Abstract
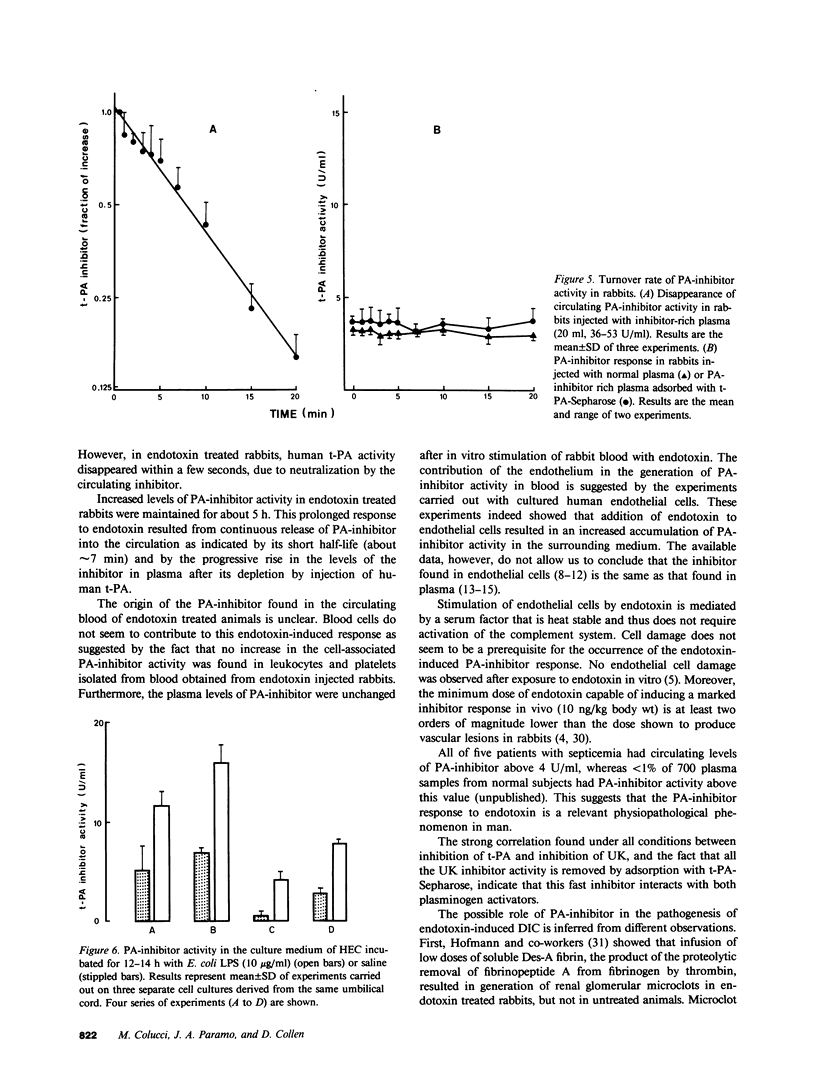
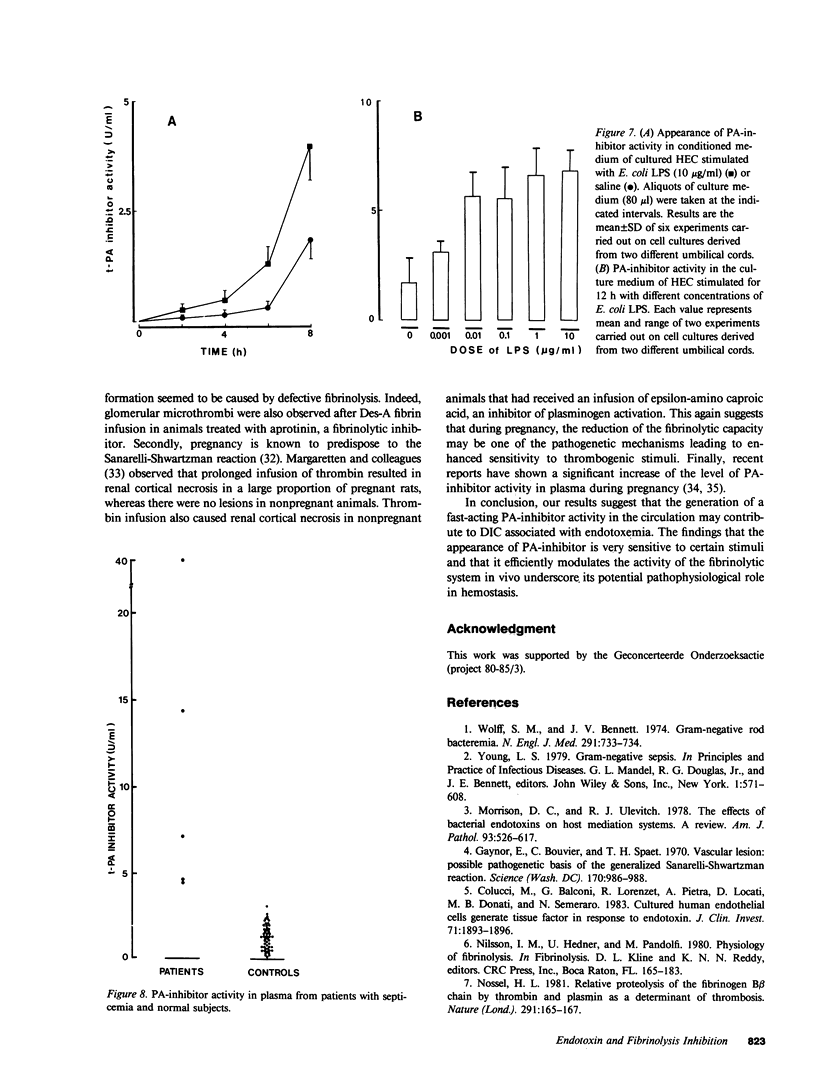
Endotoxin producing bacteria cause disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC); however, the mechanism of endotoxin action in man is still unclear. Impairment of the fibrinolytic system has been suggested as a contributing mechanism. A single injection of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide in rabbits resulted in a marked and prolonged increase of the levels of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activator (PA-inhibitor) in plasma (from 3.9 +/- 0.7 to 41 +/- 13.2 U/ml after 3 h). Gel filtration studies indicated that inhibition of human tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) by rabbit plasma is accompanied by a change in the elution profile of the activator compatible with the formation of an enzyme-inhibitor complex with an apparent molecular weight of 100,000. Injection of human t-PA (1,500 IU/kg body wt) in endotoxin treated animals resulted in very fast inhibition of t-PA and formation of a similar complex. The half-life of circulating PA-inhibitor activity in rabbits was about 7 min as estimated by donor receiver plasma transfusion experiments. Stimulation of cultured human endothelial cells with endotoxin resulted in enhanced rate of accumulation of PA-inhibitor activity in the culture medium (two- to sevenfold increase). In five patients with septicemia, markedly increased levels of PA-inhibitor (14.3 +/- 15.5 U/ml) as compared with control subjects (1.3 +/- 0.7 U/ml) were observed in plasma. A very strong correlation (r = 0.98) was found between inhibition of t-PA and of urokinase in all conditions, suggesting that this fast-acting inhibitor reacts with both plasminogen activators. These data suggest that the appearance of this fast-acting PA-inhibitor is very sensitive to endotoxin stimulation. The marked increase in the level of PA-inhibitor in blood may contribute to the pathogenesis of DIC in septicemia.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRUP T., MULLERTZ S. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Oct;40(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøyum A. Isolation of lymphocytes, granulocytes and macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Balconi G., Lorenzet R., Pietra A., Locati D., Donati M. B., Semeraro N. Cultured human endothelial cells generate tissue factor in response to endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1893–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI110945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosne A. M., Dupuy E., Bodevin E. Production of a fibrinolytic inhibitor by cultured endothelial cells derived from human umbilical vein. Thromb Res. 1978 Mar;12(3):377–387. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90309-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., van Hinsbergh V. W., Verheijen J. H., Wijngaards G. Inhibition of tissue-type plasminogen activator by conditioned medium from cultured human and porcine vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):392–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91161-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor E., Bouvier C., Spaet T. H. Vascular lesions: possible pathogenetic basis of the generalized Shwartzman reaction. Science. 1970 Nov 27;170(3961):986–988. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3961.986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoylaerts M., Rijken D. C., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the activation of plasminogen by human tissue plasminogen activator. Role of fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2912–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhan-Vague I., Moerman B., De Cock F., Aillaud M. F., Collen D. Plasma levels of a specific inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator (and urokinase) in normal and pathological conditions. Thromb Res. 1984 Mar 1;33(5):523–530. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korninger C., Stassen J. M., Collen D. Turnover of human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in rabbits. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Oct;46(3):658–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagarde M., Bryon P. A., Guichardant M., Dechavanne M. A simple and efficient method for platelet isolation from their plasma. Thromb Res. 1980 Feb 1;17(3-4):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G. Latent tissue plasminogen activator produced by human endothelial cells in culture: evidence for an enzyme-inhibitor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6804–6808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Loskutoff D. J. Cultured bovine endothelial cells produce both urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activators. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):631–636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Uytterhoeven M., Collen D. Inhibition of trypsin-like serine proteinases by tripeptide arginyl and lysyl chloromethylketones. Thromb Res. 1984 Jun 1;34(5):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90247-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., van Mourik J. A., Erickson L. A., Lawrence D. Detection of an unusually stable fibrinolytic inhibitor produced by bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGARETTEN W., ZUNKER H. O., MCKAY D. G. PRODUCTION OF THE GENERALIZED SHWARTZMAN REACTION IN PREGNANT RATS BY INTRAVENOUS INFUSION OF THROMBIN. Lab Invest. 1964 Jun;13:552–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. M., Stewart G. J. The effects of endotoxin on vascular endothelium. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):833–848. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ulevitch R. J. The effects of bacterial endotoxins on host mediation systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):526–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L. Relative proteolysis of the fibrinogen B beta chain by thrombin and plasmin as a determinant of thrombosis. Nature. 1981 May 14;291(5811):165–167. doi: 10.1038/291165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Juhan-Vague I., de Cock F., Collen D. Measurement of human tissue-type plasminogen activator by a two-site immunoradiometric assay. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Feb;101(2):274–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Tobia A., Ossowski L., Quigley J. P., Rifkin D. B., Reich E. An enzymatic function associated with transformation of fibroblasts by oncogenic viruses. I. Chick embryo fibroblast cultures transformed by avian RNA tumor viruses. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):85–111. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen J. H., Mullaart E., Chang G. T., Kluft C., Wijngaards G. A simple, sensitive spectrophotometric assay for extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator applicable to measurements in plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Dec 27;48(3):266–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WONG T. C. A study on the generalized Shwartzman reaction in pregnant rats induced by bacterial endotoxin. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1962 Sep 15;84:786–797. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(62)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Mellbring G., Rånby M. Plasminogen activator release during venous stasis and exercise as determined by a new specific assay. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jan 24;127(2):279–288. doi: 10.1016/s0009-8981(83)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S. M., Bennett J. V. Editorial: Gram-negative-rod bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 3;291(14):733–734. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410032911411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


