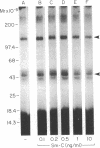
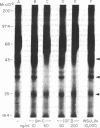
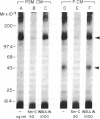
Abstract
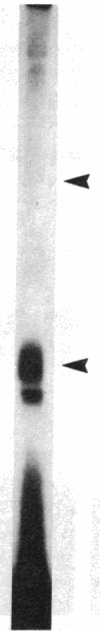
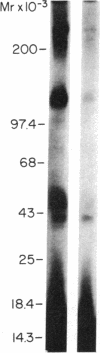
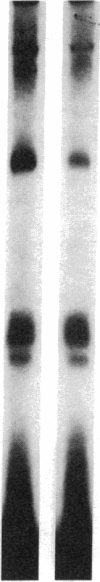
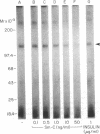
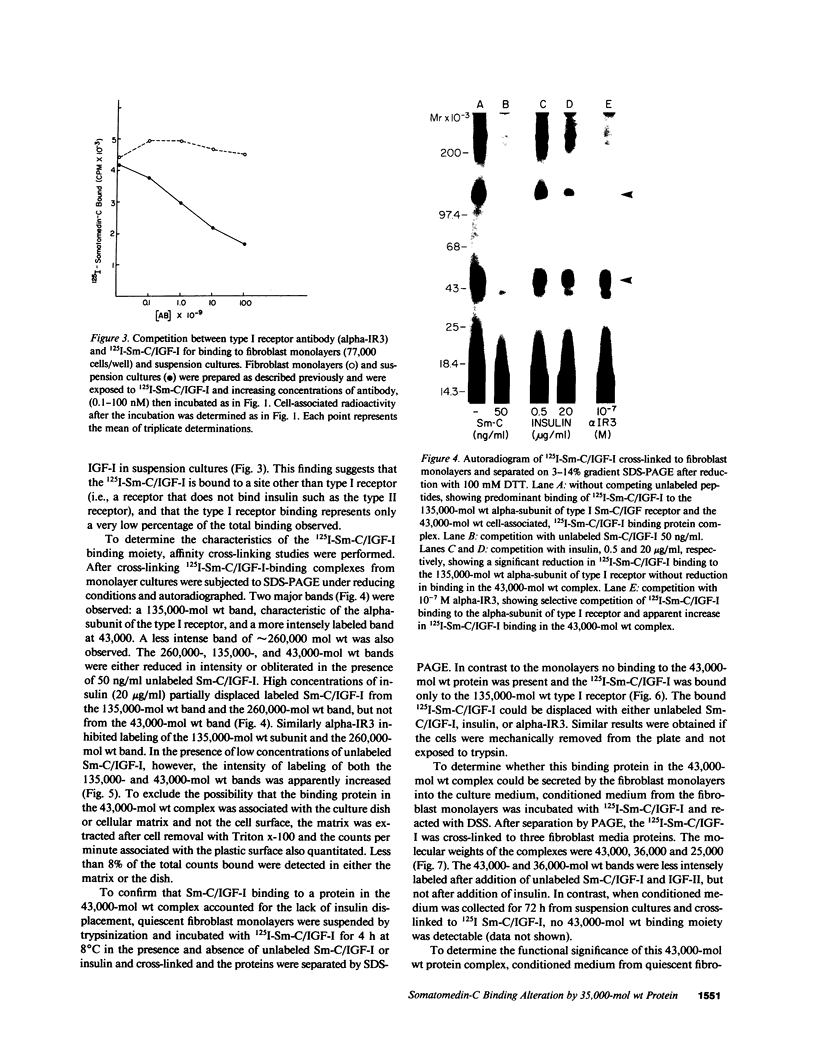
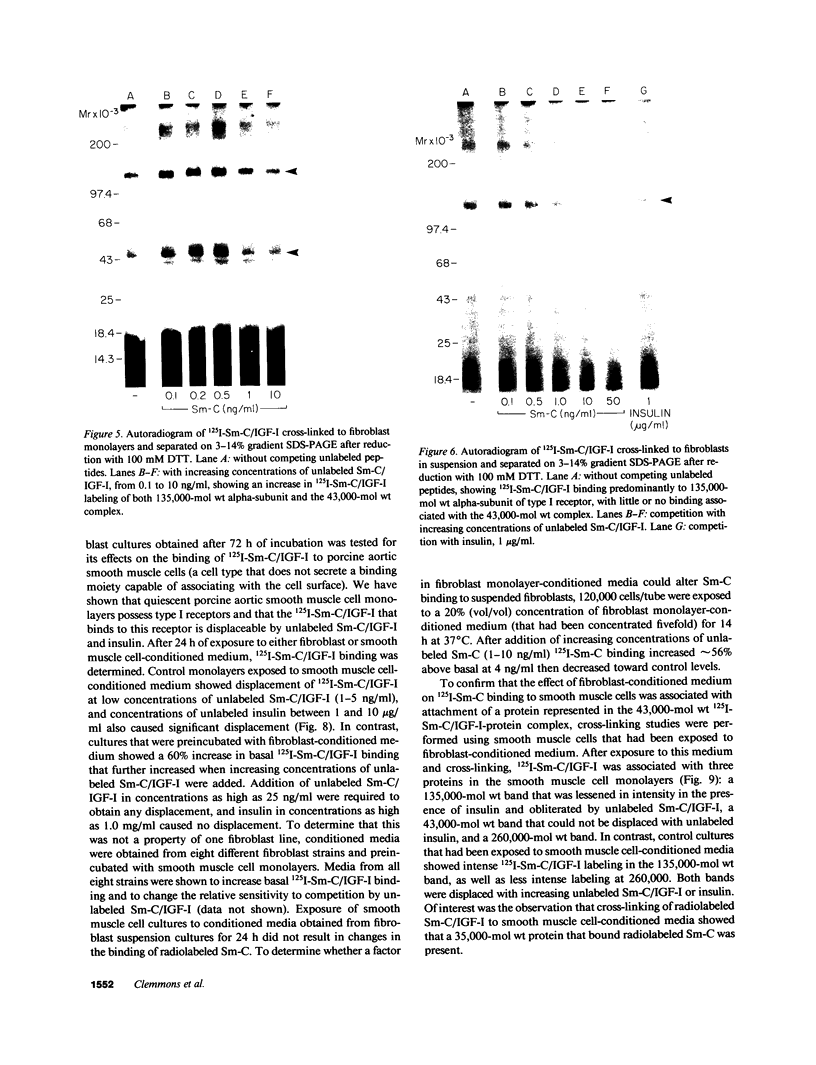
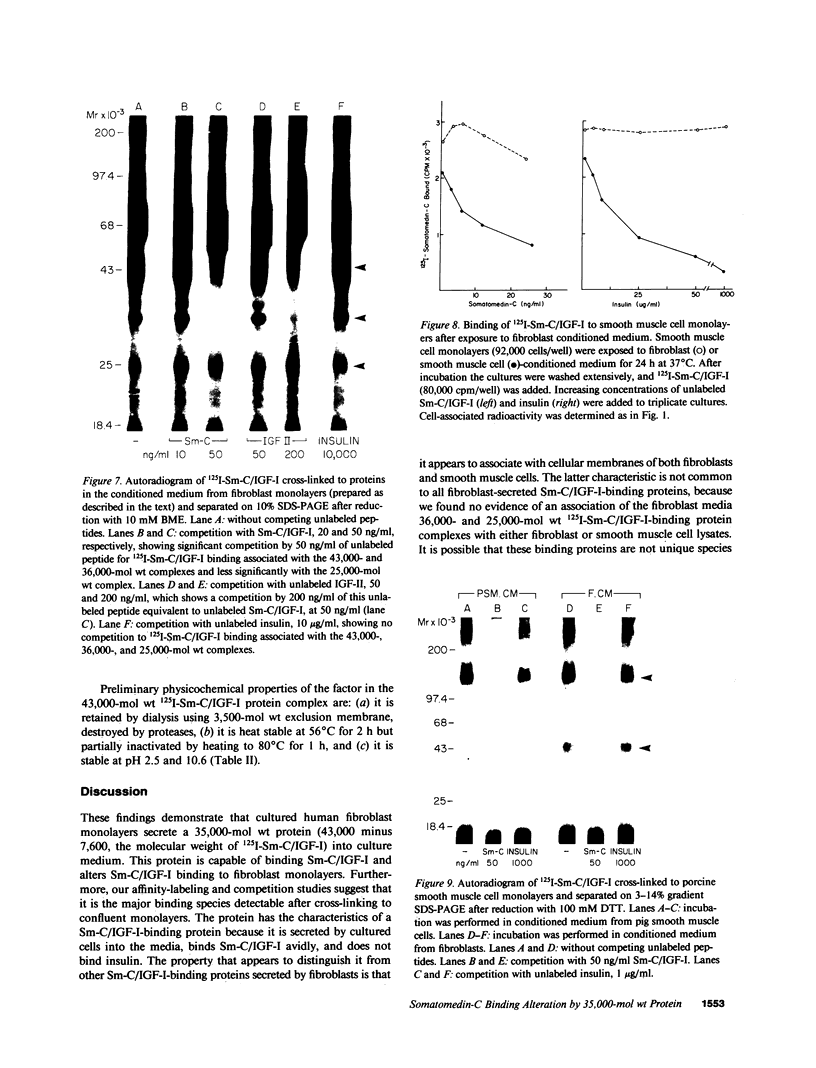
We studied somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor (Sm-C/IGF-I) binding to human fibroblasts in both adherent monolayers and in suspension cultures. The addition of Sm-C/IGF-I in concentrations between 0.5 and 10 ng/ml to monolayers cultures resulted in a paradoxical increase in 125I-Sm-C/IGF-I binding and concentrations between 25 and 300 ng/ml were required to displace the labeled peptide. The addition of unlabeled insulin resulted in no displacement of labeled Sm-C/IGF-I from the adherent cells. When fibroblast suspensions were used Sm-C/IGF-I concentrations between 1 and 10 ng/ml caused displacement, the paradoxical increase in 125I-Sm-C/IGF-I binding was not detected, and insulin displaced 60% of the labeled peptide. Affinity cross-linking to fibroblast monolayers revealed a 43,000-mol wt 125I-Sm-C-binding-protein complex that was not detected after cross-linking to suspended cells. The 43,000-mol wt complex was not detected after cross-linking to smooth muscle cell monolayers, and binding studies showed that 125I-Sm-C/IGF-I was displaced greater than 90% by Sm-C/IGF-I using concentrations between 0.5 and 10 ng/ml. Because fibroblast-conditioned medium contains the 43,000-mol wt complex, smooth muscle cells were incubated with conditioned medium for 24 h prior to initiation of the binding studies. 125I-Sm-C/IGF-I-binding increased 1.6-fold compared to control cultures and after cross-linking the 43,000-mol wt complex could be detected on the smooth muscle cell surface. Human fibroblast monolayers secrete a protein that binds 125I-Sm-C/IGF-I which can be transferred to the smooth muscle cell surface and alters 125I-Sm-C/IGF-I binding.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. O., Nissley S. P., Kasuga M., Foley T. P., Jr, Rechler M. M. Receptors for insulin-like growth factors and growth effects of multiplication-stimulating activity (rat insulin-like growth factor II) in rat embryo fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1983 Mar;112(3):971–978. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-3-971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong G. D., Hollenberg M. D., Bhaumick B., Bala R. M. Comparative studies on human placental insulin and basic somatomedin receptors. J Cell Biochem. 1982;20(3):283–292. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240200308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong M. L., Heistad D. D., Marcus M. L., Piegors D. J., Abboud F. M. Hemodynamic sequelae of regression of experimental atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):104–113. doi: 10.1172/JCI110738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D., Jr, Prince M., Tsai P., Johnson C., Lotan R., Rubenstein A. H., Olefsky J. M. Insulin binding, internalization, and receptor regulation in cultured human fibroblasts. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):E251–E260. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.241.3.E251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernausek S. D., Jacobs S., Van Wyk J. J. Structural similarities between human receptors for somatomedin C and insulin: analysis by affinity labeling. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 22;20(26):7345–7350. doi: 10.1021/bi00529a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Shaw D. S. Variables controlling somatomedin production by cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1983 May;115(2):137–142. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J. Hormonal control of immunoreactive somatomedin production by cultured human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):10–19. doi: 10.1172/JCI110001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover C. A., Dollar L. A., Hintz R. L., Rosenfeld R. G. Insulin-like growth factor I/somatomedin-C (IGF-I/SM-C) and glucocorticoids synergistically regulate mitosis in competent human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Aug;116(2):191–197. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041160210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Underwood L. E., Groelke J., Plet A. Leprechaunism: studies of the relationship among hyperinsulinism, insulin resistance, and growth retardation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Mar;48(3):495–502. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-3-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grizzard J. D., D'Ercole A. J., Wilkins J. R., Moats-Staats B. M., Williams R. W. Affinity-labeled somatomedin-C receptors and binding proteins from the human fetus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;58(3):535–543. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-3-535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Van Obberghen E., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Demonstration of two subtypes of insulin-like growth factor receptors by affinity cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5305–5308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauer D. J., Cunningham D. D. Epidermal growth factor carrier protein binds to cells via a complex with released carried protein nexin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2310–2314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Monoclonal antibodies to receptors for insulin and somatomedin-C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6561–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Czech M. P. The subunit structures of two distinct receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II and their relationship to the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5038–5045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M. Leprechaunism and related syndromes with primary insulin resistance: heterogeneity of molecular defects. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;97:245–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M., Goldfine I. D., Wells C. A. DNA synthesis in human fibroblasts: stimulation by insulin and by nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-S). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Sep;39(3):512–521. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-3-512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R. G., Dollar L. A. Characterization of the somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I (SM-C/IGF-I) receptor on cultured human fibroblast monolayers: regulation of receptor concentrations by SM-C/IGF-I and insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Sep;55(3):434–440. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-3-434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R. G., Dollar L. A., Conover C. A. Density-associated loss of functional receptors for somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I (SM-C/IGF-I) on cultured human fibroblast monolayers. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Nov;121(2):419–424. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Purification of somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:798–816. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E. E., Rechler M. M., Romanus J. A., Knight A. B., Nissley S. P., Humbel R. E. Receptors for insulinlike growth factor I are defective in fibroblasts cultured from a patient with leprechaunism. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1356–1365. doi: 10.1172/JCI110383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk J. J., Graves D. C., Casella S. J., Jacobs S. Evidence from monoclonal antibody studies that insulin stimulates deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis through the type I somatomedin receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Oct;61(4):639–643. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-4-639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins J. R., D'Ercole A. J. Affinity-labeled plasma somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I binding proteins. Evidence of growth hormone dependence and subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1350–1358. doi: 10.1172/JCI111836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]