Abstract
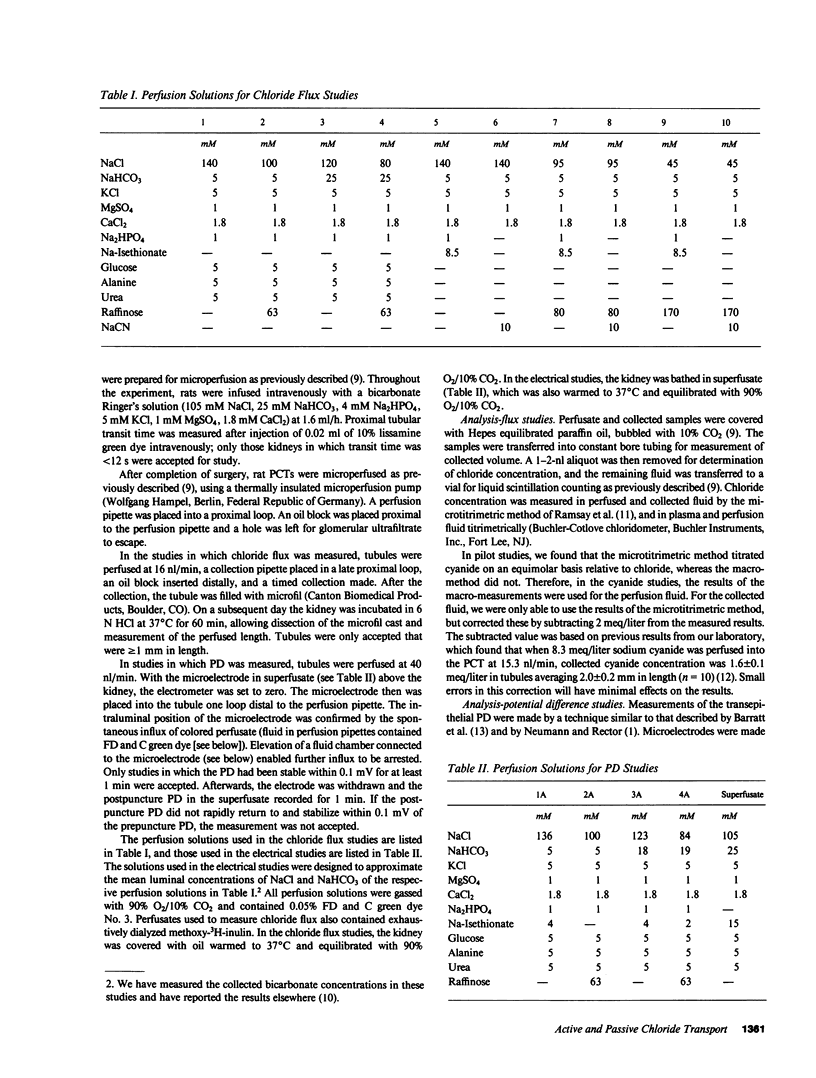
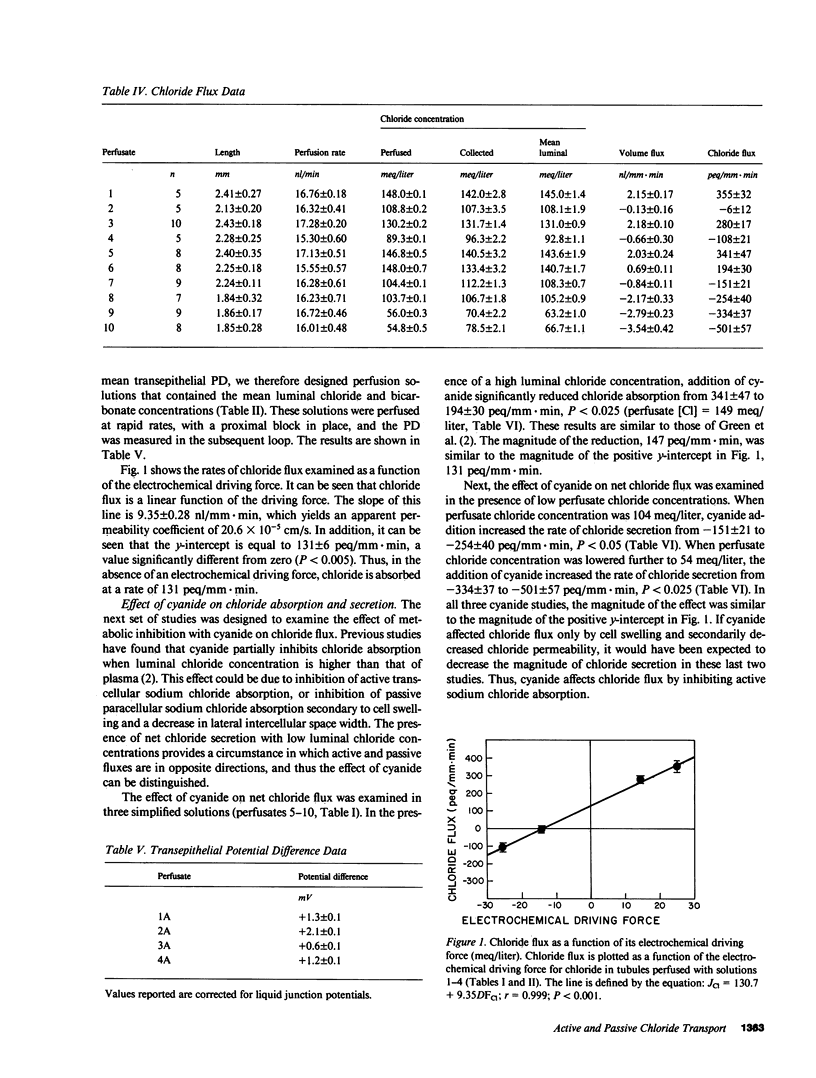
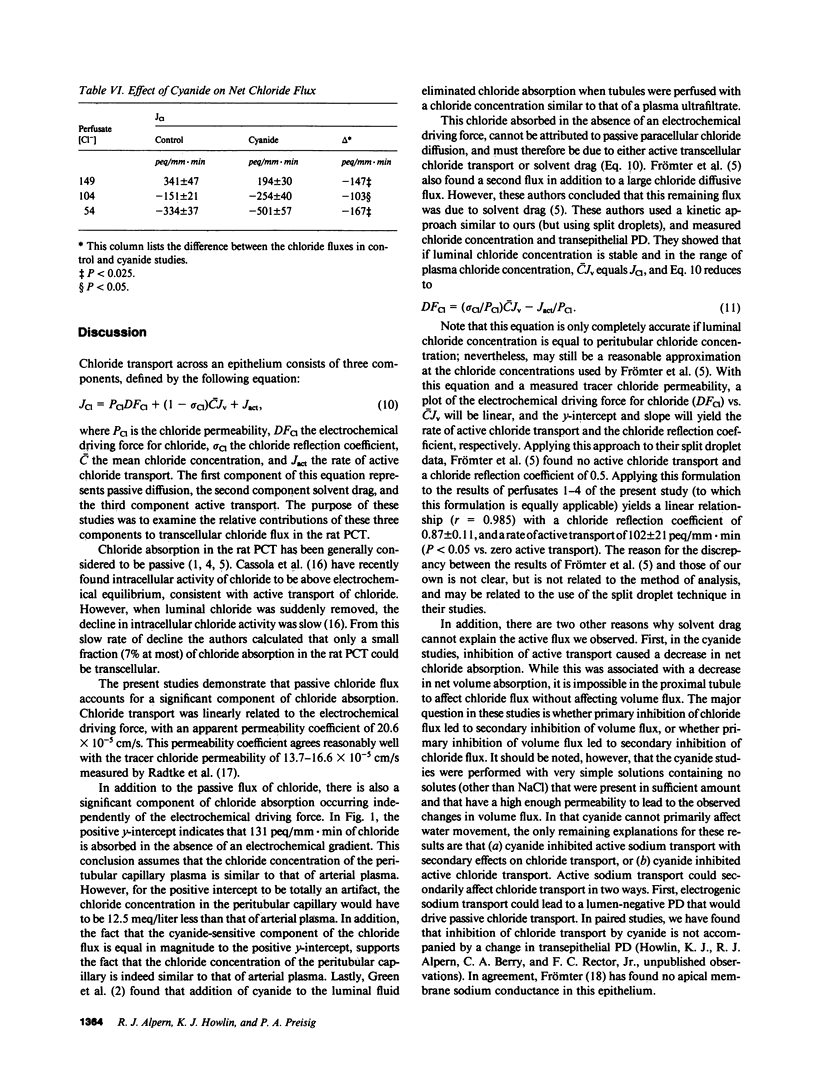
Rat proximal convoluted tubules were perfused in vivo to examine the active and passive components of chloride absorption. Chloride flux was a linear function of the transepithelial electrochemical driving force, yielding a permeability coefficient of 20.6 X 10(-5) cm/s. In the absence of an electrochemical driving force, chloride absorption persisted at the rate of 131 peq/mm X min, thus demonstrating active absorption of chloride. Addition of luminal cyanide to tubules absorbing chloride inhibited net chloride absorption. In tubules perfused with a low luminal chloride concentration in which there was net chloride secretion, addition of luminal cyanide increased the magnitude of net chloride secretion. These studies demonstrate that transepithelial chloride transport involves two components: a passive paracellular flux and an active transcellular flux. Cyanide affects net chloride flux by inhibiting active transcellular chloride absorption.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpern R. J. Bicarbonate-water interactions in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. An effect of volume flux on active proton secretion. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Nov;84(5):753–770. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.5.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Effect of luminal bicarbonate concentration on proximal acidification in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):F53–F59. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.1.F53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barratt L. J., Rector F. C., Jr, Kokko J. P., Seldin D. W. Factors governing the transepithelial potential difference across the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):454–464. doi: 10.1172/JCI107579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum M., Berry C. A. Evidence for neutral transcellular NaCl transport and neutral basolateral chloride exit in the rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):205–211. doi: 10.1172/JCI111403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C. A. Lack of effect of peritubular protein on passive NaCl transport in the rabbit proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):268–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI110767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassola A. C., Mollenhauer M., Frömter E. The intracellular chloride activity of rat kidney proximal tubular cells. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Dec;399(4):259–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00652749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Proximal reabsorption during metabolic acidosis in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):F499–F507. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.5.F499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Rumrich G., Ullrich K. J. Phenomenologic description of Na+, Cl- and HCO-3 absorption from proximal tubules of rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Oct 22;343(3):189–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00586045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Bishop J. H., Giebisch G. Ionic requirements of proximal tubular sodium transport. III. Selective luminal anion substitution. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):F268–F277. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.3.F268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson H. R. Characteristics of volume reabsorption in rabbit superficial and juxtamedullary proximal convoluted tubules. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):410–418. doi: 10.1172/JCI109317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucci M. S., Warnock D. G. Effects of anion-transport inhibitors on NaCl reabsorption in the rat superficial proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):570–579. doi: 10.1172/JCI109495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann K. H., Rector F. C., Jr Mechanism of NaCl and water reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule of rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1110–1118. doi: 10.1172/JCI108563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radtke H. W., Rumrich G., Klöss S., Ullrich K. J. Influence of luminal diameter and flow velocity on the isotonic fluid absorption and 36Cl permeability of the proximal convolution of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1971;324(4):288–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00592457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


