Abstract
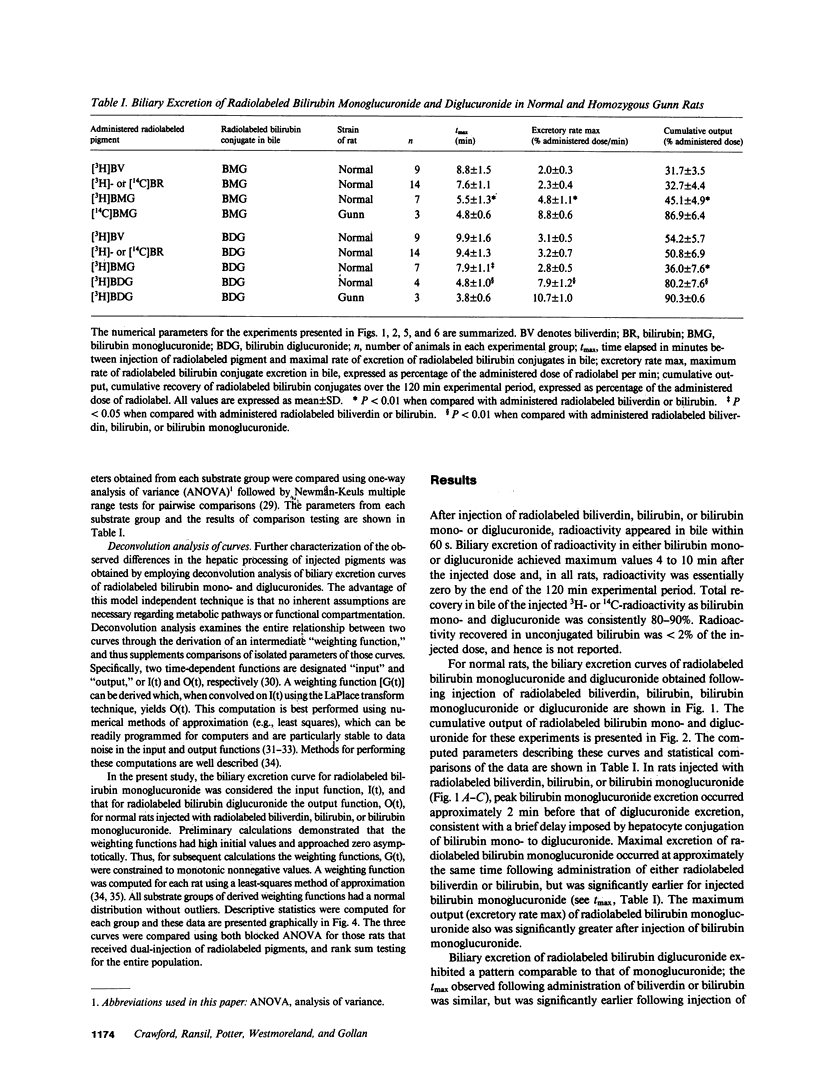
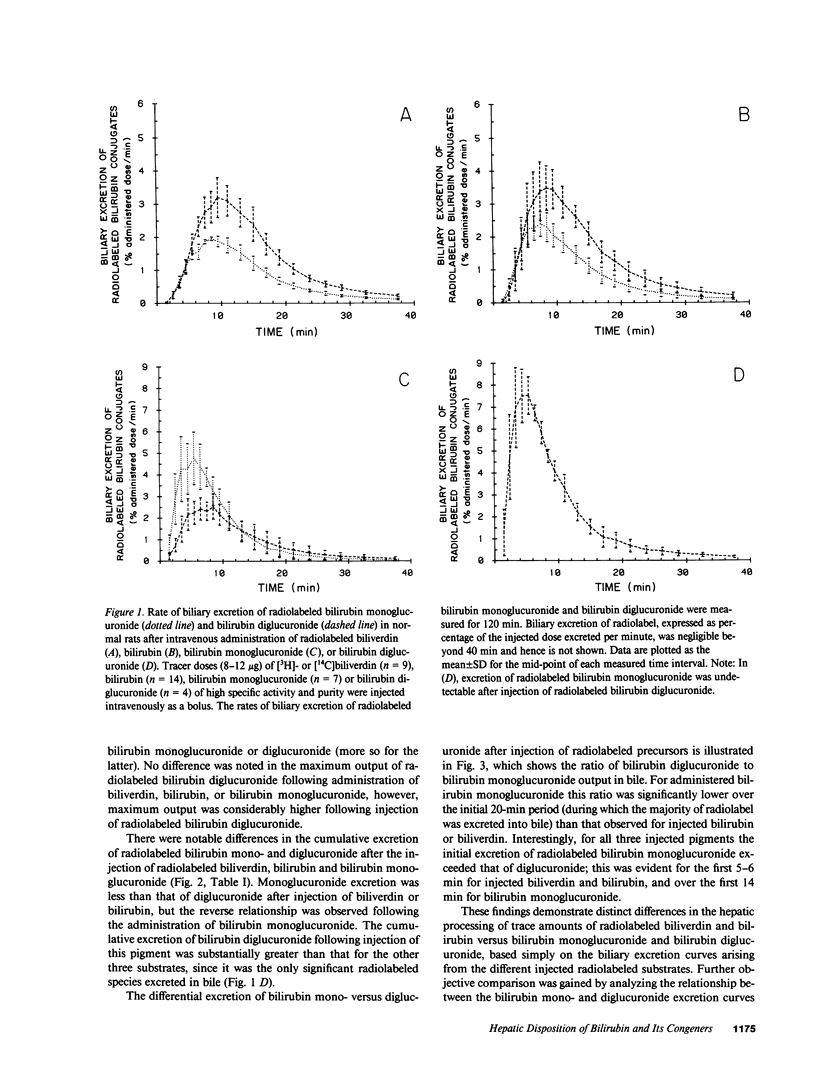
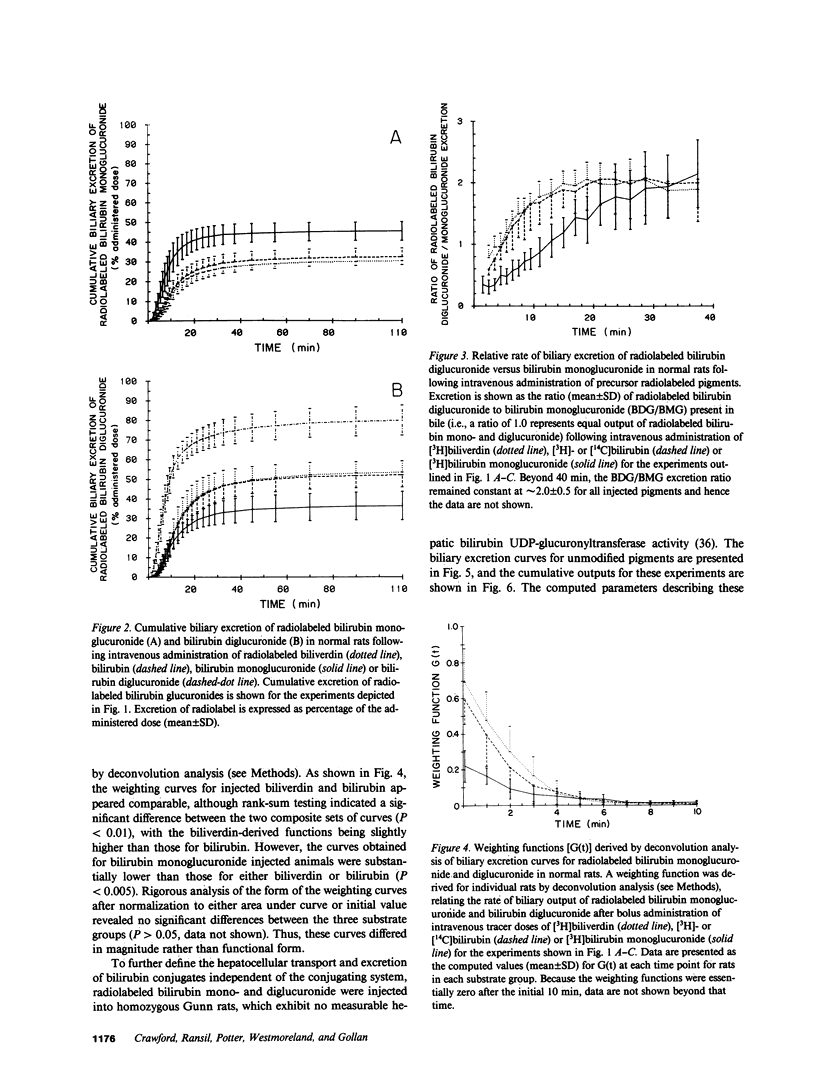
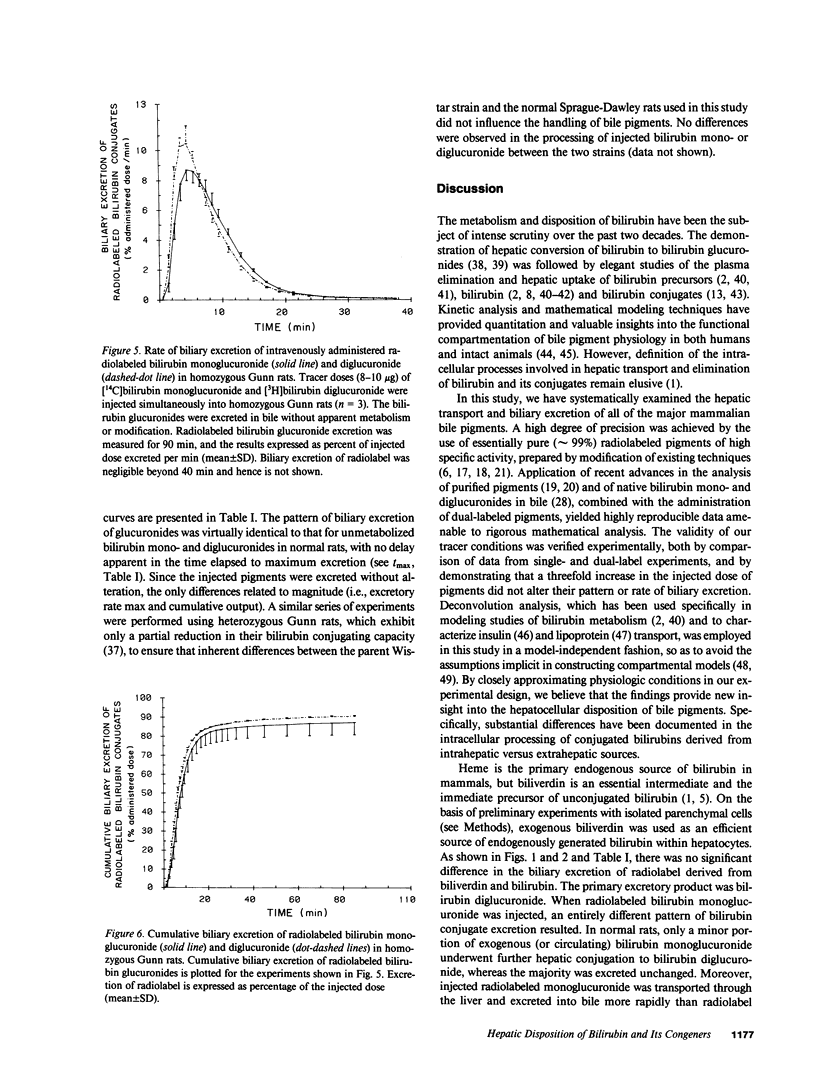
Mechanisms for transport of bilirubin and its conjugates in hepatocytes have not been defined. We investigated the hepatic processing of bilirubin glucuronides and their precursors, and characterized the disposition of bile pigments arising from intraversus extrahepatic sources. Tracer doses of purified radiolabeled biliverdin, bilirubin, bilirubin monoglucuronide (BMG) or diglucuronide (BDG) were administered intravenously to intact normal or jaundiced homozygous Gunn rats. Rapid sequential analysis of radiolabeled BMG and BDG in bile revealed comparable excretion patterns following biliverdin and bilirubin injection, with BDG as the major pigment. Biliary excretion of radiolabeled conjugates from injected BMG was more rapid, with BMG predominating. Excretion of injected BDG in normal rats and BMG or BDG in Gunn rats was virtually identical to that of unaltered BMG in normal rats. Model independent analysis by deconvolution provided objective comparison of the disposition of radiolabeled pigments from the different sources. These findings indicate that bilirubin glucuronides formed in the liver from endogenous (hepatic) and exogenous (extrahepatic) sources of bilirubin follow a similar excretory pathway. BMG formed endogenously is converted preferentially to BDG, whereas circulating BMG is excreted predominantly unchanged. Exogenous conjugated bilirubins are excreted more rapidly than those generated intrahepatically, by a transcellular pathway that is largely independent of the conjugation system.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARBER-RILEY G. RAT BILIARY TREE DURING SHORT PERIODS OF OBSTRUCTION OF COMMON DUCT. Am J Physiol. 1963 Dec;205:1127–1131. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BILLING B. H., COLE P. G., LATHE G. H. The excretion of bilirubin as a diglucuronide giving the direct van den Bergh reaction. Biochem J. 1957 Apr;65(4):774–784. doi: 10.1042/bj0650774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates J. H., Janus E. D. Deconvolution in the study of lipoprotein metabolism. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 1983 Oct-Dec;6(4):174–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk P. D., Blaschke T. F., Scharschmidt B. F., Waggoner J. G., Berlin N. I. A new approach to quantitation of the various sources of bilrubin in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 May;87(5):767–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk P. D., Howe R. B., Bloomer J. R., Berlin N. I. Studies of bilirubin kinetics in normal adults. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2176–2190. doi: 10.1172/JCI106184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell D. M., Hammaker L., Schmid R. Liver sinusoidal cells. Identification of a subpopulation for erythrocyte catabolism. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jul;54(1):107–119. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanckaert N. Analysis of bilirubin and bilirubin mono- and di-conjugates. Determination of their relative amounts in biological samples. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 1;185(1):115–128. doi: 10.1042/bj1850115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanckaert N., Gollan J., Schmid R. Bilirubin diglucuronide synthesis by a UDP-glucuronic acid-dependent enzyme system in rat liver microsomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2037–2041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanckaert N., Kabra P. M., Farina F. A., Stafford B. E., Marton L. J., Schmid R. Measurement of bilirubin and its monoconjugates and diconjugates in human serum by alkaline methanolysis and high-performance liquid chromatography. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Aug;96(2):198–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronikowski T. A., Dawson C. A., Linehan J. H. Model-free deconvolution techniques for estimating vascular transport functions. Int J Biomed Comput. 1983 Sep;14(5):411–429. doi: 10.1016/0020-7101(83)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson E. R., Jones E. A. Use of kinetic analysis and mathematical modeling in the study of metabolic pathways in vivo. Applications to hepatic organic anion metabolism. (First of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1979 May 3;300(18):1016–1027. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905033001804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler D. J. Linear systems analysis in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Jun;6(3):265–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01312266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., ter Haar E. M., Jansen P. L. UDP-glucuronyltransferase-catalyzed deconjugation of bilirubin monoglucuronide. Hepatology. 1984 Sep-Oct;4(5):918–922. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dills R. L., Klaassen C. D. Decreased glucuronidation of bilirubin by diethyl ether anesthesia. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 1;33(17):2813–2814. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90700-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollan J., Hammaker L., Licko V., Schmid R. Bilirubin kinetics in intact rats and isolated perfused liver. Evidence for hepatic deconjugation of bilirubin glucuronides. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1003–1015. doi: 10.1172/JCI110111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourley G. R., Mogilevsky W., Arend R. A., Siegel F. L., Odell G. B. Effects of anesthetic agents on bile pigment excretion in the rat. Hepatology. 1985 Jul-Aug;5(4):610–614. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser S. C., Ziurys J. C., Gollan J. L. Regulation of bilirubin glucuronide synthesis in primate (Macaca fascicularis) liver. Kinetic analysis of microsomal bilirubin uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase. Gastroenterology. 1986 Aug;91(2):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90559-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser S. C., Ziurys J. C., Gollan J. L. Subcellular distribution and regulation of hepatic bilirubin UDP-glucuronyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4527–4533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. A., Shrager R., Bloomer J. R., Berk P. D., Howe R. B., Berlin N. I. Quantitative studies of the delivery of hepatic-synthesized bilirubin to plasma utilizing -aminolevulinic acid-4- 14 C and bilirubin- 3 H in man. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2450–2458. doi: 10.1172/JCI107058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshenbaum G., Shames D. M., Schmid R. An expanded model of bilirubin kinetics: effect of feeding, fasting, and phenobarbital in Gilbert's syndrome. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1976 Apr;4(2):115–155. doi: 10.1007/BF01086150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuruc A., Caldicott W. J., Treves S. An improved deconvolution technique for the calculation of renal retention functions. Comput Biomed Res. 1982 Feb;15(1):46–56. doi: 10.1016/0010-4809(82)90052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuruc A., Treves S., Parker J. A. Accuracy of deconvolution algorithms assessed by simulation studies: concise communication. J Nucl Med. 1983 Mar;24(3):258–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. R., Licko V., Van Dyke R. W., Scharschmidt B. F. Biliary secretion of fluid-phase markers by the isolated perfused rat liver. Role of transcellular vesicular transport. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):676–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI112021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R., Klein P. D. Bile pigment excretion: a comparison of the biliary excretion of bilirubin and bilirubin derivatives. J Clin Invest. 1966 Dec;45(12):1839–1846. doi: 10.1172/JCI105487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F., Assisi F. Commercial bilirubin: A trinity of isomers. FEBS Lett. 1971 Nov 1;18(2):315–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80475-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F., Assisi F. The ready isomerization of bilirubin IX- in aqueous solution. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):797–800. doi: 10.1042/bj1290797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F., Palma L. A., Lauff J. J., Wu T. W. Origin of mammalian biliprotein and rearrangement of bilirubin glucuronides in vivo in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):763–770. doi: 10.1172/JCI111492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F., Palma L. A. Preparation and properties of crystalline biliverdin IX alpha. Simple methods for preparing isomerically homogeneous biliverdin and [14C[biliverdin by using 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyanobenzoquinone. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 1;189(2):193–208. doi: 10.1042/bj1890193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSTROW J. D., HAMMAKER L., SCHMID R. The preparation of crystalline bilirubin-C14. J Clin Invest. 1961 Aug;40:1442–1452. doi: 10.1172/JCI104375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrow J. D., Murphy N. H. Isolation and properties of conjugated bilirubin from bile. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):311–327. doi: 10.1042/bj1200311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilo A., Ferrannini E., Navalesi R. Measurement of glucose-induced insulin delivery rate in man by deconvolution analysis. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):E500–E508. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.233.6.E500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID R., AXELROD J., HAMMAKER L., SWARM R. L. Congenital jaundice in rats, due to a defect in glucuronide formation. J Clin Invest. 1958 Aug;37(8):1123–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI103702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID R. The identification of direct-reacting bilirubin as bilirubin glucuronide. J Biol Chem. 1957 Dec;229(2):881–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. A., Fisher M. M. Hepatic transport of fluorescent molecules: in vivo studies using intravital TV microscopy. Hepatology. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):444–449. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shupeck M., Wolkoff A. W., Scharschmidt B. F., Waggoner J. G., Berk P. D. Studies of the kinetics of purified conjugated bilirubin-3H in the rat. Am J Gastroenterol. 1978 Sep;70(3):259–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak W., Carey M. C. Reverse-phase h.p.l.c. separation, quantification and preparation of bilirubin and its conjugates from native bile. Quantitative analysis of the intact tetrapyrroles based on h.p.l.c. of their ethyl anthranilate azo derivatives. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 1;225(3):787–805. doi: 10.1042/bj2250787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Steenbergen W., Fevery J. Maximal biliary secretion of bilirubin in the anaesthetized rat: dependence on UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activity. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 May;62(5):521–528. doi: 10.1042/cs0620521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan D. P. Approximation in point-area deconvolution algorithm as mathematical basis of empirical instantaneous midpoint-input deconvolution method. J Pharm Sci. 1981 Jul;70(7):831–832. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600700739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. S., Gautam A., Lauff J. J., Sundberg M. W., Jatlow P., Boyer J. L., Seligson D. The clinical importance of a protein-bound fraction of serum bilirubin in patients with hyperbilirubinemia. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jul 21;309(3):147–150. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198307213090305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolkoff A. W., Goresky C. A., Sellin J., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Role of ligandin in transfer of bilirubin from plasma into liver. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):E638–E648. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.6.E638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga T., Sassa S., Kappas A. The occurrence of molecular interactions among NADPH-cytochrome c reductase, heme oxygenase, and biliverdin reductase in heme degradation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7786–7793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


