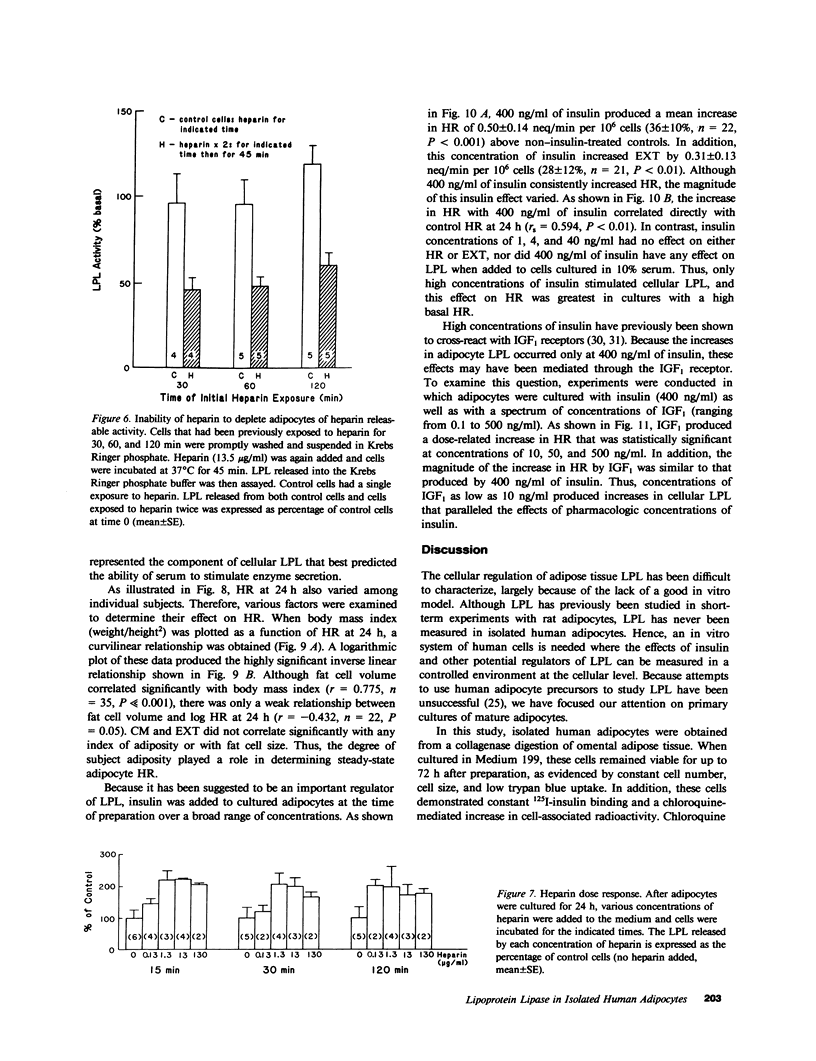
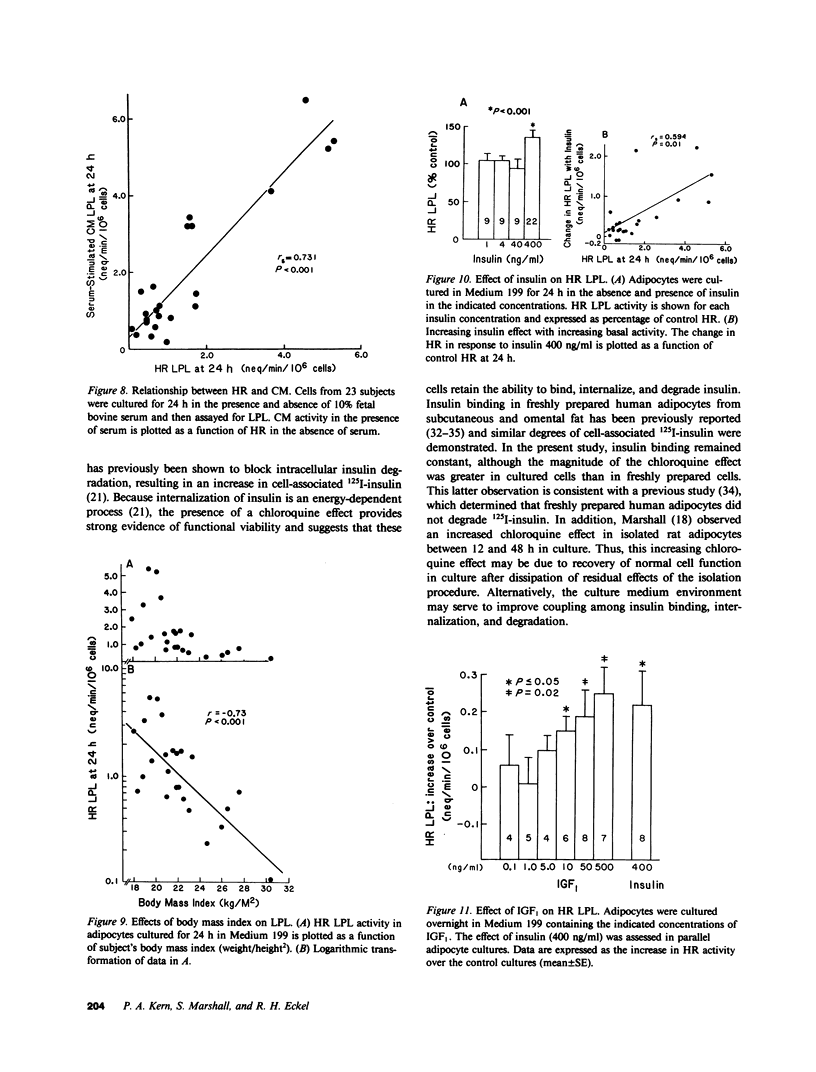
To study the regulation of adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase (LPL) in human adipocytes, omental adipose tissue was obtained from healthy subjects and digested in collagenase. The isolated adipocytes thus obtained were suspended in Medium 199 and cultured at 37 degrees C. Cell viability was demonstrated in adipocytes cultured for up to 72 h by constancy of cell number, cell size, trypan-blue exclusion, and specific 125I-insulin binding. In addition, chloroquine induced an increase in cell-associated 125I-insulin at 24, 48, and 72 h after preparation. Thus, isolated adipocytes retained their ability to bind, internalize, and degrade insulin. LPL was measured as activity secreted into the culture medium (CM), released from cells by heparin (HR), and extracted from cell digests. A broad range of heparin concentrations produced a prompt release of LPL from a rapidly replenishable pool of cellular activity. When cells were cultured in medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, there was a marked stimulation of CM and HR. The secretory response to serum (CM) correlated strongly with HR 24 h after preparation (rs = 0.731, P less than 0.001). In addition, HR was found to correlate logarithmically and inversely with body mass index (r = -0.731, P less than 0.001). Insulin, at 400 ng/ml only, increased HR by 36 +/- 10%, an effect simulated by lower concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1). Thus, LPL is produced and regulated in isolated human adipocytes. The degree of adiposity and serum are important regulators of HR activity, whereas insulin is stimulatory only at a pharmacologic concentration. This effect of insulin may be mediated through the IGF1 receptor. Isolated human adipocytes represent a novel and useful system for the study of LPL and lipid metabolism as well as for other aspects of adipocyte biology.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby P., Bennett D. P., Spencer I. M., Robinson D. S. Post-translational regulation of lipoprotein lipase activity in adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):865–872. doi: 10.1042/bj1760865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfrage P., Vaughan M. Simple liquid-liquid partition system for isolation of labeled oleic acid from mixtures with glycerides. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolinder J., Kager L., Ostman J., Arner P. Differences at the receptor and postreceptor levels between human omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue in the action of insulin on lipolysis. Diabetes. 1983 Feb;32(2):117–123. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunzell J. D., Schwartz R. S., Eckel R. H., Goldberg A. P. Insulin and adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase activity in humans. Int J Obes. 1981;5(6):685–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chait A., Iverius P. H., Brunzell J. D. Lipoprotein lipase secretion by human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):490–493. doi: 10.1172/JCI110473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelain P. G., Van Wyk J., Copeland K. C., Blethen S. L., Underwood L. E. Effect of in vitro action of serum proteases or exposure to acid on measurable immunoreactive somatomedin-C in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Feb;56(2):376–383. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-2-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham V. J., Robinson D. S. Clearing-factor lipase in adipose tissue. Distinction of different states of the enzyme and the possible role of the fat cell in the maintenance of tissue activity. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(2):203–209. doi: 10.1042/bj1120203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Structural and functional homologies in the receptors for insulin and the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):8–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Ward A. P., Goldberg A. C., Trivedi B., Kapadia M. Characterization of somatomedin binding in human serum by ultracentrifugation and gel filtration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):916–921. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo M., Mendlinger S., Fertig J. W. A simple method to determine fat cell size and number in four mammalian species. Am J Physiol. 1971 Sep;221(3):850–858. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.3.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H., Fujimoto W. Y., Brunzell J. D. Development of lipoprotein lipase in cultured 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):288–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91252-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H., Fujimoto W. Y., Brunzell J. D. Effect of in-vitro lifespan of 3T3-L1 cells on hormonal responsiveness of lipoprotein lipase activity. Int J Obes. 1981;5(6):571–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H., Fujimoto W. Y., Brunzell J. D. Insulin regulation of lipoprotein lipase in cultured 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 30;84(4):1069–1075. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91692-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H., Fujimoto W. Y. Quantification of cell death in human fibroblasts by measuring the loss of [14C]thymidine from prelabeled cell monolayers. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):118–124. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90461-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H., Prasad J. E., Kern P. A., Marshall S. Insulin regulation of lipoprotein lipase in cultured isolated rat adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1984 May;114(5):1665–1671. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-5-1665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eder H. A., Gidez L. I. The clinical significance of the plasma high density lipoproteins. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Mar;66(2):431–440. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkeles R. S. Lipoprotein lipase in human adipose tissue. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Jun;46(6):753–762. doi: 10.1042/cs0460753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel A. G., Nilsson-ehle P., Schotz M. C. Regulation of lipoprotein lipase. Induction by insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 23;424(2):264–273. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A., Sherrard D. J., Brunzell J. D. Adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase in chronic hemodialysis: role in plasma triglyceride metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Dec;47(6):1173–1182. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-6-1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausman G. J., Campion D. R., Martin R. J. Search for the adipocyte precursor cell and factors that promote its differentiation. J Lipid Res. 1980 Aug;21(6):657–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L. Plasma forms of somatomedin and the binding protein phenomenon. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J., Gallian E. Methods for the determination of adipose cell size in man and animals. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jan;9(1):110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern P. A., Eckel R. H. Absence of lipoprotein lipase in cultured human adipose stromal cells. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):232–237. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.3.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornhauser D. M., Vaughan M. Release of lipoprotein lipase from fat cells in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 24;380(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S. Kinetics of insulin receptor biosynthesis and membrane insertion. Relationship to cellular function. Diabetes. 1983 Apr;32(4):319–325. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.4.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Olefsky J. M. Effects of lysosomotropic agents on insulin interactions with adipocytes. Evidence for a lysosomal pathway for insulin processing and degradation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10153–10160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merimee T. J., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Dwarfism in the pygmy. An isolated deficiency of insulin-like growth factor I. N Engl J Med. 1981 Oct 22;305(17):965–968. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198110223051701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merimee T. J., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors. Studies in diabetics with and without retinopathy. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 1;309(9):527–530. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309013090904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle P., Carlström S., Belfrage P. Rapid effect on lipoprotein lipase activity in adipose tissue of humans after carbohydrate and lipid intake. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1975 Jul;35(4):373–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle P., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Intra- and extracellular forms of lipoprotein lipase in adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 22;431(1):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle P., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Lipolytic enzymes and plasma lipoprotein metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:667–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Somatomedin/insulin-like growth factor tissue receptors. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):43–67. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Négrel R., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Establishment of preadipocyte clonal line from epididymal fat pad of ob/ob mouse that responds to insulin and to lipolytic hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6054–6058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Jen P., Reaven G. M., Alto P. Insulin binding to isolated human adipocytes. Diabetes. 1974 Jul;23(7):565–571. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.7.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. LIlly lecture 1980. Insulin resistance and insulin action. An in vitro and in vivo perspective. Diabetes. 1981 Feb;30(2):148–162. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.2.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivecrona T., Bengtsson G., Marklund S. E., Lindahl U., Hök M. Heparin-lipoprotein lipase interactions. Fed Proc. 1977 Jan;36(1):60–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin S. M., Walker K., Ashby P., Robinson D. S. Effects of glucose and insulin on the activation of lipoprotin lipase and on protein-synthesis in rat adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):193–199. doi: 10.1042/bj1880193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen O., Hjøllund E., Beck-Nielsen H., Lindskov H. O., Sonne O., Gliemann J. Insulin receptor binding and receptor-mediated insulin degradation in human adipocytes. Diabetologia. 1981 Jun;20(6):636–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson B., Hood B., Angervall G. Effects of prolonged fast on lipoprotein lipase activity eluted from human adipose tissue. Acta Med Scand. 1970 Sep;188(3):225–229. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1970.tb08030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pokrajac N., Lossow W. J., Chaikoff I. L. The effect of nutritional state on lipoprotein lipase activity in isolated rat adipose tissue cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 16;139(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pykälistö O. J., Smith P. H., Brunzell J. D. Determinants of human adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase. Effect of diabetes and obesity on basal- and diet-induced activity. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1108–1117. doi: 10.1172/JCI108185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pykälistö O., Goldberg A. P., Brunzell J. D. Reversal of decreased human adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase and hypertriglyceridemia after treatment of hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Sep;43(3):591–600. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-3-591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Polypeptides with nonsuppressible insulin-like and cell-growth promoting activities in human serum: isolation, chemical characterization, and some biological properties of forms I and II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2365–2369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblat G. H., DeMartinis F. D. Release of lipoprotein lipase from rat adipose tissue cells grown in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91219-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadur C. N., Eckel R. H. Insulin stimulation of adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase. Use of the euglycemic clamp technique. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1119–1125. doi: 10.1172/JCI110547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. S., Brunzell J. D. Increase of adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase activity with weight loss. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1425–1430. doi: 10.1172/JCI110171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer I. M., Hutchinson A., Robinson D. S. The effect of nutritional state on the lipoprotein lipase activity of isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 28;530(3):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner P. M., Chernick S. S., Garrison M. M., Scow R. O. Insulin regulation of lipoprotein lipase activity and release in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Separation and dependence of hormonal effects on hexose metabolism and synthesis of RNA and protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10021–10029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. E., Schotz M. C. Release of lipoprotein lipase activity from isolated fat cells. II. Effect of heparin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):904–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. E., Schotz M. C. Stimulation of release of lipoprotein lipase activity from isolated fat cells by rat serum. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 22;244(138):250–251. doi: 10.1038/newbio244250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taskinen M. R., Nikkilä E. A. Effects of caloric restriction on lipid metabolism in man: changes of tissue lipoprotein lipase activities and of serum lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis. 1979 Mar;32(3):289–299. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(79)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taskinen M. R., Nikkilä E. A. High density lipoprotein subfractions in relation to lipoprotein lipase activity of tissues in man--evidence for reciprocal regulation of HDL2 and HDL3 levels by lipoprotein lipase. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 May;112(3):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90455-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taskinen M. R., Nikkilä E. A. Lipoprotein lipase activity of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle in insulin-deficient human diabetes. Relation to high-density and very-low-density lipoproteins and response to treatment. Diabetologia. 1979 Dec;17(6):351–356. doi: 10.1007/BF01236268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taskinen M. R., Nikkilä E. A. Lipoprotein lipase of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle in human obesity: response to glucose and to semistarvation. Metabolism. 1981 Aug;30(8):810–817. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdemarsson S., Hedner P., Nilsson-Ehle P. Reversal of decreased hepatic lipase and lipoprotein lipase activities after treatment of hypothyroidism. Eur J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;12(5):423–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1982.tb00690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schmid C., Froesch E. R. Biological and immunological properties of insulin-like growth factors (IGF) I and II. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):3–30. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors I and II: some biological actions and receptor binding characteristics of two purified constituents of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):285–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Waldvogel M., Sand I., Froesch E. R. Effect of trypsin treatment of rat adipocytes on biological effects and binding of insulin and insulin-like growth factors: further evidence for the action of insulin-like growth factors through the insulin receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jan;113(3):605–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


