Abstract
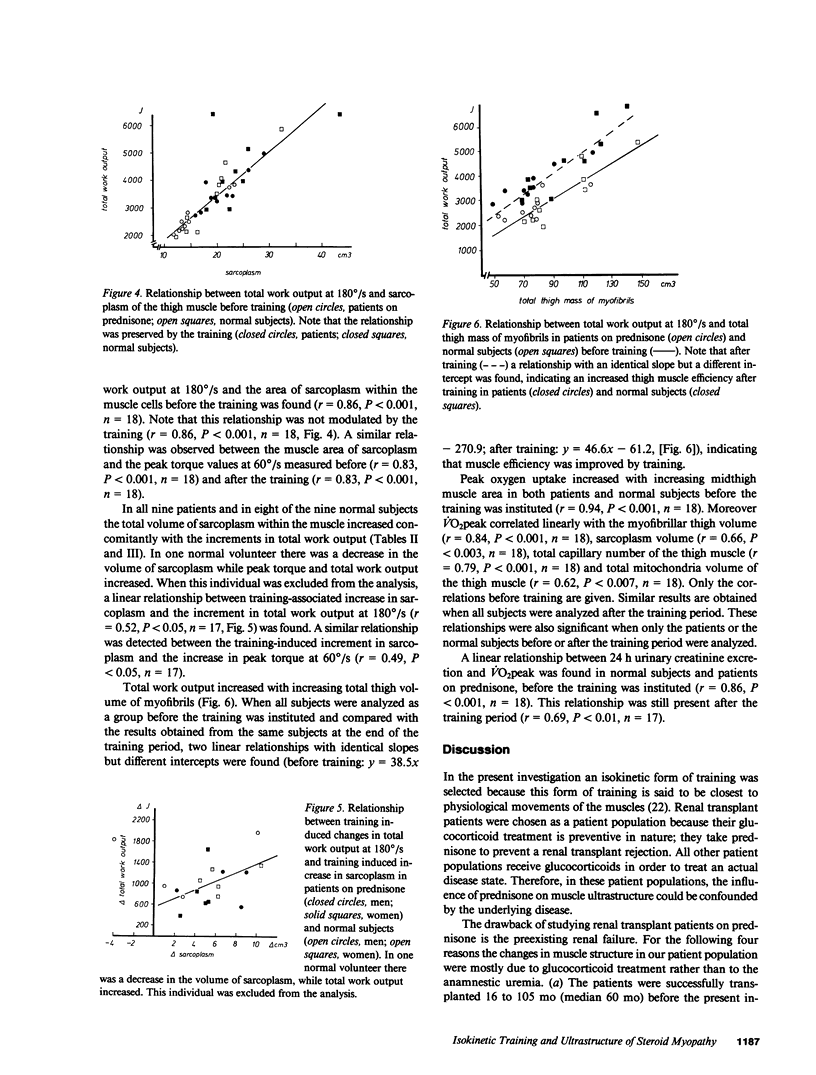
Exercise-training might be a logical method to reverse muscle atrophy and weakness in patients treated with glucocorticoids. The purpose of the present investigation was to establish whether a treatment with low dose prednisone (10 +/- 2.9 mg/d) modulates the effect of a moderate strength type isokinetic training during 7 wk (21 sessions of 20 min) on "muscle efficiency" (power output/muscle mass) and on concomitant changes in ultrastructure of the thigh muscle measured by quantitative electron-microscopic morphometry. Training caused a similar increase in "muscle efficiency" in patients on prednisone (n = 9) as in normal volunteers (n = 9). In normal subjects the increase in muscle efficiency was associated with an increase in sarcoplasm, whereas in patients on prednisone the functional improvement was associated with an increase in sarcoplasm, capillaries, and mitochondria content. Thus, a therapy with low dose prednisone does not abrogate training-induced improvement of muscle efficiency but modulates the ultrastructural response of the muscle to the training.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afifi A. K., Bergman R. A., Harvey J. C. Steroid myopathy. Clinical, histologic and cytologic observations. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1968 Oct;123(4):158–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahonen R. E. Light microscopic study of striated muscle in uremia. Acta Neuropathol. 1980;49(1):51–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00692219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellinghieri G., Savica V., Mallamace A., Di Stefano C., Consolo F., Spagnoli L. G., Villaschi S., Palmieri G., Corsi M., Maccari F. Correlation between increased serum and tissue L-carnitine levels and improved muscle symptoms in hemodialyzed patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 1983 Oct;38(4):523–531. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/38.4.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundschu H. D., Schlote W. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen der Skelettmuskulatur bei terminaler Niereninsuffizienz. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Oct;23(2):243–254. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle E. F., Feiring D. C., Rotkis T. C., Cote R. W., 3rd, Roby F. B., Lee W., Wilmore J. H. Specificity of power improvements through slow and fast isokinetic training. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Dec;51(6):1437–1442. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.6.1437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSEN L. The nature of the intermediate tetrapyrroles in protoporphyrin and heme biosynthesis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1962;14:11–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G. Electron microscopic observations in thyrotoxic and corticosteroid-induced myopathies. Mayo Clin Proc. 1966 Nov;41(11):785–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd M., Ayyar D. R., Barwick D. D., Hudgson P., Weightman D. Myopathy in chronic renal failure. Q J Med. 1974 Oct;43(172):509–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDING D. N., MURRAY S. M., PEARCE G. W., THOMPSON M. Corticosteroid myopathy. Ann Phys Med. 1961 Nov;6:171–177. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/6.4.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindrod S., Tofts P., Edwards R. Investigation of human skeletal muscle structure and composition by X-ray computerised tomography. Eur J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;13(6):465–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1983.tb00130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymsfield S. B., Olafson R. P., Kutner M. H., Nixon D. W. A radiographic method of quantifying protein-calorie undernutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Mar;32(3):693–702. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.3.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppeler H., Lüthi P., Claassen H., Weibel E. R., Howald H. The ultrastructure of the normal human skeletal muscle. A morphometric analysis on untrained men, women and well-trained orienteers. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Nov 28;344(3):217–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00588462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horber F. F., Hoppeler H., Herren D., Claassen H., Howald H., Gerber C., Frey F. J. Altered skeletal muscle ultrastructure in renal transplant patients on prednisone. Kidney Int. 1986 Sep;30(3):411–416. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horber F. F., Scheidegger J. R., Grünig B. E., Frey F. J. Evidence that prednisone-induced myopathy is reversed by physical training. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Jul;61(1):83–88. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horber F. F., Scheidegger J. R., Grünig B. E., Frey F. J. Thigh muscle mass and function in patients treated with glucocorticoids. Eur J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;15(6):302–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1985.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horber F. F., Zürcher R. M., Herren H., Crivelli M. A., Robotti G., Frey F. J. Altered body fat distribution in patients with glucocorticoid treatment and in patients on long-term dialysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986 May;43(5):758–769. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/43.5.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston M. E., Froese E. A., Valeriote S. P., Green H. J., Ranney D. A. Muscle performance, morphology and metabolic capacity during strength training and detraining: a one leg model. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1983;51(1):25–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00952534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husdan H., Rapoport A. Estimation of creatinine by the Jaffe reaction. A comparison of three methods. Clin Chem. 1968 Mar;14(3):222–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häggmark T., Jansson E., Svane B. Cross-sectional area of the thigh muscle in man measured by computed tomography. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1978 Jun;38(4):355–360. doi: 10.3109/00365517809108434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly F. J., Goldspink D. F. The differing responses of four muscle types to dexamethasone treatment in the rat. Biochem J. 1982 Oct 15;208(1):147–151. doi: 10.1042/bj2080147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaleeli A. A., Edwards R. H., Gohil K., McPhail G., Rennie M. J., Round J., Ross E. J. Corticosteroid myopathy: a clinical and pathological study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1983 Feb;18(2):155–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1983.tb03198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesmes G. R., Costill D. L., Coyle E. F., Fink W. J. Muscle strength and power changes during maximal isokinetic training. Med Sci Sports. 1978 Winter;10(4):266–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthi J. M., Howald H., Claassen H., Rösler K., Vock P., Hoppeler H. Structural changes in skeletal muscle tissue with heavy-resistance exercise. Int J Sports Med. 1986 Jun;7(3):123–127. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1025748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER R., KUGELBERG E. Myopathy in Cushing's syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1959 Nov;22:314–319. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.22.4.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastaglia F. L. Adverse effects of drugs on muscle. Drugs. 1982 Oct;24(4):304–321. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198224040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu O., Cruz-Orive L. M., Hoppeler H., Weibel E. R. Measuring error and sampling variation in stereology: comparison of the efficiency of various methods for planar image analysis. J Microsc. 1981 Jan;121(Pt 1):75–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1981.tb01200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-Brown H. S., Stein R. B., Lee R. G. Synchronization of human motor units: possible roles of exercise and supraspinal reflexes. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1975 Mar;38(3):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(75)90245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritani T., deVries H. A. Neural factors versus hypertrophy in the time course of muscle strength gain. Am J Phys Med. 1979 Jun;58(3):115–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKOFF G. T., SILBER R., TYLER F. H., CARTWRIGHT G. E., WINTROBE M. M. Studies in disorders of muscle. XII. Myopathy due to the administration of therapeutic amounts of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids. Am J Med. 1959 Jun;26(6):891–898. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipes T. V., Wilmore J. H. Isokinetic vs isotonic strength training in adult men. Med Sci Sports. 1975 Winter;7(4):262–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichmann H., Hoppeler H., Mathieu-Costello O., von Bergen F., Pette D. Biochemical and ultrastructural changes of skeletal muscle mitochondria after chronic electrical stimulation in rabbits. Pflugers Arch. 1985 May;404(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00581484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. M., Delitto A., Sinacore D. R., Rose S. J. Muscle function in rheumatic disease patients treated with corticosteroids. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Feb;6(2):128–135. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale D. G., McComas A. J., MacDougall J. D., Upton A. R. Neuromuscular adaptation in human thenar muscles following strength training and immobilization. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Aug;53(2):419–424. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.2.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott S. G. Current concepts in the rehabilitation of the injured athlete. Mayo Clin Proc. 1984 Feb;59(2):83–90. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah A. J., Sahgal V., Quintanilla A. P., Subramani V., Singh H., Hughes R. Muscle in chronic uremia--a histochemical and morphometric study of human quadriceps muscle biopsies. Clin Neuropathol. 1983;2(2):83–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Pennington R. J. The effect of cortisone on protein breakdown and synthesis in rat skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1977 Jan;6(3):159–169. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(77)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignos P. J., Jr, Greene R. Oxidative respiration of skeletal muscle in experimental corticosteroid myopathy. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Mar;81(3):365–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh G., DeVivo D., Olson W. Histochemical and ultrastructural changes in rat muscle. Occurrence following adrenal corticotrophic hormone, glucocorticoids, and starvation. Arch Neurol. 1971 Jan;24(1):83–93. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00480310111012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





