Abstract
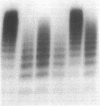
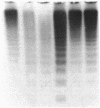
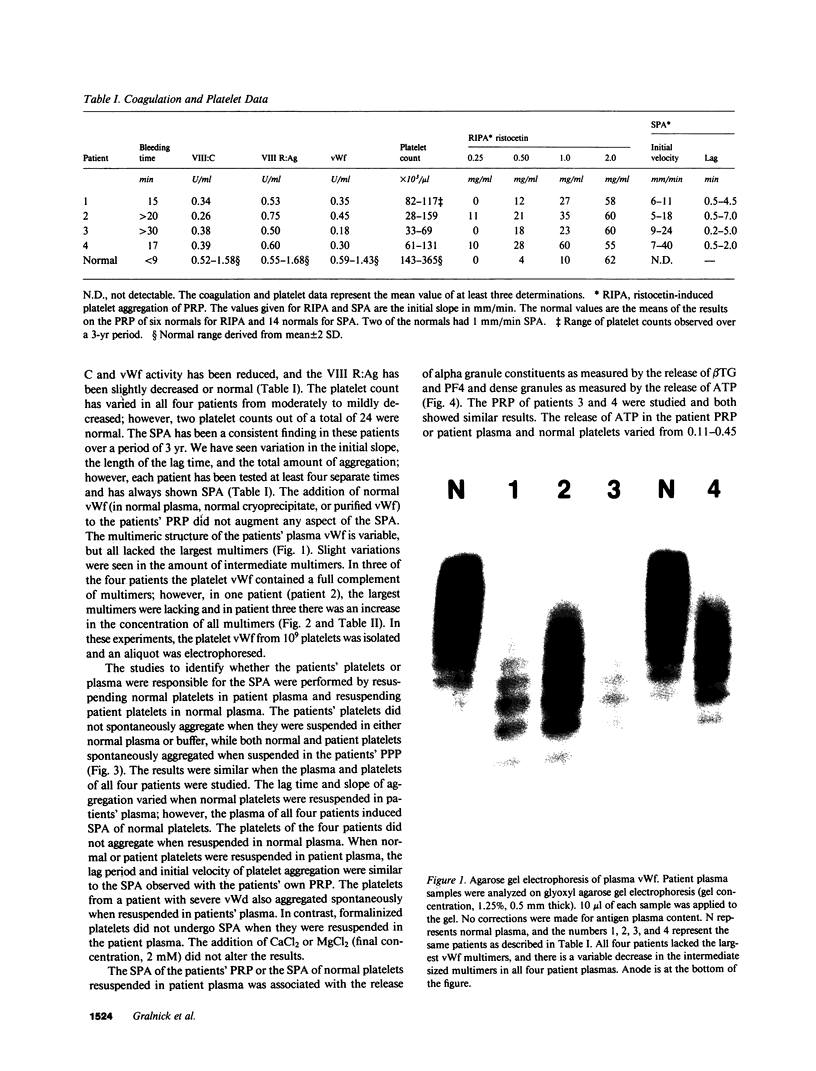
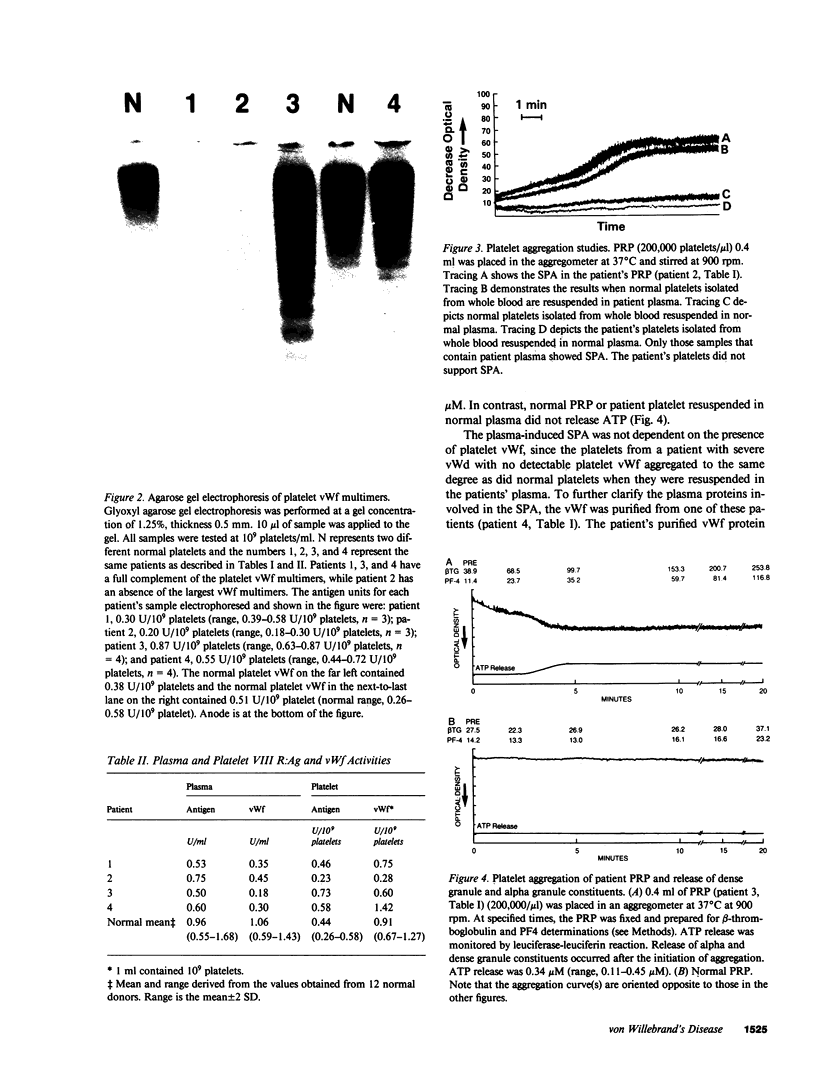
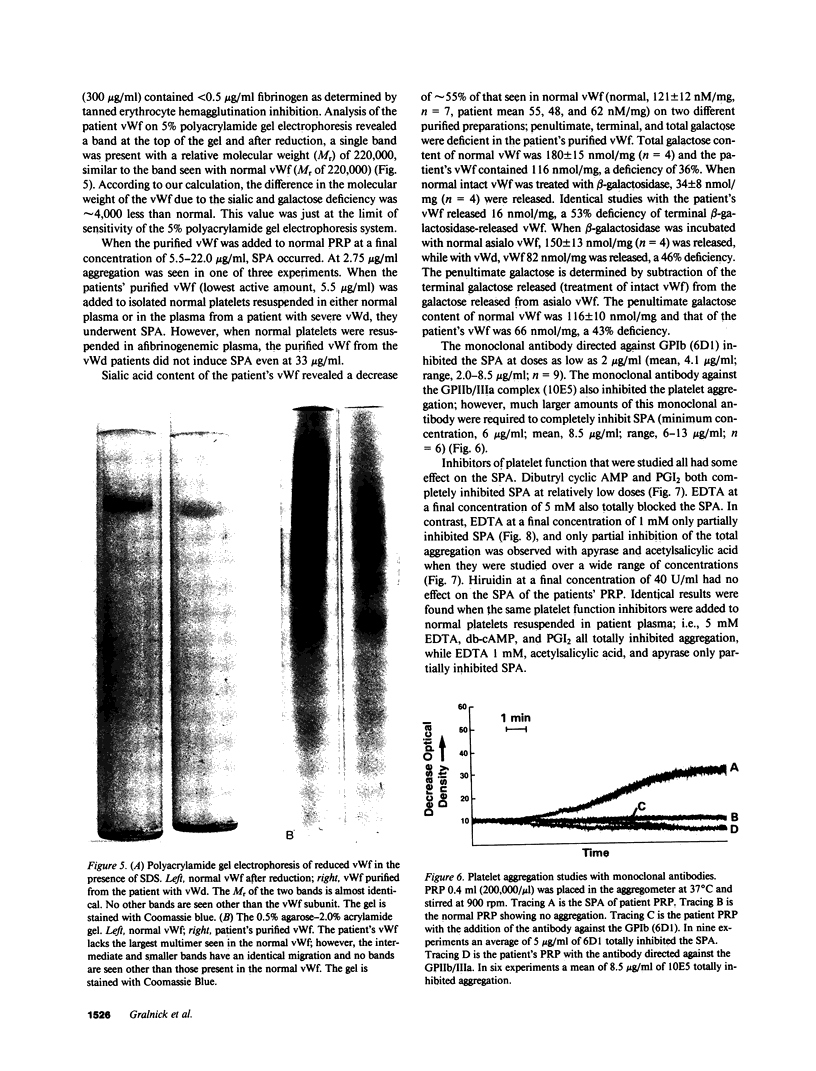
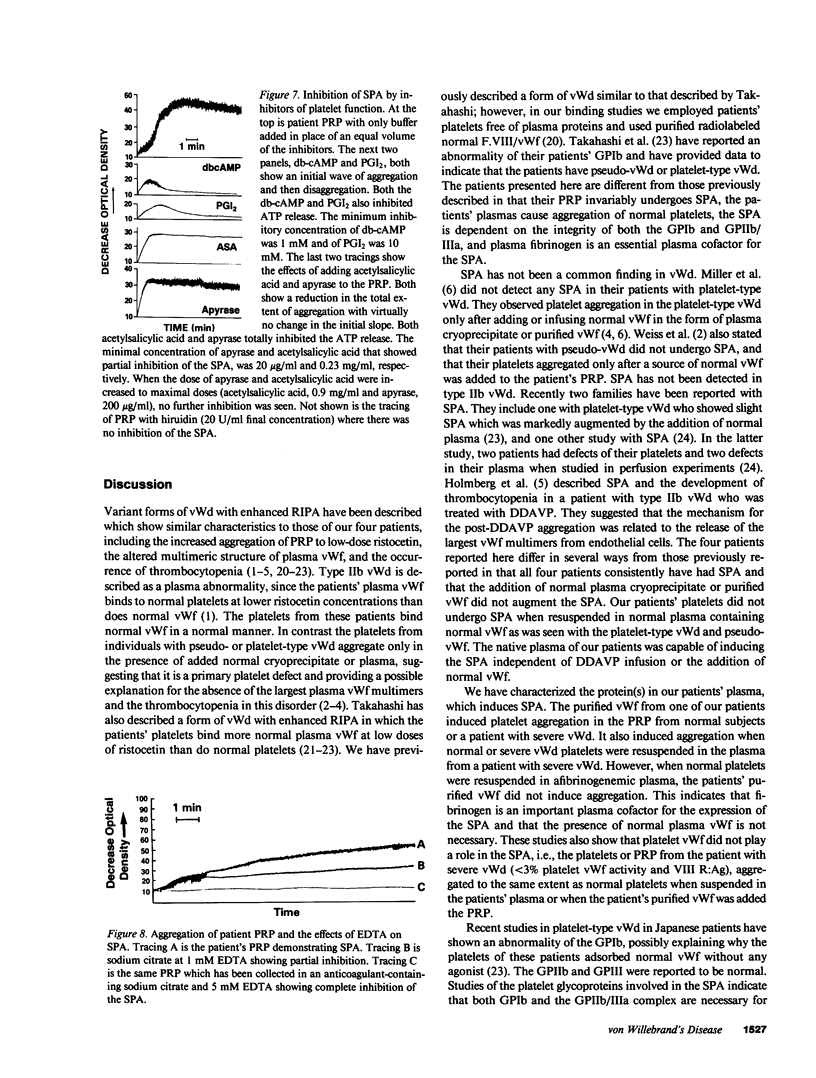
We have investigated and characterized the abnormalities in four unrelated patients with von Willebrand's disease (vWd) who have (a) enhanced ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation (RIPA) at low ristocetin concentrations, (b) absence of the largest plasma von Willebrand factor (vWf) multimers, and (c) thrombocytopenia. The platelet-rich plasma of these patients aggregates spontaneously without the addition of any agonists. When isolated normal platelets are resuspended in patient plasma spontaneous aggregation occurs; however, the patients' plasmas did not induce platelet aggregation of normal washed formalinized platelets. When the patients' platelets are suspended in normal plasma, spontaneous aggregation is not observed. The spontaneous platelet aggregation (SPA) is associated with dense granule secretion as measured by ATP release and alpha granule release as measured by beta-thromboglobulin and platelet factor 4 release. The SPA is totally inhibited by 5 mM EDTA, prostaglandin I2, and dibutryl cyclic AMP, while it is only partially inhibited by 1 mM EDTA, acetylsalicylic acid, or apyrase. A monoclonal antibody directed against glycoprotein Ib (GPIb) and/or a monoclonal antibody against the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GPIIb/IIIa) complex totally inhibits the SPA. The vWf was isolated from the plasma of one of these patients. The purified vWf induced platelet aggregation of normal platelets resuspended in either normal or severe vWd plasma, but the vWf did not induce platelet aggregation of normal platelets resuspended in afibrinognemic plasma. Sialic acid and galactose quantification of the patient's vWf revealed approximately a 50% reduction compared with normal vWf. These studies indicate that a form of vWd exists, which is characterized by SPA that is induced by the abnormal plasma vWf. The SPA is dependent on the presence of plasma fibrinogen, and the availability of the GPIb and the GPIIb/IIIa complex. In this variant form of vWd the abnormal vWf causes enhanced RIPA, SPA, and thrombocytopenia.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coller B. S. Inhibition of von Willebrand factor-dependent platelet function by increased platelet cyclic AMP and its prevention by cytoskeleton-disrupting agents. Blood. 1981 May;57(5):846–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Peerschke E. I., Scudder L. E., Sullivan C. A. A murine monoclonal antibody that completely blocks the binding of fibrinogen to platelets produces a thrombasthenic-like state in normal platelets and binds to glycoproteins IIb and/or IIIa. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):325–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI110973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Peerschke E. I., Scudder L. E., Sullivan C. A. Studies with a murine monoclonal antibody that abolishes ristocetin-induced binding of von Willebrand factor to platelets: additional evidence in support of GPIb as a platelet receptor for von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1983 Jan;61(1):99–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corash L., Shafer B., Perlow M. Heterogeneity of human whole blood platelet subpopulations. II. Use of a subhuman primate model to analyze the relationship between density and platelet age. Blood. 1978 Oct;52(4):726–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Girolami A., Russell S., Ruggeri Z. M. Interaction of asialo von Willebrand factor with glycoprotein Ib induces fibrinogen binding to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex and mediates platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1198–1203. doi: 10.1172/JCI111816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Shapiro S. S. Properties of human asialo-factor VIII. A ristocetin-independent platelet-aggregating agent. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):321–328. doi: 10.1172/JCI110259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto T., Ohara S., Hawiger J. Thrombin-induced exposure and prostacyclin inhibition of the receptor for factor VIII/von Willebrand factor on human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1212–1222. doi: 10.1172/JCI110560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber S. E., Hawiger J. Evidence that changes in platelet cyclic AMP levels regulate the fibrinogen receptor on human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14606–14609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainick H. R., Williams S. B., Coller B. S. Asialo von Willebrand factor interactions with platelets. Interdependence of glycoproteins Ib and IIb/IIIa for binding and aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):19–25. doi: 10.1172/JCI111673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Coller B. S., Sultan Y. Studies of the human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor protein. III. Qualitative defects in von Willebrand's disease. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):814–827. doi: 10.1172/JCI108160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Cregger M. C., Williams S. B. Characterization of the defect of the factor VIII/von Willebrand factor protein in von Willebrand's disease. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):542–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Williams S. B., Coller B. S. Fibrinogen competes with von Willebrand factor for binding to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex when platelets are stimulated with thrombin. Blood. 1984 Oct;64(4):797–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Williams S. B., Morisato D. K. Effect of multimeric structure of the factor VIII/von Willebrand factor protein on binding to platelets. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):387–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Parkinson S., Timmons S. Prostacyclin inhibits mobilisation of fibrinogen-binding sites on human ADP- and thrombin-treated platelets. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):195–197. doi: 10.1038/283195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Nilsson I. M., Borge L., Gunnarsson M., Sjörin E. Platelet aggregation induced by 1-desamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin (DDAVP) in Type IIB von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 6;309(14):816–821. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310063091402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Boselli B. D., Kupinski J. M. In vivo interaction of von Willebrand factor with platelets following cryoprecipitate transfusion in platelet-type von Willebrand's disease. Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):226–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Castella A. Platelet-type von Willebrand's disease: characterization of a new bleeding disorder. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):790–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Castella A. Platelet-type von Willebrand's disease: characterization of a new bleeding disorder. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):790–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Kupinski J. M., Castella A., Ruggeri Z. M. von Willebrand factor binds to platelets and induces aggregation in platelet-type but not type IIB von Willebrand disease. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1532–1542. doi: 10.1172/JCI111112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piétu G., Cherel G., Marguerie G., Meyer D. Inhibition of von Willebrand factor-platelet interaction by fibrinogen. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):648–649. doi: 10.1038/308648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Srouji A. H., Meyer D., Marguerie G., Ginsberg M. H. Evidence that three adhesive proteins interact with a common recognition site on activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5388–5391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Bader R., de Marco L. Glanzmann thrombasthenia: deficient binding of von Willebrand factor to thrombin-stimulated platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6038–6041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., De Marco L., Gatti L., Bader R., Montgomery R. R. Platelets have more than one binding site for von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):1–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI110946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Pareti F. I., Mannucci P. M., Ciavarella N., Zimmerman T. S. Heightened interaction between platelets and factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in a new subtype of von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 8;302(19):1047–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005083021902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakariassen K. S., Nieuwenhuis H. K., Sixma J. J. Differentiation of patients with subtype IIb-like von Willebrand's disease by means of perfusion experiments with reconstituted blood. Br J Haematol. 1985 Mar;59(3):459–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb07333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schullek J., Jordan J., Montgomery R. R. Interaction of von Willebrand factor with human platelets in the plasma milieu. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):421–428. doi: 10.1172/JCI111228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Handa M., Watanabe K., Ando Y., Nagayama R., Hattori A., Shibata A., Federici A. B., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Further characterization of platelet-type von Willebrand's disease in Japan. Blood. 1984 Dec;64(6):1254–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Sakuragawa N., Shibata A. Von Willebrand disease with an increased ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation and a qualitative abnormality of the factor VIII protein. Am J Hematol. 1980;8(3):299–308. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830080308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H. Studies on the pathophysiology and treatment of von Willebrand's disease. IV. Mechanism of increased ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation in von Willebrand's disease. Thromb Res. 1980 Sep 15;19(6):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermylen J., Bottecchia D., Szpilman H. Factor VIII and human platelet aggregation. III. Further studies on aggregation of humna platelets by neuraminidase-treated human factor VIII. Br J Haematol. 1976 Oct;34(2):321–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb00202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermylen J., De Gaetano G., Donati M. B., Verstraete M. Platelet-aggregating activity in neuraminidase-treated human cryoprecipitates: its correlation with factor-VIII-related antigen. Br J Haematol. 1974 Apr;26(4):645–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb00507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermylen J., Donati M. B., De Gaetano G., Verstraete M. Aggregation of human platelets by bovine or human factor VIII: role of carbohydrate side chains. Nature. 1973 Jul 20;244(5412):167–168. doi: 10.1038/244167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Meyer D., Rabinowitz R., Pietu G., Girma J. P., Vicic W. J., Rogers J. Pseudo-von Willebrand's disease. An intrinsic platelet defect with aggregation by unmodified human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor and enhanced adsorption of its high-molecular-weight multimers. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 11;306(6):326–333. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202113060603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]