Abstract
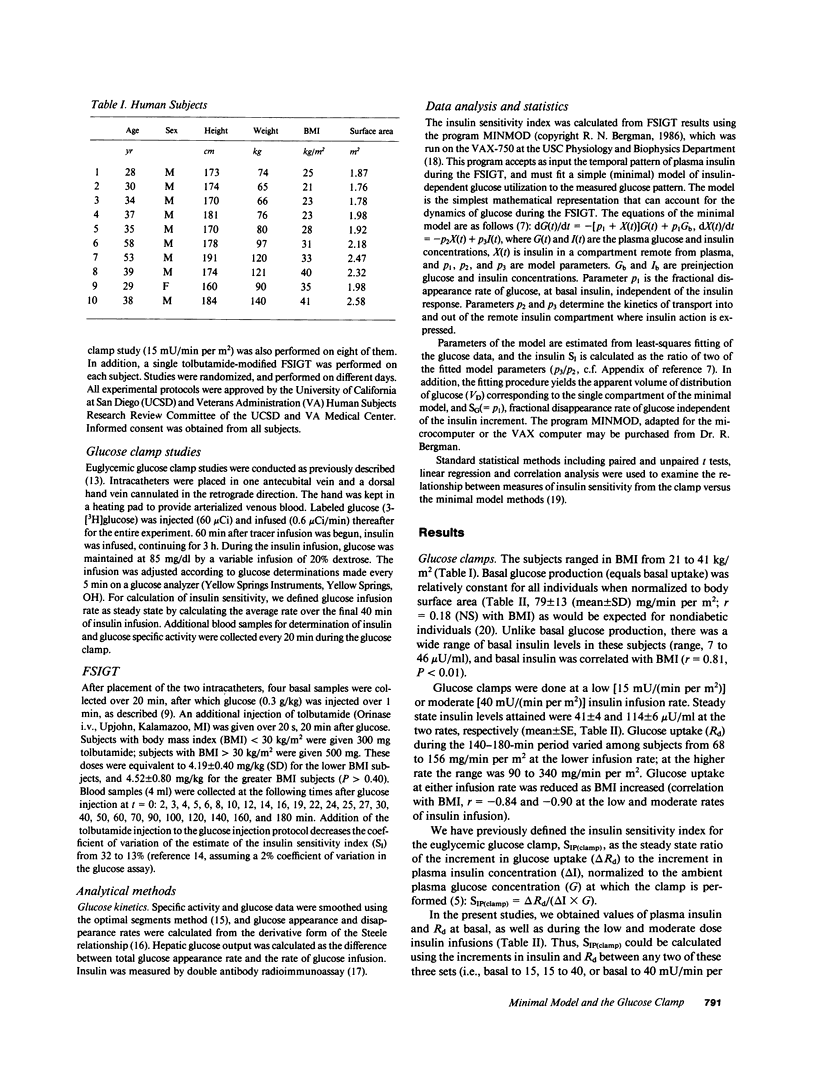
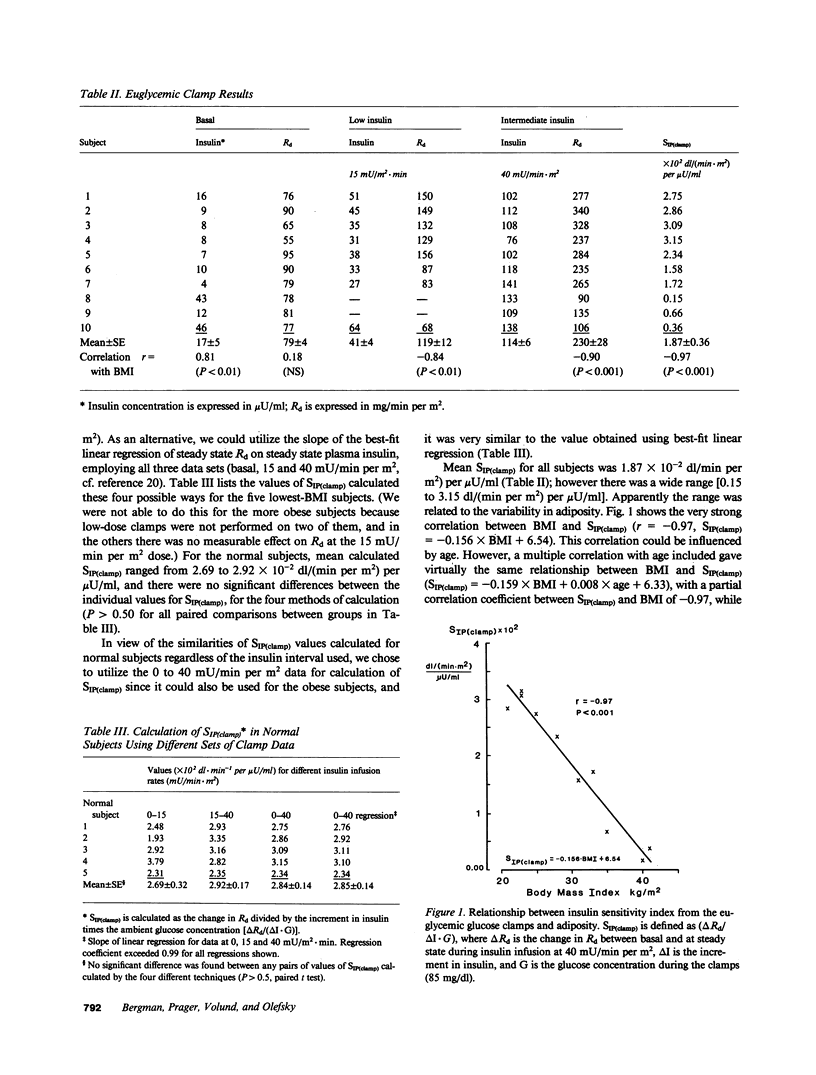
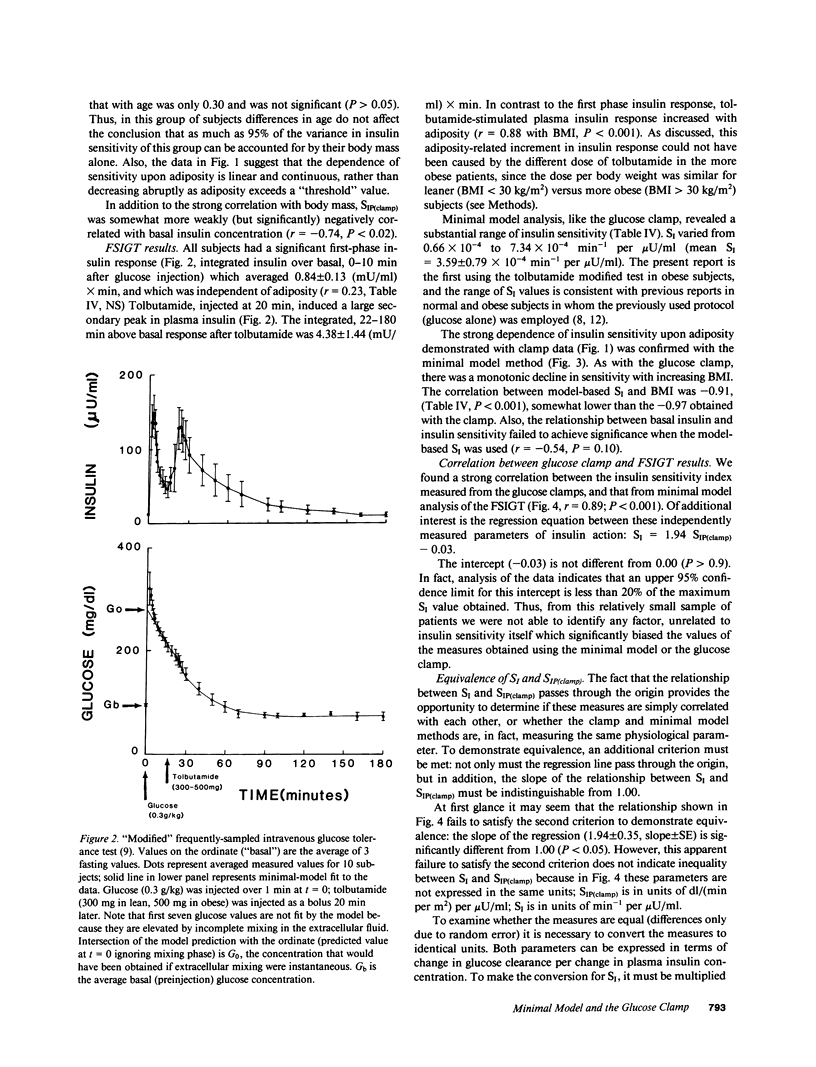
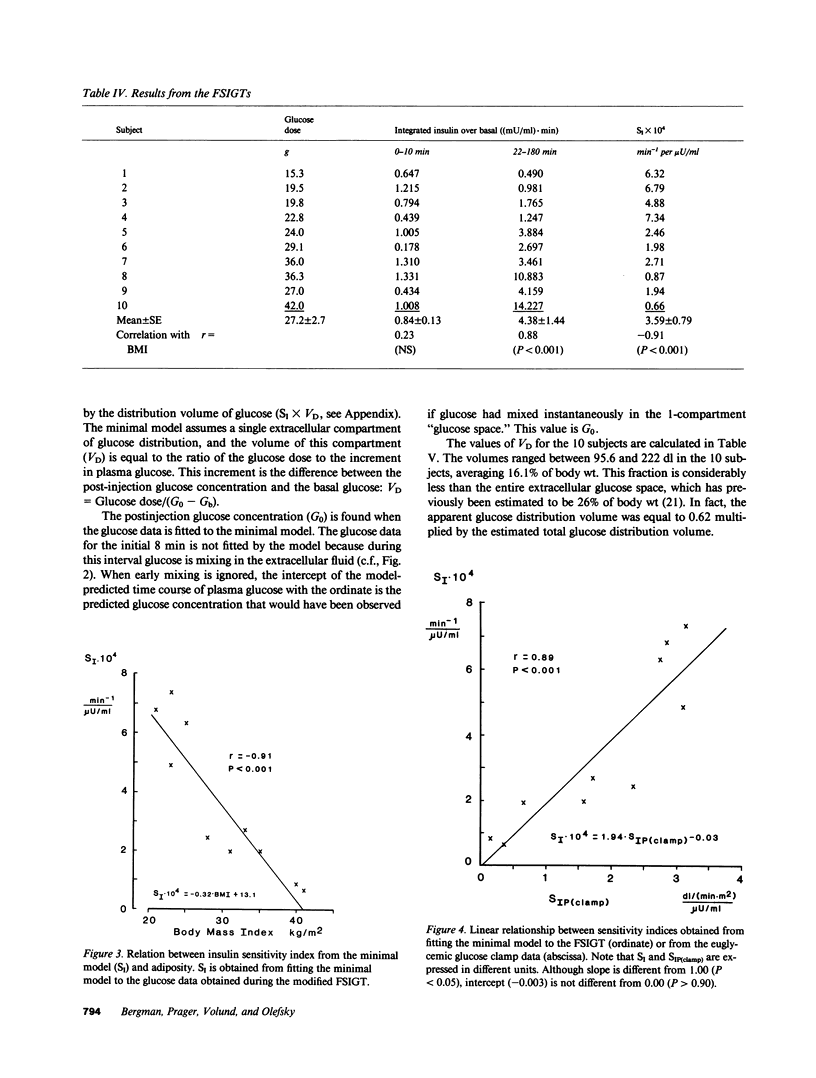
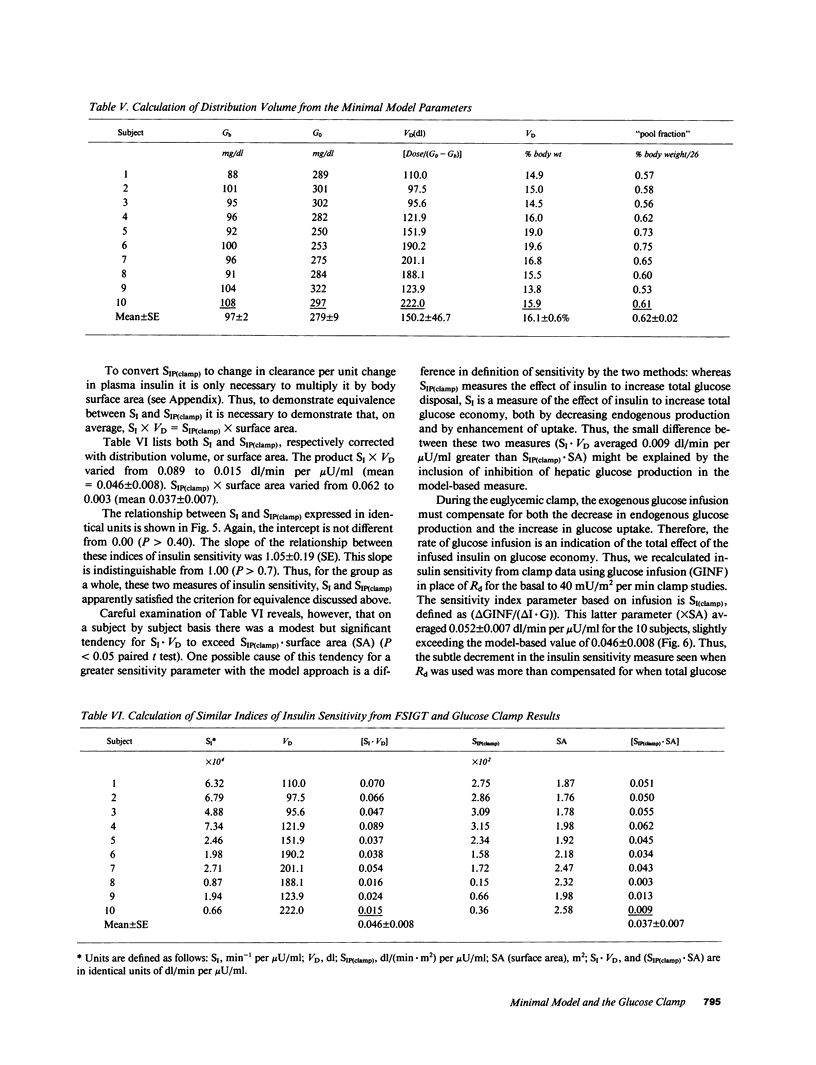
Studies were done to determine whether the minimal model approach and the glucose clamp measure equivalent indices of insulin action. Euglycemic glucose clamps (glucose, G: 85 mg/dl) were performed at two rates of insulin (I) infusion (15 and 40 mU/min per m2) in 10 subjects (body mass index, BMI, from 21 to 41 kg/m2). Insulin sensitivity index (SI) from clamps varied from 0.15 to 3.15 (mean: 1.87 +/- 0.36 X 10(-2) dl/[min per m2] per microU/ml), and declined linearly with increasing adiposity (versus BMI: r = -0.97; P less than 0.001). SI from modeling the modified frequently sampled intravenous tolerance test varied from 0.66 to 7.34 X 10(-4) min-1 per microU/ml, and was strongly correlated with SIP(clamp) (r = 0.89; P less than 0.001). SI and SIP(clamp) were similar (0.046 +/- 0.008 vs. 0.037 +/- 0.007 dl/min per microU/ml, P greater than 0.35); the relation had a slope not different from unity (1.05 P greater than 0.70) and passed through the origin (P greater than 0.40). However, on a period basis, SI exceeded SIP(clamp) slightly, due to inhibition of hepatic glucose output during the FSIGT, not included in SIP(clamp). These methods are equivalent for assessment of overall insulin sensitivity in normal and insulin-resistant nondiabetic subjects.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMATUZIO D. S., STUTZMAN F. L., VANDERBILT M. J., NESBITT S. Interpretation of the rapid intravenous glucose tolerance test in normal individuals and in mild diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1953 May;32(5):428–435. doi: 10.1172/JCI102755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ader M., Pacini G., Yang Y. J., Bergman R. N. Importance of glucose per se to intravenous glucose tolerance. Comparison of the minimal-model prediction with direct measurements. Diabetes. 1985 Nov;34(11):1092–1103. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.11.1092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Levis W. R., Rechler M. M., Harrison L. C., Siebert C., Podskalny J., Roth J., Muggeo M. Extreme insulin resistance in ataxia telangiectasia: defect in affinity of insulin receptors. N Engl J Med. 1978 May 25;298(21):1164–1171. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197805252982103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard J. C., Bergman R. N., Ward W. K., Porte D., Jr The insulin sensitivity index in nondiabetic man. Correlation between clamp-derived and IVGTT-derived values. Diabetes. 1986 Mar;35(3):362–369. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.3.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. N., Finegood D. T., Ader M. Assessment of insulin sensitivity in vivo. Endocr Rev. 1985 Winter;6(1):45–86. doi: 10.1210/edrv-6-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. N., Ider Y. Z., Bowden C. R., Cobelli C. Quantitative estimation of insulin sensitivity. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):E667–E677. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.6.E667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. N., Phillips L. S., Cobelli C. Physiologic evaluation of factors controlling glucose tolerance in man: measurement of insulin sensitivity and beta-cell glucose sensitivity from the response to intravenous glucose. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1456–1467. doi: 10.1172/JCI110398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defronzo R. A. Glucose intolerance and aging: evidence for tissue insensitivity to insulin. Diabetes. 1979 Dec;28(12):1095–1101. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.12.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Aurbach G. D. Use of polyethylene glycol to separate free and antibody-bound peptide hormones in radioimmunoassays. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Nov;33(5):732–738. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-5-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner C. C., Fraze E., Chen Y. D., Hollenbeck C. B., Foley J. E., Reaven G. M. Presentation of a new method for specific measurement of in vivo insulin-stimulated glucose disposal in humans: comparison of this approach with the insulin clamp and minimal model techniques. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Apr;60(4):723–726. doi: 10.1210/jcem-60-4-723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber J. P., Jéquier E. Glucose storage deficiency as a cause of insulin resistance in obese-hyperinsulinaemic diabetes. Int J Obes. 1982;6 (Suppl 1):131–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegood D. T., Bergman R. N. Optimal segments: a method for smoothing tracer data to calculate metabolic fluxes. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):E472–E479. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.5.E472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley J. E., Chen Y. D., Lardinois C. K., Hollenbeck C. B., Liu G. C., Reaven G. M. Estimates of in vivo insulin action in humans: comparison of the insulin clamp and the minimal model techniques. Horm Metab Res. 1985 Aug;17(8):406–409. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1013559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg H., Kimmerling G., Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Demonstration of insulin resistance in untreated adult onset diabetic subjects with fasting hyperglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):454–461. doi: 10.1172/JCI107951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg H., Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Evaluation of insulin resistance in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Mar;148(3):942–945. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman I., Mandarino L., Gerich J. Use of glucose uptake and glucose clearance for the evaluation of insulin action in vivo. Diabetes. 1984 Feb;33(2):184–191. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R. S., Scarlett J. A., Griffin J., Olefsky J. M., Kolterman O. G. In vivo deactivation of peripheral, hepatic, and pancreatic insulin action in man. Diabetes. 1982 Oct;31(10):929–936. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.10.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IKKOS D., LUFT R. On the intravenous glucose tolerance test. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1957 Jul;25(3):312–334. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0250312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Insel J., Saekow M., Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in human obesity: evidence for receptor and postreceptor defects. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1272–1284. doi: 10.1172/JCI109790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Reaven G. M., Olefsky J. M. Relationship between in vivo insulin resistance and decreased insulin receptors in obese man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Mar;48(3):487–494. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-3-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacini G., Bergman R. N. MINMOD: a computer program to calculate insulin sensitivity and pancreatic responsivity from the frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 1986 Oct;23(2):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0169-2607(86)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk J., Norwich K. H., Vranic M. Experimental validation of measurements of glucose turnover in nonsteady state. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):E84–E93. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.1.E84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Moore J., Greenfield M. Quantification of insulin secretion and in vivo insulin action in nonobese and moderately obese individuals with normal glucose tolerance. Diabetes. 1983 Jul;32(7):600–604. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.7.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R. Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., WALL J. S., DE BODO R. C., ALTSZULER N. Measurement of size and turnover rate of body glucose pool by the isotope dilution method. Am J Physiol. 1956 Sep;187(1):15–24. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. W., Reaven G. M., Farquhar J. W. Comparison of impedance to insulin-mediated glucose uptake in normal subjects and in subjects with latent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2151–2160. doi: 10.1172/JCI106433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Kramer K. J., Tobin J. D., Insel P. A., Liljenquist J. E., Berman M., Andres R. A model of the kinetics of insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1481–1492. doi: 10.1172/JCI107697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


