Abstract
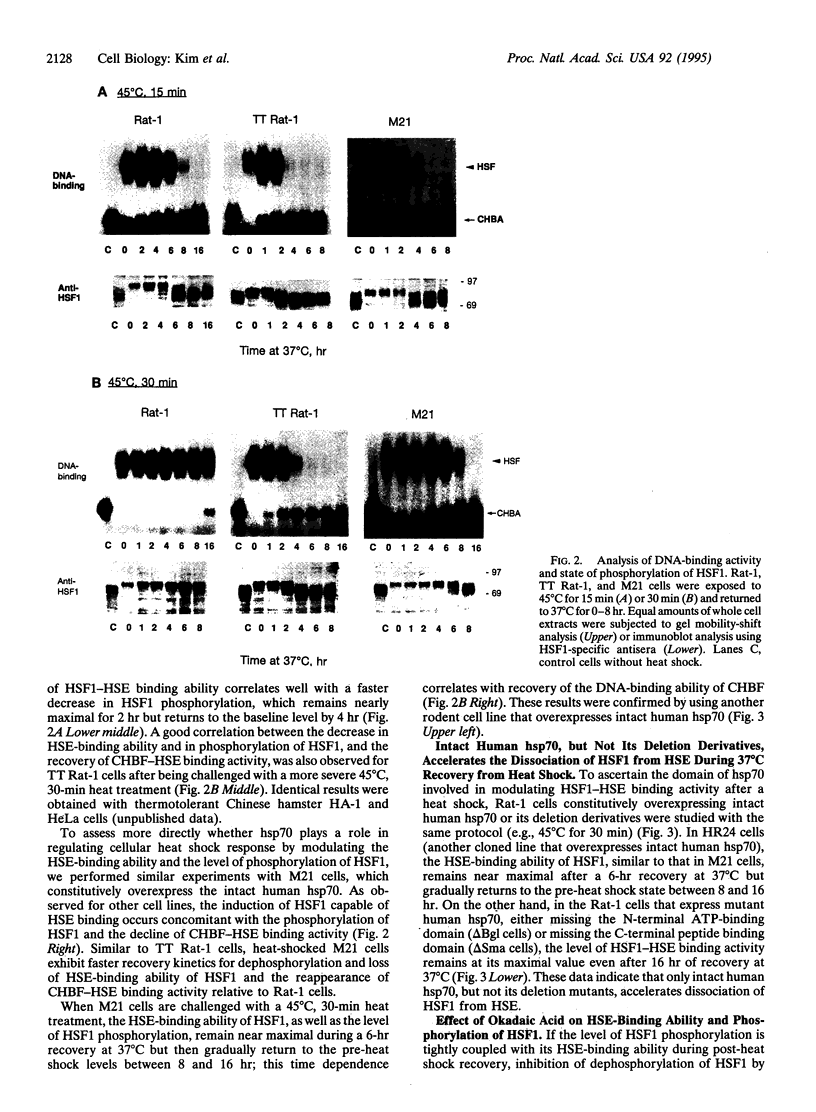
The role of mammalian 70-kDa heat shock protein (hsp70) in regulating cellular response to heat shock was examined by using three closely related rat cells: control Rat-1 cells, thermotolerant Rat-1 (TT Rat-1) cells, and heat-resistant M21 cells, a derivative of Rat-1 cells that constitutively overexpress human hsp70. In all these cells, after a prescribed heat shock, the level of the phosphorylated form of heat shock transcription factor HSF1 and that of HSF1 capable of binding to its cognitive DNA sequence heat shock element (HSE) exhibit similar time dependence. The amount of a constitutive HSE-binding activity (CHBA), on the other hand, inversely correlates with those of the two aforementioned forms of HSF1. The recovery kinetics from heat shock are different for the three cell lines, with the thermal-resistant TT Rat-1 and M21 cells showing faster recovery in terms of the state of phosphorylation of HSF1 and its ability to bind HSE or in terms of the reappearance of CHBA. Treatment with okadaic acid, a serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitor, delays the recovery kinetics of Rat-1 cells but not that of thermal-resistant M21 cells. These results are interpreted in terms of a role for hsp70 in the recovery of heat-shocked mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abravaya K., Myers M. P., Murphy S. P., Morimoto R. I. The human heat shock protein hsp70 interacts with HSF, the transcription factor that regulates heat shock gene expression. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1153–1164. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baler R., Welch W. J., Voellmy R. Heat shock gene regulation by nascent polypeptides and denatured proteins: hsp70 as a potential autoregulatory factor. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1151–1159. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Westwood J. T., Becker P. B., Wilson S., Lambert K., Wu C. Molecular cloning and expression of a hexameric Drosophila heat shock factor subject to negative regulation. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1085–1097. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90511-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDomenico B. J., Bugaisky G. E., Lindquist S. The heat shock response is self-regulated at both the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):593–603. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson J. S., Schuetz T. J., Kingston R. E. Activation in vitro of sequence-specific DNA binding by a human regulatory factor. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):372–375. doi: 10.1038/335372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Li L. G., Liu Y. K., Mak J. Y., Chen L. L., Lee W. M. Thermal response of rat fibroblasts stably transfected with the human 70-kDa heat shock protein-encoding gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1681–1685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Li L., Liu R. Y., Rehman M., Lee W. M. Heat shock protein hsp70 protects cells from thermal stress even after deletion of its ATP-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2036–2040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu R. Y., Kim D., Yang S. H., Li G. C. Dual control of heat shock response: involvement of a constitutive heat shock element-binding factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):3078–3082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu R. Y., Li X., Li L., Li G. C. Expression of human hsp70 in rat fibroblasts enhances cell survival and facilitates recovery from translational and transcriptional inhibition following heat shock. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 1;52(13):3667–3673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mivechi N. F., Trainor L. D., Hahn G. M. Purified mammalian HSP-70 KDA activates phosphoprotein phosphatases in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 30;192(2):954–963. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. D., Duchaine J., Massie B. The DNA-binding activity of the human heat shock transcription factor is regulated in vivo by hsp70. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5427–5438. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. D., Kotzbauer P. T., Sarge K. D., Morimoto R. I. In vitro activation of heat shock transcription factor DNA-binding by calcium and biochemical conditions that affect protein conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3748–3752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. D., Theodorakis N. G., Morimoto R. I. Coordinate changes in heat shock element-binding activity and HSP70 gene transcription rates in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4736–4744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabindran S. K., Haroun R. I., Clos J., Wisniewski J., Wu C. Regulation of heat shock factor trimer formation: role of a conserved leucine zipper. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):230–234. doi: 10.1126/science.8421783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabindran S. K., Wisniewski J., Li L., Li G. C., Wu C. Interaction between heat shock factor and hsp70 is insufficient to suppress induction of DNA-binding activity in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6552–6560. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarge K. D., Murphy S. P., Morimoto R. I. Activation of heat shock gene transcription by heat shock factor 1 involves oligomerization, acquisition of DNA-binding activity, and nuclear localization and can occur in the absence of stress. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1392–1407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarge K. D., Zimarino V., Holm K., Wu C., Morimoto R. I. Cloning and characterization of two mouse heat shock factors with distinct inducible and constitutive DNA-binding ability. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1902–1911. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz T. J., Gallo G. J., Sheldon L., Tempst P., Kingston R. E. Isolation of a cDNA for HSF2: evidence for two heat shock factor genes in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6911–6915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. M., Rossi J. M., Golic K., McGarry T., Lindquist S. Changes in hsp70 alter thermotolerance and heat-shock regulation in Drosophila. New Biol. 1991 Nov;3(11):1106–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K. Heat shock factor and the heat shock response. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):363–366. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90452-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Nelson H. C. Trimerization of a yeast transcriptional activator via a coiled-coil motif. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K. Yeast heat shock factor contains separable transient and sustained response transcriptional activators. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):793–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90123-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westwood J. T., Clos J., Wu C. Stress-induced oligomerization and chromosomal relocalization of heat-shock factor. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):822–827. doi: 10.1038/353822a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]