Abstract
The bacterial extracellular matrix encases cells and protects them from host-related and environmental insults. The Escherichia coli master biofilm regulator CsgD is required for the production of the matrix components curli and cellulose. CsgD activates the diguanylate cyclase AdrA, which in turn stimulates cellulose production through cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP). Here, we identified and characterized a CsgD- and AdrA-independent cellulose production pathway that was maximally active when cultures were grown under reducing conditions or when the disulfide bonding system (DSB) was compromised. The CsgD-independent cellulose activation pathway was dependent on a second diguanylate cyclase, called YfiN. c-di-GMP production by YfiN was repressed by the periplasmic protein YfiR, and deletion of yfiR promoted CsgD-independent cellulose production. Conversely, when YfiR was overexpressed, cellulose production was decreased. Finally, we found that YfiR was oxidized by DsbA and that intraprotein YfiR disulfide bonds stabilized YfiR in the periplasm. Altogether, we showed that reducing conditions and mutations in the DSB system caused hyperactivation of YfiN and subsequent CsgD-independent cellulose production.
INTRODUCTION
Organisms often cluster together into homotypic aggregates that help the population resist environmental pressures (1). Similarly, bacteria form communities known as biofilms, in which cells are encased in a protective extracellular matrix (ECM) composed of proteins, polysaccharides, and DNA (2–5). The ECM provides bacteria with resistance to environmental insults like antimicrobial compounds, desiccation, and host immune responses (6–8).
Curli and cellulose are structural components of Escherichia coli and Salmonella species biofilms. Amyloids (including curli) are a common component of natural biofilms, and homologs of the curli genes are found in at least four different bacterial phyla (9, 10). Expression of curli and cellulose requires the master biofilm regulator CsgD (3, 11). The regulation of CsgD involves upwards of 13 transcriptional regulators, multiple small RNAs (sRNAs), and posttranslational phosphorylation (12). The complex regulation of csgD allows for precise control of curli and cellulose production in low-glucose, low-temperature, and low-salt environments (13–15). CsgD induces csgBAC transcription, leading to the production of the major and minor curli subunits CsgA and CsgB, respectively (11). CsgD also positively regulates adrA, which encodes an inner membrane diguanylate cyclase (3). Diguanylate cyclases produce the secondary messenger cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP), which activates the cellulose synthase BcsA in a concentration-dependent manner by binding to the RXXXR residues in the PilZ domain (3, 16, 17). Activated BcsA links UDP–d-glucose molecules together via a β-1,4 linkage, forming bacterial cellulose (3, 16).
When E. coli produces curli and cellulose on agar plates, the bacteria form a wrinkled colony that spreads away from the original inoculation site. These colonies are called rugose or rdar (red, dry, and rough) biofilms. Various bacterial species form rugose biofilms, including E. coli, Salmonella spp., Citrobacter koseri, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Bacillus subtilis, etc. (18–22). Uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) isolate UTI89 forms curli- and cellulose-dependent rugose biofilms (19). The major ECM components in E. coli and Salmonella species rugose biofilms are the proteinaceous amyloid fiber curli and the polysaccharide cellulose (23). Within UTI89 rugose biofilms, matrix production occurs at the air-colony interface, and the air-exposed matrix-encased cells demonstrate increased resistance to H2O2 compared to interior, non-matrix-encased cells (19). Curli and cellulose bind the dye Congo red (CR), leading to red (curli only or curli and cellulose) or pink (cellulose only) colonies (3, 18). Genetic disruption of curli or cellulose production in Salmonella or E. coli results in colonies that spread less and have a smaller colony diameter (3, 7). Deletion of csgD leads to smooth colonies that do not bind CR, due to the absence of curli and cellulose (3). While most E. coli strains, including UTI89, produce cellulose through the CsgD-dependent pathway, exceptions have been reported (19). For instance, E. coli 1094 produces cellulose in a CsgD-independent manner that is reliant on the diguanylate cyclase YedQ (24).
We discovered a CsgD- and AdrA-independent cellulose activation pathway that is linked to the disulfide bonding (DSB) machinery in E. coli. DsbB and DsbA coordinate disulfide bond formation in periplasmic proteins (25). DsbB is an inner membrane protein that oxidizes the periplasmic oxidoreductase DsbA, and DsbA in turn oxidizes periplasmic proteins by catalyzing disulfide bond formation (26, 27). Deletion of dsbA or dsbB results in a nonfunctional DSB system (25). We report here that DSB mutant colonies have increased colony diameter in comparison to wild-type (WT) colonies and produce cellulose in a CsgD- and AdrA-independent manner. Unlike CsgD-dependent cellulose production, the CsgD-independent pathway that is active in DSB mutants promotes cellulose production under many growth conditions. The CsgD-independent pathway requires the diguanylate cyclase YfiN. The periplasmic protein YfiR regulates YfiN and is a direct target of the DSB system.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains and growth conditions.
Starting cultures were grown with agitation at 37°C overnight in Luria broth (LB) medium. UTI89 mutants were constructed by using the lambda red recombinase technique (28). The primers used for mutations can be found in the supplemental material. The mutant strain names can be found in the supplemental material. In the manuscript, we refer to the strains by the mutations constructed.
Colony biofilms were grown from 4-μl dots of a cell suspension at an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 1.0. Bacterial pellets were washed twice in YESCA medium (10 g Casamino Acids, 1 g yeast extract/liter) before plating onto YESCA-Congo red (CR) medium plates (50 μg CR/ml and 20 g agar/liter). Pellicles were grown in liquid YESCA-CR medium (1.67 μg CR/ml). Bacteria were then incubated for 48 h at 26°C, and the colony images were captured by using an Olympus SZX16 microscope with an Olympus DP72 camera. Glucose plates contained 0.4% (wt/vol) dextrose (d-glucose) and were buffered with 15 mM morpholineethanesulfonic acid (MES) (pH 6.6). Increased acetic acid production from glucose metabolism is most likely the cause of this darker pigment, as CR is a pH indicator which can darken in low-pH environments (29). Motility plates contained 0.25% agar with LB or YESCA medium. To inoculate motility plates, pipette tips were dipped into a culture grown overnight and then into the plate. Motility plates were incubated at 37°C for 5 h prior to imaging. For the dithiothreitol (DTT) addition assay, 20 μl of 200 mM Tris buffer (pH 8.6) with or without 500 mM DTT was added to a sterile paper filter disk. Colony biofilms were grown as described above, 1.5 cm from the sterile filter paper disk, at 37°C for 24 h.
Pellicle bead assay.
The pellicle bead assay was adapted from a method described previously by Monteiro et al. (30). Sterile 3-mm glass beads were added via tweezers to pellicles that had grown for 48 h at 26°C. After 5 s, the next glass bead was added. Only beads that were held for the complete duration of 5 s were counted as being held by the pellicle.
Calcofluor staining and cellulose quantification.
Colonies were grown on YESCA plates and were washed with 0.001% calcofluor and water for 5 min. Colonies were then washed with water three times for 20 s. A UV lamp was used to illuminate the stained colonies during imaging. Recent work with Arabidopsis thaliana showed that Pontamine Fast Scarlet 4B (S4B) binds more specifically to cellulose than does calcofluor and that S4B fluoresces more brightly in the presence of cellulose than Solophenyl Flavine 7GFE and calcofluor (31). To quantitate cellulose using S4B, 4-μl colonies were grown as indicated and collected in 800 μl of 50 mM potassium phosphate (KPi) buffer (pH 7.2). Cells were tissue homogenized for 15 s on setting 3 with a Fisher Tissuemizer. Cells were incubated with 0.05 mg/ml S4B (32), briefly vortexed, and incubated for 10 min at room temperature (RT) on a rocking shaker at 200 rpm. Cells were then centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 1 min, washed twice with KPi, and then resuspended in 100 μl of KPi. Cell suspensions were diluted 1:10 into a 96-well plate and read on a Tecan Infinite 200 plate reader, at an excitation wavelength of 535 nm and an emission wavelength of 595 nm. Readings from unstained cell suspensions were subtracted from readings from the stained cell suspensions. Cells suspensions were normalized by the OD600. Error bars represent standard deviations from biological triplicate samples.
β-Galactosidase assay.
β-Galactosidase activity assays were adapted from methods described previously by Miller and DePas et al. (19, 33). Colonies were grown for 48 h and resuspended in 1 ml 50 mM KPi (pH 7.2). Cells were tissue homogenized for 15 s at setting 3 and allowed to incubate for 3 min. Cells at the top of the mixture were diluted 1:10, and 100 μl of this dilution was added to a 96-well plate. Reaction buffer (90 μl) and cell dilutions (7 μl) were incubated for 20 min at 30°C prior to the addition of 2 0 μl of 4 mg/ml ortho-nitrophenyl-β-galactoside (ONPG). In order to stop the reaction, 50 μl of 1 M Na2CO3 was added after the reaction mixture reached a light yellow color. The OD600 absorbance of the cell and KPi dilutions were recorded, along with readings of the absorbances of the reaction at 420 nm and 550 nm on a Tecan Infinite 200 plate reader. Assays were performed on 3 biological triplicates of strains with the pRJ800 empty vector (EV) (pRJ800 without a promoter upstream of lacZ), and data were averaged. The average EV reading was subtracted from the reading for each biological triplicate of the strain carrying pRJ800-adrA or pRJ800-16S. Averages and standard deviations were determined from the biological triplicates with the EV values subtracted.
Transposon screen.
The transposon screen was adapted from a method described previously by Rubin et al. (34). WT UTI89 or UTI89 ΔcsgD ΔdsbB cells were grown in streptomycin to select for antibiotic-resistant isolates. These isolates were conjugated with a donor strain, BW25113, transformed with pFD1 containing an isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG)-inducible transposase (NDH587). Cultures of both BW25113 NDH587 and UTI89 ΔcsgD ΔdsbB cells (750 μl each) were mixed, pelleted, and resuspended in 50 μl YESCA medium. Resuspended cultures were added to a cellulose filter that was placed on top of a YESCA medium plate. The bacteria on the plate were incubated at 37°C for 2.5 h. The cellulose filter was then removed from the plate, and the cells were removed by washing this filter with 10 ml liquid YESCA medium containing streptomycin and 1 mM IPTG and collected into a 15-ml tube. The cells were then incubated at 37°C for 3 h. The cells were then pelleted and resuspended in 10 ml fresh YESCA medium containing streptomycin and kanamycin for 1 h at 37°C. Cells were then diluted 1:10,000 and were plated onto YESCA-Congo red medium plates containing streptomycin and kanamycin. Transposons were verified by using random primed sequencing. Colony PCR with the mariner 1 and mariner 2 primers yielded the DNA flanking the transposon. Nested PCR of this DNA fragment with mariner 3 and mariner 4 then amplified this DNA segment. Sanger sequencing was then performed at the University of Michigan Sequencing Core by using the mariner 4 primer. Sequences were then aligned to the genome of UTI89 to reveal the locations of the mutations in the genome. Whole-gene deletions were made via the lambda red recombinase method.
Western blot analysis.
Western blot assays were performed by adapting a procedure described previously (35) (CsgA Western blots). Colony biofilms were grown at 26°C for 48 h. Colonies were then resuspended in 50 mM KPi buffer (pH 7.2). Cells were homogenized with a Fisher Tissuemizer tissue homogenizer on setting 3 for 20 s. Colony debris was then able to settle for 3 min prior to spectrophotometric measurement to normalize cells at an OD600 of 1. One hundred fifty microliters of normalized cells was resuspended in 2× SDS running buffer or hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP). HFIP was removed from HFIP-treated cells via a Thermo Savant SPD SpeedVac at 45°C for 45 min. Samples were then resuspended in 2× SDS running buffer. All samples were then heated at 95°C for 10 min prior to loading and electrophoresis of 8 μl on a 15% SDS-PAGE gel for 45 min at 25 mA. The samples were then transferred onto a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane via transfer on a semidry transfer apparatus at 10 V for 25 min at room temperature. Blots were blocked overnight in 5% milk with Tris-buffered saline–Tween 20 (TBST) buffer at 4°C. Primary antibody treatment was done for 1 h (1:8,000 dilution of anti-CsgA [36] in 5% milk in TBST), followed by three 5-min TBST washes. Secondary antibody treatment was done for 1 h (1:15,000 dilution of Licor anti-rabbit or anti-mouse antibody–IRDye). Blots were then dried and imaged on a Licor Odyssey CLX imager. Anti-CsgD (1:5,000 dilution of anti-rabbit antibody; a generous gift from Ute Römling), anti-His (1:5,000 dilution of anti-mouse antibody; Abgent Inc., San Diego, CA), and anti-σ70 (1:10,000 dilution of anti-mouse Santa Cruz RNA polymerase σD antibody) blots had an altered procedure. The SDS-PAGE gel was prepared in the same manner without the HFIP treatment. Samples were wet transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane in 25 mM CAPS (N-cyclohexyl-3-aminopropanesulfonic acid) transfer buffer in 10% methanol (pH 11.2) at 12 V overnight at 4°C.
Anti-His and anti-maltose binding protein (anti-MBP [1:10,000 dilution of anti-mouse antibody; a generous gift from Jim Bardwell, New England BioLabs, Ipswich, MA]) Western blots contained periplasmic protein samples, which were normalized by the protein concentration via the Pierce bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay (Thermo Scientific). Samples were incubated with 2× SDS sample buffer containing no β-mercaptoethanol with or without 5 mM the reducing agent DTT for 10 min with shaking at room temperature prior to loading onto an SDS-PAGE gel containing 18% nitrocellulose.
Periplasmic protein isolation.
We isolated periplasmic proteins according to a procedure adapted from a method described previously by Quan et al. (37). Two hundred microliters of cells at an OD600 of 1 was evenly spread onto YESCA plates amended with 10 μM IPTG and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. Cells were harvested, resuspended in osmotic shock buffer (30 mM Tris [pH 7.2], 40% sucrose, 2 mM EDTA), and incubated at room temperature for 10 min. Cells were centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was removed, and the pellet was resuspended with 450 μl ice-cold water, followed by the addition of 50 μl of 20 mM MgCl2. Samples were incubated on ice for 3 min prior to centrifugation at 4°C at 13,000 rpm for 10 min. The periplasmic extract is the supernatant fraction. Protein concentrations of the periplasmic extracts were normalized via the Pierce BCA protein assay (Thermo Scientific) (38). Anti-MBP Western blots were used to ensure that there were no aberrations in periplasmic protein isolated between samples.
RESULTS
Disulfide bonding mutants form hyperbiofilms.
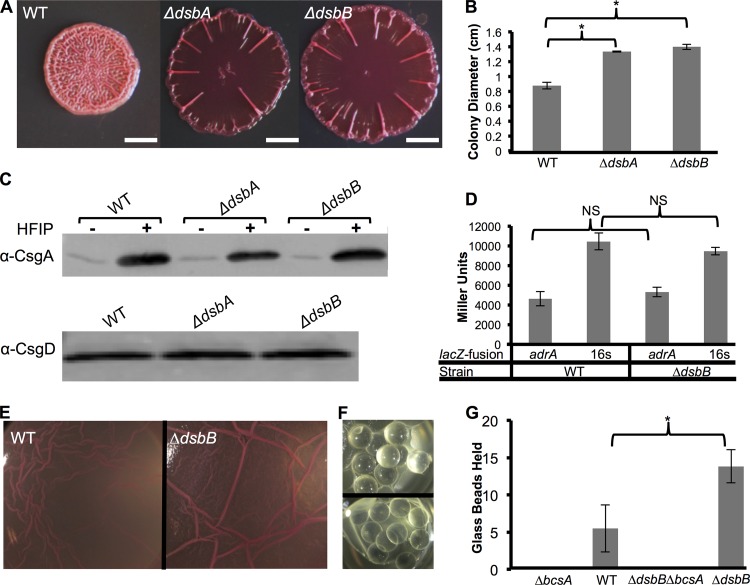
Many enteric bacteria, including UTI89, require an extracellular matrix (ECM) that contains both curli and cellulose for rugose colony formation. E. coli rugose colonies are typified by a wrinkled morphology and increased diameter compared to a colony that does not produce curli or cellulose (3, 7, 19). Therefore, colony diameter can be a simple proxy for curli and cellulose production. To identify additional components of the genetic network controlling ECM production in UTI89, a Tn5 mutant library was screened for hyperspreading strains. By using the mariner Tn5 conjugation system (34), an unsaturated screen of approximately 20,000 UTI89 transposon mutants revealed three isolates that had an increased colony diameter in comparison to that of the WT: two dsbA mutants and a dsbB mutant (data not shown). Clean deletions of the dsbA and dsbB coding regions via lambda red mutagenesis were constructed in UTI89. dsb mutant colonies (ΔdsbA and ΔdsbB) had increased colony diameters compared to that of the WT but were less wrinkled (Fig. 1A and B). Since ΔdsbA and ΔdsbB colony phenotypes were similar, we focused on the ΔdsbB strain for most of the subsequent experiments.
FIG 1.
Δdsb colonies had increased spreading but curli levels and adrA transcription similar to those of the WT. (A) UTI89 colonies were grown on YESCA-CR plates for 48 h at 26°C. ΔdsbB and ΔdsbA colonies formed hyperspreading colonies that had a lack of wrinkling in the center of the colony. Bars, 0.25 cm. (B) ΔdsbB and ΔdsbA strains had increased colony diameters compared to that of the WT. Colony diameters were measured in biological triplicates, and error bars represent standard deviations of data from biological triplicates. Significance was determined by Student's two-tailed t test (*, P value of >0.01). (C) CsgA Western blot showing that WT, ΔdsbA, and ΔdsbB strains had similar levels of CsgA when grown at 26°C for 48 h. Hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) is a strong denaturant that was added to monomerize the aggregated curli fibers. CsgD Western blot analysis was performed on colonies that were grown at 26°C for 24 h. (D) β-Galactosidase assays were performed on WT and ΔdsbB strains transformed with pRJ800, pRJ800-adrA, or pRJ800-16S (rrsA). The averages of biological triplicate readings from pRJ800 were subtracted from readings from strains containing pRJ800-adrA (adrA promoter upstream of lacZ) and pRJ800-16S (16S promoter upstream of lacZ). adrA and 16S transcription levels were similar between the WT and ΔdsbB strains. Error bars are the standard deviations of Miller units from biological triplicates. Significance was determined by using Student's two-tailed t test. NS, not significant. (E) UTI89 derivatives were grown statically in 24-well plates after 2 μl of a culture grown overnight was inoculated into 2 ml YESCA broth that contained 1.67 μg/ml of CR. Pellicles formed at the air-liquid interface with WT UTI89 and DSB mutants. (F) Glass beads were added to WT and ΔdsbB pellicles every 5 s, until the pellicle could no longer hold the glass beads. The image at the top shows a pellicle holding glass beads, while the image at the bottom shows a collapsed pellicle. (G) WT pellicles held ∼5 glass beads in YESCA-CR medium at 48 h, while ΔdsbB pellicles held ∼13 glass beads. Mutation of the cellulose synthase BcsA in WT and ΔdsbB strains yielded cultures that could not produce pellicles or hold glass beads. Error bars represent standard deviations of data from six biological replicates. P values were calculated by using Student's two-tailed t test (P value of <0.01).
Because disulfide bonding (DSB) mutants had an increased colony diameter in comparison to that of the WT, we hypothesized that mutations in the DSB system caused an upregulation of curli or cellulose. However, Western blot analysis revealed that dsbA and dsbB mutants had CsgA and CsgD protein levels similar to those of the WT, suggesting that curli production was not significantly changed (Fig. 1C). We measured adrA transcription levels as a proxy for cellulose induction. adrA transcription levels as measured by β-galactosidase assays were similar in WT and ΔdsbB colonies (Fig. 1D). These data suggested that levels of CsgD-regulated curli and cellulose production were not increased in the DSB mutants.
We next tested how mutations in DSB affected biofilm formation under other environmental conditions. WT UTI89 forms a pellicle biofilm at the air-liquid interface when grown in YESCA-CR medium at 26°C in static culture for 48 h (Fig. 1E) (39). Like rugose colonies, pellicle biofilms are dependent on both curli and cellulose (40). A ΔdsbB mutant formed a more robust and wrinkled pellicle than did the WT (Fig. 1E). We quantified pellicle integrity by measuring the ability of the pellicle to hold weight using a modified glass bead assay (30). The top panel of Fig. 1F shows glass beads held by the pellicle above the culture, while the bottom panel of Fig. 1F shows a pellicle that collapsed into the culture from glass bead addition. ΔdsbB pellicles held an average of 14 glass beads, while WT pellicles held <6 glass beads on average (Fig. 1G). A bcsA cellulose synthase mutant did not form a pellicle and could not support glass beads (Fig. 1G).
CsgD-independent activation of cellulose synthesis.
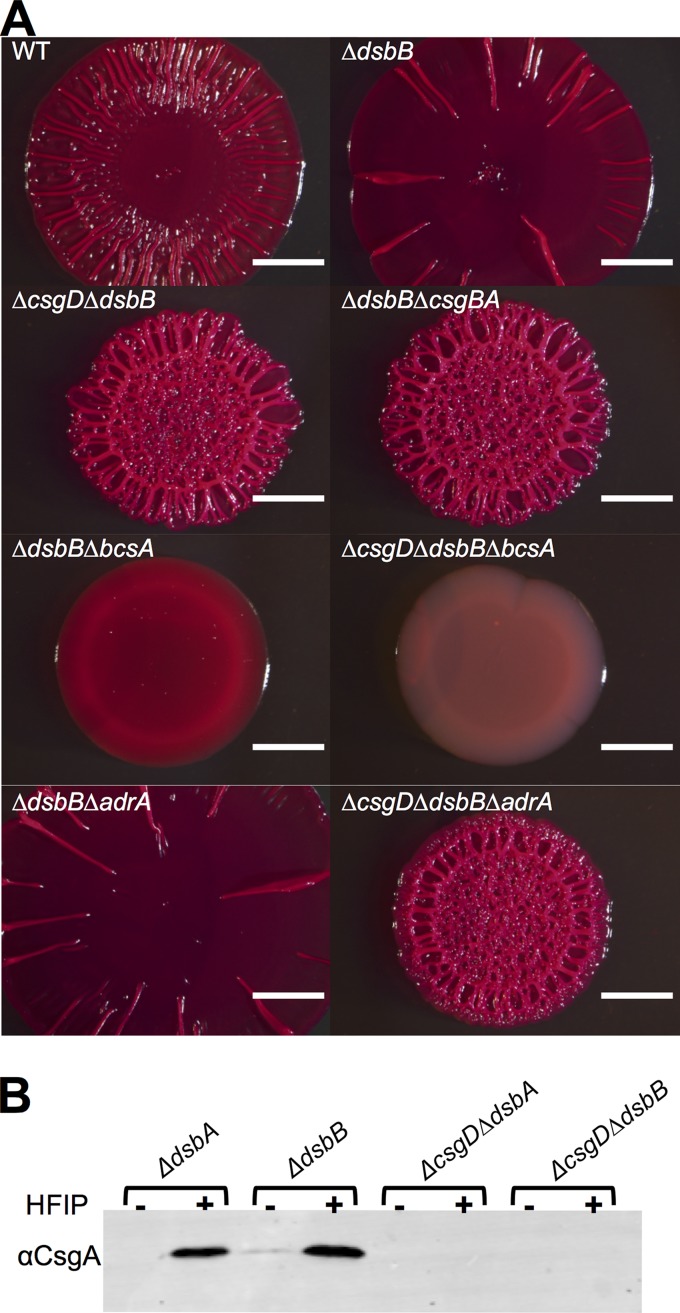
We next investigated which components of the CsgD-dependent matrix production pathway were necessary for the DSB mutant colony morphotype, since curli protein levels and adrA transcription were not dramatically different between DSB mutants and the WT. Mutation of the curli biosynthetic genes in a dsbB background (ΔdsbB ΔcsgBA) produced colonies that were light red on CR and wrinkled but that had a small colony diameter (Fig. 2A), suggesting that cellulose was still being produced. Mutation of the cellulose synthase in a DSB mutant (ΔdsbB ΔbcsA) yielded colonies that had a small colony diameter and did not wrinkle but did bind CR (Fig. 2A), suggesting that curli was still being produced. Unexpectedly, mutation of the master biofilm regulator CsgD in a DSB mutant (ΔcsgD ΔdsbB) resulted in colonies that wrinkled in a manner similar to that of ΔdsbB ΔcsgBA colonies (Fig. 2A). We hypothesized that the ability of the ΔcsgD ΔdsbB strains to form wrinkled colonies was dependent on cellulose production. Indeed, mutation of the cellulose synthase in a ΔcsgD ΔdsbB background (ΔcsgD ΔdsbB ΔbcsA) led to smooth, small-diameter colonies that failed to bind CR (Fig. 2A). Curli did not contribute to CR binding by ΔcsgD ΔdsbB strains, as the ΔcsgD ΔdsbB strain did not produce the major curli subunit CsgA (Fig. 2B). To confirm cellulose production in DSB mutant backgrounds, colonies were probed with the cellulose-specific stain Pontamine Fast Scarlet 4B (S4B) (32). S4B bound ΔcsgBA, ΔdsbB ΔcsgBA, and ΔcsgD ΔdsbB colonies at similar levels (see Fig. S1A in the supplemental material). S4B did not significantly bind to ΔcsgBA ΔbcsA or ΔcsgD ΔdsbB ΔbcsA colonies, as these strains were unable to produce cellulose (see Fig. S1A in the supplemental material).
FIG 2.
Δdsb colonies wrinkle due to csgD- and adrA-independent cellulose production. (A) Colonies were grown in YESCA medium for 48 h on YESCA-CR plates at 26°C. Bar, 0.25 cm. (B) CsgA protein levels were assessed via Western blot analysis. Samples were treated with HFIP to solubilize CsgA fibers.
CsgD in WT E. coli promotes cellulose production by upregulating the expression of the diguanylate cyclase AdrA (3). However, since cellulose production in DSB mutants was CsgD independent, we tested if it was also AdrA independent. The appearance of ΔdsbB ΔadrA colonies was similar to that of ΔdsbB colonies, suggesting that the CsgD-independent pathway did not require AdrA (Fig. 2A). Furthermore, mutation of adrA did not affect colony formation of ΔcsgD ΔdsbB colonies (Fig. 2A).
DSB mutants produce cellulose under many growth conditions.
We next tested if CsgD-independent cellulose production occurred under diverse growth conditions. WT colonies grown on plates that were amended with 0.4% glucose did not wrinkle and had a small colony diameter (Fig. 3A), likely because Cra and Crp-cyclic AMP (cAMP) are activated under low-sugar conditions, and both positively regulate csgD expression (13, 41). Interestingly, ΔdsbB and ΔcsgD ΔdsbB colonies wrinkled and bound to CR on glucose-supplemented medium (Fig. 3A). High-osmolarity and -salt conditions also inhibit csgD transcription (15), and on LB-CR plates, which have increased salt compared to YESCA medium, WT UTI89 colonies did not bind to CR and did not wrinkle (Fig. 3A). In contrast, ΔdsbB and ΔcsgD ΔdsbB colonies wrinkled when grown on LB CR plates (Fig. 3A). S4B staining confirmed that ΔdsbB and ΔcsgD ΔdsbB colonies were producing cellulose (see Fig. S1B in the supplemental material). Finally, E. coli cellulose production is temperature dependent and maximal at 26°C (42). WT UTI89 colonies grown at 37°C were smooth, while ΔcsgD ΔdsbB colonies wrinkled (Fig. 3B).
FIG 3.
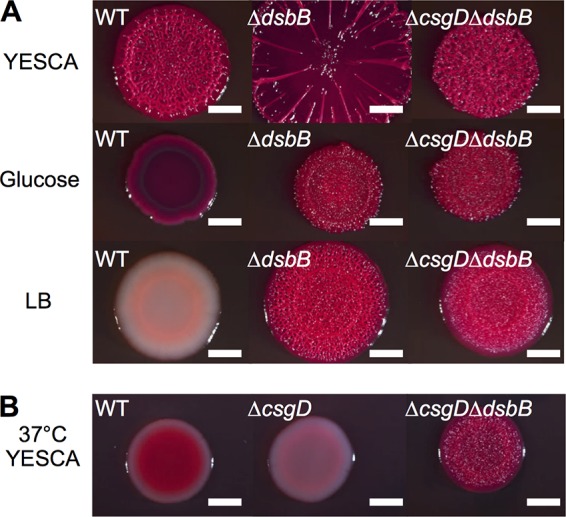
UTI89 Δdsb colonies wrinkle at 37°C, on dextrose, and on LB plates. (A) Strains were grown on YESCA medium buffered with 15 mM MES to pH 6.6 at 26°C for 48 h. WT, ΔdsbB, and ΔcsgD ΔdsbB colony morphotypes were not affected by buffering of the plates. In the middle row, colonies were grown on YESCA medium with 0.4% dextrose buffered with 15 mM MES to pH 6.6 at 26°C for 48 h. In the bottom row, strains were grown on LB-CR (1:200) plates at 26°C for 48 h. WT colonies were white and nonspreading or wrinkling on LB, while ΔdsbB and ΔcsgD ΔdsbB colonies both wrinkled on LB. (B) Colonies were grown for 24 h at 37°C on YESCA-CR plates. Bars, 0.25 cm.
Transposon screen for factors that affect the CsgD-independent cellulose activation pathway.
The CsgD-mediated cellulose production pathway requires c-di-GMP, and we therefore asked if the CsgD-independent pathway was also dependent on c-di-GMP. c-di-GMP levels were manipulated by overexpressing the phosphodiesterase yoaD. YoaD has been proposed to break down the pool of c-di-GMP that activates BcsA (43). yoaD expressed from an inducible tac promoter in the ΔdsbB strain resulted in decreased colony diameter and wrinkling (see Fig. S2A in the supplemental material), implying that c-di-GMP is involved in the CsgD-independent cellulose activation pathway.
To identify the diguanylate cyclase responsible for producing AdrA-independent c-di-GMP in the DSB mutant, we performed a transposon screen. A transposon library of ∼20,000 mutants was created in a UTI89 ΔcsgD ΔdsbB background (34). The mutants were plated onto YESCA-CR medium and incubated at 26°C until colonies were visually screened for the failure to wrinkle or bind to Congo red. We isolated 32 mutants that were white and unwrinkled (see Table S1 in the supplemental material), including bcsA, bcsB, bcsC, bcsE, and galU, which had all been shown to be involved in cellulose production (44–46). We also isolated mutations in genes that had not previously been associated with cellulose production in E. coli. These genes included nhaA, a sodium antiporter; nrdB, a ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase; and seqA, a protein involved in the regulation of DNA replication (47–50). Finally, one of the mutants that failed to bind Congo red and wrinkle was in a gene encoding a diguanylate cyclase called yfiN (51). We therefore hypothesized that the CsgD-independent cellulose production present in DSB mutants was activated through the diguanylate cyclase YfiN.
YfiN and YfiR can control cellulose production in UTI89.
YfiN is a diguanylate cyclase encoded within the yfiRNB operon that, when activated, contributes to biofilm formation via the production of c-di-GMP (52, 53). A clean deletion of yfiN was constructed in the UTI89 ΔcsgD ΔdsbB background. This triple mutant (ΔcsgD ΔdsbB ΔyfiN) formed smooth and white colonies on YESCA medium at 26°C and 37°C (Fig. 4A). Additionally, deletion of yfiN in UTI89 (ΔyfiN) resulted in decreased CR binding and wrinkling, suggesting that YfiN was required for cellulose production by both the CsgD-independent pathway and the canonical CsgD-dependent pathway (Fig. 4A). The ΔyfiN strain had lower levels of CsgD protein by Western blotting (see Fig. S2B in the supplemental material), which might account for the lack of CR binding and wrinkling by this strain (Fig. 4A).
FIG 4.
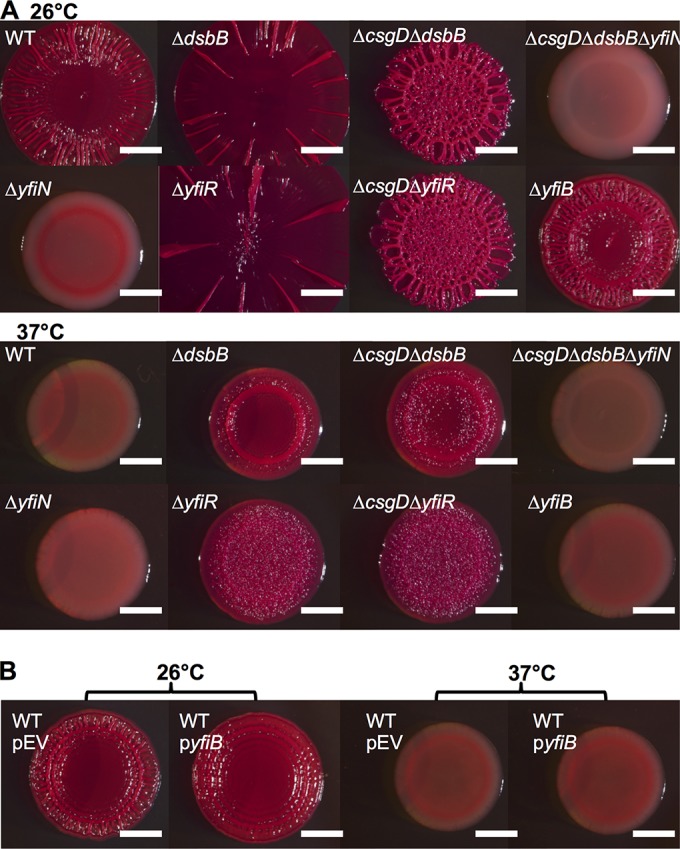
Cellulose production in the ΔcsgD ΔdsbB strain is dependent on the diguanylate cyclase YfiN. (A) Strains were grown on YESCA-CR medium. The top row shows strains that were grown at 26°C for 48 h, and the bottom row shows strains that were grown at 37°C for 24 h. (B) Strains were grown on YESCA-CR medium supplemented with 15 μM IPTG for 48 h at 26°C or for 24 h at 37°C. Bars, 0.25 cm.
YfiN′s role in cellulose production prompted an investigation of the periplasmic regulator YfiR, which inhibits YfiN activity in P. aeruginosa (53). We expected that deletion of yfiR in E. coli would result in greater c-di-GMP production by YfiN and increased cellulose production. Indeed, ΔyfiR colonies had an increased colony diameter compared to that of the WT at 26°C and wrinkled at 37°C (Fig. 4A). Also, ΔcsgD ΔyfiR colonies wrinkled with a small colony diameter at 26°C and 37°C (Fig. 4A), which suggested that the CsgD-independent cellulose production pathway was active in the yfiR deletion strain. In P. aeruginosa, YfiR can be inactivated by an outer membrane protein called YfiB (53). However, yfiB did not appear to play a role in UTI89 cellulose production, as the ΔyfiB and WT strains had similar colony phenotypes at 26°C and 37°C (Fig. 4A). In concert with this result, overexpression of yfiB did not appear to affect the WT colony morphotype (Fig. 4B). These results suggested that YfiR, but not YfiB, played a role in UTI89 cellulose production.
Because the deletion of yfiR activated CsgD-independent cellulose production, we tested whether overexpression of YfiR inhibited cellulose production and rugose colony formation. The WT, ΔdsbB, and ΔcsgD ΔdsbB strains were transformed with a plasmid that overexpressed yfiR (pyfiR) or with the same plasmid that was missing the yfiR gene (pEV). The ΔdsbB strain overexpressing yfiR displayed decreased colony spreading at 26°C and decreased CR binding at 37°C (Fig. 5A and B). The ΔcsgD ΔdsbB strain overexpressing yfiR had decreased CR binding and wrinkling at 37°C and at 26°C (Fig. 5A). The WT strain overexpressing yfiR had decreased wrinkling and colony diameter at 26°C compared to WT colonies transformed with pEV but still bound CR (Fig. 5A and B). CsgD levels were decreased when yfiR was overexpressed in the WT, and yfiR overexpression led to a minor decrease in CsgA levels in the WT (see Fig. S3A in the supplemental material). Additionally, ΔyfiR strains were attenuated in their swimming motility (see Fig. S3B in the supplemental material), similar to results seen with E. coli CFT073 (52).
FIG 5.
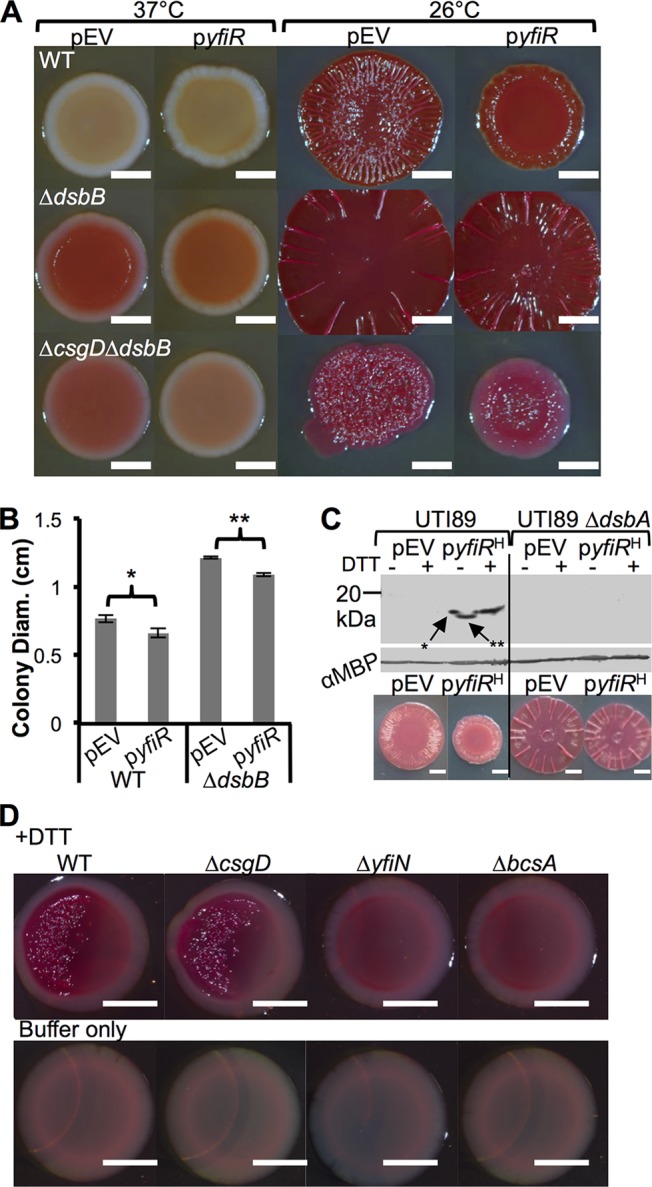
yfiR overexpression inhibits alternate cellulose expression. (A) WT, ΔdsbB, and ΔcsgD ΔdsbB strains were transformed with pCKR101-EV (pEV) or pCKR101-yfiR (pyfiR). Colonies were grown on YESCA-CR plates with 10 μM IPTG. The colonies on the left were grown at 37°C for 24 h, and the plates on the right were grown at 26°C for 48 h. (B) Colony diameter measurements were taken from biological triplicates of colonies that were grown on YESCA medium at 26°C for 48 h. Error bars show the standard deviations of the measured diameters. P values represent values determined by Student's two-tailed t test (*, P value of <0.04; **, P value of <0.01). (C) UTI89 WT and ΔdsbA strains were transformed with pEV and pyfiRHis (pyfiRH) and grown for 24 h at 37°C on YESCA-IPTG plates. Periplasms were isolated from the cells and were incubated with nonreducing SDS sample buffer with or without 5 mM DTT for 10 min. Anti-His Western blot analysis revealed that YfiR was oxidized in WT UTI89, as DTT treatment led to reduced YfiR levels with decreased migration through the gel. Without DTT, YfiR ran further on the gel (**); however, there was a spur on the left side of the band (*). Spurs develop from reducing agent diffusion from adjacent lanes causing a reduction of the protein on one side of the protein band and are indicative of proteins containing disulfide bonds (56). MBP levels were assayed to ensure that similar periplasmic protein concentrations were loaded for each sample. Underneath the Western blot are pictures of WT pEV and pCKR101-yfiRHis and ΔdsbA pEV and pCKR101-yfiRHis colonies grown on YESCA-CR plates for 48 h at 26°C. (D) Colonies were grown at 37°C for 24 h 1.5 cm away from a filter paper disk containing 20 μl of 500 mM DTT suspended in 200 mM Tris buffer (pH 8.6) or buffer alone. Bars, 0.25 cm.
The result that YfiN induced CsgD-independent cellulose production in a DSB mutant background was interesting because of the prospect that the DSB system could directly act on the periplasmic YfiN repressor YfiR. In P. aeruginosa, YfiR whole-cell protein levels are decreased in DSB mutant strains (54). Furthermore, YfiR contains four cysteine residues, at positions 55, 92, 127, and 134. To directly test whether DSB oxidizes YfiR, the UTI89 WT and ΔdsbA strains were transformed with pCKR101 (pEV) and pCKR101 with a tac promoter driving the expression of yfiR with a His tag on the C terminus of YfiR (pyfiRHis) so that YfiR could be monitored by Western blotting. The UTI89 WT pEV and pyfiRHis strains along with the ΔdsbA pEV and pyfiRHis strains were plated onto YESCA-IPTG plates and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. Periplasmic extracts were isolated, incubated in SDS sample buffer with or without the reducing agent dithiothreitol (DTT), and incubated for 10 min. Western blot analysis revealed that YfiR-His was not present in ΔdsbA periplasmic extracts, suggesting that YfiR was not stable and was degraded in the absence of the DSB system (Fig. 5C). Furthermore, DTT caused a mobility shift in YfiR-His (Fig. 5C). Interestingly, there is a “spur” on the left side of the YfiR-His band without DTT (Fig. 5C). Spurs are commonly attributed to the diffusion of the reducing agent present in the adjacent lane (55, 56). The spur and the higher-molecular-weight shift due to reduction are indicative of an oxidized protein that contains disulfide bonds (56). We therefore conclude that mutation of the DSB system results in YfiR degradation and causes YfiN-mediated activation of the cellulose synthase.
Finally, we considered environmental conditions that could activate the DSB mutant-induced cellulose production pathway in WT strain UTI89. Since oxidation of YfiR is necessary for its periplasmic stability, we hypothesized that growth under reducing conditions would result in YfiR destabilization and production of cellulose via YfiN-mediated cellulose synthase activation. Colonies were spotted near a sterile paper disk that contained buffer or the reducing agent DTT. After incubation at 37°C, both WT and ΔcsgD cells wrinkled and bound CR when spotted 1.5 cm from the DTT disk (Fig. 5D). YfiN was required for cellulose production in the presence of DTT, as ΔyfiN colonies were smooth and did not bind CR (Fig. 5D). ΔbcsA cellulose synthase mutants were also smooth and did not bind CR (Fig. 5D). These experiments demonstrate that reducing conditions induce YfiN-mediated cellulose production in WT E. coli.
DISCUSSION
Here, we describe a YfiN-mediated cellulose synthase activation pathway in E. coli. The YfiN-mediated pathway is dependent on the cellulose synthase BcsA but is independent of CsgD and the previously described BcsA activator AdrA. YfiN is a diguanylate cyclase that is repressed by YfiR. We found that YfiN is active in DSB mutants because YfiR is unstable.
YfiN was identified by a transposon screen done in a ΔcsgD ΔdsbB background. We isolated 32 transposon mutants that appeared white on CR plates (see Table S1 in the supplemental material). The ΔcsgD ΔdsbB strain was used in the screen because we wanted to focus on the CsgD-independent cellulose production pathway. Many of the mutants identified in the screen could have been predicted a priori. For example, the bcs genes (bcsA, bcsB, bcsC, and bcsE) are required for cellulose synthesis in E. coli and are required for the CsgD-independent cellulose production pathway (see Table S1 in the supplemental material) (3, 45). galU is required, as it is necessary for the production of the building block of bacterial cellulose, UDP–d-glucose (46). However, a few additional genes were identified in the screen, which will require further work to fully understand their role in cellulose production. These genes include nhaA, a sodium antiporter; nrdB, a ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase; and seqA, a regulator of DNA replication. nhaA, nrdB, and seqA were not previously identified in a UTI89 transposon screen for genes affecting biofilms in UTI89, suggesting that they may not affect the CsgD-mediated cellulose production pathway (57).
YfiN plays an important role across species in the regulation of matrix production. YfiN (or TpbB) in P. aeruginosa leads to increased production of exopolysaccharide (EPS) and the development of small-colony variants (53, 58). P. aeruginosa YfiN is localized to the inner membrane and is activated via homodimerization to produce the second messenger c-di-GMP (53, 54). YfiN homodimerization is inhibited by the periplasmic protein YfiR (53, 54). yfiRNB are in a single operon in E. coli, and YfiR and YfiN have similar activities in E. coli as those in P. aeruginosa (51–53, 59). Previous work has also shown that the YfiN homolog AwsR controls Pseudomonas fluorescens cellulose and biofilm formation (60), and in Yersinia pestis, the YfiN and YfiR homologs, HmsD and HmsC, respectively, contribute to biofilm formation and the blockage of blood intake in the rat flea Xenopsylla cheopis (61, 62). The inhibition of YfiN by YfiR can be overcome in P. aeruginosa via overexpression of the outer membrane protein YfiB, which sequesters YfiR away from YfiN (53). Interestingly, our results showed that deletion or overexpression of yfiB had little to no effect on cellulose production in UTI89 (Fig. 4A and B). In Y. pestis, biofilm formation was only modestly affected by deletion or overexpression of the YfiB homolog HmsE (61, 62). In UPEC strain CFT073, yfiR deletion leads to an increase in cellulose and curli production along with attenuation of bladder and kidney titers in a murine urinary tract infection (UTI) model (52). In UTI89, a yfiLR::Tn mutant has decreased bladder titers, intracellular bacterial communities, and motility (57).
The periplasmic protein YfiR tempers YfiN-dependent cellulose production. YfiR has four cysteine residues that are available for disulfide bonding. Previous work with P. aeruginosa showed that YfiR whole-cell protein levels are decreased in a ΔdsbA background (54). Similarly, we show here that the stability of YfiR in E. coli is dependent on a functioning DSB system (Fig. 5C). Furthermore, we expanded this analysis by closely monitoring the migration of oxidized and reduced YfiR by SDS-PAGE. YfiR migrated slower on an SDS-PAGE gel when it was reduced by DTT (Fig. 5C), which is indicative of proteins that have a redox-sensitive disulfide bond (55, 56). Interestingly, we observed a spur in the lane containing oxidized YfiR, which was directly adjacent to the DTT-reduced lane (Fig. 5C). Spurs are a distinguishing characteristic of disulfide-bonded proteins that are partially reduced by the DTT in the adjacent lane (55, 56). These results indicate that the DSB system normally oxidizes YfiR and that in the absence of the DSB system, YfiR is unstable and degraded (Fig. 5C and 6).
FIG 6.
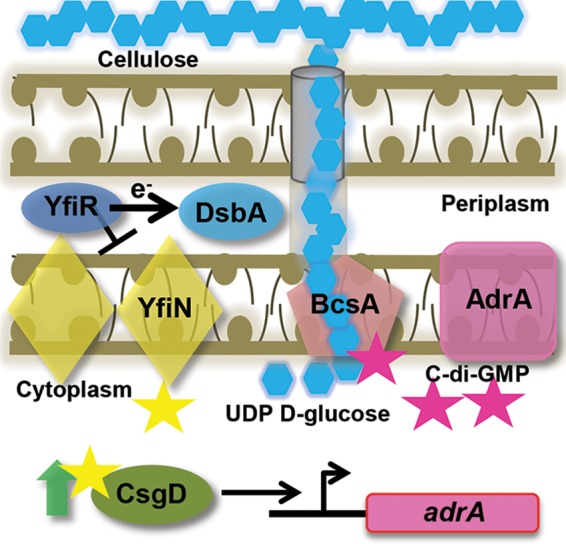
Updated model of cellulose production in UTI89. YfiN is inhibited by YfiR, which requires the DSB system to properly fold. YfiN produces small amounts of c-di-GMP (yellow stars) that are required for normal CsgD protein levels. CsgD positively regulates adrA, which encodes the diguanylate cyclase that produces c-di-GMP (pink stars) to bind to PilZ of BcsA and activate the cellulose synthase complex. UDP–d-glucose molecules are the monomers of cellulose production. In the absence of the DSB system or YfiR, YfiR is not present, and YfiN dimerizes and leads to uninhibited production of c-di-GMP. YfiN produces c-di-GMP that leads to BcsA activation, even in the absence of CsgD or AdrA.
ΔyfiR colonies have an increased colony diameter similar to that of Δdsb colonies, and ΔcsgD ΔyfiR colonies phenocopy ΔcsgD ΔdsbB colonies (Fig. 4A). Overexpression of yfiR in ΔdsbB and ΔcsgD ΔdsbB colonies inhibits CsgD-independent cellulose production, as these colonies no longer bind CR at 37°C (Fig. 5A). Also, yfiR expression in the ΔdsbB strain decreases colony diameter at 26°C, and yfiR expression in the ΔcsgD ΔdsbB strain decreases colony diameter and binding to CR at 26°C (Fig. 5A and B). These data support a model where YfiR quells cellulose production by inhibiting YfiN (Fig. 6).
Since YfiR requires oxidative folding for protein stability, we reasoned that YfiN and cellulose production would be induced under reducing conditions. Indeed, the addition of DTT to colonies promoted CsgD-independent cellulose production at 37°C (Fig. 5D). Thus, it is possible that anaerobic or reducing environments, such as those in the lower intestinal tract, induce cellulose production through YfiN activation.
There is at least one additional instance of CsgD-independent cellulose activation. YedQ is the primary cellulose activator in WT E. coli strain 1094 and is independent of the CsgD-mediated activation pathway (24). E. coli UTI89, in contrast, utilizes the CsgD-dependent diguanylate cyclase AdrA for WT cellulose activation (19). YfiN activation is similar to YedQ activation, as it is CsgD independent; however, it is an alternate or secondary diguanylate cyclase that activates cellulose only under specific reducing conditions.
Not only is YfiN required for CsgD-independent cellulose production in DSB mutants, it also plays a role in the CsgD-dependent canonical cellulose production pathway in WT strain UTI89. Deletion of yfiN led to smooth and white colonies in UTI89 (Fig. 4A) and decreased CsgD protein levels in comparison to the WT (see Fig. S2B in the supplemental material). DSB mutations in yfiN mutants cause increases in CsgD and CsgA protein levels in comparison to the levels in yfiN single mutants (see Fig. S2B in the supplemental material). This could be due to DSB mutations activating additional diguanylate cyclases, which then produce enough c-di-GMP to increase CsgD protein levels. c-di-GMP and diguanylate cyclases were previously implicated in controlling csgD transcription levels (63, 64). Furthermore, yfiR overexpression in the WT leads to decreased CsgD protein levels (Fig. 5; see also Fig. S3A in the supplemental material). yfiR overexpression in DSB mutants did not decrease CsgD or CsgA protein levels. This phenomenon could also be explained by multiple diguanylate cyclases being activated by DSB mutation. yfiR overexpression could quell YfiN activation in DSB mutants, but other diguanylate cyclases might help maintain CsgD at WT levels (see Fig. S3A in the supplemental material). The ability of YfiR to modulate CsgD protein levels and cellulose production in WT UTI89 demonstrates that it has roles in both canonical cellulose production and the CsgD-independent pathway (Fig. 6).
Besides cellulose production, the DSB system is also important for many other E. coli virulence traits. The E. coli flagellar machinery (65), P pili (66), type III secretion system (67), and enterotoxin production (68) all require the DSB system for proper function. The necessity of DSB for these virulence traits led to the suggestion that DSB might be a promising drug target (69). However, because cellulose production and biofilm formation by E. coli can confer resistance to host factors and environmental insults (70), targeting of the DSB system might promote cellulose production and unwanted outcomes. Cellulose expression in DSB mutants may not have been noticed in other studies since cellulose is not produced in K-12 strains due to a mutation in the bcs operon (71).
CsgD-independent cellulose production may provide a means for industrial production of cellulose. Cellulose is widely utilized in industrial applications (textiles, dietary supplements, gauze, scaffolds for tissue regeneration, and even headphones) (72, 73). Microbial cellulose is coveted because of its purity and is typically harvested from Gluconacetobacter xylinus (73, 74). One of the largest problems with the industrial production of microbial cellulose from G. xylinus is the high production costs (74). Glucose-based medium is used for G. xylinus growth and cellulose production, and the metabolic by-products produced during growth actually inhibit cellulose production (74). CsgD-independent cellulose production allows E. coli to produce cellulose under many conditions, including conditions of high temperature, high glucose, and high salt (Fig. 4). Genetically modifying E. coli has been proposed as a tractable method for producing microbial cellulose (74), in part due to the ability of E. coli to flourish in a variety of nutrient sources. Cellulose could be harvested by feeding a DSB or YfiR mutant with a variety of inexpensive and environmentally friendly nutrients (such as waste from various industrial processes). Similar types of studies have already been attempted with G. xylinus (75, 76). The work presented here might increase the financial feasibility of microbial cellulose production and helps further the understanding of matrix production in microbial biofilms.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Blaise Boles and James Bardwell for laboratory supplies and helpful discussion on the project. We thank Scott Hultgren for supplying UTI89 (77), James Imlay for supplying pCKR101, and Ute Römling for supplying the anti-CsgD antibody. We thank Erik Nielsen for the S4B stain and for helpful discussions. We thank Ann Miller for the use of her dissecting scope. We thank Robert Bender and members of the Chapman laboratory for scientific discussions on the project.
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant RO1 A1073847-6.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 11 August 2014
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JB.02019-14.
REFERENCES
- 1.Dittmer CG. 1931. Animal aggregations: a study in general sociology. J. Educ. Sociol. 5:130. 10.2307/2961735. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vidal O, Longin R, Prigent-Combaret C, Dorel C, Hooreman M, Lejeune P. 1998. Isolation of an Escherichia coli K-12 mutant strain able to form biofilms on inert surfaces: involvement of a new ompR allele that increases curli expression. J. Bacteriol. 180:2442–2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zogaj X, Nimtz M, Rohde M, Bokranz W, Romling U. 2001. The multicellular morphotypes of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli produce cellulose as the second component of the extracellular matrix. Mol. Microbiol. 39:1452–1463. 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wu JF, Xi CW. 2009. Evaluation of different methods for extracting extracellular DNA from the biofilm matrix. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75:5390–5395. 10.1128/AEM.00400-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Whitchurch CB, Tolker-Nielsen T, Ragas PC, Mattick JS. 2002. Extracellular DNA required for bacterial biofilm formation. Science 295:1487. 10.1126/science.295.5559.1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Epstein AK, Pokroy B, Seminara A, Aizenberg J. 2011. Bacterial biofilm shows persistent resistance to liquid wetting and gas penetration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108:995–1000. 10.1073/pnas.1011033108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.White AP, Gibson DL, Kim W, Kay WW, Surette MG. 2006. Thin aggregative fimbriae and cellulose enhance long-term survival and persistence of Salmonella. J. Bacteriol. 188:3219–3227. 10.1128/JB.188.9.3219-3227.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kai-Larsen Y, Luthje P, Chromek M, Peters V, Wang X, Holm A, Kadas L, Hedlund K-O, Johansson J, Chapman MR, Jacobson SH, Romling U, Agerberth B, Brauner A. 2010. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli modulates immune responses and its curli fimbriae interact with the antimicrobial peptide LL-37. PLoS Pathog. 6:e1001010. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Larsen P, Nielsen JL, Dueholm MS, Wetzel R, Otzen D, Nielsen PH. 2007. Amyloid adhesins are abundant in natural biofilms. Environ. Microbiol. 9:3077–3090. 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dueholm MS, Albertsen M, Otzen D, Nielsen PH. 2012. Curli functional amyloid systems are phylogenetically widespread and display large diversity in operon and protein structure. PLoS One 7:e51274. 10.1371/journal.pone.0051274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hammar M, Arnqvist A, Bian Z, Olsen A, Normark S. 1995. Expression of two csg operons is required for production of fibronectin- and Congo red-binding curli polymers in Escherichia coli K-12. Mol. Microbiol. 18:661–670. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.mmi_18040661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Evans ML, Chapman MR. 2014. Curli biogenesis: order out of disorder. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1843:1551–1558. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.09.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Reshamwala SM, Noronha SB. 2011. Biofilm formation in Escherichia coli cra mutants is impaired due to down-regulation of curli biosynthesis. Arch. Microbiol. 193:711–722. 10.1007/s00203-011-0708-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bougdour A, Lelong C, Geiselmann J. 2004. Crl, a low temperature-induced protein in Escherichia coli that binds directly to the stationary phase sigma subunit of RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 279:19540–19550. 10.1074/jbc.M314145200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jubelin G, Vianney A, Beloin C, Ghigo JM, Lazzaroni JC, Lejeune P, Dorel C. 2005. CpxR/OmpR interplay regulates curli gene expression in response to osmolarity in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 187:2038–2049. 10.1128/JB.187.6.2038-2049.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ryjenkov DA, Simm R, Romling U, Gomelsky M. 2006. The PilZ domain is a receptor for the second messenger c-di-GMP: the PilZ domain protein YcgR controls motility in enterobacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 281:30310–30314. 10.1074/jbc.C600179200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Omadjela O, Narahari A, Strumillo J, Melida H, Mazur O, Bulone V, Zimmer J. 2013. BcsA and BcsB form the catalytically active core of bacterial cellulose synthase sufficient for in vitro cellulose synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110:17856–17861. 10.1073/pnas.1314063110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Romling U, Sierralta WD, Eriksson K, Normark S. 1998. Multicellular and aggregative behaviour of Salmonella typhimurium strains is controlled by mutations in the agfD promoter. Mol. Microbiol. 28:249–264. 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.DePas WH, Hufnagel DA, Lee JS, Blanco LP, Bernstein HC, Fisher ST, James GA, Stewart PS, Chapman MR. 2013. Iron induces bimodal population development by Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110:2629–2634. 10.1073/pnas.1218703110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Proctor RA, von Eiff C, Kahl BC, Becker K, McNamara P, Herrmann M, Peters G. 2006. Small colony variants: a pathogenic form of bacteria that facilitates persistent and recurrent infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4:295–305. 10.1038/nrmicro1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dietrich LEP, Okegbe C, Price-Whelan A, Sakhtah H, Hunter RC, Newman DK. 2013. Bacterial community morphogenesis is intimately linked to the intracellular redox state. J. Bacteriol. 195:1371–1380. 10.1128/JB.02273-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Branda SS, Gonzalez-Pastor JE, Ben-Yehuda S, Losick R, Kolter R. 2001. Fruiting body formation by Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98:11621–11626. 10.1073/pnas.191384198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.McCrate OA, Zhou XX, Reichhardt C, Cegelski L. 2013. Sum of the parts: composition and architecture of the bacterial extracellular matrix. J. Mol. Biol. 425:4286–4294. 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.06.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Da Re S, Ghigo JM. 2006. A CsgD-independent pathway for cellulose production and biofilm formation in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 188:3073–3087. 10.1128/JB.188.8.3073-3087.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bardwell JC, Lee JO, Jander G, Martin N, Belin D, Beckwith J. 1993. A pathway for disulfide bond formation in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90:1038–1042. 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nakamoto H, Bardwell JC. 2004. Catalysis of disulfide bond formation and isomerization in the Escherichia coli periplasm. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1694:111–119. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bardwell JC. 1994. Building bridges: disulphide bond formation in the cell. Mol. Microbiol. 14:199–205. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Datsenko KA, Wanner BL. 2000. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97:6640–6645. 10.1073/pnas.120163297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Steensma DP. 2001. “Congo” red: out of Africa? Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 125:250–252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Monteiro C, Papenfort K, Hentrich K, Ahmad I, Le Guyon S, Reimann R, Grantcharova N, Romling U. 2012. Hfq and Hfq-dependent small RNAs are major contributors to multicellular development in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. RNA Biol. 9:489–502. 10.4161/rna.19682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Anderson CT, Carroll A, Akhmetova L, Somerville C. 2010. Real-time imaging of cellulose reorientation during cell wall expansion in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol. 152:787–796. 10.1104/pp.109.150128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hoch HC, Galvani CD, Szarowski DH, Turner JN. 2005. Two new fluorescent dyes applicable for visualization of fungal cell walls. Mycologia 97:580–588. 10.3852/mycologia.97.3.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Miller J. 1972. Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rubin EJ, Akerley BJ, Novik VN, Lampe DJ, Husson RN, Mekalanos JJ. 1999. In vivo transposition of mariner-based elements in enteric bacteria and mycobacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96:1645–1650. 10.1073/pnas.96.4.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhou Y, Smith DR, Hufnagel DA, Chapman MR. 2013. Experimental manipulation of the microbial functional amyloid called curli. Methods Mol. Biol. 966:53–75. 10.1007/978-1-62703-245-2_4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Barnhart MM, Lynem J, Chapman MR. 2006. GlcNAc-6P levels modulate the expression of curli fibers by Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 188:5212–5219. 10.1128/JB.00234-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Quan S, Hiniker A, Collet JF, Bardwell JC. 2013. Isolation of bacteria envelope proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 966:359–366. 10.1007/978-1-62703-245-2_22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sorensen K, Brodbeck U. 1986. A sensitive protein assay-method using micro-titer plates. Experientia 42:161–162. 10.1007/BF01952446. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cegelski L, Pinkner JS, Hammer ND, Cusumano CK, Hung CS, Chorell E, Aberg V, Walker JN, Seed PC, Almqvist F, Chapman MR, Hultgren SJ. 2009. Small-molecule inhibitors target Escherichia coli amyloid biogenesis and biofilm formation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 5:913–919. 10.1038/nchembio.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hung C, Zhou YZ, Pinkner JS, Dodson KW, Crowley JR, Heuser J, Chapman MR, Hadjifrangiskou M, Henderson JP, Hultgren SJ. 2013. Escherichia coli biofilms have an organized and complex extracellular matrix structure. mBio 4(5):e00645-13. 10.1128/mBio.00645-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zheng D, Constantinidou C, Hobman JL, Minchin SD. 2004. Identification of the CRP regulon using in vitro and in vivo transcriptional profiling. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:5874–5893. 10.1093/nar/gkh908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gualdi L, Tagliabue L, Bertagnoli S, Ierano T, De Castro C, Landini P. 2008. Cellulose modulates biofilm formation by counteracting curli-mediated colonization of solid surfaces in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 154(Part 7):2017–2024. 10.1099/mic.0.2008/018093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Brombacher E, Baratto A, Dorel C, Landini P. 2006. Gene expression regulation by the curli activator CsgD protein: modulation of cellulose biosynthesis and control of negative determinants for microbial adhesion. J. Bacteriol. 188:2027–2037. 10.1128/JB.188.6.2027-2037.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ross P, Mayer R, Benziman M. 1991. Cellulose biosynthesis and function in bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 55:35–58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Solano C, Garcia B, Valle J, Berasain C, Ghigo JM, Gamazo C, Lasa I. 2002. Genetic analysis of Salmonella enteritidis biofilm formation: critical role of cellulose. Mol. Microbiol. 43:793–808. 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Weissborn AC, Liu Q, Rumley MK, Kennedy EP. 1994. UTP:alpha-D-glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase of Escherichia coli: isolation and DNA sequence of the galU gene and purification of the enzyme. J. Bacteriol. 176:2611–2618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Taglicht D, Padan E, Schuldiner S. 1991. Overproduction and purification of a functional Na+/H+ antiporter coded by nhaA (ant) from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 266:11289–11294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mao SS, Yu GX, Chalfoun D, Stubbe J. 1992. Characterization of C439SR1, a mutant of Escherichia coli ribonucleotide diphosphate reductase: evidence that C439 is a residue essential for nucleotide reduction and C439SR1 is a protein possessing novel thioredoxin-like activity. Biochemistry 31:9752–9759. 10.1021/bi00155a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lu M, Campbell JL, Boye E, Kleckner N. 1994. SeqA: a negative modulator of replication initiation in E. coli. Cell 77:413–426. 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Waldminghaus T, Skarstad K. 2009. The Escherichia coli SeqA protein. Plasmid 61:141–150. 10.1016/j.plasmid.2009.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sanchez-Torres V, Hu H, Wood TK. 2011. GGDEF proteins YeaI, YedQ, and YfiN reduce early biofilm formation and swimming motility in Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 90:651–658. 10.1007/s00253-010-3074-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Raterman EL, Shapiro DD, Stevens DJ, Schwartz KJ, Welch RA. 2013. Genetic analysis of the role of yfiR in the ability of Escherichia coli CFT073 to control cellular cyclic dimeric GMP levels and to persist in the urinary tract. Infect. Immun. 81:3089–3098. 10.1128/IAI.01396-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Malone JG, Jaeger T, Spangler C, Ritz D, Spang A, Arrieumerlou C, Kaever V, Landmann R, Jenal U. 2010. YfiBNR mediates cyclic di-GMP dependent small colony variant formation and persistence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathog. 6:e1000804. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Malone JG, Jaeger T, Manfredi P, Dotsch A, Blanka A, Bos R, Cornelis GR, Haussler S. 2012. The YfiBNR signal transduction mechanism reveals novel targets for the evolution of persistent Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis airways. PLoS Pathog. 8:e1002760. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zander T, Phadke ND, Bardwell JC. 1998. Disulfide bond catalysts in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 290:59–74. 10.1016/S0076-6879(98)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Allore RJ, Barber BH. 1984. A recommendation for visualizing disulfide bonding by one-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 137:523–527. 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90121-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hadjifrangiskou M, Gu AP, Pinkner JS, Kostakioti M, Zhang EW, Greene SE, Hultgren SJ. 2012. Transposon mutagenesis identifies uropathogenic Escherichia coli biofilm factors. J. Bacteriol. 194:6195–6205. 10.1128/JB.01012-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ueda A, Wood TK. 2009. Connecting quorum sensing, c-di-GMP, pel polysaccharide, and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through tyrosine phosphatase TpbA (PA3885). PLoS Pathog. 5:e1000483. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Girgis HS, Liu Y, Ryu WS, Tavazoie S. 2007. A comprehensive genetic characterization of bacterial motility. PLoS Genet. 3:1644–1660. 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Giddens SR, Jackson RW, Moon CD, Jacobs MA, Zhang XX, Gehrig SM, Rainey PB. 2007. Mutational activation of niche-specific genes provides insight into regulatory networks and bacterial function in a complex environment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104:18247–18252. 10.1073/pnas.0706739104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ren GX, Yan HQ, Zhu H, Guo XP, Sun YC. 2014. HmsC, a periplasmic protein, controls biofilm formation via repression of HmsD, a diguanylate cyclase in Yersinia pestis. Environ. Microbiol. 16:1202–1216. 10.1111/1462-2920.12323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bobrov AG, Kirillina O, Vadyvaloo V, Koestler BJ, Hinz AK, Mack D, Waters CM, Perry RD. 11 March 2014. The Yersinia pestis HmsCDE regulatory system is essential for blockage of the oriental rat flea (Xenopsylla cheopis), a classic plague vector. Environ. Microbiol. 10.1111/1462-2920.12419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Kader A, Simm R, Gerstel U, Morr M, Romling U. 2006. Hierarchical involvement of various GGDEF domain proteins in rdar morphotype development of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 60:602–616. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Weber H, Pesavento C, Possling A, Tischendorf G, Hengge R. 2006. Cyclic-di-GMP-mediated signalling within the sigma(S) network of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 62:1014–1034. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Dailey FE, Berg HC. 1993. Mutants in disulfide bond formation that disrupt flagellar assembly in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90:1043–1047. 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Jacob-Dubuisson F, Pinkner J, Xu Z, Striker R, Padmanhaban A, Hultgren SJ. 1994. PapD chaperone function in pilus biogenesis depends on oxidant and chaperone-like activities of DsbA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 91:11552–11556. 10.1073/pnas.91.24.11552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Miki T, Okada N, Kim Y, Abe A, Danbara H. 2008. DsbA directs efficient expression of outer membrane secretin EscC of the enteropathogenic Escherichia coli type III secretion apparatus. Microb. Pathog. 44:151–158. 10.1016/j.micpath.2007.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wulfing C, Rappuoli R. 1997. Efficient production of heat-labile enterotoxin mutant proteins by overexpression of dsbA in a degP-deficient Escherichia coli strain. Arch. Microbiol. 167:280–283. 10.1007/s002030050444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Heras B, Shouldice SR, Totsika M, Scanlon MJ, Schembri MA, Martin JL. 2009. DSB proteins and bacterial pathogenicity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7:215–225. 10.1038/nrmicro2087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hufnagel DA, Tukel C, Chapman MR. 2013. Disease to dirt: the biology of microbial amyloids. PLoS Pathog. 9:e1003740. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Serra DO, Richter AM, Hengge R. 2013. Cellulose as an architectural element in spatially structured Escherichia coli biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 195:5540–5554. 10.1128/JB.00946-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Meftahi A, Khajavi R, Rashidi A, Sattari M, Yazdanshenas ME, Torabi M. 2010. The effects of cotton gauze coating with microbial cellulose. Cellulose 17:199–204. 10.1007/s10570-009-9377-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Czaja WK, Young DJ, Kawecki M, Brown RM. 2007. The future prospects of microbial cellulose in biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 8:1–12. 10.1021/bm060620d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Lin SP, Calvar IL, Catchmark JM, Liu JR, Demirci A, Cheng KC. 2013. Biosynthesis, production and applications of bacterial cellulose. Cellulose 20:2191–2219. 10.1007/s10570-013-9994-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Cavka A, Guo X, Tang SJ, Winestrand S, Jonsson LJ, Hong F. 2013. Production of bacterial cellulose and enzyme from waste fiber sludge. Biotechnol. Biofuels 6:25. 10.1186/1754-6834-6-25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Thompson DN, Hamilton MA. 2001. Production of bacterial cellulose from alternate feedstocks. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 91–93:503–513. 10.1385/ABAB:91-93:1-9:503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Mulvey MA, Schilling JD, Hultgren SJ. 2001. Establishment of a persistent Escherichia coli reservoir during the acute phase of a bladder infection. Infect. Immun. 69:4572–4579. 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4572-4579.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.