Abstract
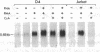
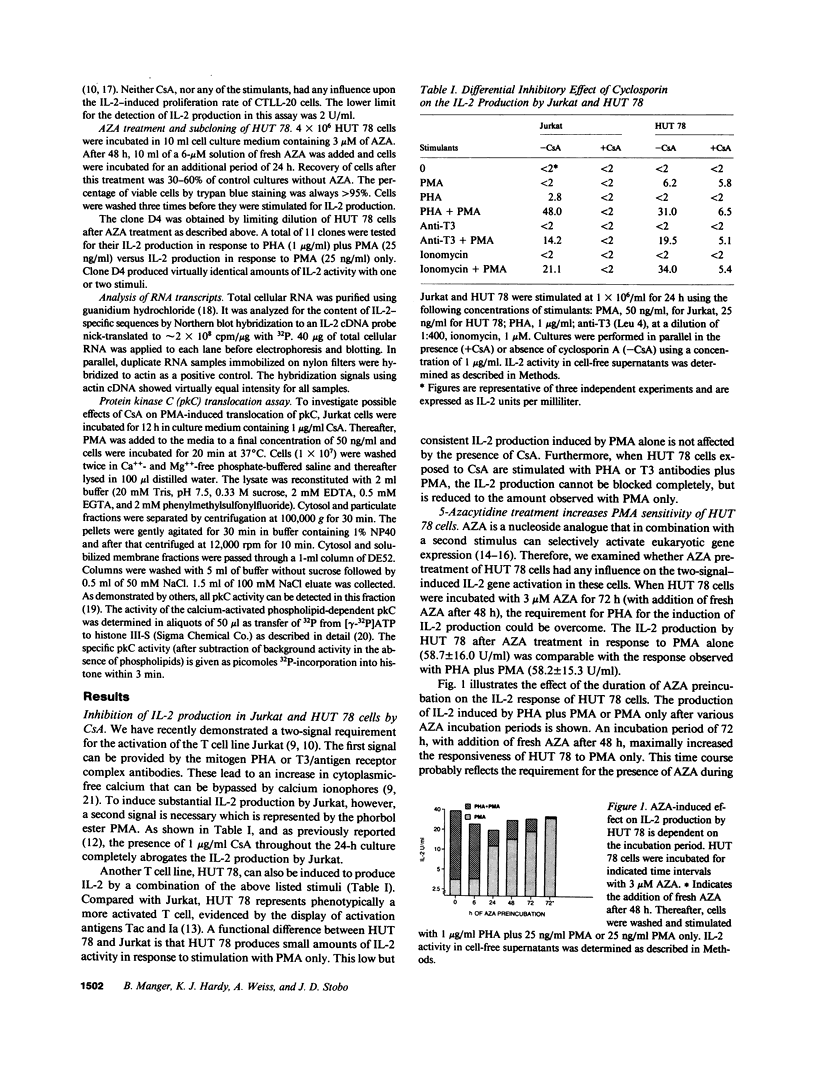
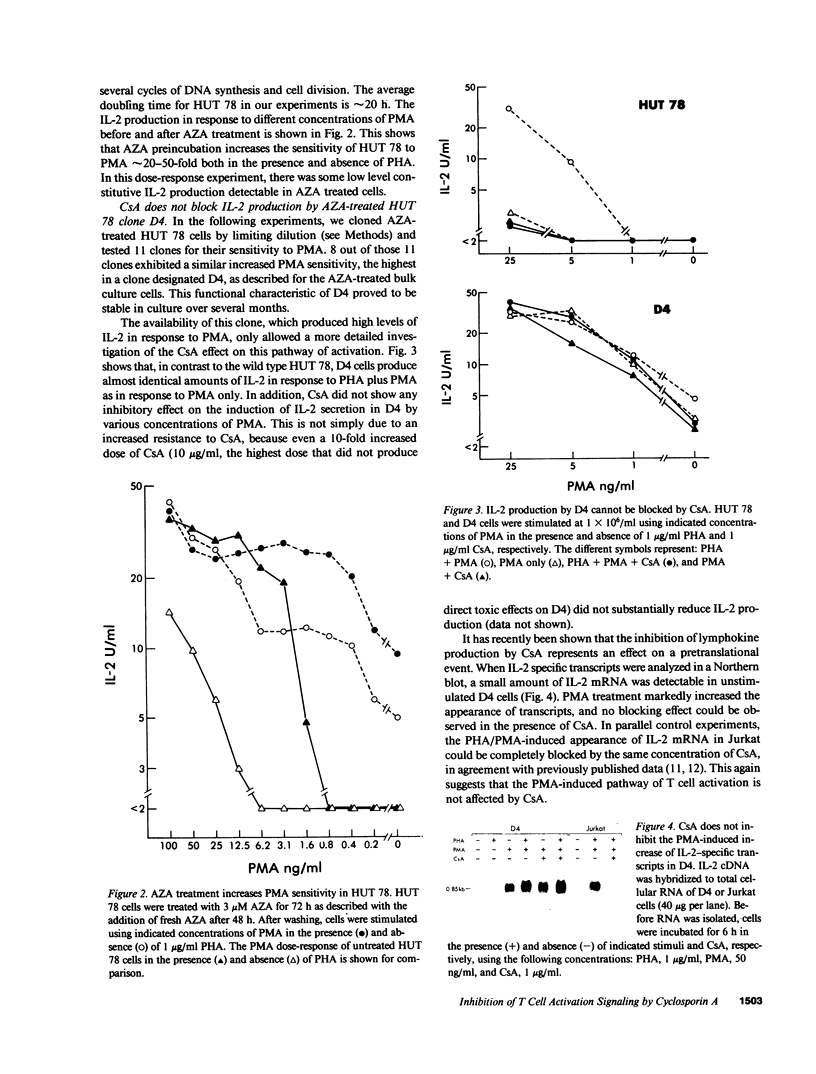
Different T cell lines, which can be induced to secrete interleukin 2 (IL-2) in vitro, were used to dissect the effect of cyclosporin A (CsA). The T leukemia cell Jurkat requires an increase in cytoplasmic calcium concentration ([Ca++]i) and phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) for the induction of IL-2 production, which is completely blocked by CsA. Another T cell line, HUT 78, also produces IL-2 in response to a rise in [Ca++]i and PMA; however, in HUT 78, PMA alone induces low levels of IL-2 production that is not blocked by CsA. After treatment with 5-azacytidine, HUT 78 cells produced maximal levels of IL-2 in response to PMA alone without requiring [Ca++]i increasing stimuli. In these cells no inhibitory effect of CsA on PMA-induced activation could be demonstrated. In addition, CsA does not inhibit PMA-induced translocation of protein kinase C. These data suggest that CsA does not globally inhibit IL-2 gene expression, but rather interferes with signaling events of T cell activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borel J. F., Feurer C., Magnée C., Stähelin H. Effects of the new anti-lymphocytic peptide cyclosporin A in animals. Immunology. 1977 Jun;32(6):1017–1025. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton S., Palacios R. Cyclosporin A--usefulness, risks and mechanism of action. Immunol Rev. 1982;65:5–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunjes D., Hardt C., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. Cyclosporin A mediates immunosuppression of primary cytotoxic T cell responses by impairing the release of interleukin 1 and interleukin 2. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Aug;11(8):657–661. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheley S., Anderson R. A reproducible microanalytical method for the detection of specific RNA sequences by dot-blot hybridization. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):15–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90339-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombani P. M., Robb A., Hess A. D. Cyclosporin A binding to calmodulin: a possible site of action on T lymphocytes. Science. 1985 Apr 19;228(4697):337–339. doi: 10.1126/science.3885394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compere S. J., Palmiter R. D. DNA methylation controls the inducibility of the mouse metallothionein-I gene lymphoid cells. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. F., Lin Y., Mizel S. B., Bleackley R. C., Harnish D. G., Paetkau V. Induction of interleukin 2 messenger RNA inhibited by cyclosporin A. Science. 1984 Dec 21;226(4681):1439–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.6334364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Fuller-Farrar J., Simon P. L., Hilfiker M. L., Stadler B. M., Farrar W. L. Thymoma production of T cell growth factor (Interleukin 2). J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2555–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginder G. D., Whitters M. J., Pohlman J. K. Activation of a chicken embryonic globin gene in adult erythroid cells by 5-azacytidine and sodium butyrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3954–3958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Inaba K., Steinman R. M. Stimulation of lymphokine release from T lymphoblasts. Requirement for mRNA synthesis and inhibition by cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1792–1802. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handschumacher R. E., Harding M. W., Rice J., Drugge R. J., Speicher D. W. Cyclophilin: a specific cytosolic binding protein for cyclosporin A. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):544–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6238408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess A. D., Tutschka P. J., Pu Z., Santos G. W. Effect of cyclosporin A on human lymphocyte responses in vitro. IV. Production of T cell stimulatory growth factors and development of responsiveness to these growth factors in CsA-treated primary MLR cultures. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):360–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Weiss A., Stobo J. D. The antigen receptor on a human T cell line initiates activation by increasing cytoplasmic free calcium. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):663–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A. Altering gene expression with 5-azacytidine. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):485–486. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B., Cooper H. L., Sando J. J. Decrease in cytosolic calcium/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity following phorbol ester treatment of EL4 thymoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13193–13196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol esters increase the amount of Ca2+, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase associated with plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):621–623. doi: 10.1038/301621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Cyclosporin A inhibits T-cell growth factor gene expression at the level of mRNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L. Cyclosporin A and dexamethasone suppress T cell responses by selectively acting at distinct sites of the triggering process. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2828–2833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillehoj H. S., Malek T. R., Shevach E. M. Differential effect of cyclosporin A on the expression of T and B lymphocyte activation antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manger B., Weiss A., Hardy K. J., Stobo J. D. A transferrin receptor antibody represents one signal for the induction of IL 2 production by a human T cell line. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):532–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manger B., Weiss A., Weyand C., Goronzy J., Stobo J. D. T cell activation: differences in the signals required for IL 2 production by nonactivated and activated T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3669–3673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki T., Yachie A., Ohzeki S., Nagaoki T., Taniguchi N. Cyclosporin A does not prevent expression of Tac antigen, a probable TCGF receptor molecule, on mitogen-stimulated human T cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2737–2742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterlin B. M., Gonwa T. A., Stobo J. D. Expression of HLA-DR by a human monocyte cell line is under transcriptional control. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1984;1(3):191–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reem G. H., Cook L. A., Vilcek J. Gamma interferon synthesis by human thymocytes and T lymphocytes inhibited by cyclosporin A. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.6407112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M. The effects of cyclosporin A on the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:397–423. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Shoback D., Stobo J. Role of T3 surface molecules in human T-cell activation: T3-dependent activation results in an increase in cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4169–4173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Wiskocil R. L., Stobo J. D. The role of T3 surface molecules in the activation of human T cells: a two-stimulus requirement for IL 2 production reflects events occurring at a pre-translational level. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Weiss A., Imboden J., Kamin-Lewis R., Stobo J. Activation of a human T cell line: a two-stimulus requirement in the pretranslational events involved in the coordinate expression of interleukin 2 and gamma-interferon genes. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1599–1603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]