Abstract
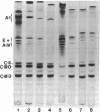
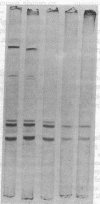
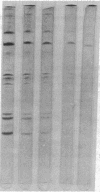
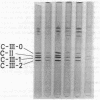
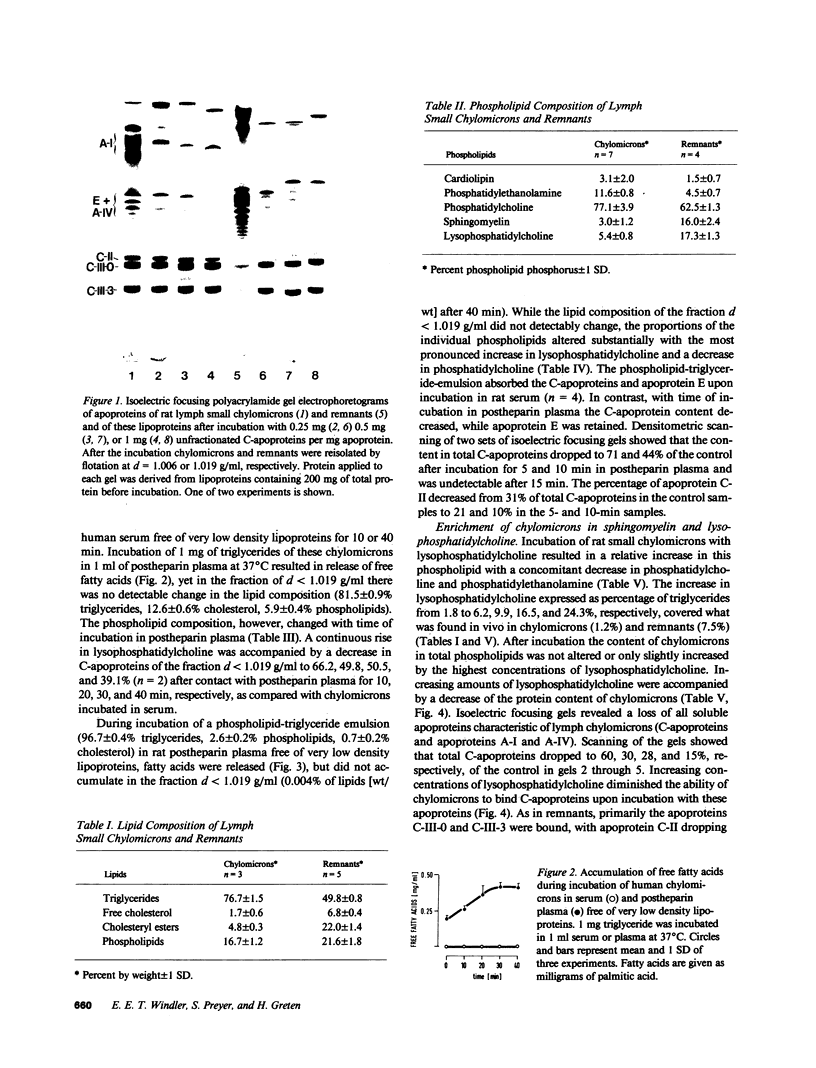
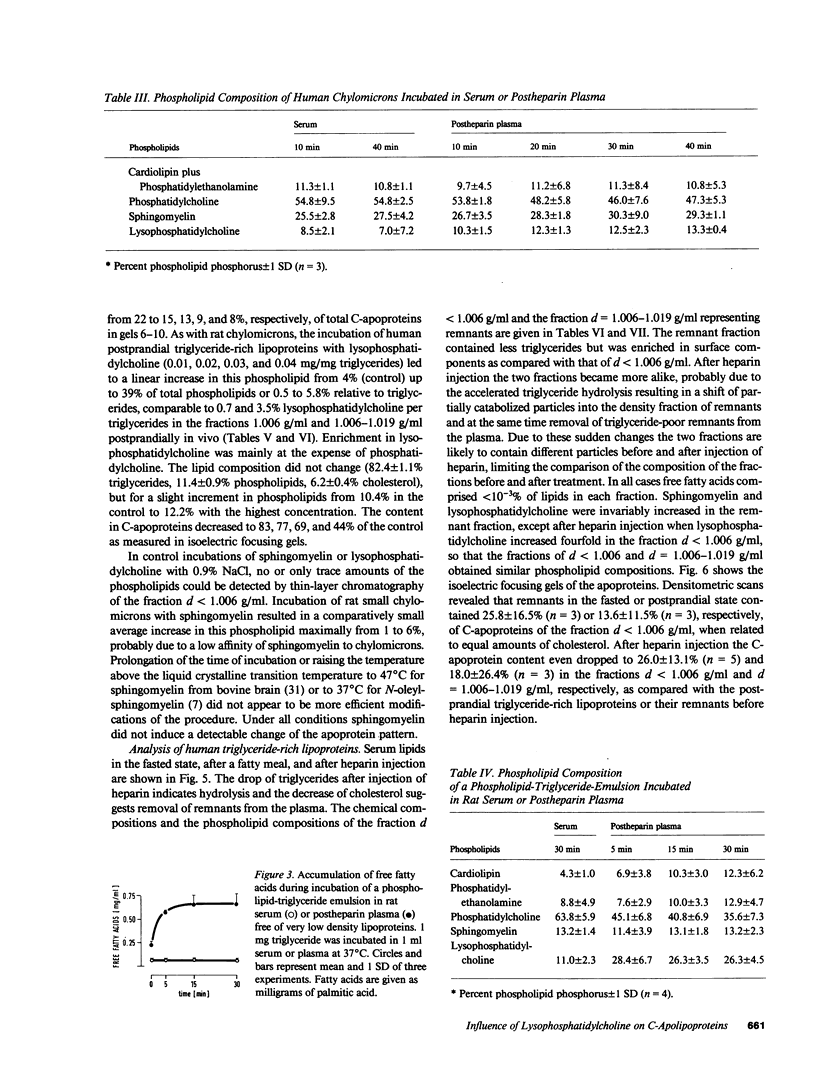
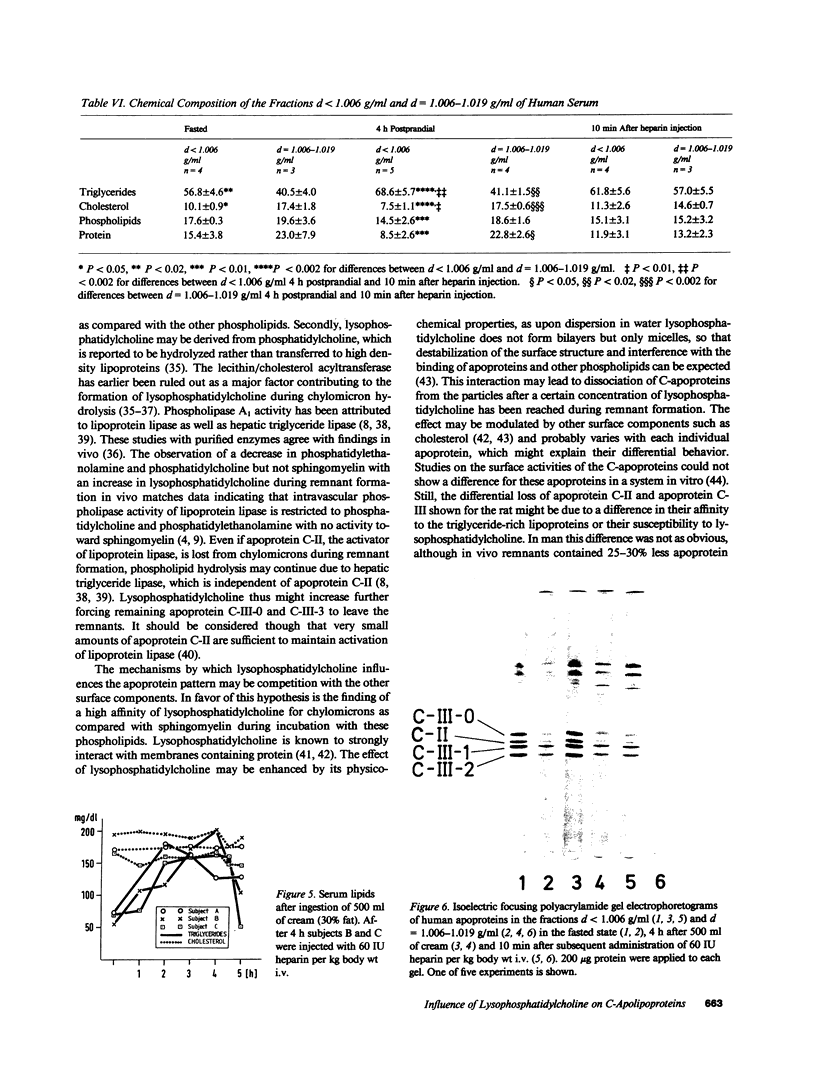
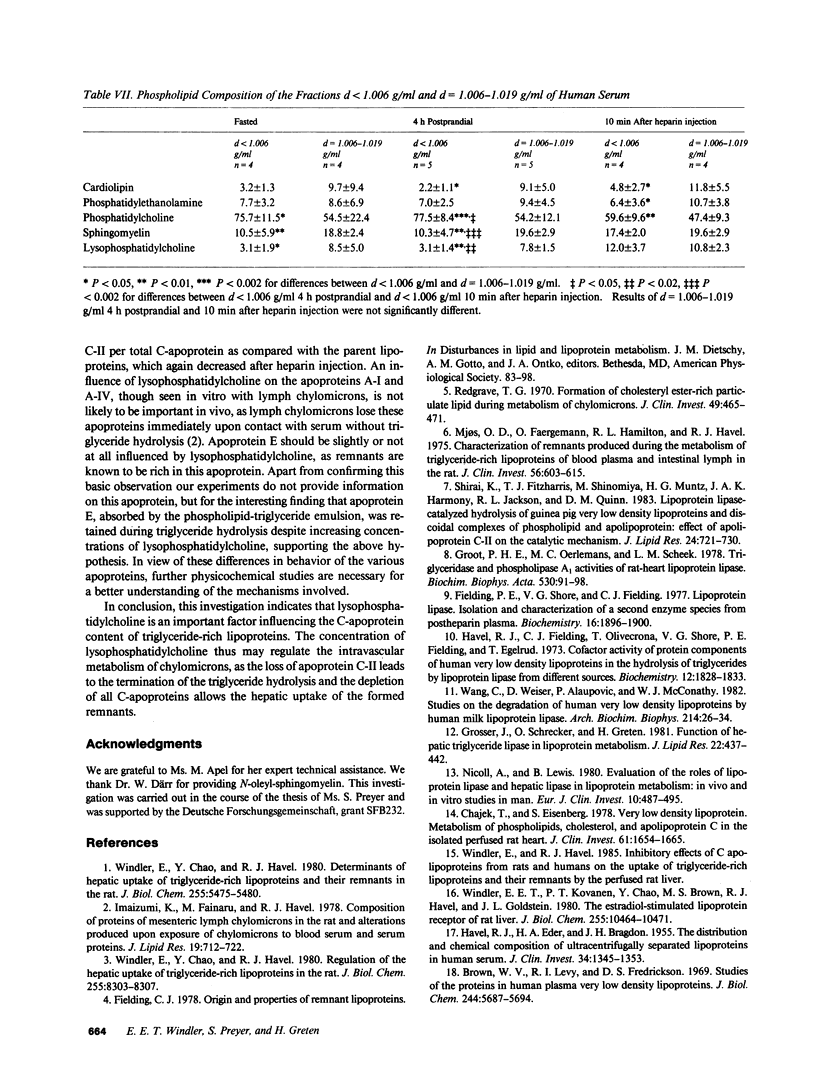
Remnants produced from rat chylomicrons in hepatectomized rats or from human chylomicrons by incubation in postheparin plasma contained much less C-apolipoproteins, but more lysophosphatidylcholine than the parent chylomicrons. A phospholipid-triglyceride emulsion absorbed C-apolipoproteins during incubation in serum, yet not in postheparin plasma, which led to lipid-hydrolysis and increased in lysophosphatidylcholine. The fraction d = 1.006-1.019 g/ml of human serum comprised more lysophosphatidylcholine and less C-apolipoproteins than the fraction d less than 1.006 g/ml. Injection of heparin induced hydrolysis with an increase in lysophosphatidylcholine and loss of C-apolipoproteins in both fractions. These inverse changes of lysophosphatidylcholine and C-apolipoproteins during lipid-hydrolysis suggest a causal relationship, which is strongly supported by the induction of loss of C-apolipoproteins from rat chylomicrons and human triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by addition of lysophosphatidylcholine in vitro. Apolipoprotein C-II was more affected than C-III. These results may elucidate a mechanism for the regulation of the termination of the triglyceride hydrolysis and the final hepatic uptake of remnants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T. Apolipoprotein CII enhances hydrolysis of monoglycerides by lipoprotein lipase, but the effect is abolished by fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 15;106(2):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80529-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Studies of the proteins in human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5687–5694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catapano A. L., Jackson R. L., Gilliam E. B., Gotto A. M., Jr, Smith L. C. Quantification of apoC-II and apoC-III of human very low density lipoproteins by analytical isoelectric focusing. J Lipid Res. 1978 Nov;19(8):1047–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Eisenberg S. Very low density lipoprotein. Metabolism of phospholipids, cholesterol, and apolipoprotein C in the isolated perfused rat heart. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1654–1665. doi: 10.1172/JCI109086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. B., Norum K. R. The lecithin-cholesterol acyl transferase activity of rat intestinal lymph. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):293–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNCOMBE W. G. THE COLORIMETRIC MICRO-DETERMINATION OF NON-ESTERIFIED FATTY ACIDS IN PLASMA. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Feb;9:122–125. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Schurr D. Phospholipid removal during degradation of rat plasma very low density lipoprotein in vitro. J Lipid Res. 1976 Nov;17(6):578–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Havel R. J., Imaizumi K. Apoprotein content of plasma lipoproteins of the rat separated by gel chromatography or ultracentrifugation. Biochem Med. 1977 Jun;17(3):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(77)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Chylomicron protein content and the rate of lipoprotein lipase activity. J Lipid Res. 1976 Jul;17(4):419–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J. Monoglyceride hydrolase activities of rat plasma and platelets. Their properties and roles in the activity of lipoprotein lipase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):876–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding P. E., Shore V. G., Fielding C. J. Lipoprotein lipase. Isolation and characterization of a second enzyme species from postheparin plasma. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1896–1900. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. B., Sprecher H. Unidimensional thin-layer chromatography of phospholipids on boric acid-impregnated plates. J Lipid Res. 1982 May;23(4):660–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groot P. H., Oerlemans M. C., Scheek L. M. Triglyceridase and phospholipase A1 activities of rat-heart lipoprotein lipase. Influence of apolipoproteins C-II and C-III. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 25;530(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosser J., Schrecker O., Greten H. Function of hepatic triglyceride lipase in lipoprotein metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1981 Mar;22(3):437–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Fielding C. J., Olivecrona T., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E., Egelrud T. Cofactor activity of protein components of human very low density lipoproteins in the hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoproteins lipase from different sources. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 24;12(9):1828–1833. doi: 10.1021/bi00733a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi K., Fainaru M., Havel R. J. Composition of proteins of mesenteric lymph chylomicrons in the rat and alterations produced upon exposure of chylomicrons to blood serum and serum proteins. J Lipid Res. 1978 Aug;19(6):712–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen G. L., Daggy B., Bensadoun A. Triacylglycerol lipase, monoacylglycerol lipase and phospholipase activities of highly purified rat hepatic lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 12;710(3):464–470. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs K. E., Phillips M. C., Sparks C. E. A comparison of the surface activities of rat plasma apolipoproteins C-II, C-III-0, C-III-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 16;751(3):470–473. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurakata S., Nojima S., Inoue K. The interactions of lysophosphatidylcholine with protein-containing liposomes. J Biochem. 1981 Sep;90(3):657–663. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos O. D., Faergeman O., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Characterization of remnants produced during the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of blood plasma and intestinal lymph in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):603–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI108130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll A., Lewis B. Evaluation of the roles of lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase in lipoprotein metabolism: in vivo and in vitro studies in man. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;10(6):487–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb02090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle P., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Lipolytic enzymes and plasma lipoprotein metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:667–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagnan A., Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kotite L. Characterization of human very low density lipoproteins containing two electrophoretic populations: double pre-beta lipoproteinemia and primary dysbetalipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1977 Sep;18(5):613–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G. Formation of cholesteryl ester-rich particulate lipid during metabolism of chylomicrons. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):465–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI106255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sata T., Havel R. J., Jones A. L. Characterization of subfractions of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins separated by gel chromatography from blood plasma of normolipemic and hyperlipemic humans. J Lipid Res. 1972 Nov;13(6):757–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. G., Avecilla L. S., Small D. M. Phase behavior and structure of aqueous dispersions of sphingomyelin. J Lipid Res. 1974 Mar;15(2):124–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai K., Fitzharris T. J., Shinomiya M., Muntz H. G., Harmony J. A., Jackson R. L., Quinn D. M. Lipoprotein lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine of guinea pig very low density lipoproteins and discoidal complexes of phospholipid and apolipoprotein: effect of apolipoprotein C-II on the catalytic mechanism. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jun;24(6):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., Därr W., Salm K. P. Lipid-protein interactions between human apolipoprotein A-I and defined sphingomyelin species. A 13C-NMR spectroscopic study. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Jan;358(1):1–11. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1977.358.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stähler F., Gruber W., Stinshoff K., Röschlau P. Eine praxisgerechte enzymatische Cholesterin-Bestimmung. Med Lab (Stuttg) 1977 Feb;30(2):29–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R., Lange Y. Interaction of cholesterol, phospholipid and apoprotein in high density lipoprotein recombinants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 2;513(2):185–197. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Echteld C. J., De Kruijff B., Mandersloot J. G., De Gier J. Effects of lysophosphatidylcholines on phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol liposome systems as revealed by 31P-NMR, electron microscopy and permeability studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 7;649(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90408-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. S., Weiser D., Alaupovic P., McConathy W. J. Studies on the degradation of human very low density lipoproteins by human milk lipoprotein lipase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Mar;214(1):26–34. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E. E., Kovanen P. T., Chao Y. S., Brown M. S., Havel R. J., Goldstein J. L. The estradiol-stimulated lipoprotein receptor of rat liver. A binding site that membrane mediates the uptake of rat lipoproteins containing apoproteins B and E. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10464–10471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Determinants of hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5475–5480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Regulation of the hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in the rat. Opposing effects of homologous apolipoprotein E and individual C apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8303–8307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tol A., van Gent T., Jansen H. Degradation of high density lipoprotein by heparin-releasable liver lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80193-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]