Abstract
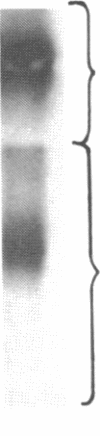
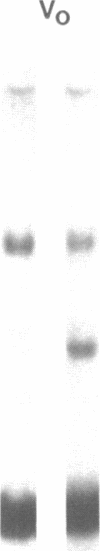
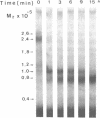
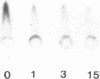
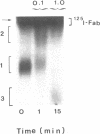
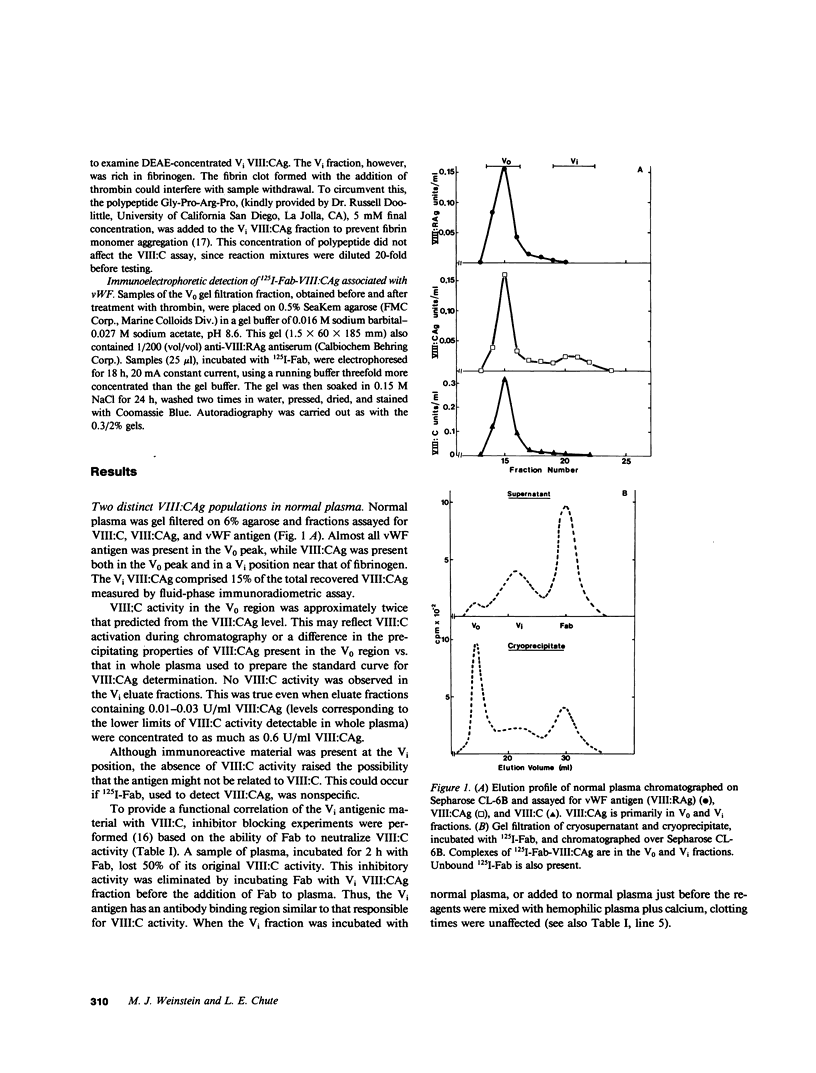
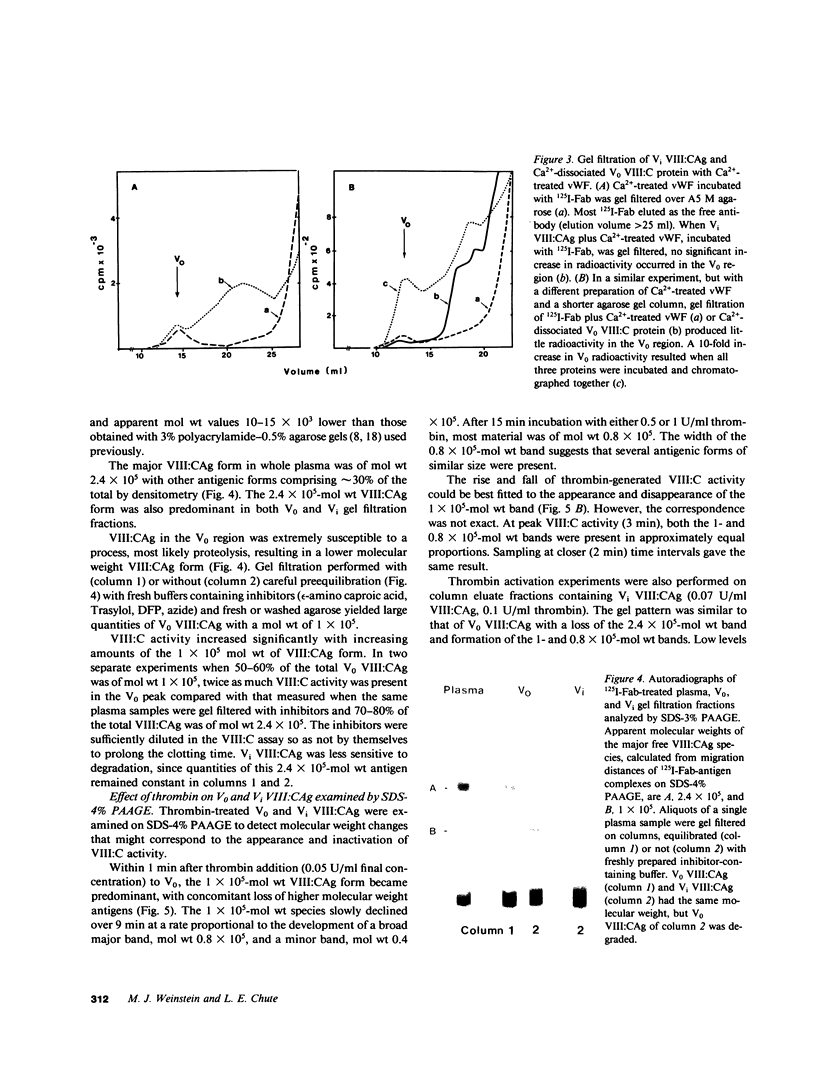
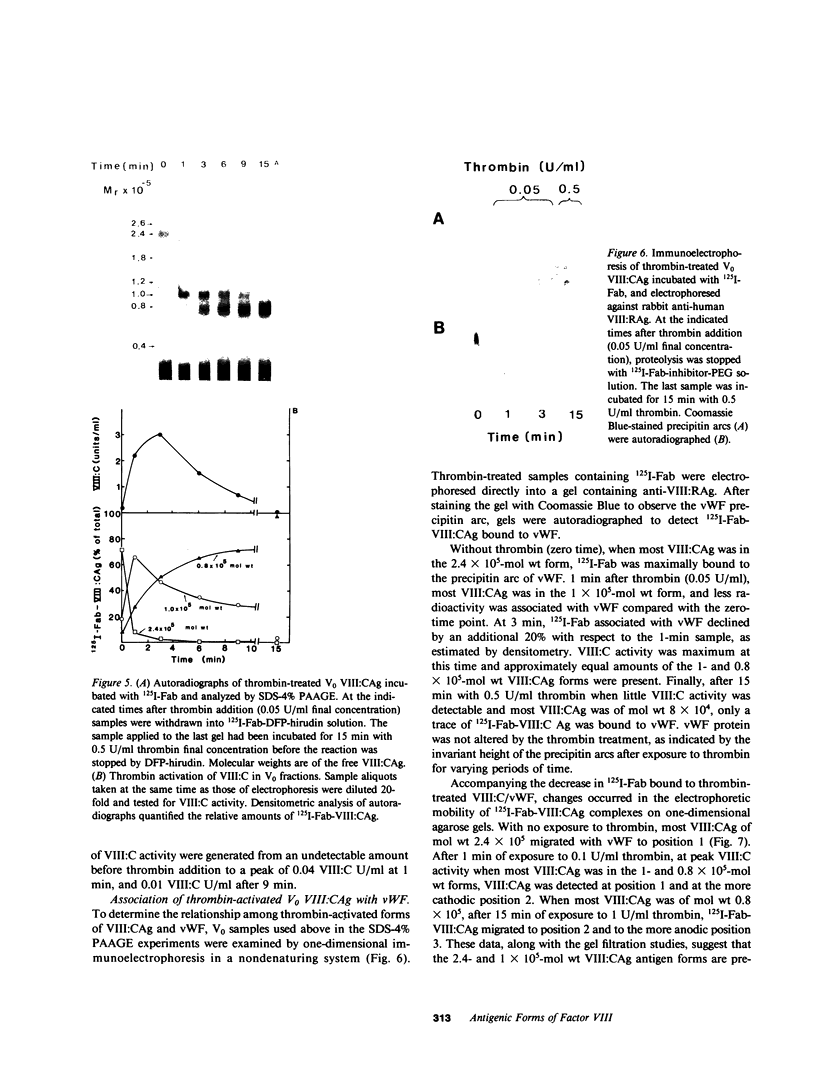
We have characterized Factor VIII coagulant protein, present in normal human plasma, that reacts with a specific human 125I-labeled anti-human VIII:C antigen Fab antibody fragment. Two major Factor VIII coagulant antigen populations were present. The first, approximately 85% of the total antigen, was bound to von Willebrand factor and when tested in a standard one-stage assay had Factor VIII coagulant activity. The second antigenic population, eluting near fibrinogen when plasma was gel filtered, was not bound to von Willebrand protein, did not have Factor VIII coagulant activity unless activated, but did block anti-VIII:C Fab neutralization of clotting activity. The two antigenic populations were separable by cryoprecipitation and agarose gel electrophoresis. Although the two antigenic populations differed in their Factor VIII coagulant activity and in their binding to von Willebrand factor, the principal member of both populations is of mol wt 2.4 X 10(5). Both antigens, when proteolyzed by thrombin, were quickly converted to a 1 X 10(5)-mol wt form in association with the appearance of VIII:C activity. The 1 X 10(5)-mol wt antigen was further slowly degraded to an 8 X 10(4)-mol wt form while Factor VIII coagulant activity declined. These results demonstrate the presence of an inactive Factor VIII coagulant protein in plasma, not associated with von Willebrand factor, that can react with thrombin to yield Factor VIII coagulant activity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H. The defect in hemophilic and von Willebrand's disease plasmas studied by a recombination technique. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1093–1099. doi: 10.1172/JCI107853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counts R. B. Solid-phase immunoradiometric assay of factor-VIII protein. Br J Haematol. 1975 Dec;31(4):429–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B. L., Furlong R. A., Peake I. R. Studies on the relationship between factor VIII related antigen (VIIIRAg) and factor VIII clotting antigen (VIIICAg) by immunoelectrophoresis and autoradiography using 125I anti VIIICAg. Thromb Res. 1981 Apr 1;22(1-2):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P. J., Chavin S. I., Schroeder D., Young F. E., Marder V. J. Purification and characterization of a highly purified human factor VIII consisting of a single type of polypeptide chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7200–7204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Roberts J. R., Zimmerman T. S. Thrombin proteolysis of purified factor viii procoagulant protein: correlation of activation with generation of a specific polypeptide. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Zimmerman T. S. Characterization of the human factor VIII procoagulant protein with a heterologous precipitating antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Zimmerman T. S. Characterization of the human factor VIII procoagulant protein with a heterologous precipitating antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Trabold N. C. The effect of thrombin on human factor VIII. Cleavage of the factor VIII procoagulant protein during activation. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jan;97(1):50–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin M. B., Jesty J. The activation and inactivation of human factor VIII by thrombin: effect of inhibitors of thrombin. Blood. 1981 Mar;57(3):476–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudano A. P., Doolittle R. F. Studies on synthetic peptides that bind to fibrinogen and prevent fibrin polymerization. Structural requirements, number of binding sites, and species differences. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):1013–1019. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laura R., Robison D. J., Bing D. H. (p-Amidinophenyl)methanesulfonyl fluoride, an irreversible inhibitor of serine proteases. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4859–4864. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarchick J., Hoyer L. W. Immunoradiometric measurement of the factor VIII procoagulant antigen. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1048–1052. doi: 10.1172/JCI109209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarchick J., Hoyer L. W. The properties of immune complexes formed by human antibodies to factor VIII. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1070–1079. doi: 10.1172/JCI108858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Weinstein M. J., Troll J. H., Chute L. E., Colannino N. M. Direct radioimmune detection in human plasma of the association between factor VIII procoagulant protein and von Willebrand factor, and the interaction of von Willebrand factor-bound procoagulant VIII with platelets. Blood. 1983 Jun;61(6):1163–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Wagner R. H. Antihemophilic factor: separation of an active fragment following dissociation by salts or detergents. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Jul 31;27(3):502–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPAPORT S. I., SCHIFFMAN S., PATCH M. J., AMES S. B. The importance of activation of antihemophilic globulin and proaccelerin by traces of thrombin in the generation of intrinsic prothrombinase activity. Blood. 1963 Feb;21:221–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick M. E., Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). V. Immunologic properties of AHF subunits produced by salt dissociation. Blood. 1973 Nov;42(5):737–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotblat F., Tuddenham E. G. Immunologic studies of factor VIII coagulant activity (VIII:C) 1. Assays based on a haemophilic and an acquired antibody to VIII:C. 1981 Feb 15-Mar 1Thromb Res. 21(4-5):431–445. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Reactions of thrombin with human factor VIII/von Willebrande factor protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10606–10611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. Is there a precursive, relatively procoagulant-inactive form of normal antihemophilic factor (factor VIII)? Blood. 1979 Oct;54(4):916–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Davie E. W. Preparation and properties of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):401–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. J., Fulcher C. A., Chute L. E., Zimmerman T. S. Apparent molecular weight of purified human factor VIII procoagulant protein compared with purified and plasma factor VIII procoagulant protein antigen. Blood. 1983 Nov;62(5):1114–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M., Chute L., Deykin D. Analysis of factor VIII coagulant antigen in normal, thrombin-treated, and hemophilic plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5137–5141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M., Deykin D. Comparison of factor VIII-related von Willebrand factor proteins prepared from human cryoprecipitate and factor VIII concentrate. Blood. 1979 Jun;53(6):1095–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Baumgartner H. R., Tschopp T. B., Turitto V. T., Cohen D. Correction by factor VIII of the impaired platelet adhesion to subendothelium in von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1978 Feb;51(2):267–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Kochwa S. Molecular forms of antihaemophilic globulin in plasma, cryoprecipitate and after thrombin activation. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jan;18(1):89–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Sussman I. I., Hoyer L. W. Stabilization of factor VIII in plasma by the von Willebrand factor. Studies on posttransfusion and dissociated factor VIII and in patients with von Willebrand's disease. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):390–404. doi: 10.1172/JCI108788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., de la Pointe L., Edgington T. S. Interaction of factor VIII antigen in hemophilic plasmas with human antibodies to factor VIII. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):984–989. doi: 10.1172/JCI108721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Soberano M. E., Johnson A. J., Fulton A. J., Kowalski S., Adler M. The in vitro association of antihemophilic factor and von Willebrand factor. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Feb 28;49(1):37–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]