Abstract
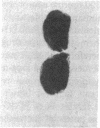
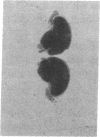
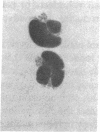
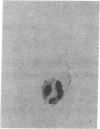
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase catalyzes the formation of mevalonate, an essential precursor for isoprenoid compounds in mammalian cells. Recent studies have shown that mevinolin, a competitive inhibitor of the reductase, inhibits cell proliferation and induces differentiation in cultured C1300 (Neuro-2A) murine neuroblastoma cells. We now report that mevinolin can inhibit neuroblastoma growth in vivo. The specific activity of HMG-CoA reductase in subcutaneous neuroblastomas increased more than 20-fold between the fifth and eighth days after tumor inoculation, and remained elevated for the remainder of the tumor lifetime in mice. The increase in reductase activity was correlated with a marked increase in tumor DNA content and exponential increase in tumor weight. Using an in vitro assay to monitor the ability of mouse serum to suppress sterol synthesis, we determined that mevinolin was inactivated or cleared from the circulation within 3-6 h after a single subcutaneous injection. However, by using subcutaneous osmotic pumps to deliver a constant infusion of mevinolin, we were able to maintain adequate blood levels of the drug for 7 d. Mevinolin (5 mg/kg per h) suppressed tumor growth (wet weight) significantly when treatment was carried out between day 1 and day 8 or between day 5 and day 12 after tumor inoculation. Histopathological examination of tumors from mevinolin-treated mice revealed few or no mitotic figures and marked cellular degeneration. Measurements of incorporation of (3H)acetate into neuroblastoma sterols and ubiquinones 24 h after implantation of osmotic pumps showed that mevinolin produced a marked inhibition of isoprenoid synthesis in the tumors in vivo. The data suggest that, in addition to their demonstrated utility as cholesterol-lowering drugs, competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase may have considerable potential as novel antineoplastic agents.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. W., Chen J., Kuron G., Hunt V., Huff J., Hoffman C., Rothrock J., Lopez M., Joshua H., Harris E. Mevinolin: a highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Grundy S. M., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Mevinolin and colestipol stimulate receptor-mediated clearance of low density lipoprotein from plasma in familial hypercholesterolemia heterozygotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4124–4128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Faust J. R., Goldstein J. L., Kaneko I., Endo A. Induction of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity in human fibroblasts incubated with compactin (ML-236B), a competitive inhibitor of the reductase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1121–1128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Multivalent feedback regulation of HMG CoA reductase, a control mechanism coordinating isoprenoid synthesis and cell growth. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jul;21(5):505–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A., Lan S. F., Fogelman A. M. Alterations in the rates of synthesis and degradation of rat liver 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase produced by cholestyramine and mevinolin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10219–10222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo A., Kuroda M., Tanzawa K. Competitive inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by ML-236A and ML-236B fungal metabolites, having hypocholesterolemic activity. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 31;72(2):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80996-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo A., Tsujita Y., Kuroda M., Tanzawa K. Effects of ML-236B on cholesterol metabolism in mice and rats: lack of hypocholesterolemic activity in normal animals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 21;575(2):266–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks K. P., Witte L. D., Goodman D. S. Relationship between mevalonate and mitogenesis in human fibroblasts stimulated with platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1546–1551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust J. R., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Synthesis of delta 2-isopentenyl tRNA from mevalonate in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6546–6548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust J. R., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Synthesis of ubiquinone and cholesterol in human fibroblasts: regulation of a branched pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jan;192(1):86–99. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finklestein J. Z., Arima E., Byfield P. E., Byfield J. E., Fonkalsrud E. W. Murine neuroblastoma: a model of human disease. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1973 Nov-Dec;57(4):405–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finklestein J. Z., Tittle K., Rubenstein J., Meshnik R., Weiner J. Combination chemotherapy in murine neuroblastoma. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1976;2(3):279–289. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950020309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Helgeson J. A., Brown M. S. Inhibition of cholesterol synthesis with compactin renders growth of cultured cells dependent on the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5403–5409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough D. P., Hemming F. W. The characterization and stereochemistry of biosynthesis of dolichols in rat liver. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):163–166. doi: 10.1042/bj1180163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg R. G., Sabine J. R., Wilce P. A. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase in rat liver and Morris hepatomas 5123C, 9618A and 5123t.c. Biochem J. 1982 May 15;204(2):457–462. doi: 10.1042/bj2040457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht A. J., Glomset J. A., Ross R. Relation of cholesterol and mevalonic acid to the cell cycle in smooth muscle and swiss 3T3 cells stimulated to divide by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5134–5140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. H. N6-(delta 2-isopentenyl)adenosine: chemical reactions, biosynthesis, metabolism, and significance to the structure and function of tRNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1970;10:57–86. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60561-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth D. R., Connor W. E. Hypercholesterolemia persisting after distal ileal bypass: response to mevinolin. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Jun;100(6):850–851. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-6-850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth D. R., Sexton G. J. Hypocholesterolemic effects of mevinolin in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):1972–1978. doi: 10.1172/JCI111618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M. A new specific cholesterol assay gives reduced cholesterol/phospholipid molar ratios in cell membranes. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jun;95(2):344–350. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90737-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandutsch A. A., Hancock R. L. Regulation of the rate of sterol synthesis and the level of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity in mouse liver and hepatomas. Cancer Res. 1971 Oct;31(10):1396–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko I., Hazama-Shimada Y., Endo A. Inhibitory effects on lipid metabolism in cultured cells of ML-236B, a potent inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme-A reductase. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):313–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Feedback regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in livers of mice treated with mevinolin, a competitive inhibitor of the reductase. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1094–1100. doi: 10.1172/JCI109938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNKRES K. D., RICHARDS F. M. THE PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF NEUROSPORA MALATE DEHYDROGENASE. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Mar;109:466–479. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90391-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi H., Haba T., Tatami R., Miyamoto S., Sakai Y., Wakasugi T., Watanabe A., Koizumi J., Takeda R. Effect of an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methyglutaryl coenzyme A reductase on serum lipoproteins and ubiquinone-10-levels in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 27;305(9):478–482. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108273050902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi H., Sakai T., Sakai Y., Yoshimura A., Watanabe A., Wakasugi T., Koizumi J., Takeda R. Reduction of serum cholesterol in heterozygous patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Additive effects of compactin and cholestyramine. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 17;308(11):609–613. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303173081101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltese W. A. 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in human brain tumors. Neurology. 1983 Oct;33(10):1294–1299. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.10.1294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltese W. A. Induction of differentiation in murine neuroblastoma cells by mevinolin, a competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 30;120(2):454–460. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltese W. A., Reitz B. A., Volpe J. J. Effects of prior sterol depletion on neurite outgrowth in neuroblastoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Sep;108(3):475–482. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041080322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. G., Thorne K. J. Synthesis of radioactive dolichol from (4S-3H)mevalonate in the regenerating rat liver. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;138(2):277–280. doi: 10.1042/bj1380277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A. D., Pugh T. D., Goldfarb S. Partial "feedback control" of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity in primary hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1978 Dec;38(12):4474–4477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. P., Williams P., Keogh B. Chemotherapy of a murine neuroblastoma model. J Surg Oncol. 1975;7(6):521–524. doi: 10.1002/jso.2930070612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nambudiri A. M., Ranganathan S., Rudney H. The role of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity in the regulation of ubiquinone synthesis in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5894–5899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons G., O'Dea R. F., Mirkin B. L. Biological characterization of the C-1300 murine neuroblastoma: an in vivo neural crest tumor model. Cancer Res. 1982 Sep;42(9):3719–3723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesney-Huneeus V., Galick H. A., Siperstein M. D., Erickson S. K., Spencer T. A., Nelson J. A. The dual role of mevalonate in the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):378–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesney-Huneeus V., Wiley M. H., Siperstein M. D. Essential role for mevalonate synthesis in DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5056–5060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. N., Kottapally S., Shinozuka H. Lipid composition and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase activity of acinar cell carcinoma of rat pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 23;759(1-2):74–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell V. W., Nordstrom J. L., Mitschelen J. J. Regulation of HMG-CoA reductase. Adv Lipid Res. 1976;14:1–74. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024914-5.50008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. A., Schneider C. J., Glomset J. A. Evidence for post-translational incorporation of a product of mevalonic acid into Swiss 3T3 cell proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10175–10180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroepfer G. J., Jr Sterol biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:585–621. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M., Logel J. Inhibition of degradation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by mevinolin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8547–8549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siperstein M. D., Gyde A. M., Morris H. P. Loss of feedback control of hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in hepatomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):315–317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theeuwes F., Yum S. I. Principles of the design and operation of generic osmotic pumps for the delivery of semisolid or liquid drug formulations. Ann Biomed Eng. 1976 Dec;4(4):343–353. doi: 10.1007/BF02584524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobert J. A., Bell G. D., Birtwell J., James I., Kukovetz W. R., Pryor J. S., Buntinx A., Holmes I. B., Chao Y. S., Bolognese J. A. Cholesterol-lowering effect of mevinolin, an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase, in healthy volunteers. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):913–919. doi: 10.1172/JCI110530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobert J. A., Hitzenberger G., Kukovetz W. R., Holmes I. B., Jones K. H. Rapid and substantial lowering of human serum cholesterol by mevinolin (MK-803), an inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Atherosclerosis. 1982 Jan;41(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(82)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J., Hennessy S. W. Cholesterol biosynthesis and 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase in cultured glial and neuronal cells. Regulation by lipoprotein and by certain free sterols. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 25;486(3):408–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A., Sudo H., Endo A. Therapeutic effects of ML-236B in primary hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 1980 Mar;35(3):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(80)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]