Abstract
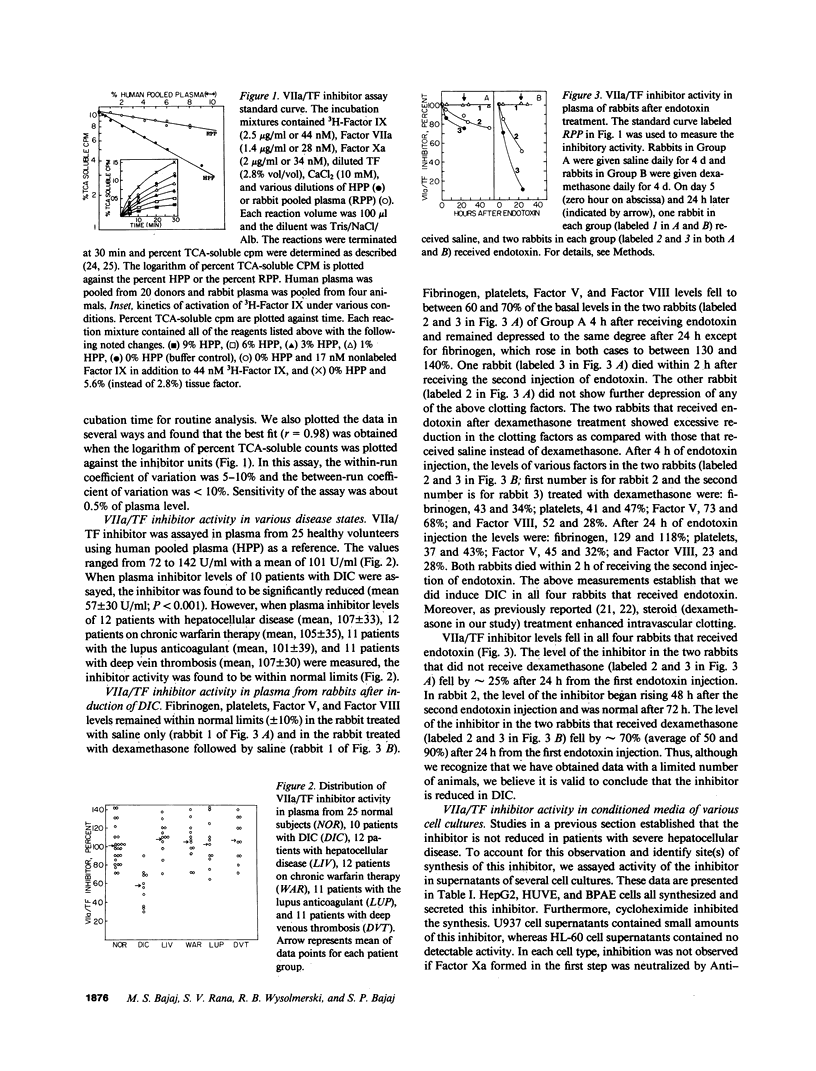
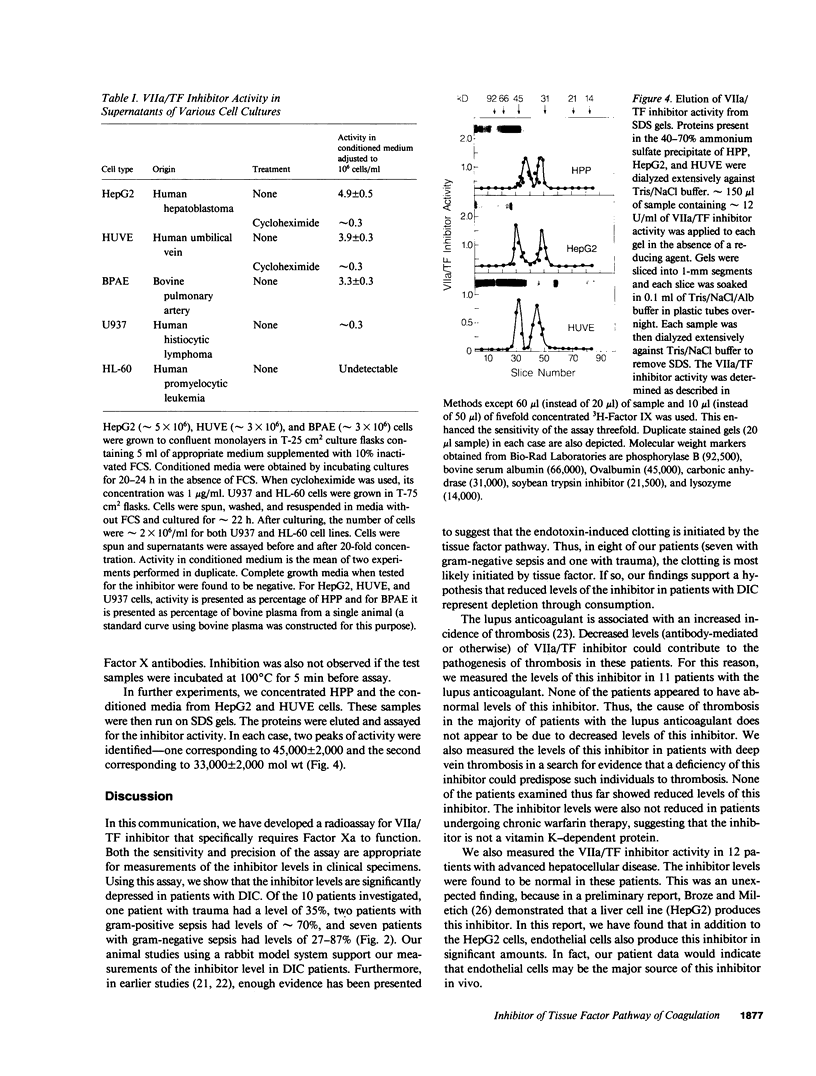
Inhibition of Factor VIIa-tissue factor activity by a plasma component(s) that requires factor Xa has been described recently. In this communication, we have developed a specific radiometric assay (which utilizes 3H-Factor IX and is sensitive to less than 1% of plasma level) for this inhibitor and have measured its activity in various disease states. Strikingly, the levels of this inhibitor were found to be normal in patients with advanced chronic hepatocellular disease but low in patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). When endotoxin was used to induce DIC in rabbits, the levels of this inhibitor fell by 25-90%. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVE), bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells, and a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2) all synthesized and secreted this inhibitor, whereas a promyelocytic cell line (HL-60) did not and a monocytic cell line (U937) appears to synthesize only small amounts. When ammonium sulfate-fractionated human plasma and serum-free conditioned media from both HUVE and HepG2 cells were electrophoresed on sodium dodecyl sulfate acrylamide gels, two activity peaks corresponding to Mr approximately 45,000 and Mr approximately 33,000 were eluted in each case. These observations suggest that (a) the inhibitor is consumed in DIC and that (b) endothelial cells (or other cells) synthesize sufficient amounts of this inhibitor in vivo to compensate for any decreased production by liver cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aden D. P., Fogel A., Plotkin S., Damjanov I., Knowles B. B. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):615–616. doi: 10.1038/282615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj S. P. Cooperative Ca2+ binding to human factor IX. Effects of Ca2+ on the kinetic parameters of the activation of factor IX by factor XIa. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4127–4132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj S. P., Rapaport S. I., Brown S. F. Isolation and characterization of human factor VII. Activation of factor VII by factor Xa. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):253–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj S. P., Rapaport S. I., Maki S. L., Brown S. F. A procedure for isolation of human protein C and protein S as by-products of the purification of factors VII, IX, X and prothrombin. Prep Biochem. 1983;13(3):191–214. doi: 10.1080/00327488308064248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj S. P., Rapaport S. I., Prodanos C. A simplified procedure for purification of human prothrombin, factor IX and factor X. Prep Biochem. 1981;11(4):397–412. doi: 10.1080/00327488108065531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj S. P., Rapaport S. I., Russell W. A. Redetermination of the rate-limiting step in the activation of factor IX by factor XIa and by factor VIIa/tissue factor. Explanation for different electrophoretic radioactivity profiles obtained on activation of 3H- and 125I-labeled factor IX. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 16;22(17):4047–4053. doi: 10.1021/bi00286a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson S. D. Plasma high density lipoproteins inhibit the activation of coagulation factor X by factor VIIa and tissue factor. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 14;132(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80422-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Vecchio P. J., Smith J. R. Expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in cultured pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Sep;108(3):337–345. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041080307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudig D., Bajaj S. P. Tissue factor-like activity of the human monocytic tumor cell line U937. Thromb Res. 1982 Aug 1;27(3):321–332. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCHANTIN G. F., WARE A. G. Identification of a thromboplastin inhibitor in serum and in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1953 Apr;32(4):381–389. doi: 10.1172/JCI102749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. G., Rapaport S. I., Spitzer J. M. Endotoxin-induced intravascular clotting: the need for granulocytes. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Dec 31;20(3):430–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueh J. R., Herbst K. D., Rapaport S. I. Thrombosis in patients with the lupus anticoagulant. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Feb;92(2 Pt 1):156–159. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-2-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I. Activation of factor IX by the reaction product of tissue factor and factor VII: additional pathway for initiating blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5260–5264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L. V., Bajaj S. P. Purification of human factor VII utilizing O-(diethylaminoethyl)-Sephadex and Sulfopropyl-Sephadex chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders N. L., Bajaj S. P., Zivelin A., Rapaport S. I. Inhibition of tissue factor/factor VIIa activity in plasma requires factor X and an additional plasma component. Blood. 1985 Jul;66(1):204–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. M., Rapaport S. I. Increased fibrinogen consumption following endotoxin injection in cortisone-treated rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Mar;145(3):851–854. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-37909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lenten L., Ashwell G. Studies on the chemical and enzymatic modification of glycoproteins. A general method for the tritiation of sialic acid-containing glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1889–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warn-Cramer B. J., Bajaj S. P. Intrinsic versus extrinsic coagulation. Kinetic considerations. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):757–762. doi: 10.1042/bj2390757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warn-Cramer B. J., Bajaj S. P. Stoichiometry of binding of high molecular weight kininogen to factor XI/XIa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90922-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysolmerski R., Lagunoff D. The effect of ethchlorvynol on cultured endothelial cells. A model for the study of the mechanism of increased vascular permeability. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):505–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zur M., Nemerson Y. Kinetics of factor IX activation via the extrinsic pathway. Dependence of Km on tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5703–5707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



