Abstract
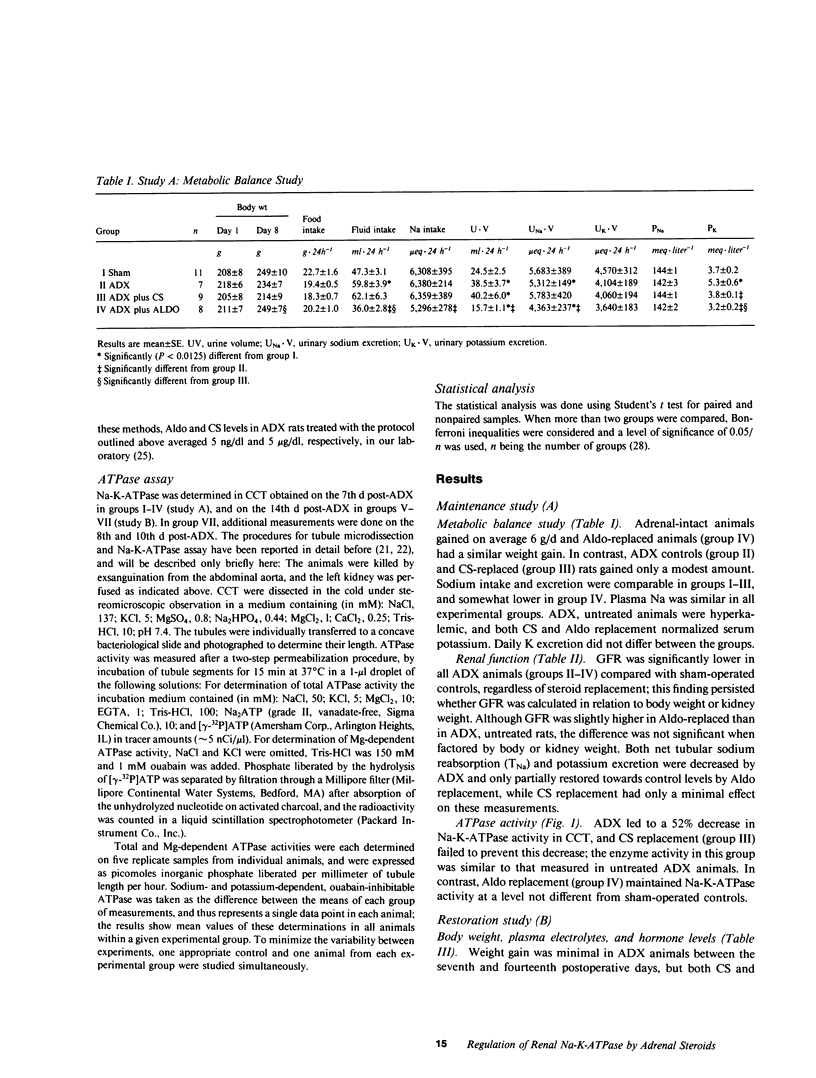
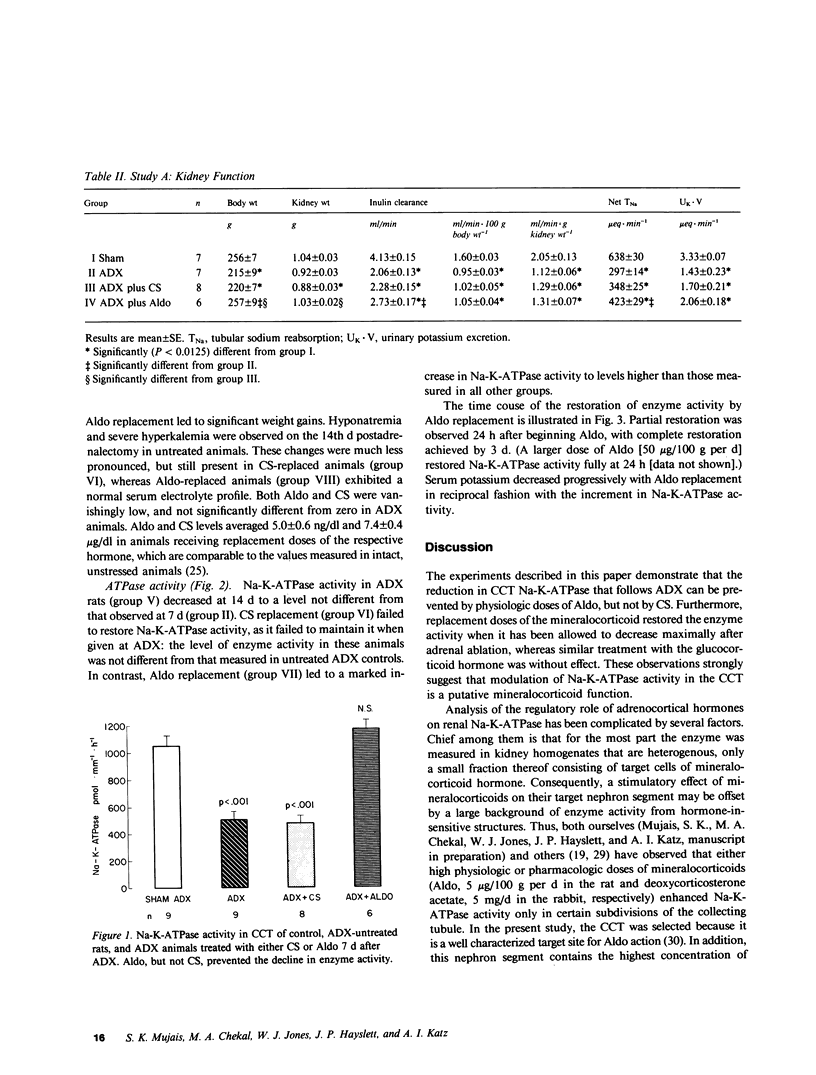
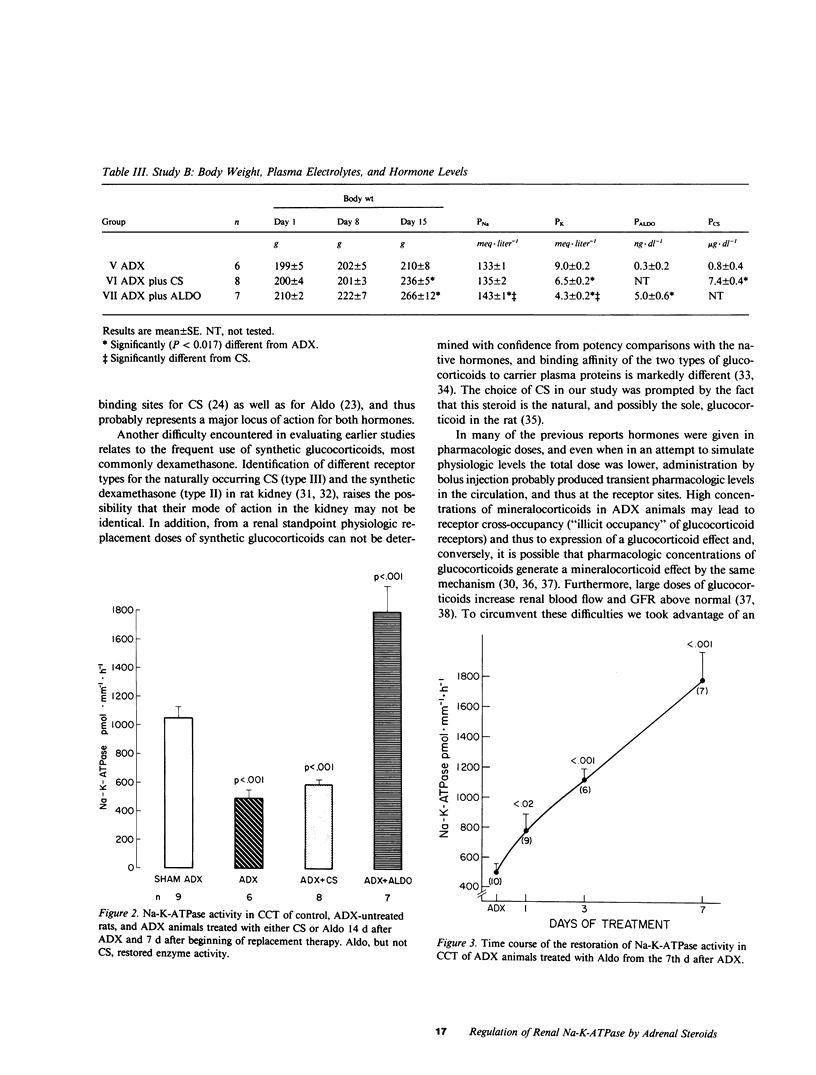
Both mineralo- and glucocorticoids stimulate renal Na-K-ATPase, but their relative role in the regulation of the enzyme remains controversial. In this study we measured Na-K-ATPase activity in the cortical collecting tubule (CCT) of adrenalectomized rats replaced with either the native mineralocorticoid (aldosterone) or glucocorticoid (corticosterone) in doses calculated to yield previously determined physiologic concentrations of these hormones (5 ng X dl-1 and 5 micrograms X dl-1, respectively). This was achieved by continuous delivery of aldosterone (1 microgram X 100 g-1 X d-1) from an osmotic minipump or of corticosterone (2 pellets of 20 mg each), implanted subcutaneously either at adrenalectomy or 7 d later, when Na-K-ATPase activity reached its nadir. Adrenalectomized rats not receiving hormone replacement and adrenal-intact animals served as controls. The CCT was chosen because it contains the highest concentration of binding sites for both hormones. Na-K-ATPase activity declined 52% in the CCT of untreated adrenalectomized rats after 7 d, and remained unchanged thereafter. Physiologic replacement doses of aldosterone prevented this decline and restored the activity of the enzyme after it had been allowed to decrease maximally following adrenal ablation, whereas similar replacement of corticosterone was without effect. These observations suggest that under physiologic conditions Na-K-ATPase in the CCT, a probable target nephron segment of both hormones, is under mineralocorticoid rather than glucocorticoid control.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borsch-Galetke E., Dransfeld H., Greeff K. Specific activity and sensitivity of strophanthin of the Na + +K + -activated ATPase in rats and guinea-pigs with hypoadrenalism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;274(1):74–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00501008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney A. N., Silva P., Besarab A., Epstein F. H. Separate effects of aldosterone, DOCA, and methylprednisolone on renal Na-K-ATPase,. Am J Physiol. 1974 Aug;227(2):345–350. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chignell C. F., Titus E. Effect of adrenal steroids on a Na+- and K+-requiring adenosine triphosphatase from rat kidney. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 10;241(21):5083–5089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBermudez L., Hayslett J. P. Effect of methylprednisolone on renal function and the zonal distribution of blood flow in the rat. Circ Res. 1972 Jul;31(1):44–52. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet A., Katz A. I. Mineralcorticoid receptors along the nephron: [3H]aldosterone binding in rabbit tubules. Am J Physiol. 1981 Dec;241(6):F605–F611. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.6.F605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet A., Katz A. I., Morel F. Determination of Na-K-ATPase activity in single segments of the mammalian nephron. Am J Physiol. 1979 Aug;237(2):F105–F113. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.237.2.F105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet A., Katz A. I. Short-term effect of aldosterone on Na-K-ATPase in single nephron segments. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):F273–F278. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.3.F273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman I. S. Receptors and effectors in hormone action on the kidney. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F333–F339. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman D., Funder J. W., Edelman I. S. Evidence for a new class of corticosterone receptors in the rat kidney. Endocrinology. 1973 May;92(5):1429–1441. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-5-1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funder J. W., Feldman D., Edelman I. S. Glucocorticoid receptors in rat kidney: the binding of tritiated-dexamethasone. Endocrinology. 1973 Apr;92(4):1005–1013. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-4-1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gala R. R., Westphal U. Corticosteroid-binding globulin in the rat: studies on the sex difference. Endocrinology. 1965 Nov;77(5):841–851. doi: 10.1210/endo-77-5-841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Knepper M. A., Burg M. B. Mineralocorticoid effects on Na-K-ATPase in individual nephron segments. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):F536–F544. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.6.F536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendler E. D., Torretti J., Kupor L., Epstein F. H. Effects of adrenalectomy and hormone replacement on Na- K-ATPase in renal tissue. Am J Physiol. 1972 Mar;222(3):754–760. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.3.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horster M., Schmid H., Schmidt U. Aldosterone in vitro restores nephron Na-K-ATPase of distal segments from adrenalectomized rabbits. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Apr;384(3):203–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00584554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Regulation of the (Na+ + K+)-activated ATP hydrolyzing enzyme system in rat kidney. I. The effect of adrenalectomy and the supply of sodium on the enzyme system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 8;151(1):212–224. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Regulation of the (Na+ equals K+)-activated ATP hydrolyzing enzyme system in rat kidney. II. The effect of aldosterone on the activity in kidneys of adrenalectomized rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 18;192(2):326–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. I., Doucet A., Morel F. Na-K-ATPase activity along the rabbit, rat, and mouse nephron. Am J Physiol. 1979 Aug;237(2):F114–F120. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.237.2.F114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. I., Epstein F. H. The role of sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase in the reabsorption of sodium by the kidney. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1999–2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI105689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. I. Renal Na-K-ATPase: its role in tubular sodium and potassium transport. Am J Physiol. 1982 Mar;242(3):F207–F219. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.3.F207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox W. H., Sen A. K. Mechanism of action of aldosterone with particular reference to (Na plus K)-ATPase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;242(0):471–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb19111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDDLE G. W. Effects of anti-inflammatory steroids on electrolvte metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Oct 14;82:854–867. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb44967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landon E. J., Jazab N., Forte L. Aldosterone and sodium-potassium-dependent ATPase activity of rat kidney membranes. Am J Physiol. 1966 Oct;211(4):1050–1056. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.4.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Hir M., Kaissling B., Dubach U. C. Distal tubular segments of the rabbit kidney after adaptation to altered Na- and K-intake. II. Changes in Na-K-ATPase activity. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;224(3):493–504. doi: 10.1007/BF00213747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. M., Chekal M. A., Katz A. I. Corticosterone binding sites along the rat nephron. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):F504–F509. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.5.F504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. S., Jones W. J., Hayslett J. P. Animal model to study the effect of adrenal hormones on epithelial function. Kidney Int. 1983 Sep;24(3):386–391. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marver D., Kokko J. P. Renal target sites and the mechanism of action of aldosterone. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1983 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. E. Some studies of the protein-binding of steroids and their application to the routine micro and ultramicro measurement of various steroids in body fluids by competitive protein-binding radioassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Jul;27(7):973–990. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-7-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peets E. A., Staub M., Symchowicz S. Plasma binding of betamethasone-3H, dexamethasone-3H, and cortisol-14C--a comparative study. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Jul;18(7):1655–1663. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90153-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty K. J., Kokko J. P., Marver D. Secondary effect of aldosterone on Na-KATPase activity in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1514–1521. doi: 10.1172/JCI110405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayson B. M., Edelman I. S. Glucocorticoid stimulation of Na-K-ATPase in superfused distal segments of kidney tubules in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):F463–F470. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.5.F463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez H. J., Sinha S. K., Starling J., Klahr S. Regulation of renal Na+-K+-ATPase in the rat by adrenal steroids. Am J Physiol. 1981 Aug;241(2):F186–F195. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.2.F186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt U., Dubach U. C. Sensitivity of Na K adenosine triphosphatase activity in various structures of the rat nephron: studies with adrenalectomy. Eur J Clin Invest. 1971 May;1(5):307–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1971.tb00636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt U., Schmid J., Schmid H., Dubach U. C. Sodium- and potassium-activated ATPase. A possible target of aldosterone. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):655–660. doi: 10.1172/JCI107973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha S. K., Rodriguez H. J., Hogan W. C., Klahr S. Mechanisms of activation of renal (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in the rat. Effects of acute and chronic administration of dexamethasone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 20;641(1):20–35. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90566-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Ogawa E. Experimental studies on the carbonic anhydrase activity. XII. Effect of adrenocorticosteroids on carbonic anhydrase and Na+-K+-activated adenosine triphosphatase from kidney of adrenalectomized mice and rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 May;18(5):993–1003. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


