Abstract
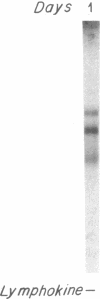
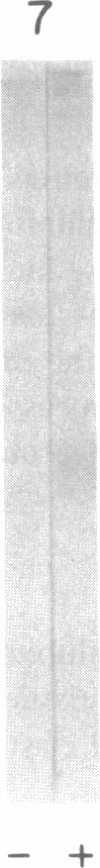
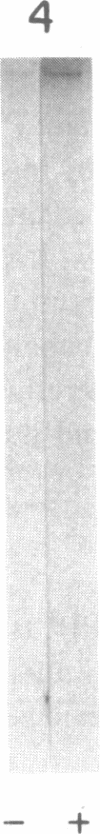
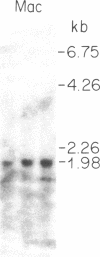
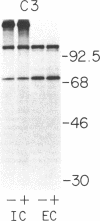
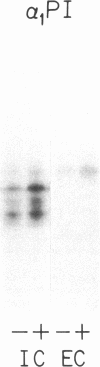
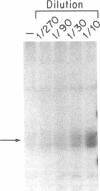
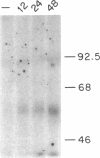
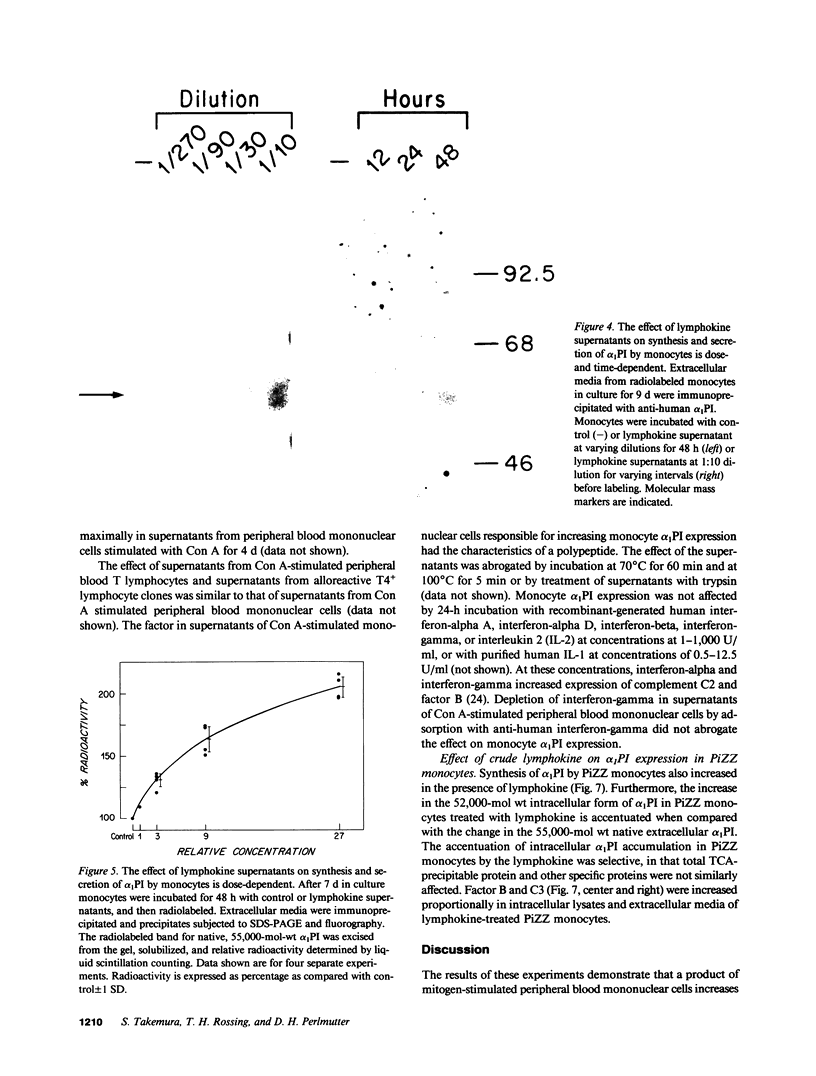
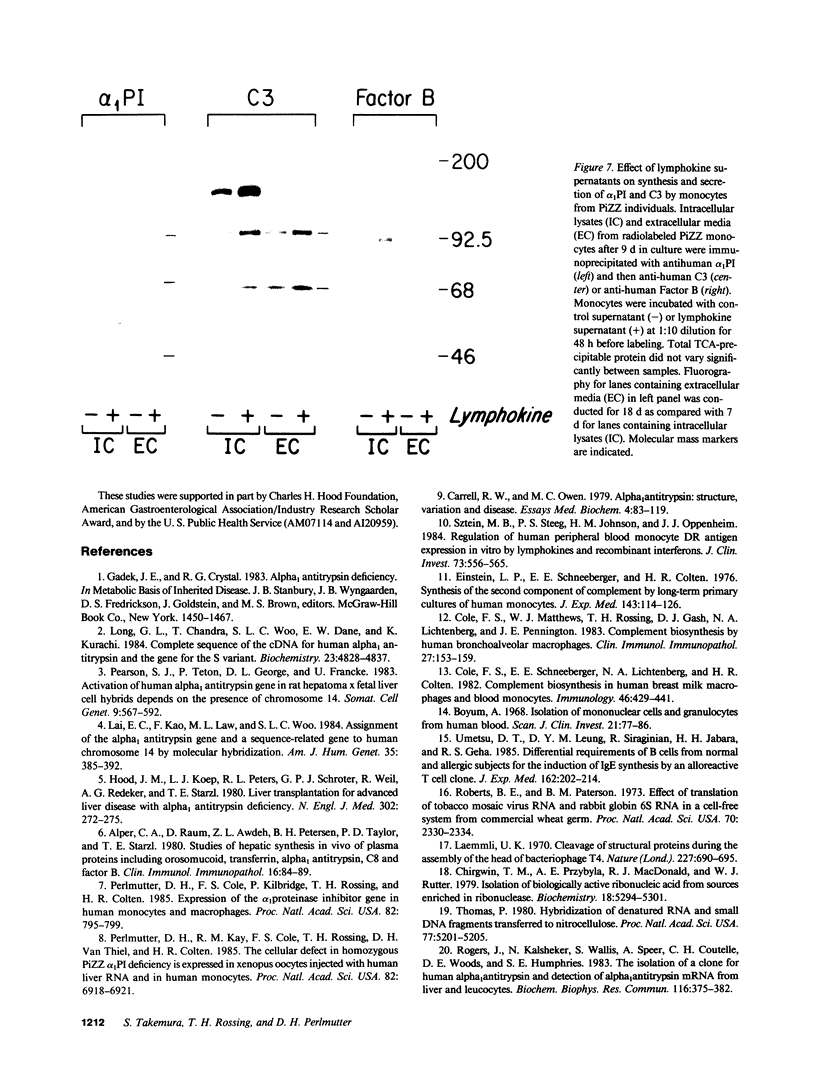
Biosynthesis and secretion of alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor (alpha 1 PI) has been demonstrated in primary cultures of human mononuclear phagocytes, making it possible to study regulation of alpha 1 PI in normal (PiMM) and homozygous-deficient (PiZZ) individuals. In this study, expression of alpha 1 PI by blood monocytes, bronchoalveolar, and breast milk macrophages decreased during 1 wk in culture whereas expression of other secreted proteins increased. The addition of crude supernatants from mitogen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells to confluent monolayers of mononuclear phagocytes after 1 wk in culture resulted in a 2- to 2.5-fold increase in alpha 1 PI expression. The increase in alpha 1 PI expression was dose- and time-dependent, and involved a mechanism acting at a pretranslational level as shown by an increase in specific messenger RNA content corresponding to the increase in synthesis and secretion of alpha 1 PI. Although alpha 1 PI was expressed in native form and in forms complexed with serine protease by monocytes early in culture, it was expressed in its native form alone when monocytes were incubated with the lymphokine after 1 wk in culture. The regulating factor had the characteristics of a polypeptide and was derived from T lymphocytes, but it was not interferon-alpha, -beta, -gamma, or interleukin 2. This lymphokine also stimulated synthesis of alpha 1 PI in monocytes of homozygous-deficient PiZZ individuals, but had minimal effect on secretion, thereby increasing the intracellular accumulation of the inhibitor and exaggerating the defect in secretion of alpha 1 PI in these individuals. Regulation of mononuclear phagocyte alpha 1 PI expression by a lymphokine provides a model for further analysis of the effect of enhanced synthesis on a defect in posttranslational processing/secretion and for analysis of differential regulation of protease and inhibitor expressed in the same cells.
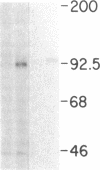
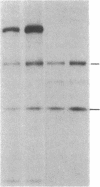
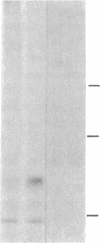
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Raum D., Awdeh Z. L., Petersen B. H., Taylor P. D., Starzl T. E. Studies of hepatic synthesis in vivo of plasma proteins, including orosomucoid, transferrin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, C8, and factor B. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 May;16(1):84–89. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensa J. C., Reboul A., Colomb M. G. Biosynthesis in vitro of complement subcomponents C1q, C1s and C1 inhibitor by resting and stimulated human monocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 15;216(2):385–392. doi: 10.1042/bj2160385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldt D. H., Chan S. K., Keaton K. Cell surface alpha 1-protease inhibitor on human peripheral mononuclear cells in culture. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1830–1836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole F. S., Matthews W. J., Jr, Rossing T. H., Gash D. J., Lichtenberg N. A., Pennington J. E. Complement biosynthesis by human bronchoalveolar macrophages. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 May;27(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole F. S., Schneeberger E. E., Lichtenberg N. A., Colten H. R. Complement biosynthesis in human breast-milk macrophages and blood monocytes. Immunology. 1982 Jun;46(2):429–441. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einstein L. P., Schneeberger E. E., Colten H. R. Synthesis of the second component of complement by long-term primary cultures of human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Jan 1;143(1):114–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory S. A., Edgington T. S. Tissue factor induction in human monocytes. Two distinct mechanisms displayed by different alloantigen-responsive T cell clones. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2440–2445. doi: 10.1172/JCI112260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin H. J., Fox R. I., Edgington T. S. The instructor cell for the human procoagulant monocyte response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide is a Leu-3a+ T cell by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):749–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin H., Edgington T. S. A distinct "slow" cellular pathway involving soluble mediators for the T cell-instructed induction of monocyte tissue factor activity in an allogeneic immune response. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2457–2463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood J. M., Koep L. J., Peters R. L., Schröter G. P., Weil R., 3rd, Redeker A. G., Starzl T. E. Liver transplantation for advanced liver disease with alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 31;302(5):272–275. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001313020505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Kao F. T., Law M. L., Woo S. L. Assignment of the alpha 1-antitrypsin gene and a sequence-related gene to human chromosome 14 by molecular hybridization. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 May;35(3):385–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G. A., Edgington T. S. Lymphocyte cooperation is required for amplification of macrophage procoagulant activity. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1232–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long G. L., Chandra T., Woo S. L., Davie E. W., Kurachi K. Complete sequence of the cDNA for human alpha 1-antitrypsin and the gene for the S variant. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):4828–4837. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson S. J., Tetri P., George D. L., Francke U. Activation of human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene in rat hepatoma x human fetal liver cell hybrids depends on presence of human chromosome 14. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 Sep;9(5):567–592. doi: 10.1007/BF01574259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Cole F. S., Kilbridge P., Rossing T. H., Colten H. R. Expression of the alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor gene in human monocytes and macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):795–799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Kay R. M., Cole F. S., Rossing T. H., Van Thiel D., Colten H. R. The cellular defect in alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor (alpha 1-PI) deficiency is expressed in human monocytes and in Xenopus oocytes injected with human liver mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6918–6921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Kalsheker N., Wallis S., Speer A., Coutelle C. H., Woods D., Humphries S. E. The isolation of a clone for human alpha 1-antitrypsin and the detection of alpha 1-antitrypsin in mRNA from liver and leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):375–382. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90532-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Cole F. S., Perlmutter D. H., Colten H. R. gamma-Interferon increases expression of class III complement genes C2 and factor B in human monocytes and in murine fibroblasts transfected with human C2 and factor B genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15280–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Whitehead A. S., Cole F. S. Pretranslational regulation of the synthesis of the third component of complement in human mononuclear phagocytes by the lipid A portion of lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):985–990. doi: 10.1172/JCI112099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztein M. B., Steeg P. S., Johnson H. M., Oppenheim J. J. Regulation of human peripheral blood monocyte DR antigen expression in vitro by lymphokines and recombinant interferons. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):556–565. doi: 10.1172/JCI111243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umetsu D. T., Leung D. Y., Siraganian R., Jabara H. H., Geha R. S. Differential requirements of B cells from normal and allergic subjects for the induction of IgE synthesis by an alloreactive T cell clone. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):202–214. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Reich E. Macrophage plasminogen activator: induction by products of activated lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):429–437. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]