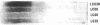Abstract
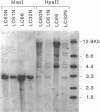
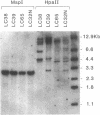
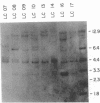
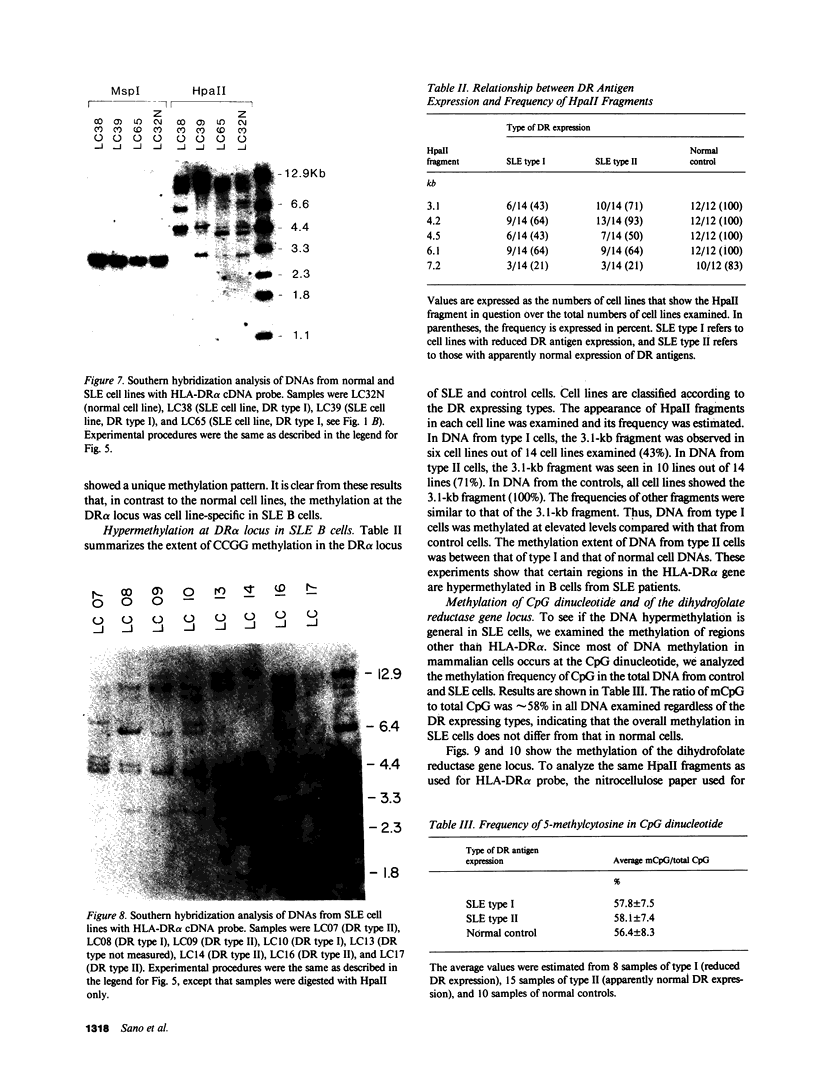
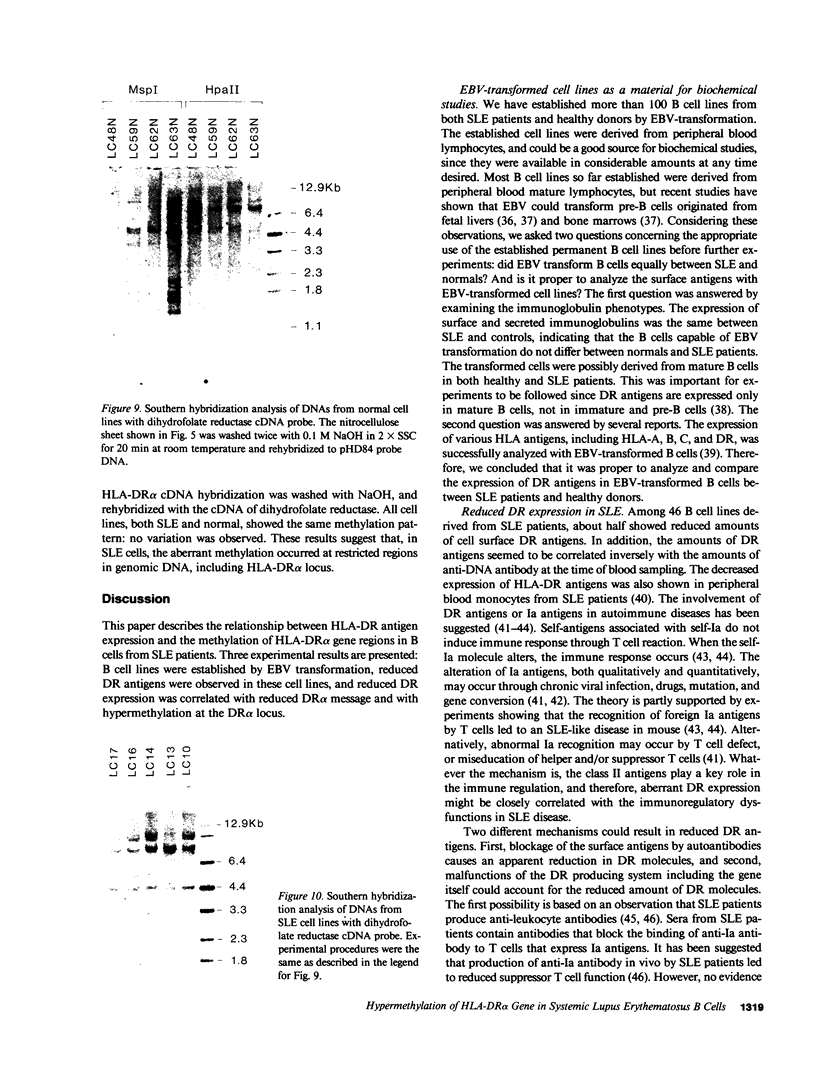
The relationship between the expression of HLA-DR antigens and the HLA-DR alpha gene methylation was examined in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Using permanent B cell lines, we found reduced DR expression in SLE. The low DR expression was correlated with high anti-DNA antibody titers in patients' sera. The amounts of DR alpha message were lower in SLE cells than in normal controls, suggesting that the low expression of DR antigens is associated with gene functions. The extent of DNA methylation was examined at five CCGG sites in the HLA-DR alpha locus. DNA from both SLE and normal cells showed variable methylation patterns. Since the DR alpha gene is a single-copy gene, such a variability is the result of assaying a mixture of transformed clones containing methylated DR alpha gene, with other clones containing unmethylated DR alpha gene. A distinctive feature of normal cells was a consistent methylation pattern: 12 normal cell lines showed exactly the same pattern. In contrast, 28 SLE cell lines showed a cell-line-specific methylation, and hypermethylation at the DR alpha locus. The hypermethylation is often associated with transcriptionally inactive genes. Thus, our results suggest that (a) B cells with hypermethylated DR genes might express no or few DR antigens; (b) the ratio of cells with differently methylated DR genes is consistent in normal individuals, while, in SLE patients, cells with hypermethylated DR genes predominate, resulting in apparently reduced DR antigen expression; and (c) the aberrant DR expression could be associated directly with immunoregulatory dysfunctions in SLE disease.
Full text
PDF




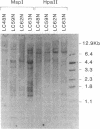
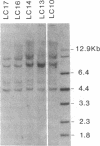
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. L., Davis T., Fulton J., Kirk D., Qureshi M., Burdon R. H. Eukaryotic DNA methylase--properties and action on native DNA and chromatin. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;108:142–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aman P., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Klein G. Epstein-Barr virus susceptibility of normal human B lymphocyte populations. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):208–220. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Kuo J., DeMars R., Strominger J. L. A minimum of four human class II alpha-chain genes are encoded in the HLA region of chromosome 6. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):174–177. doi: 10.1038/304174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B. Role of MHC gene products in immune regulation. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1229–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.6165083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestor T. H., Hellewell S. B., Ingram V. M. Differentiation of two mouse cell lines is associated with hypomethylation of their genomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1800–1806. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. DNA methylation--how important in gene control? Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):503–504. doi: 10.1038/307503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Hurst J., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation and the regulation of globin gene expression. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. T., Rossen R. D. Effects of corticosteroids on immunity in man. I. Decreased serum IgG concentration caused by 3 or 5 days of high doses of methylprednisolone. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2629–2640. doi: 10.1172/JCI107455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton L. J., Steinberg A. D., Sano H. Nuclear DNA degradation in lymphocytes of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):213–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs R. R., Wilson A. B., Eremin O., Gurner B. W., Haegert D. G., Lawson Y. A., Bright S., Munro A. J. Comparison of the direct antiglobulin rosetting reaction with the mixed antiglobulin rosetting reaction for the detection of immunoglobulin on lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1977;18(1-2):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. F. Estrogen withdrawal in chick oviduct. Selective loss of high abundance classes of polyadenylated messenger RNA. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 26;16(15):3433–3443. doi: 10.1021/bi00634a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupps T. R., Edgar L. C., Thomas C. A., Fauci A. S. Multiple mechanisms of B cell immunoregulation in man after administration of in vivo corticosteroids. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):170–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOSKOCIL J., SORM F. Distribution of 5-methylcytosine in pyrimidine sequences of deoxyribonucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 11;55:953–959. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90909-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., Lawrance S. K., Weissman S. M. Structure and nucleotide sequence of the heavy chain gene of HLA-DR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3543–3547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dausset J. The major histocompatibility complex in man. Science. 1981 Sep 25;213(4515):1469–1474. doi: 10.1126/science.6792704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker J. L., Steinberg A. D., Reinertsen J. L., Plotz P. H., Balow J. E., Klippel J. H. NIH conference. Systemic lupus erythematosus: evolving concepts. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Oct;91(4):587–604. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-4-587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich M., Wang R. Y. 5-Methylcytosine in eukaryotic DNA. Science. 1981 Jun 19;212(4501):1350–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.6262918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Cohen P. L. Class II major histocompatibility antigens and the etiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Oct;29(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradin A., Manley J. L., Prives C. L. Methylation of simian virus 40 Hpa II site affects late, but not early, viral gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5142–5146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg W. W., Finkelman F. D., Lipsky P. E. Circulating and pokeweed mitogen-induced immunoglobulin-secreting cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jan;35(1):76–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleichmann E., Van Elven E. H., Van der Veen J. P. A systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)-like disease in mice induced by abnormal T-B cell cooperation. Preferential formation of autoantibodies characteristic of SLE. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Feb;12(2):152–159. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hang L., Slack J. H., Amundson C., Izui S., Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Induction of murine autoimmune disease by chronic polyclonal B cell activation. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):874–883. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson M., Falk K., Ernberg I. Epstein-Barr virus transformation of human pre-B cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):616–622. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. A., Morris M. A., Haynes B. F., Eisenbarth G. S. Increased circulating Ia-antigen-bearing T cells in type I diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 1;306(13):785–788. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204013061305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katamine S., Otsu M., Tada K., Tsuchiya S., Sato T., Ishida N., Honjo T., Ono Y. Epstein-Barr virus transforms precursor B cells even before immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):369–372. doi: 10.1038/309369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Auffray C., Schamboeck A., Strominger J. L. The amino acid sequence and gene organization of the heavy chain of the HLA-DR antigen: homology to immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6013–6017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Levy R. Two populations of Ia-like molecules on a human B cell line. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langner K. D., Vardimon L., Renz D., Doerfler W. DNA methylation of three 5' C-C-G-G 3' sites in the promoter and 5' region inactivate the E2a gene of adenovirus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2950–2954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Schenning L., Gustafsson K., Wiman K., Claesson L., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Complete amino acid sequence of an HLA-DR antigen-like beta chain as predicted from the nucleotide sequence: similarities with immunoglobulins and HLA-A, -B, and -C antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3687–3691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S., Ohno S. The interactions of androgen receptor with poly(A)-containing RNA and polyribonucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May 17;124(2):283–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Wake C. T., Gorski J., Mach B. Complete sequence of an HLA-dR beta chain deduced from a cDNA clone and identification of multiple non-allelic DR beta chain genes. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):389–394. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01435.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavilio F., Giampaolo A., Carè A., Migliaccio G., Calandrini M., Russo G., Pagliardi G. L., Mastroberardino G., Marinucci M., Peschle C. Molecular mechanisms of human hemoglobin switching: selective undermethylation and expression of globin genes in embryonic, fetal, and adult erythroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6907–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okudaira K., Searles R. P., Ceuppens J. L., Goodwin J. S., Williams R. C., Jr Anti-Ia reactivity in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):17–24. doi: 10.1172/JCI110428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prud'Homme G. J., Park C. L., Fieser T. M., Kofler R., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Identification of a B cell differentiation factor(s) spontaneously produced by proliferating T cells in murine lupus strains of the lpr/lpr genotype. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):730–742. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prud'homme G. J., Balderas R. S., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. B cell dependence on and response to accessory signals in murine lupus strains. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1815–1827. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Riggs A. D. DNA methylation and gene function. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):604–610. doi: 10.1126/science.6254144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Anisowicz A., Howell N. Genomic rearrangements in a mouse cell line containing integrated SV40 DNA. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Morimoto C. Isolation of DNA from DNA/anti-DNA antibody immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):538–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Noguchi H., Sager R. Characterization of DNA methyltransferase from bovine thymus cells. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 15;135(2):181–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Royer H. D., Sager R. Identification of 5-methylcytosine in DNA fragments immobilized on nitrocellulose paper. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3581–3585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Yamashita U., Suzuki H. Decrease in HLA-DR-positive monocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3560–3562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Steinberg A. D. Autoimmunity--a perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:175–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Petty H. R., Parham P., McConnell H. M. Cell surface properties of HLA antigens on Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):608–612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Huston D. P., Taurog J. D., Cowdery J. S., Ravecheé E. S. The cellular and genetic basis of murine lupus. Immunol Rev. 1981;55:121–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D., Das H., Nunberg J. H., Saiki R., Sheng-Dong R., Mullis K. B., Weissman S. M., Erlich H. A. Isolation of a cDNA clone for the human HLA-DR antigen alpha chain by using a synthetic oligonucleotide as a hybridization probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5966–5970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U., Arp B. Methylation patterns of immunoglobulin genes in lymphoid cells: correlation of expression and differentiation with undermethylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6642–6646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Etiopathogenesis of murine SLE. Immunol Rev. 1981;55:179–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Long E. O., Strubin M., Gross N., Accolla R., Carrel S., Mach B. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding HLA-DR alpha chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6979–6983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R., Kuehl M. Biosynthesis and regulation of immunoglobulins. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:393–422. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Winchester R. J., Wernet P., Fu S. M., Kunkel H. G. Nature of cold-reactive antibodies to lymphocyte surface determinants in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jan-Feb;18(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Jolly D. J., Lunnen K. D., Friedmann T., Migeon B. R. Methylation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase locus on the human X chromosome: implications for X-chromosome inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2806–2810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rappard-Van der Veen F. M., Kiesel U., Poels L., Schuler W., Melief C. J., Landegent J., Gleichmann E. Further evidence against random polyclonal antibody formation in mice with lupus-like graft-vs-host disease. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1814–1820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]