Abstract
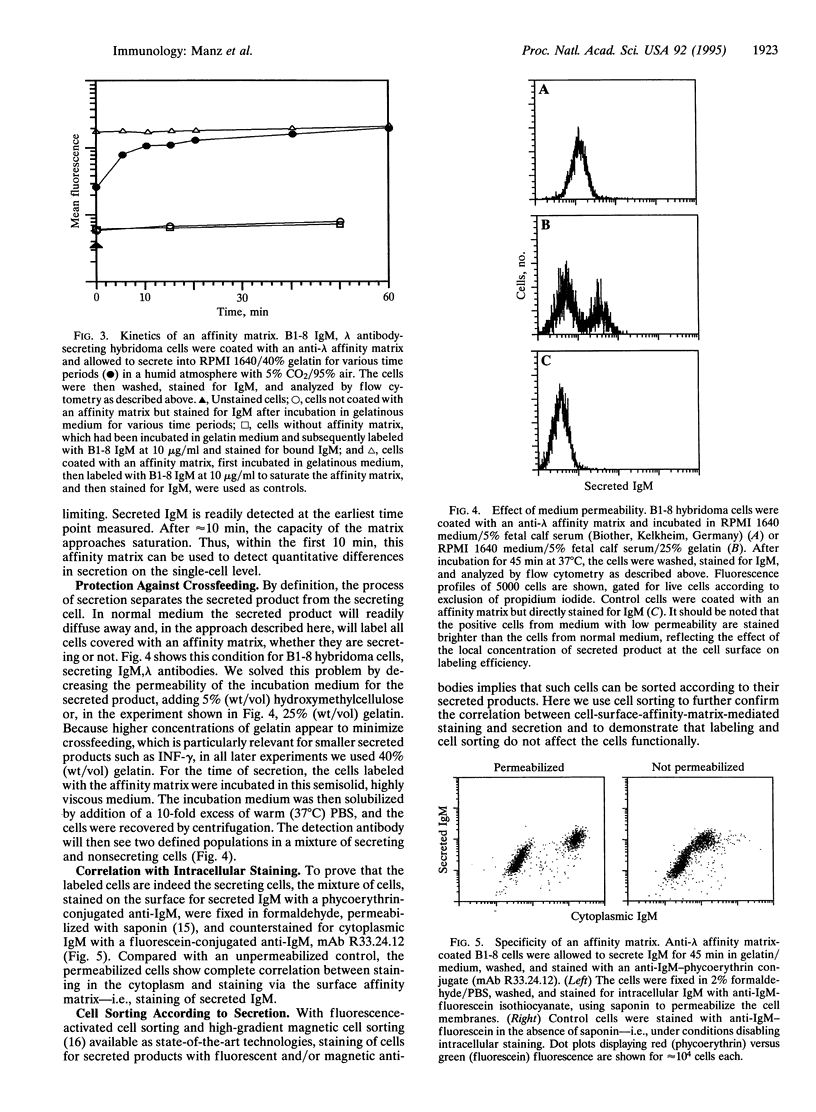
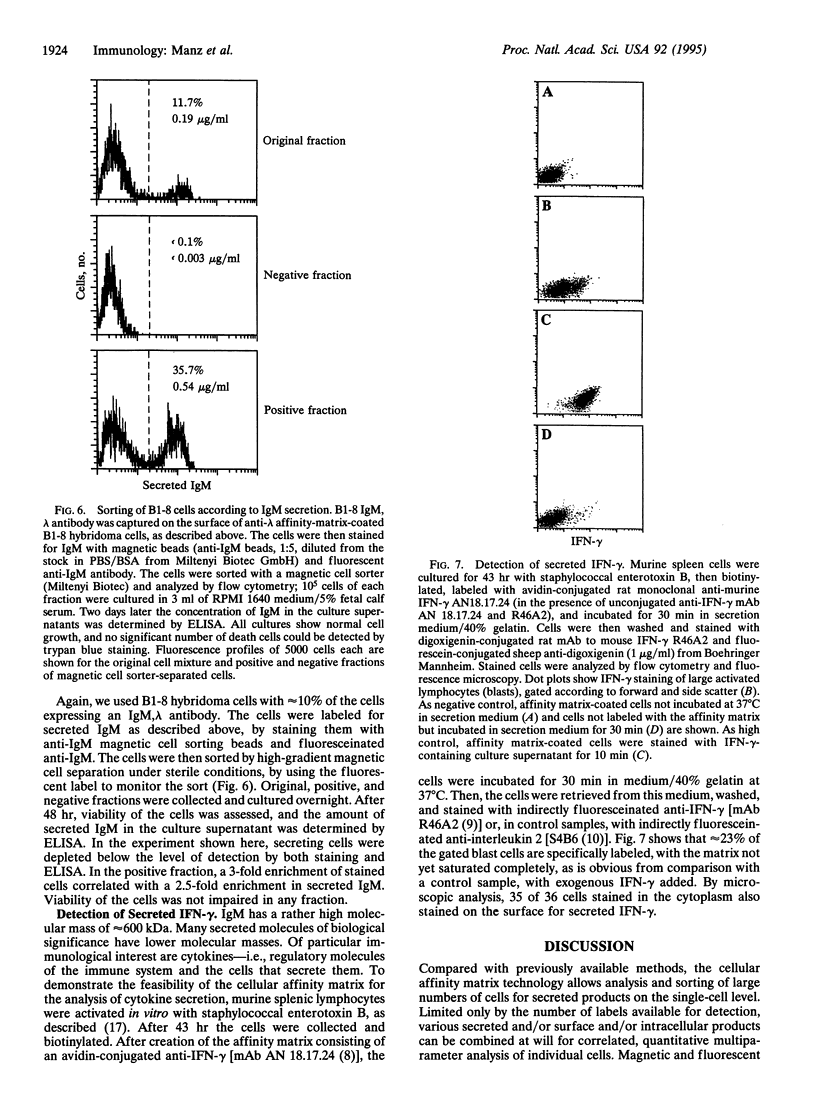
We have developed a technology for analysis and sorting of live cells according to secreted molecules. An artificial affinity matrix, specific for the secreted product of interest, is created on the cell surface, and the cells are allowed to secrete for a defined time period. The secreted molecules bind to the affinity matrix on the secreting cell and are subsequently labeled with specific fluorescent or magnetic staining reagents for cytometric analysis and cell sorting. Crossfeeding of the secreted products to other cells is prevented by decreasing the permeability of the incubation medium. This approach will have a wide range of applications in biotechnology and biomedical research. Here, we describe analysis and sorting of hybridoma cells, according to secreted antibodies, and of activated T lymphocytes, according to secreted cytokines.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Czerkinsky C. C., Nilsson L. A., Nygren H., Ouchterlony O., Tarkowski A. A solid-phase enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay for enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingalls H. M., Goodloe-Holland C. M., Luna E. J. Junctional plasma membrane domains isolated from aggregating Dictyostelium discoideum amebae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4779–4783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERNE N. K., NORDIN A. A. Plaque formation in agar by single antibody-producing cells. Science. 1963 Apr 26;140(3565):405–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob M. C., Favre M., Bensa J. C. Membrane cell permeabilization with saponin and multiparametric analysis by flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1991;12(6):550–558. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990120612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miltenyi S., Müller W., Weichel W., Radbruch A. High gradient magnetic cell separation with MACS. Cytometry. 1990;11(2):231–238. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990110203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock J. S., Londo T. R., Roess D. A., Barisas B. G. Biologic activity of antigen receptors artificially incorporated onto B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1916–1923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. T., Weaver J. C. Gel microdroplets and flow cytometry: rapid determination of antibody secretion by individual cells within a cell population. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Apr;8(4):333–337. doi: 10.1038/nbt0490-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat M., Gribaudo G., Comoglio P. M., Cavallo G., Landolfo S. Monoclonal antibodies against murine gamma interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4515–4519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M., Hämmerling G. J., Rajewsky K. Analysis of the repertoire of anti-NP antibodies in C57BL/6 mice by cell fusion. I. Characterization of antibody families in the primary and hyperimmune response. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Jun;8(6):393–400. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M., Imanishi-Kari T., Rajewsky K. Analysis of the repertoire of anti-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)acetyl (NP) antibodies in C 57 BL/6 mice by cell fusion. II. Characterization of idiotopes by monoclonal anti-idiotope antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Dec;9(12):1004–1013. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830091216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J., Radbruch A. Distinct antigen presenting cell-derived signals induce TH cell proliferation and expression of effector cytokines. Int Immunol. 1992 Jan;4(1):43–51. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitalny G. L., Havell E. A. Monoclonal antibody to murine gamma interferon inhibits lymphokine-induced antiviral and macrophage tumoricidal activities. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1560–1565. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori T., Rajewsky K. Lambda chain expression at different stages of ontogeny in C57BL/6, BALB/c and SJL mice. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Aug;11(8):618–625. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



