Abstract
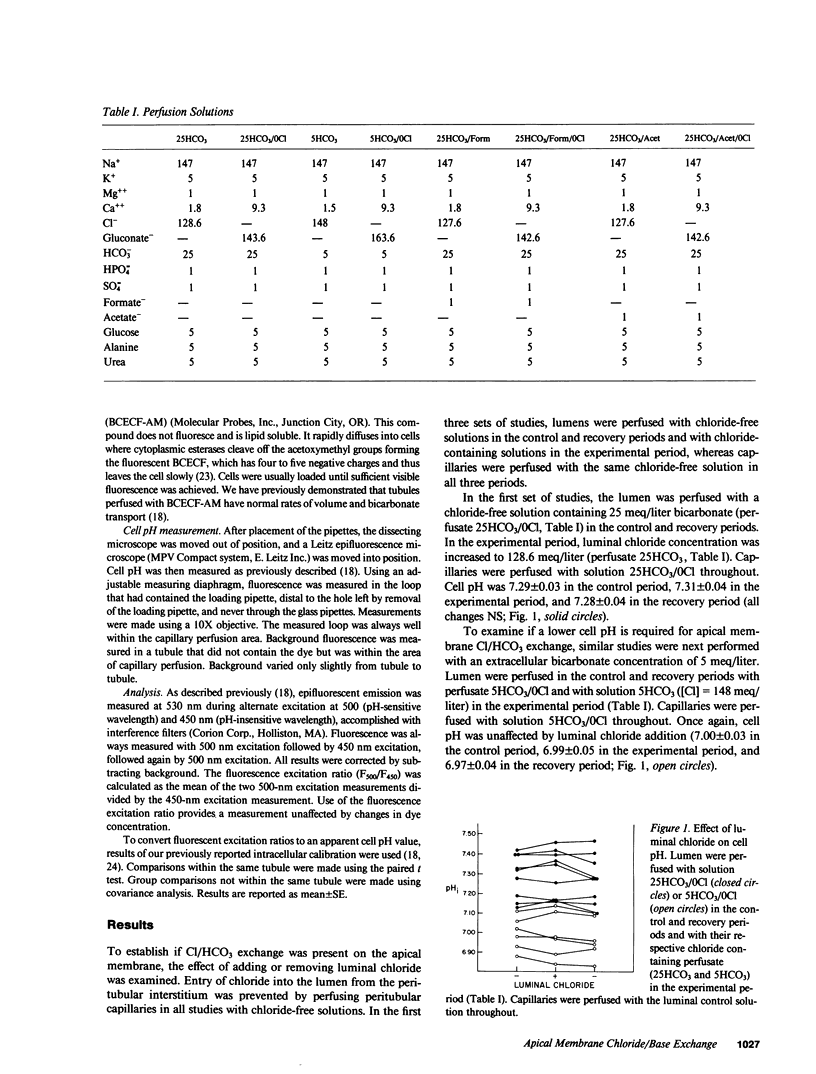
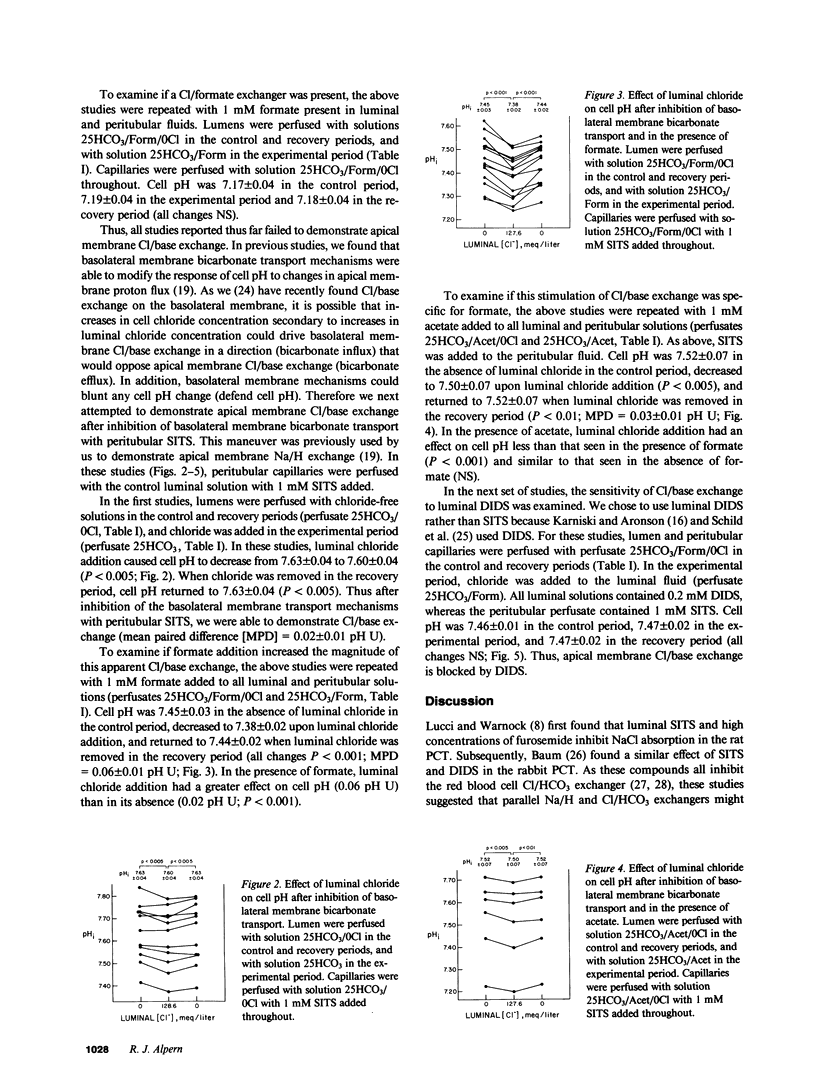
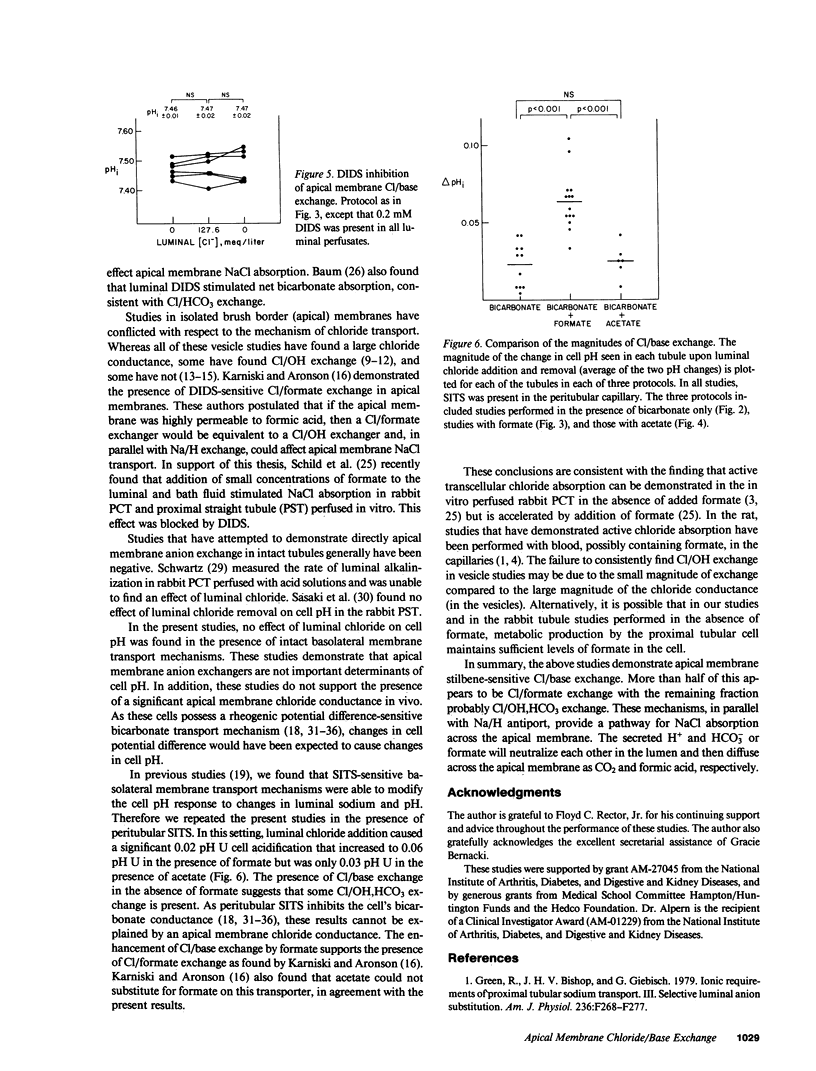
To examine whether Cl/base exchange is present on the apical membrane of the proximal convoluted tubule, cell pH was measured fluorometrically in the in vivo microperfused rat proximal tubule with (2',7')-bis(carboxyethyl)-(5,6)-carboxyfluorescein. The effect of luminal chloride addition was examined in tubules perfused symmetrically with chloride-free solutions. In the absence of inhibitors, luminal chloride addition did not affect cell pH. However, after inhibition of basolateral membrane anion transport with peritubular 4-acetamido-4'-isothiocyano-(2,2')-disulfonic-stilbene (to amplify effects of apical membrane transport on cell pH), luminal chloride addition caused a small cell acidification (delta pHi = 0.02). When 1 mM formate was added to the solutions, luminal chloride addition caused a larger change in cell pH (delta pHi = 0.06) that was inhibited by (4,4')-diisothiocyano-(2,2')-disulfonic-stilbene. This stimulation of Cl/base exchange was not seen with 1 mM acetate addition. These results demonstrate apical membrane Cl/base exchange, a significant fraction of which is dependent on the presence of formate and probably represents Cl/formate exchange.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiba T., Alpern R. J., Eveloff J., Calamina J., Warnock D. G. Electrogenic sodium/bicarbonate cotransport in rabbit renal cortical basolateral membrane vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1472–1478. doi: 10.1172/JCI112738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J. Bicarbonate-water interactions in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. An effect of volume flux on active proton secretion. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Nov;84(5):753–770. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.5.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Chambers M. Cell pH in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Regulation by luminal and peritubular pH and sodium concentration. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):502–510. doi: 10.1172/JCI112602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Howlin K. J., Preisig P. A. Active and passive components of chloride transport in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1360–1366. doi: 10.1172/JCI112111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J. Mechanism of basolateral membrane H+/OH-/HCO-3 transport in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. A sodium-coupled electrogenic process. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Nov;86(5):613–636. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.5.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum M., Berry C. A. Evidence for neutral transcellular NaCl transport and neutral basolateral chloride exit in the rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):205–211. doi: 10.1172/JCI111403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biagi B. A., Giebisch G. Temperature dependence of transepithelial potential in isolated perfused rabbit proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):F302–F310. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.3.F302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biagi B. A., Sohtell M. Electrophysiology of basolateral bicarbonate transport in the rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 2):F267–F272. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.2.F267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander. Basolateral HCO3- transport. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):53–94. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazy P. C., Gunn R. B. Furosemide inhibition of chloride transport in human red blood cells. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Dec;68(6):583–599. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.6.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burckhardt B. C., Sato K., Frömter E. Electrophysiological analysis of bicarbonate permeation across the peritubular cell membrane of rat kidney proximal tubule. I. Basic observations. Pflugers Arch. 1984 May;401(1):34–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00581530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham C., Munzesheimer C., Rabon E., Sachs G. Ion pathways in renal brush border membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 8;685(3):260–272. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. The nature of the membrane sites controlling anion permeability of human red blood cells as determined by studies with disulfonic stilbene derivatives. J Membr Biol. 1972 Dec 29;10(3):311–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01867863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassano G., Stieger B., Murer H. Na/H- and Cl/OH-exchange in rat jejunal and rat proximal tubular brush border membrane vesicles. Studies with acridine orange. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Mar;400(3):309–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00581565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Gessner K. Active transport potentials, membrane diffusion potentials and streaming potentials across rat kidney proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(1):85–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00603513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassl S. M., Aronson P. S. Na+/HCO3-co-transport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8778–8783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Bishop J. H., Giebisch G. Ionic requirements of proximal tubular sodium transport. III. Selective luminal anion substitution. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):F268–F277. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.3.F268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlin K. J., Alpern R. J., Berry C. A., Rector F. C., Jr Evidence for electroneutral sodium chloride transport in rat proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 2):F644–F648. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.4.F644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ives H. E., Chen P. Y., Verkman A. S. Mechanism of coupling between Cl- and OH- transport in renal brush-border membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 1;863(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson H. R. Characteristics of volume reabsorption in rabbit superficial and juxtamedullary proximal convoluted tubules. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):410–418. doi: 10.1172/JCI109317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karniski L. P., Aronson P. S. Chloride/formate exchange with formic acid recycling: a mechanism of active chloride transport across epithelial membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6362–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucci M. S., Warnock D. G. Effects of anion-transport inhibitors on NaCl reabsorption in the rat superficial proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):570–579. doi: 10.1172/JCI109495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Tsien R. Y., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. Na+/H+ exchange and cytoplasmic pH in the action of growth factors in human fibroblasts. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):645–648. doi: 10.1038/304645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector F. C., Jr Sodium, bicarbonate, and chloride absorption by the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):F461–F471. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.5.F461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Cytoplasmic pH and free Mg2+ in lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):189–196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabolić I., Burckhardt G. Proton pathways in rat renal brush-border and basolateral membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 12;734(2):210–220. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90119-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J. Absence of Cl- -OH- or Cl- -HCO3- exchange in the rabbit renal proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):F462–F469. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.4.F462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifter J. L., Knickelbein R., Aronson P. S. Absence of Cl-OH exchange and NaCl cotransport in rabbit renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):F753–F759. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.5.F753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiuan D., Weinstein S. W. Evidence for electroneutral chloride transport in rabbit renal cortical brush border membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):F837–F847. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.5.F837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. G., Yee V. J. Chloride uptake by brush border membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. Coupling to proton gradients and K+ diffusion potentials. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):103–115. doi: 10.1172/JCI110002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


