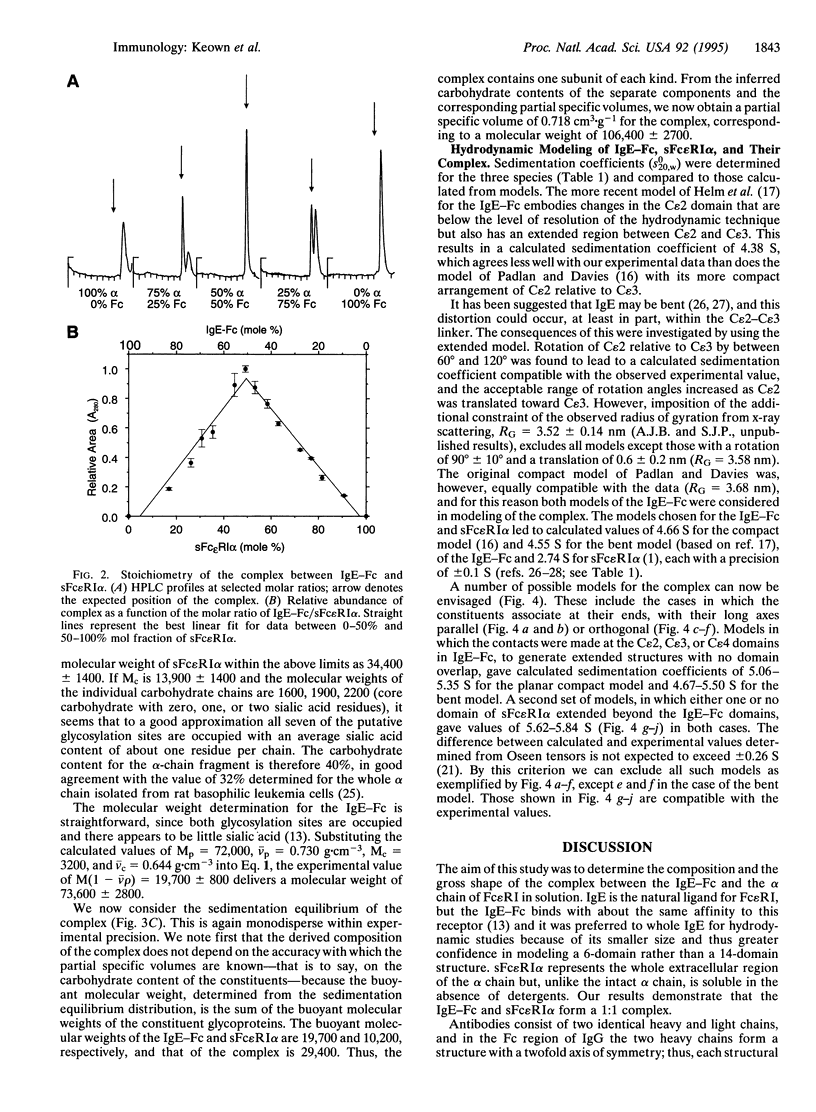
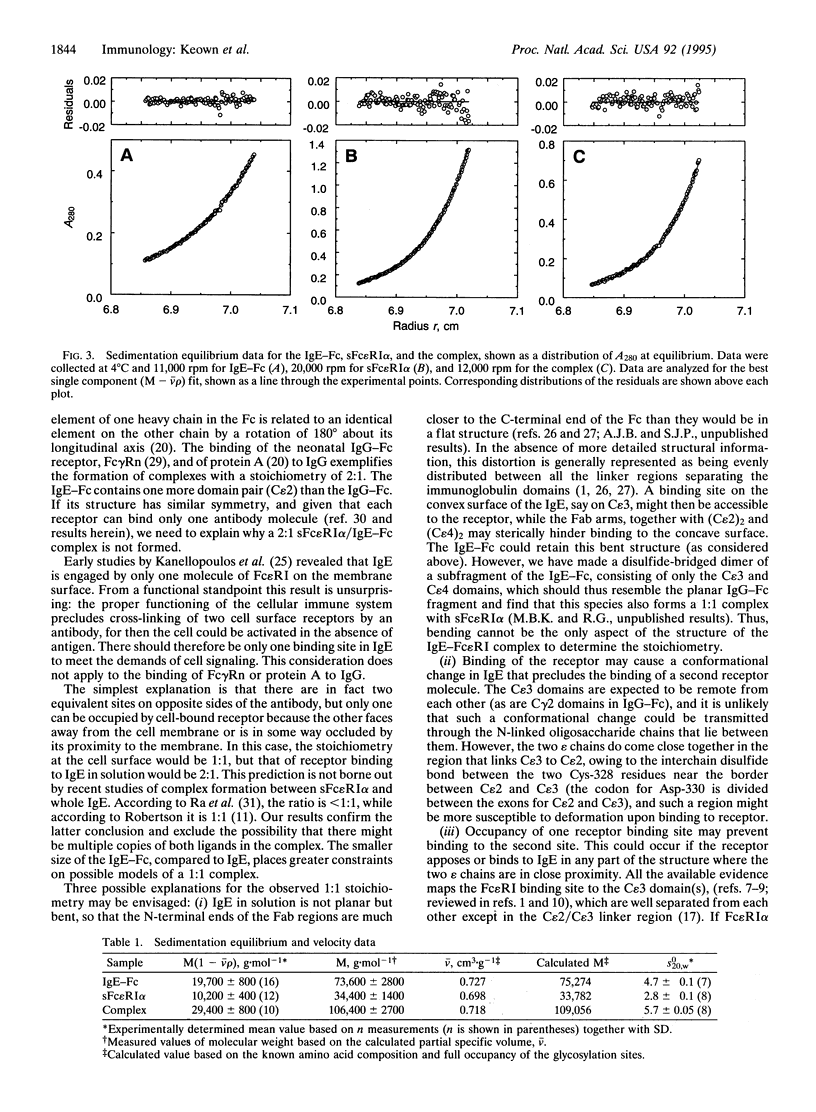
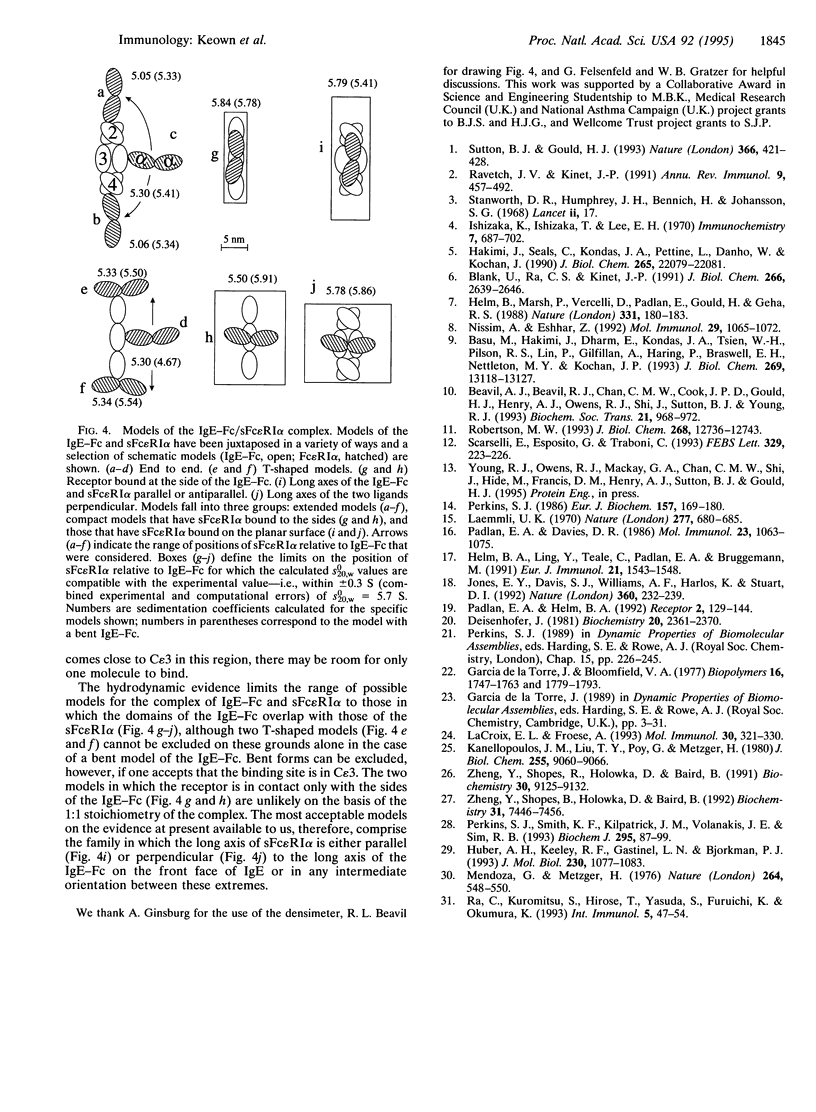
Abstract
The interaction between immunoglobulin E (IgE) and its high-affinity receptor Fc epsilon RI is central to allergic disease. The binding site for Fc epsilon RI lies in the third constant region domain of the epsilon heavy chain of IgE (C epsilon 3). Identical epitopes on the two C epsilon 3 domains in the IgE-Fc are predicted to be on opposite sides of the structure, and therefore each could bind independently to a receptor molecule. Titrations, however, reveal that the IgE-Fc forms an equimolar complex with a soluble fragment of the Fc epsilon RI alpha chain (sFc epsilon RI alpha), and the molecular weight of the complex, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium, confirms this stoichiometry. The measured sedimentation coefficients of the two ligands are in good agreement with computed values for a compact IgE-Fc and an elongated sFc epsilon RI alpha structure. The calculated sedimentation coefficients for possible models of a 1:1 complex lead to exclusion of all highly extended geometries for the complex. Possible explanations for the paradoxical stoichiometry of the IgE-Fc/sFc epsilon RI alpha complex, in terms of the curved shape of IgE, a conformational change in IgE when the receptor binds, and steric interference between two molecules of Fc epsilon RI binding to identical sites, are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu M., Hakimi J., Dharm E., Kondas J. A., Tsien W. H., Pilson R. S., Lin P., Gilfillan A., Haring P., Braswell E. H. Purification and characterization of human recombinant IgE-Fc fragments that bind to the human high affinity IgE receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13118–13127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavil A. J., Beavil R. L., Chan C. M., Cook J. P., Gould H. J., Henry A. J., Owens R. J., Shi J., Sutton B. J., Young R. J. Structural basis of the IgE-Fc epsilon RI interaction. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 Nov;21(4):968–972. doi: 10.1042/bst0210968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank U., Ra C. S., Kinet J. P. Characterization of truncated alpha chain products from human, rat, and mouse high affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2639–2646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De La Torre J. G., Bloomfield V. A. Hydrodynamics of macromolecular complexes. III. Bacterial viruses. Biopolymers. 1977 Aug;16(8):1779–1793. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J. Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of a human Fc fragment and its complex with fragment B of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus at 2.9- and 2.8-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2361–2370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakimi J., Seals C., Kondas J. A., Pettine L., Danho W., Kochan J. The alpha subunit of the human IgE receptor (FcERI) is sufficient for high affinity IgE binding. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22079–22081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helm B. A., Ling Y., Teale C., Padlan E. A., Brüggemann M. The nature and importance of the inter-epsilon chain disulfide bonds in human IgE. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jun;21(6):1543–1548. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helm B., Marsh P., Vercelli D., Padlan E., Gould H., Geha R. The mast cell binding site on human immunoglobulin E. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):180–183. doi: 10.1038/331180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber A. H., Kelley R. F., Gastinel L. N., Bjorkman P. J. Crystallization and stoichiometry of binding of a complex between a rat intestinal Fc receptor and Fc. J Mol Biol. 1993 Apr 5;230(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T., Lee E. H. Biologic function of the Fc fragments of E myeloma protein. Immunochemistry. 1970 Aug;7(8):687–702. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. Y., Davis S. J., Williams A. F., Harlos K., Stuart D. I. Crystal structure at 2.8 A resolution of a soluble form of the cell adhesion molecule CD2. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):232–239. doi: 10.1038/360232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanellopoulos J. M., Liu T. Y., Poy G., Metzger H. Composition and subunit structure of the cell receptor for immunoglobulin E. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9060–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaCroix E. L., Froese A. The N-linked oligosaccharides of the Fc epsilon receptors of rat basophilic leukemia cells. Mol Immunol. 1993 Feb;30(3):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90060-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza G., Metzger H. Distribution and valency of receptor for IgE on rodent mast cells and related tumour cells. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):548–550. doi: 10.1038/264548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissim A., Eshhar Z. The human mast cell receptor binding site maps to the third constant domain of immunoglobulin E. Mol Immunol. 1992 Sep;29(9):1065–1072. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(92)90038-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padlan E. A., Davies D. R. A model of the Fc of immunoglobulin E. Mol Immunol. 1986 Oct;23(10):1063–1075. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padlan E. A., Helm B. A. A modeling study of the alpha-subunit of human high-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin-E. Receptor. 1992 Summer;2(2):129–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J. Protein volumes and hydration effects. The calculations of partial specific volumes, neutron scattering matchpoints and 280-nm absorption coefficients for proteins and glycoproteins from amino acid sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 15;157(1):169–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J., Smith K. F., Kilpatrick J. M., Volanakis J. E., Sim R. B. Modelling of the serine-proteinase fold by X-ray and neutron scattering and sedimentation analyses: occurrence of the fold in factor D of the complement system. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 1;295(Pt 1):87–99. doi: 10.1042/bj2950087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ra C., Kuromitsu S., Hirose T., Yasuda S., Furuichi K., Okumura K. Soluble human high-affinity receptor for IgE abrogates the IgE-mediated allergic reaction. Int Immunol. 1993 Jan;5(1):47–54. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. W. Phage and Escherichia coli expression of the human high affinity immunoglobulin E receptor alpha-subunit ectodomain. Domain localization of the IgE-binding site. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12736–12743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarselli E., Esposito G., Traboni C. Receptor phage. Display of functional domains of the human high affinity IgE receptor on the M13 phage surface. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 23;329(1-2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80226-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanworth D. R., Humphrey J. H., Bennich H., Johansson S. G. Inhibition of Prausnitz-Küstner reaction by proteolytic-cleavage fragments of a human myeloma protein of immunoglobulin class E. Lancet. 1968 Jul 6;2(7558):17–18. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92889-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton B. J., Gould H. J. The human IgE network. Nature. 1993 Dec 2;366(6454):421–428. doi: 10.1038/366421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y., Shopes B., Holowka D., Baird B. Conformations of IgE bound to its receptor Fc epsilon RI and in solution. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9125–9132. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y., Shopes B., Holowka D., Baird B. Dynamic conformations compared for IgE and IgG1 in solution and bound to receptors. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 25;31(33):7446–7456. doi: 10.1021/bi00148a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]