Abstract
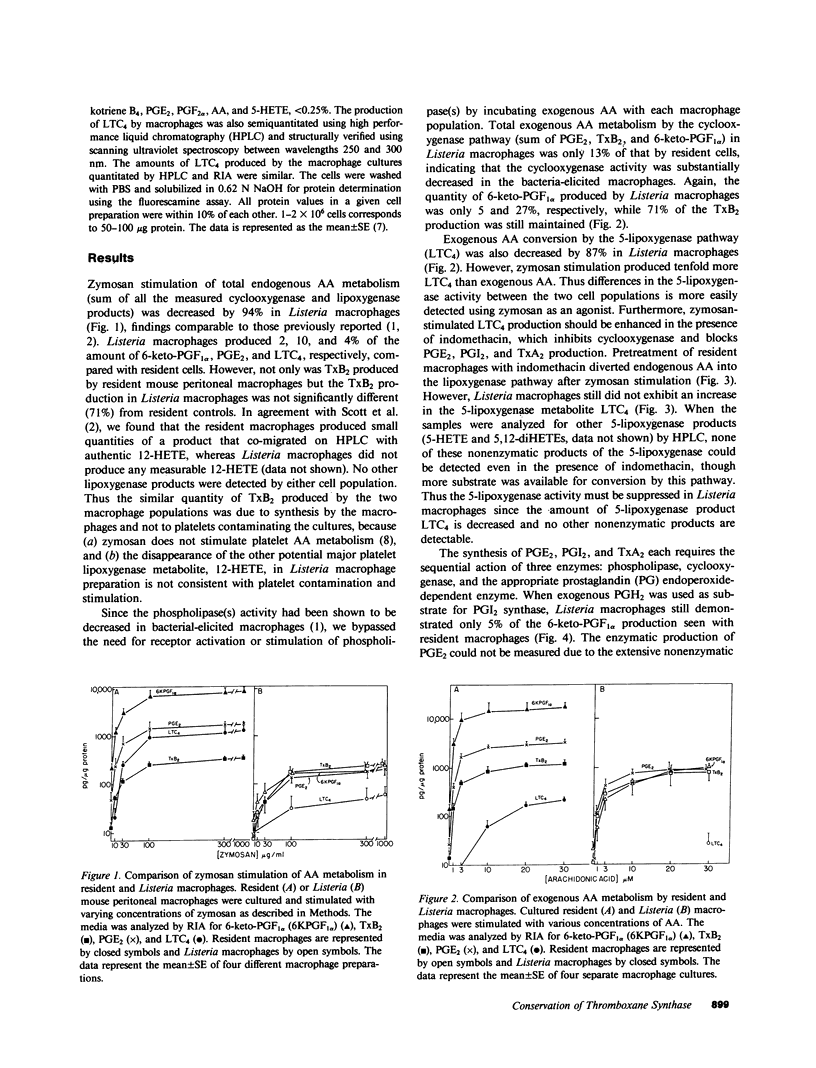
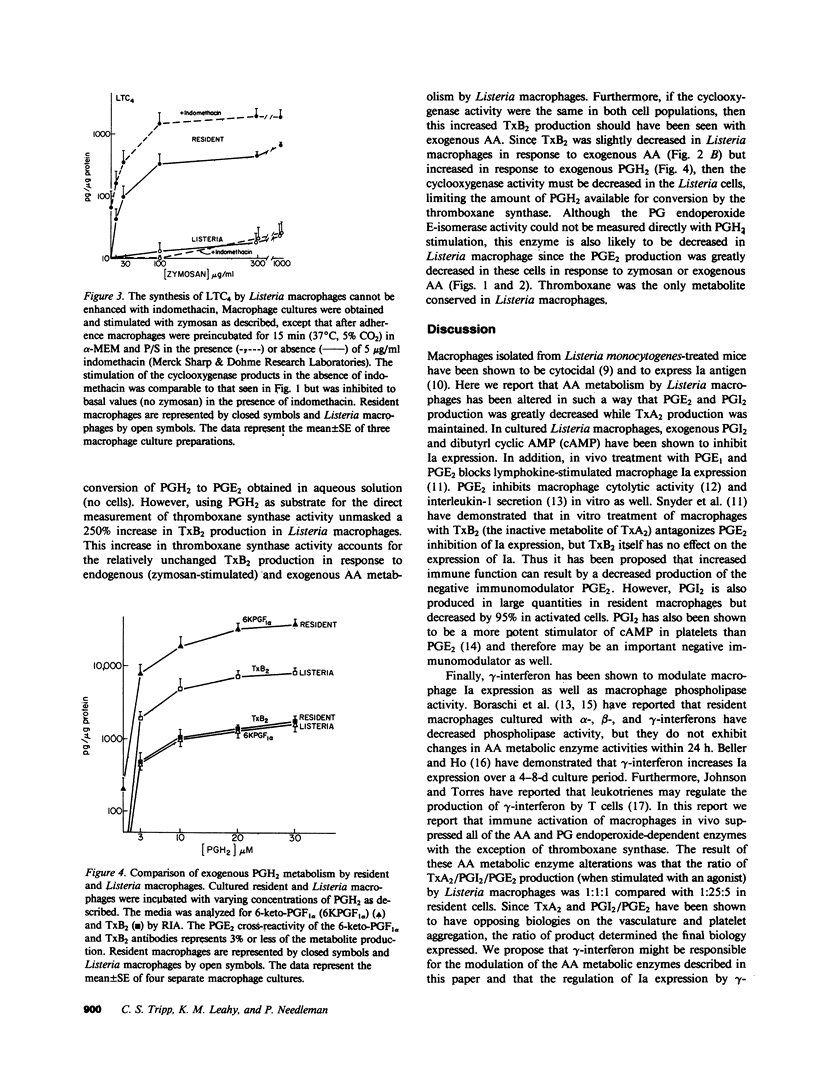
Resident macrophages isolated from uninfected animals produce large quantities of arachidonic acid (AA) metabolites. Immunizing animals with protein antigens or bacteria activates macrophages and causes an 80% reduction in the cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase metabolites relative to resident cells. Since some products have been shown to modulate immune functions, we examined how the AA metabolic enzyme activities regulate the products that are synthesized. We demonstrate that the cyclooxygenase, 5-lipoxygenase, prostacyclin synthase, and probably prostaglandin (PG) endoperoxide E-isomerase activities were decreased in activated peritoneal macrophages. In sharp contrast, thromboxane synthase activity was selectively unchanged or enhanced in the activated macrophages. Thus the immune response appears to modulate the activity of the AA and PG endoperoxide-dependent enzymes, thus dictating a major shift in the profile of metabolites synthesized by macrophages.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beller D. I., Ho K. Regulation of macrophage populations. V. Evaluation of the control of macrophage Ia expression in vitro. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):971–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Regulation of macrophage populations. I. Preferential induction of Ia-rich peritoneal exudates by immunologic stimuli. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1426–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonney R. J., Wightman P. D., Davies P., Sadowski S. J., Kuehl F. A., Jr, Humes J. L. Regulation of prostaglandin synthesis and of the selective release of lysosomal hydrolases by mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):433–442. doi: 10.1042/bj1760433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boraschi D., Censini S., Bartalini M., Scapigliati G., Barbarulli G., Vicenzi E., Donati M. B., Tagliabue A. Interferon inhibits prostaglandin biosynthesis in macrophages: effects on arachidonic acid metabolism. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1987–1992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boraschi D., Censini S., Tagliabue A. Interferon-gamma reduces macrophage-suppressive activity by inhibiting prostaglandin E2 release and inducing interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):764–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr A. G., Wechter W. J., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Induction of cytocidal macrophages after in vitro interactions between Listeria-immune T cells and macrophages--role of H-2. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2405–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman R. R., Bunting S., Miller O. V. Modulation of human platelet adenylate cyclase by prostacyclin (PGX). Prostaglandins. 1977 Mar;13(3):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman R. R., Sun F. F., Miller O. V., Johnson R. A. Prostaglandins H1 and H2. Convenient biochemical synthesis and isolation. Further biological and spectroscopic characterization. Prostaglandins. 1977 Jun;13(6):1043–1053. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes E. C., Lombardo D. L., Girard Y., Maycock A. L., Rokach J., Rosenthal A. S., Young R. N., Egan R. W., Zweerink H. J. Measuring leukotrienes of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis: development of a specific radioimmunoassay. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):429–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humes J. L., Burger S., Galavage M., Kuehl F. A., Jr, Wightman P. D., Dahlgren M. E., Davies P., Bonney R. J. The diminished production of arachidonic acid oxygenation products by elicited mouse peritoneal macrophages: possible mechanisms. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2110–2116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Torres B. A. Leukotrienes: positive signals for regulation of gamma-interferon production. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):413–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowski N. A., Kaplan G., Hamill A. L., Cohn Z. A., Scott W. A. Arachidonic acid metabolism by human monocytes. Studies with platelet-depleted cultures. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):393–412. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold D. F., Watters K., Holmberg S., Needleman P. Differential biosynthesis of prostaglandins by hydronephrotic rabbit and cat kidneys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Mar;216(3):510–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Pawlowski N. A., Murray H. W., Andreach M., Zrike J., Cohn Z. A. Regulation of arachidonic acid metabolism by macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1148–1160. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder D. S., Beller D. I., Unanue E. R. Prostaglandins modulate macrophage Ia expression. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):163–165. doi: 10.1038/299163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taffet S. M., Russell S. W. Macrophage-mediated tumor cell killing: regulation of expression of cytolytic activity by prostaglandin E. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):424–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


