Abstract
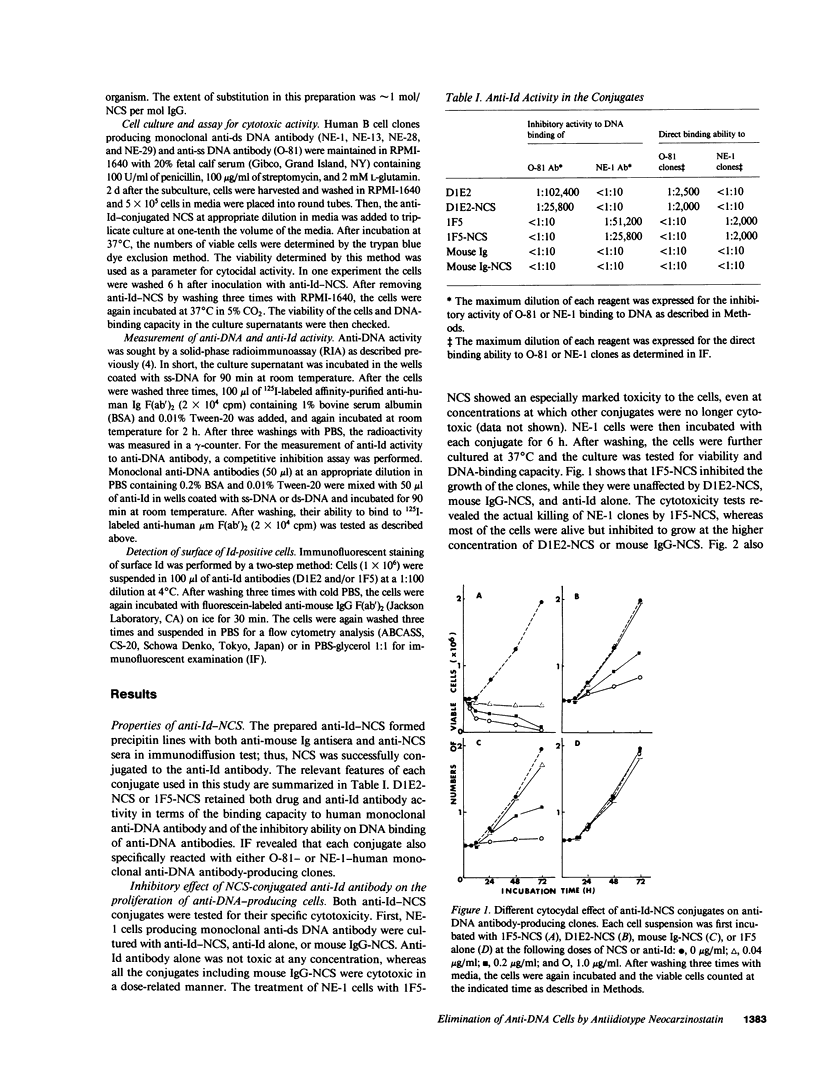
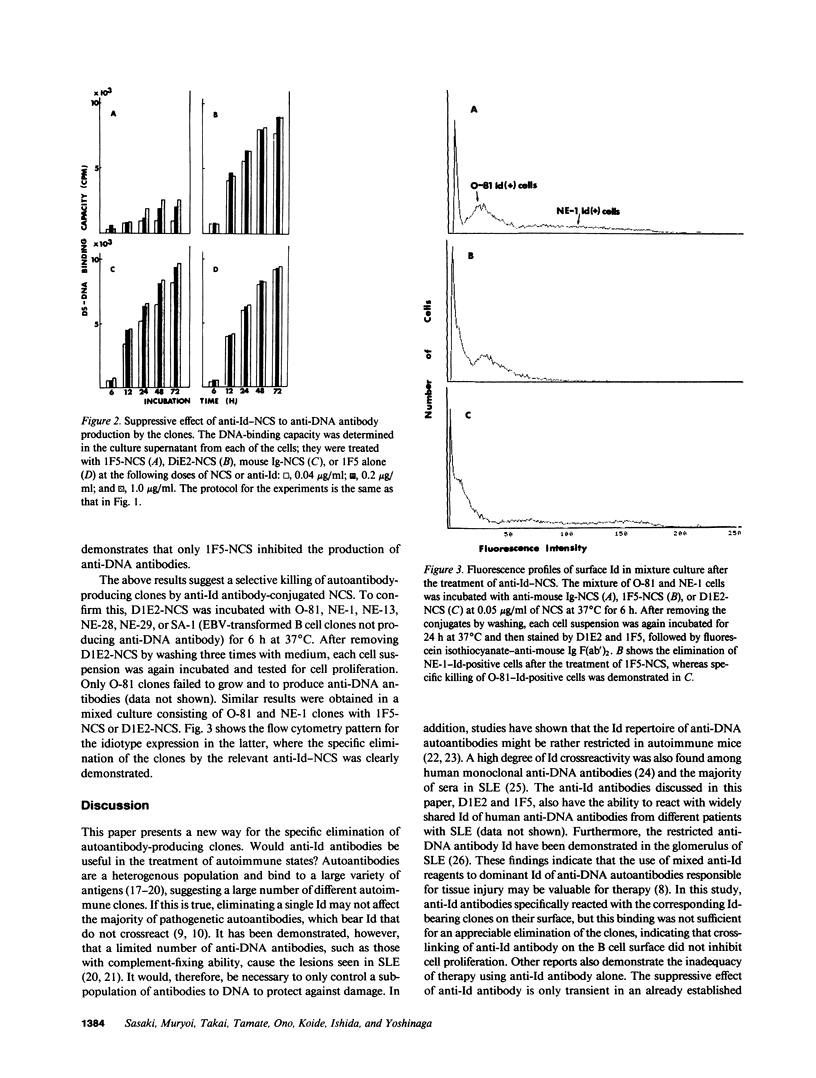
A new strategy was shown for the manipulation of autoantibody production in humans. Antiidiotypic antibody to human anti-DNA autoantibody was conjugated with neocarzinostatin (NCS), a cytotoxic agent, by using N-succimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio) propionate as a coupling agent. Human B cell clones, which produce anti-DNA autoantibodies, were killed by in vitro treatment with antiidiotype (Id)-NCS conjugates, while clones expressing an Id with irrelevant specificity were unaffected. These results indicate that treatment with anti-Id-NCS conjugates can act as a potent and specific means of generating immunosuppression of autoantibody production. This approach will have a significant advantage in aborting clones that are not effectively suppressed for the autoantibodies by anti-Id antibodies alone, and will result in a potential therapeutic treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdou N. I., Wall H., Lindsley H. B., Halsey J. F., Suzuki T. Network theory in autoimmunity. In vitro suppression of serum anti-DNA antibody binding to DNA by anti-idiotypic antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1297–1304. doi: 10.1172/JCI110158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bona C., Paul W. E. Cellular basis of regulation of expression of idiotype. I. T-suppressor cells specific for MOPC 460 idiotype regulate the expression of cells secreting anti-TNP antibodies bearing 460 idiotype. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):592–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borel Y., Lewis R. M., Stollar B. D. Prevention of murine lupus nephritis by carrier-dependent induction of immunologic tolerance to denatured DNA. Science. 1973 Oct 5;182(4107):76–78. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4107.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. A., Hughes G. R., Noel G. L., Christian C. L. Character of anti-DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Apr;8(4):551–561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Weger R. A., Dullens H. F., Den Otter W. Eradication of murine lymphoma and melanoma cells by chlorambucil-antibody complexes. Immunol Rev. 1982;62:28–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer D. S., Bradley R. J., Urquhart C. K., Kearney J. F. Naturally occurring anti-idiotypic antibodies in myasthenia gravis patients. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):611–614. doi: 10.1038/301611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebling F., Hahn B. H. Restricted subpopulations of DNA antibodies in kidneys of mice with systemic lupus. Comparison of antibodies in serum and renal eluates. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Apr;23(4):392–403. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Rajewsky K. Induction of T and B cell immunity by anti-idiotypic antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Oct;5(10):661–666. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830051002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S. Presence of auto-anti-idiotypic antibody during the normal human immune response to tetanus toxoid antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Ebling F. M. Suppression of murine lupus nephritis by administration of an anti-idiotypic antibody to anti-DNA. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Collins C. Detection of cross-reactive anti-DNA antibody idiotypes on renal tissue-bound immunoglobulins from lupus patients. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):287–294. doi: 10.1172/JCI111959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Shoenfeld Y., Madaio M. P., Rauch J., Reichlin M., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Anti-DNA antibody idiotypes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1984 Aug 25;2(8400):417–422. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92904-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen F. K., Blythman H. E., Carrière D., Casellas P., Gros O., Gros P., Laurent J. C., Paolucci F., Pau B., Poncelet P. Immunotoxins: hybrid molecules combining high specificity and potent cytotoxicity. Immunol Rev. 1982;62:185–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung G., Köhnlein W., Lüders G. Biological activity of the antitumor protein neocarzinostatin coupled to a monoclonal antibody by N-succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)-propionate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jul 30;101(2):599–606. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91301-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Carr R., Agnello V., Thoburn R., Kunkel H. G. Antibodies to polynucleotides in human sera: antigenic specificity and relation to disease. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):294–312. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Schur P. H., Kunkel H. G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman W. J., Schrohenloher R. E., Barton J. C., Greenleaf E. C. Suppression of in vitro monoclonal human rheumatoid factor synthesis by antiidiotypic antibody. Target cells and molecular requirements. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1410–1419. doi: 10.1172/JCI111097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Matsumoto M. Cytotoxic effect of neocarzinostatin on human lymphoid cells. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1979 Aug;128(4):313–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion T. N., Lawton A. R., 3rd, Kearney J. F., Briles D. E. Anti-DNA autoantibodies in (NZB X NZW)F1 mice are clonally heterogeneous, but the majority share a common idiotype. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch J., Murphy E., Roths J. B., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. A high frequency idiotypic marker of anti-DNA autoantibodies in MRL-Ipr/Ipr mice. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):236–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Endo F., Mikami M., Sekiguchi Y., Tada K., Ono Y., Ishida N., Yoshinaga K. Establishment of human monoclonal anti-DNA antibody producing cell lines. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Aug 3;72(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Kadono T., Endo F., Ishida S., Yoshinaga K. Induction of immunological tolerance to single-stranded and double-stranded DNA. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Sep;16(3):191–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Muryoi T., Sekiguchi Y., Tamate E., Yoshinaga K., Kitagawa Y. Monoclonal human anti-DNA antibodies from EB virus-transformed lymphocytes of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. J Clin Immunol. 1985 Jul;5(4):246–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00929459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Isenberg D. A., Rauch J., Madaio M. P., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Idiotypic cross-reactions of monoclonal human lupus autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):718–730. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Rauch J., Massicotte H., Datta S. K., André-Schwartz J., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Polyspecificity of monoclonal lupus autoantibodies produced by human-human hybridomas. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 24;308(8):414–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302243080802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Schur P. H., Carr R. I., Kunkel H. G. Deoxybonucleic acid (DNA) and antibodies to DNA in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1732–1740. doi: 10.1172/JCI105479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum D., Rauch J., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. In vivo effects of antibodies against a high frequency idiotype of anti-DNA antibodies in MRL mice. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1282–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo T., Friou G. J. Lupus nephritis: varying complement-fixing properties of immunoglobulin G antibodies to antigens of cell nuclei. Science. 1968 Aug 30;161(3844):904–906. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3844.904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Krolick K. A., Uhr J. W. Neoplastic B cells as targets for antibody-ricin A chain immunotoxins. Immunol Rev. 1982;62:159–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youle R. J., Neville D. M., Jr Anti-Thy 1.2 monoclonal antibody linked to ricin is a potent cell-type-specific toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5483–5486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti M., Rogers J., Katz D. H. Induction of autoantibodies to thyroglobulin by anti-idiotypic antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):240–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


