Abstract
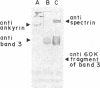
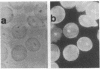
In earlier model studies we demonstrated that artificially denatured hemoglobin binds to and clusters the protein, band 3, in the plane of the erythrocyte membrane. To determine whether denatured hemoglobin also clusters band 3 in vivo, we have compared the locations of denatured hemoglobin aggregates (Heinz bodies) with band 3 in sickle cells using phase contrast and immunofluorescence microscopy. We report that where Heinz bodies are found associated with the cytoplasmic surface of the membrane, clusters of band 3 are usually colocalized within the membrane. In contrast, normal erythrocyte membranes and regions of sickle cell membranes devoid of Heinz bodies display an uninterrupted staining of band 3. Similarly, ankyrin and glycophorin are periodically seen to aggregate at Heinz body sites, but the degree of colocalization is lower than for band 3. These data demonstrate that the binding of denatured hemoglobin to the membrane forces a redistribution of several major membrane components.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Low P. S. Covalent labelling of specific membrane carbohydrate residues with fluorescent probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 10;597(2):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agre P., Casella J. F., Zinkham W. H., McMillan C., Bennett V. Partial deficiency of erythrocyte spectrin in hereditary spherocytosis. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):380–383. doi: 10.1038/314380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderman E. M., Fudenberg H. H., Lovins R. E. Isolation and characterization of an age-related antigen present on senescent human red blood cells. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):341–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appell K. C., Low P. S. Partial structural characterization of the cytoplasmic domain of the erythrocyte membrane protein, band 3. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11104–11111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartosz G., Soszyński M., Wasilewski A. Aging of the erythrocyte. XVII. Binding of autologous immunoglobulin G. Mech Ageing Dev. 1982 Nov;20(3):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(82)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P. J. Association between ankyrin and the cytoplasmic domain of band 3 isolated from the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6424–6432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P. J. Human erythrocyte ankyrin. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2540–2548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Nigg E. A., Beddard G. S. Oligosaccharide motion in erythrocyte membranes investigated by picosecond fluorescence polarization and microsecond dichroism of an optical probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5899–5903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton J. W., Berger E., White J. G., Jacob H. S. Calcium-induced damage of haemoglobin SS and normal erythrocytes. Br J Haematol. 1978 Jan;38(1):57–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb07108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M., Fukuda M. N., Hakomori S., Papayannopoulou T. Anomalous cell surface structure of sickle cell anemia erythrocytes as demonstrated by cell surface labeling and endo-beta-galactosidase treatment. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;17(3):289–297. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.380170309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Korkesh A., Kahane I., Rachmilewitz E. A. Demonstration of a natural antigalactosyl IgG antibody on thalassemic red blood cells. Blood. 1983 Jun;61(6):1258–1264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemsa D., Fudenberg H. H., Schmid R. Erythrocyte catabolism by macrophages in vitro: dissociation of phagocytosis and heme oxygenase induction. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1972;85:335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. A., Rehn M. M., Kalra V. K. Cell-bound autologous immunoglobulin in erythrocyte subpopulations from patients with sickle cell disease. Blood. 1985 May;65(5):1127–1133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves W. R., Giedd K. N., Verkleij A., Branton D. Reassociation of ankyrin with band 3 in erythrocyte membranes and in lipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11965–11972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P. Auto-oxidation and a membrane-associated 'Fenton reagent': a possible explanation for development of membrane lesions in sickle erythrocytes. Clin Haematol. 1985 Feb;14(1):129–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P., Eaton J. W., Balasingam M., Steinberg M. H. Spontaneous oxygen radical generation by sickle erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1253–1259. doi: 10.1172/JCI110724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P., Yamada O., Moldow C. F., Jacob H. S., White J. G., Eaton J. W. Abnormal adherence of sickle erythrocytes to cultured vascular endothelium: possible mechanism for microvascular occlusion in sickle cell disease. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):154–160. doi: 10.1172/JCI109646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M., Goodman S. R., Sorensen K., Whitfield C. F., Wong P., Zaki L., Rudloff V. Senescent cell antigen is immunologically related to band 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1631–1635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M. Mechanism of removal of senescent cells by human macrophages in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3521–3525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M., Sorensen K., Wong P., Bolton P. Antigenicity, storage, and aging: physiologic autoantibodies to cell membrane and serum proteins and the senescent cell antigen. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Nov 26;49(2):65–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00242486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. S., Cramer W. A., Abraham G., Bone R., Ferguson-Segall M. Evidence for restricted oligosaccharide mobility at the erythrocyte membrane surface: a fluorescence study. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Apr 1;214(2):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. S., Waugh S. M., Zinke K., Drenckhahn D. The role of hemoglobin denaturation and band 3 clustering in red blood cell aging. Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):531–533. doi: 10.1126/science.2578228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin B., Chiu D., Bastacky J., Roelofsen B., Van Deenen L. L. Abnormalities in membrane phospholipid organization in sickled erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1643–1649. doi: 10.1172/JCI110200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz H. U., Flepp R., Stringaro-Wipf G. Naturally occurring autoantibodies to exoplasmic and cryptic regions of band 3 protein, the major integral membrane protein of human red blood cells. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2610–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Karnovsky M. J. Irreversible deformation of the spectrin-actin lattice in irreversibly sickled cells. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):955–963. doi: 10.1172/JCI108549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi S. L., Steers E., Marchesi V. T., Tillack T. W. Physical and chemical properties of a protein isolated from red cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 6;9(1):50–57. doi: 10.1021/bi00803a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurdy P. R. 32-DFP and 51-Cr for measurement of red cell life span in abnormal hemoglobin syndromes. Blood. 1969 Feb;33(2):214–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurdy P. R., Sherman A. S. Irreversibly sickled cells and red cell survival in sickle cell anemia: a study with both DF32P and 51CR. Am J Med. 1978 Feb;64(2):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara K., Spiro M. J. Nonuniform loss of membrane glycoconjugates during in vivo aging of human erythrocytes: studies of normal and diabetic red cell saccharides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jul;232(1):310–322. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petz L. D., Yam P., Wilkinson L., Garratty G., Lubin B., Mentzer W. Increased IgG molecules bound to the surface of red blood cells of patients with sickle cell anemia. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):301–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt O. S., Falcone J. F., Lux S. E. Molecular defect in the sickle erythrocyte skeleton. Abnormal spectrin binding to sickle inside-our vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):266–271. doi: 10.1172/JCI111684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauenbuehler P. B., Cordes K. A., Salhany J. M. Identification of the hemoglobin binding sites on the inner surface of the erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 22;692(3):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E., Schlegel R. A., Williamson P. Endocytosis in sickle erythrocytes: a mechanism for elevated intracellular Ca2+ levels. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jan;126(1):53–59. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041260108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaklai N., Sharma V. S., Ranney H. M. Interaction of sickle cell hemoglobin with erythrocyte membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):65–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szundi I., Szelényi J. G., Breuer J. H., Bérczi A. Interactions of haemoglobin with erythrocyte membrane phospholipids in monomolecular lipid layers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;595(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. M., Hargreaves W. R., Branton D. Purification of two spectrin-binding proteins: biochemical and electron microscopic evidence for site-specific reassociation between spectrin and bands 2.1 and 4.1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5192–5196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh S. M., Low P. S. Hemichrome binding to band 3: nucleation of Heinz bodies on the erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):34–39. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]