Abstract
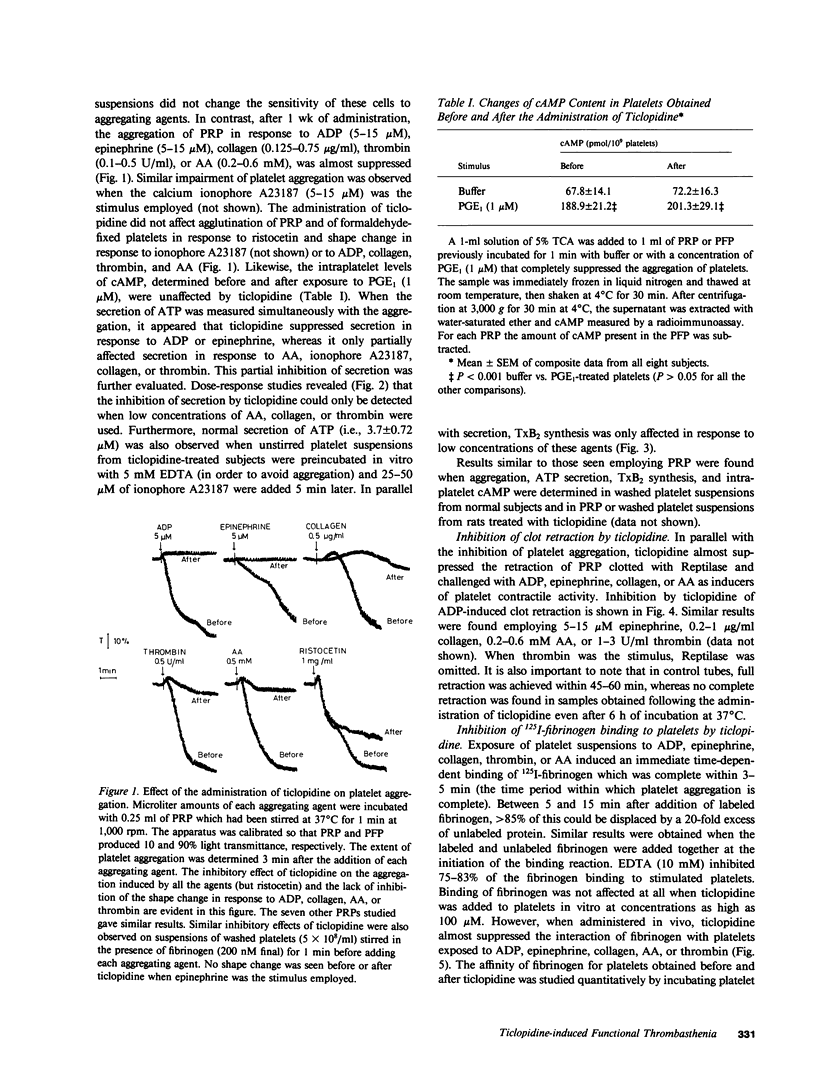
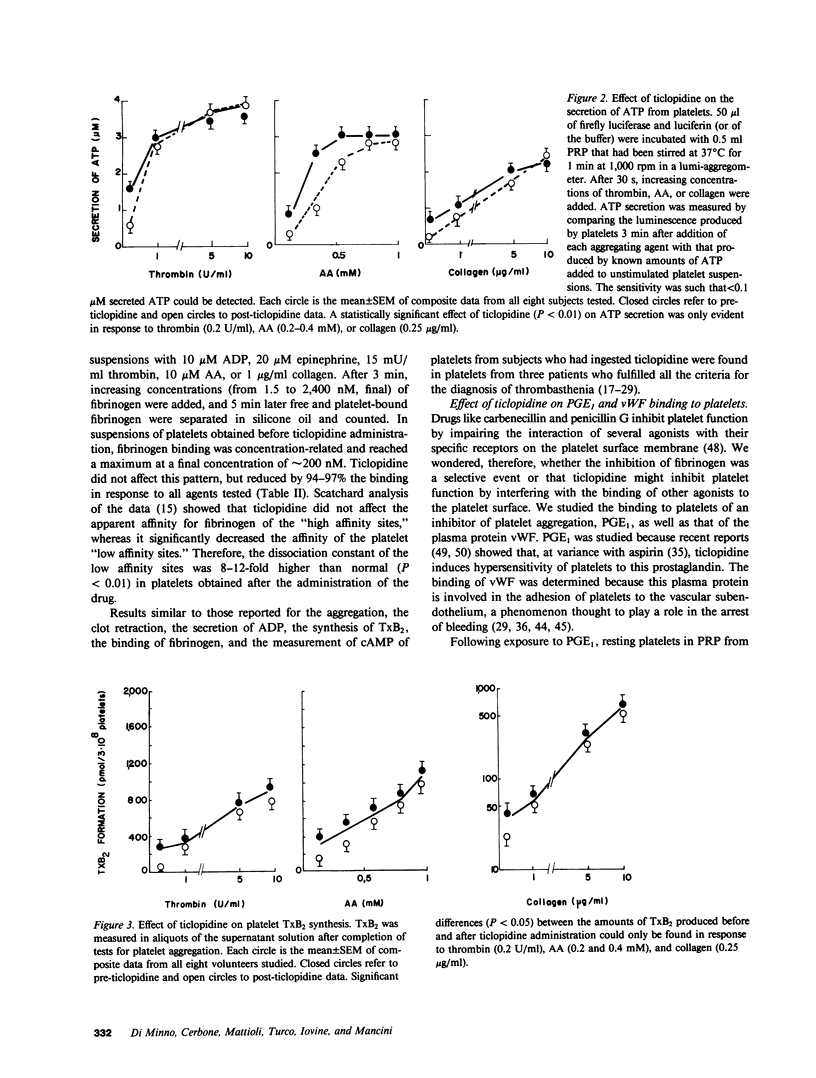
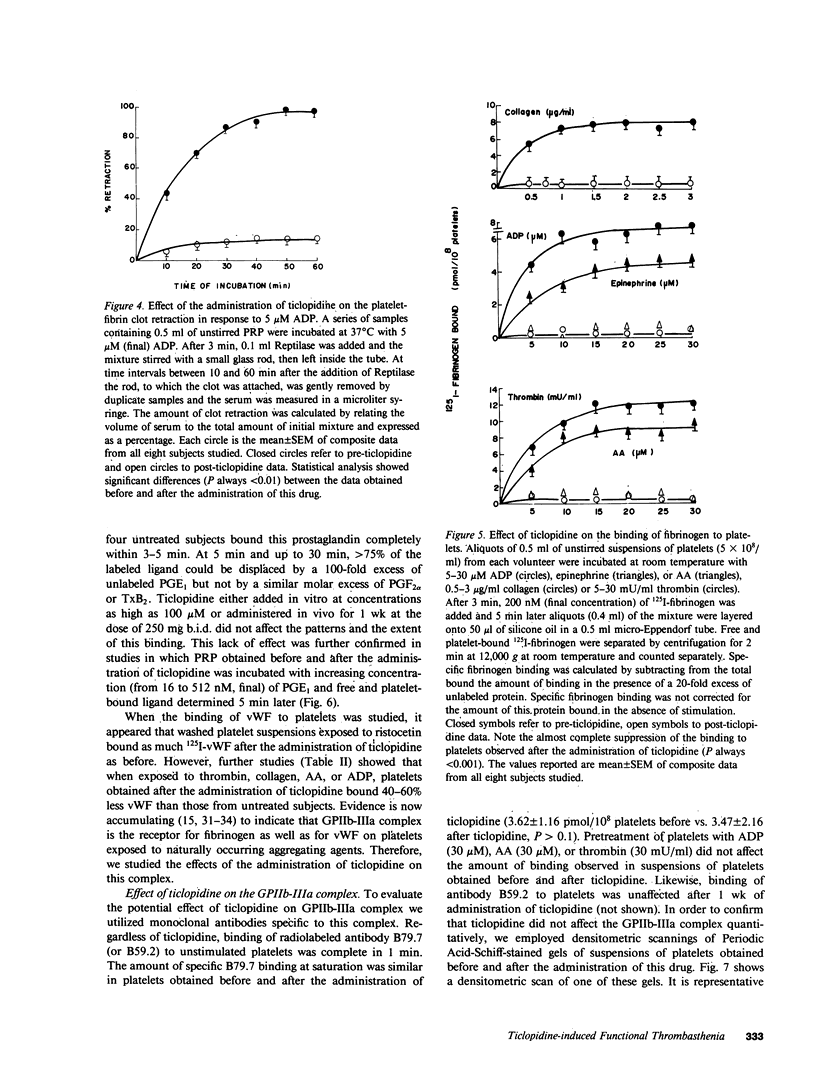
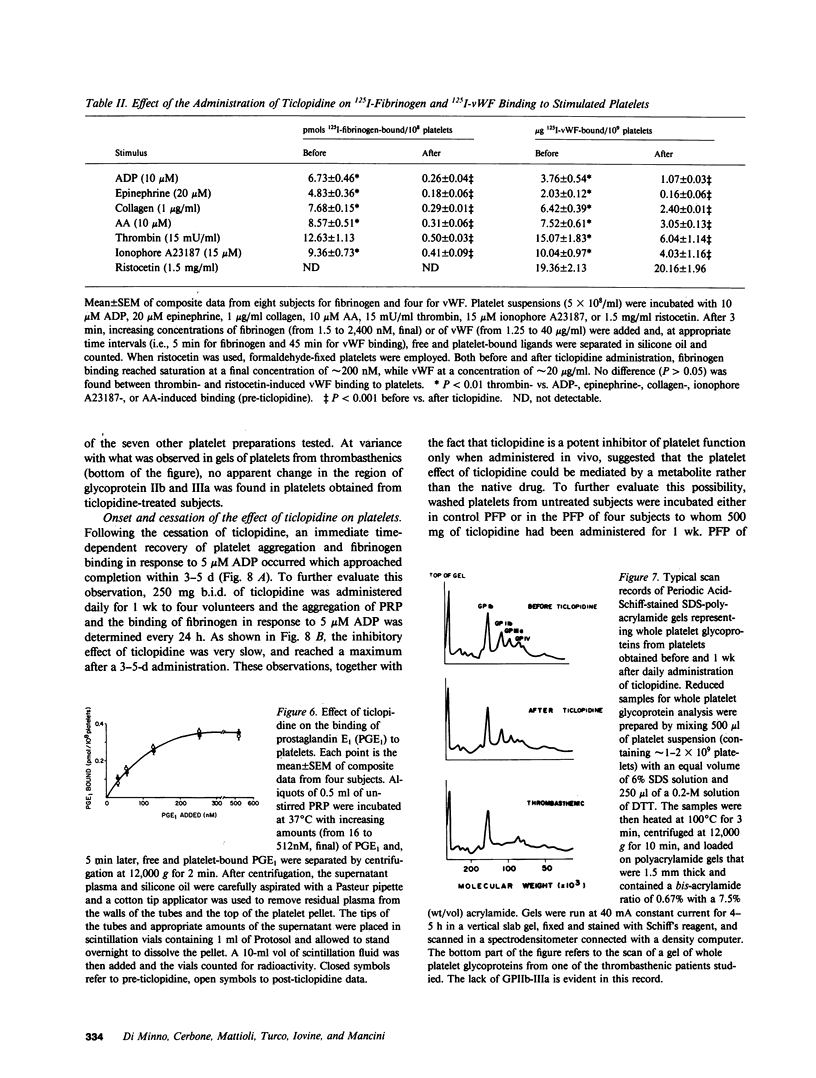
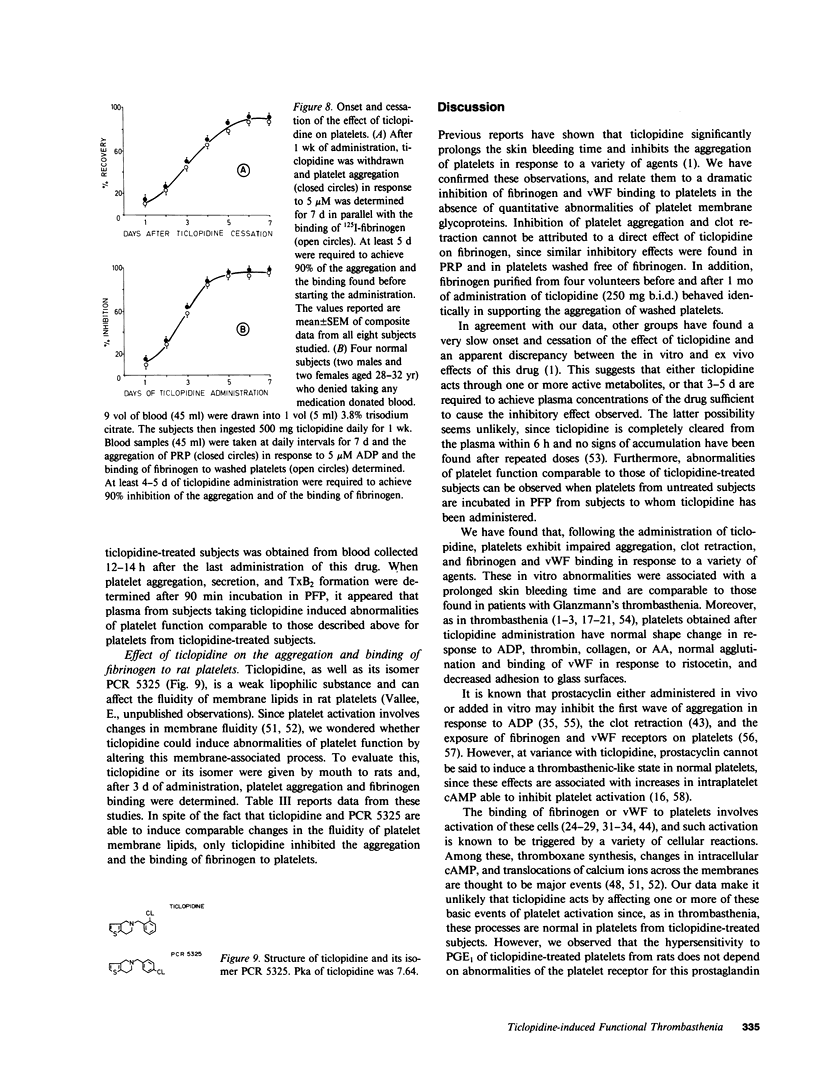
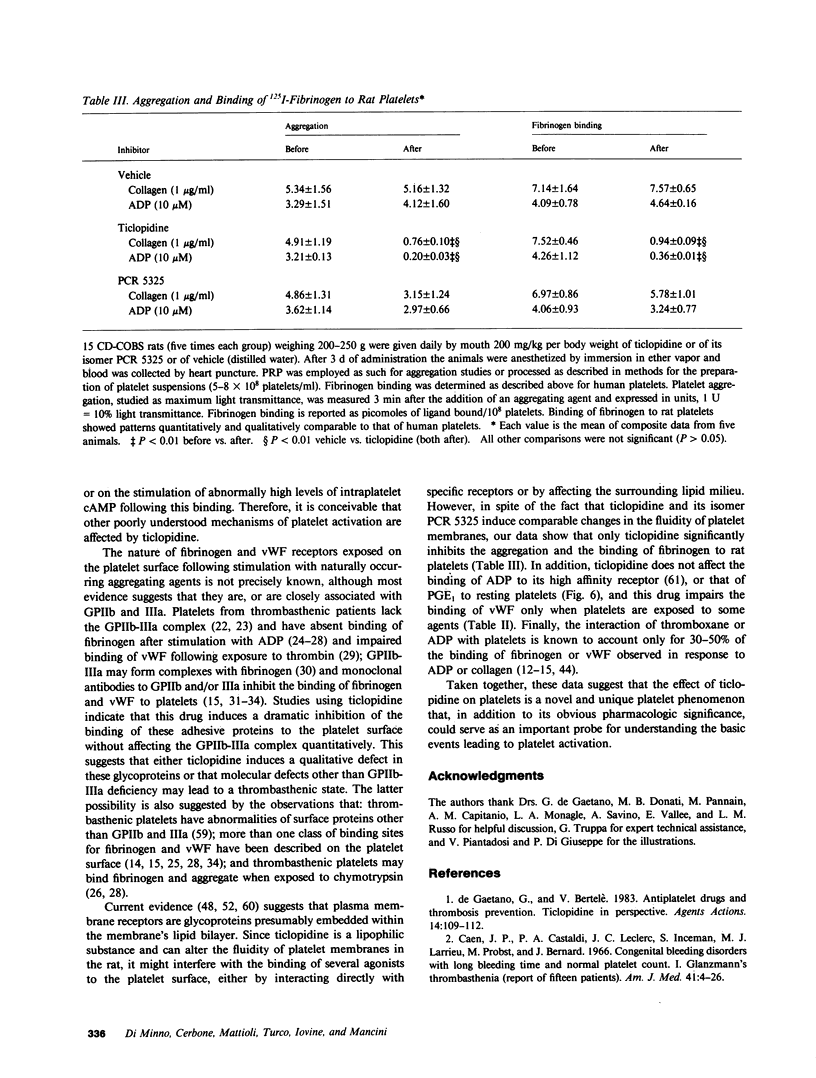
To elucidate the bleeding tendency that follows the administration of ticlopidine, we investigated the skin bleeding time and some ex vivo functions of platelets obtained from eight healthy volunteers before and 1 wk after daily administration of 500 mg of ticlopidine. We found the following: ticlopidine significantly (P less than 0.001) prolonged the skin bleeding time and impaired the binding of radiolabeled fibrinogen and von Willebrand Factor, the clot retraction and the aggregation of platelets in response to ADP, epinephrine, thrombin, ionophore A23187, collagen, or arachidonic acid. In contrast, the administration of this drug did not affect intraplatelet levels of cAMP, agglutination and binding of von Willebrand Factor in response to ristocetin, shape change in response to ADP, collagen, thrombin, or arachidonic acid, or binding of prostaglandin E1 to resting platelets. Secretion of ATP in response to ADP or epinephrine was completely inhibited, whereas secretion as well as thromboxane synthesis in response to high concentrations of collagen, arachidonic acid, calcium ionophore A23187, or thrombin was unaffected. Studies with monoclonal antibodies showed that the glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex (the putative receptor for fibrinogen and von Willebrand Factor on the surface of platelets exposed to naturally occurring aggregating agents) was quantitatively unaffected by ticlopidine. This observation was further confirmed by densitometric scannings of Periodic Acid-Schiff-stained gels of platelet suspensions. The onset, as well as the cessation of the inhibitory effect of ticlopidine on platelets was very slow, and reached a maximum after a 3-5-d administration. In addition, ticlopidine appeared to be a much more potent inhibitor when administered to subjects than when added in vitro to platelets. Finally, abnormalities comparable to those found in volunteers taking ticlopidine were observed when platelets from untreated subjects were incubated in the plasma of ticlopidine-treated subjects. We conclude that ticlopidine induces a thrombasthenic state in normal platelets without affecting the glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex quantitatively. Furthermore, our data suggest that one or more active metabolites rather than the native drug mediate the abnormalities of platelet function observed in ticlopidine-treated subjects.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashida S. I., Abiko Y. Mode of action of ticlopidine in inhibition of platelet aggregation in the rat. Thromb Haemost. 1979 Apr 23;41(2):436–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINKHOUS K. M., READ M. S., MASON R. G. PLASMA THROMBOCYTE-AGGLUTINATING ACTIVITY AND FIBRINOGEN. SYNERGISM WITH ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE. Lab Invest. 1965 Apr;14:335–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. S., Hoxie J. A., Leitman S. F., Vilaire G., Cines D. B. Inhibition of fibrinogen binding to stimulated human platelets by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2417–2421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. S., Vilaire G., Burch J. W. A role for prostaglandins and thromboxanes in the exposure of platelet fibrinogen receptors. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):981–987. doi: 10.1172/JCI110352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. S., Vilaire G. Exposure of platelet fibrinogen receptors by ADP and epinephrine. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1393–1401. doi: 10.1172/JCI109597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonne C., Martin B., Regnault F. Hypothetic mechanism of ticlopidine-induced hypersensitivity to PGE1 in rat platelets. Thromb Res. 1981 Jan 1;21(1-2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS M. J. EFFECT OF FIBRINOGEN ON THE AGGREGATION OF PLATELETS BY ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Dec 31;12:524–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caen J. P., Cronberg S., Levy-Toledano S., Kubisz P., Pinkhas J. P. New data on Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Apr;136(4):1082–1086. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chediak J., Telfer M. C., Vander Laan B., Maxey B., Cohen I. Cycles of agglutination-disagglutination induced by ristocetin in thrombasthenic platelets. Br J Haematol. 1979 Sep;43(1):113–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb03726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemetson K. J., Capitanio A., Lüscher E. F. High resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of the proteins and glycoproteins of human blood platelets and platelet membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 3;553(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Glaser T., Seligsohn U. Effects of ADP and ATP on bovine fibrinogen- and ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Br J Haematol. 1975 Nov;31(3):343–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Peerschke E. I., Scudder L. E., Sullivan C. A. A murine monoclonal antibody that completely blocks the binding of fibrinogen to platelets produces a thrombasthenic-like state in normal platelets and binds to glycoproteins IIb and/or IIIa. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):325–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI110973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Minno G., Bertelé V., Cerletti C., de Gaetano G., Silver M. J. Arachidonic acid induces human platelet-fibrin retraction: the role of platelet cyclic endoperoxides. Thromb Res. 1982 Feb 15;25(4):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Minno G., Shapiro S. S., Catalano P. M., De Marco L., Murphy S. The role of ADP secretion and thromboxane synthesis in factor VIII binding to platelets. Blood. 1983 Jul;62(1):186–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Minno G., Silver M. J., Murphy S. Monitoring the entry of new platelets into the circulation after ingestion of aspirin. Blood. 1983 Jun;61(6):1081–1085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Minno G., Silver M. J., de Gaetano G. Prostaglandins as inhibitors of human platelet aggregation. Br J Haematol. 1979 Dec;43(4):637–647. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb03797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Minno G., Thiagarajan P., Perussia B., Martinez J., Shapiro S., Trinchieri G., Murphy S. Exposure of platelet fibrinogen-binding sites by collagen, arachidonic acid, and ADP: inhibition by a monoclonal antibody to the glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. Blood. 1983 Jan;61(1):140–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto T., Ohara S., Hawiger J. Thrombin-induced exposure and prostacyclin inhibition of the receptor for factor VIII/von Willebrand factor on human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1212–1222. doi: 10.1172/JCI110560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber S. E., Hawiger J. Evidence that changes in platelet cyclic AMP levels regulate the fibrinogen receptor on human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14606–14609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gugler E., Lüscher E. F. Platelet function in congenital afibrinogenemia. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Nov 15;14(3-4):361–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Niewiarowski S., Gurewich V., Thomas D. P. Measurement of fibrinogen and fibrin degradation products in serum by staphylococcal clumping test. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jan;75(1):93–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Parkinson S., Timmons S. Prostacyclin inhibits mobilisation of fibrinogen-binding sites on human ADP- and thrombin-treated platelets. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):195–197. doi: 10.1038/283195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inceman S., Caen J., Bernard J. Aggregation, adhesion, and viscous metamorphosis of platelets in congenital fibrinogen deficiencies. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Jul;68(1):21–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K. J., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. Demonstration and characterization of specific binding sites for factor VIII/von Willebrand factor on human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):656–664. doi: 10.1172/JCI109348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen J. B., Gormsen J. The effect of ticlopidine on platelet function in normal volunteers and in patients with platelet hyperaggregability in vitro. Thromb Res. 1979;16(5-6):663–671. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90210-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornecki E., Niewiarowski S., Morinelli T. A., Kloczewiak M. Effects of chymotrypsin and adenosine diphosphate on the exposure of fibrinogen receptors on normal human and Glanzmann's thrombasthenic platelets. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5696–5701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H., Nurden A. T., Thomaidis A., Caen J. P. Relationship between fibrinogen binding and the platelet glycoprotein deficiencies in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia type I and type II. Br J Haematol. 1981 May;48(1):47–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.00047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Michel T. Plasma membrane receptors. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1185–1189. doi: 10.1172/JCI111073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lips N. P., Sixma J. J., Schiphorst M. E. The effect of ticlopidine administration to humans on the binding of adenosine diphosphate to blood platelets. Thromb Res. 1980 Jan 1;17(1-2):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machin S. J., Chamone D. A., Defreyn G., Vermylen J. The effect of clinical prostacyclin infusions in advanced arterial disease on platelet function and plasma 6-keto PGF1 alpha levels. Br J Haematol. 1981 Mar;47(3):413–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.tb02809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W. Arachidonate metabolism in vascular disorders. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1521–1525. doi: 10.1172/JCI111110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmsten C., Kindahl H., Samuelsson B., Levy-Toledano S., Tobelem G., Caen J. P. Thromboxane synthesis and the platelet release reaction in Bernard-Soulier syndrome, thrombasthenia Glanzmann and Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1977 Apr;35(4):511–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Holburn R. R., Shapiro S. S., Erslev A. J. Fibrinogen Philadelphia. A hereditary hypodysfibrinogenemia characterized by fibrinogen hypercatabolism. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):600–611. doi: 10.1172/JCI107595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. W., Stuart R. K. Interaction of prostaglandins E1 and E2 in regulation of cyclic-AMP and aggregation in human platelets: evidence for a common prostaglandin receptor. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jul;84(1):111–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEver R. P., Bennett E. M., Martin M. N. Identification of two structurally and functionally distinct sites on human platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5269–5275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor J. L., Clemetson K. J., James E., Capitanio A., Greenland T., Lüscher E. F., Dechavanne M. Glycoproteins of platelet membranes from Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. A comparison with normal using carbohydrate-specific or protein-specific labelling techniques and high-resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):379–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Katz A. J., Feinstein M. B. Plasmin inhibition of thrombin-induced platelet aggregation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Apr 30;33(2):286–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Packham M. A., Perry D. W., Harfenist E. J., Pai K. R. Comparison of fibrinogen association with normal and thrombasthenic platelets on exposure to ADP or chymotrypsin. Blood. 1979 Nov;54(5):987–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Leung L. L. Complex formation of platelet membrane glycoproteins IIb and IIIa with fibrinogen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):263–269. doi: 10.1172/JCI110448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan I., Fleisher G., Dvilansky A., Livne A., Parola A. H. Membrane dynamic alterations associated with activation of human platelets by thrombin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 23;598(2):417–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Caen J. P. An abnormal platelet glycoprotein pattern in three cases of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Br J Haematol. 1974 Oct;28(2):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I. Induction of human platelet fibrinogen receptors by epinephrine in the absence of released ADP. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):71–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I., Zucker M. B., Grant R. A., Egan J. J., Johnson M. M. Correlation between fibrinogen binding to human platelets and platelet aggregability. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):841–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jenkins C. S., Lüscher E. F., Larrieu M. Molecular differences of exposed surface proteins on thrombasthenic platelet plasma membranes. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):599–600. doi: 10.1038/257599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Marguerie G. A. Induction of the fibrinogen receptor on human platelets by epinephrine and the combination of epinephrine and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10971–10977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remuzzi G., Benigni A., Dodesini P., Schieppati A., Livio M., De Gaetano G., Day S. S., Smith W. L., Pinca E., Patrignani P. Reduced platelet thromboxane formation in uremia. Evidence for a functional cyclooxygenase defect. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):762–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI110824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Bader R., de Marco L. Glanzmann thrombasthenia: deficient binding of von Willebrand factor to thrombin-stimulated platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6038–6041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., De Marco L., Gatti L., Bader R., Montgomery R. R. Platelets have more than one binding site for von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):1–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI110946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Bennett J. S., McDonough M., Turnbull J. Carbenicillin and penicillin G inhibit platelet function in vitro by impairing the interaction of agonists with the platelet surface. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):329–337. doi: 10.1172/JCI109676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Bennett J. S. Platelets and their membranes in hemostasis: physiology and pathophysiology. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jan;94(1):108–118. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-1-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solum N. O., Stormorken H. Influence of fibrinogen on the aggregation of washed human blood platelets induced by adenosine diphosphate, thrombin, collagen, and adrenaline. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1965;17(Suppl):170+–170+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Kochwa S. Studies of platelet function and proteins in 3 patients with Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jan;71(1):153–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Rogers J. Fibrinogen and platelets in the primary arrest of bleeding. Studies in two patients with congenital afibrinogenemia. N Engl J Med. 1971 Aug 12;285(7):369–374. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197108122850703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Pert J. H., Hilgartner M. W. Platelet function in a patient with thrombasthenia. Blood. 1966 Oct;28(4):524–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Vroman L. Platelet adhesion induced by fibrinogen adsorbed onto glass. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jun;131(2):318–320. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gaetano G., Bertelé V. Antiplatelet drugs and thrombosis prevention: ticlopidine in perspective. Agents Actions. 1984 Jan;14(1):109–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01966842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Minno G., Bertelé V., Bianchi L., Barbieri B., Cerletti C., Dejana E., de Gaetano G., Silver M. J. Effects of any epoxymethano stable analogue of prostaglandin endoperoxides (U-46619) on human platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Apr 30;45(2):103–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


