Abstract
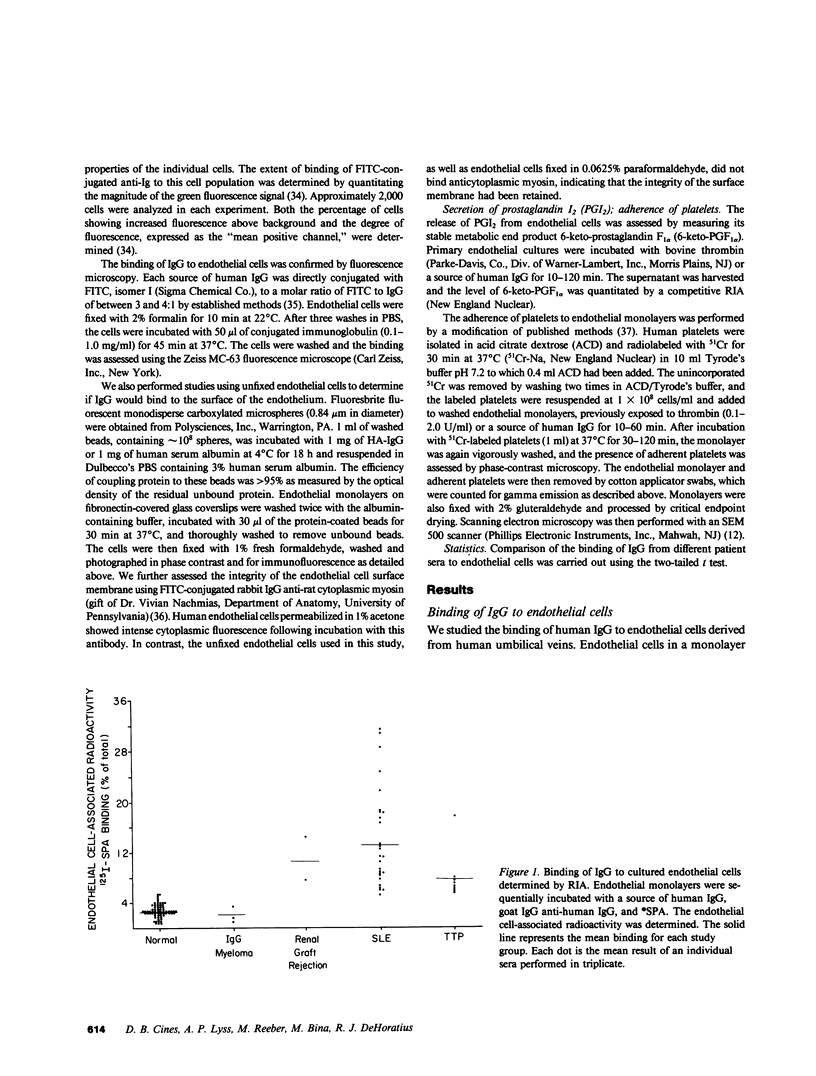
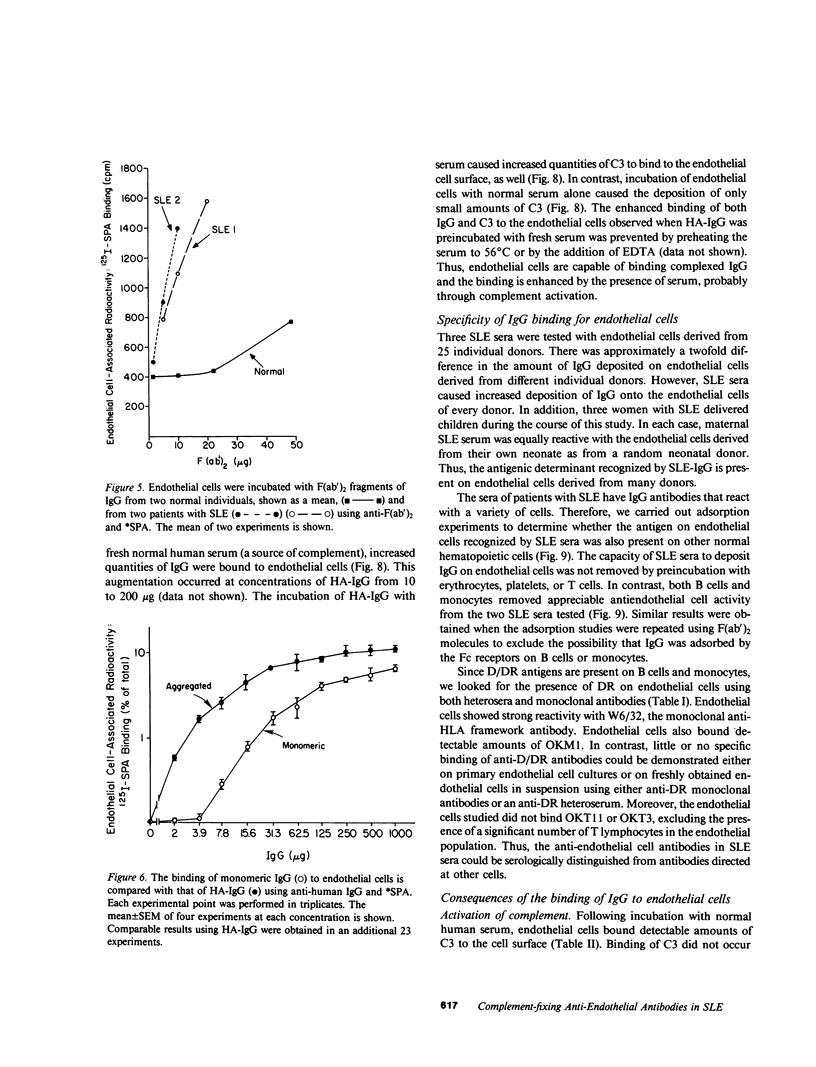
Vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is associated with the deposition of IgG and complement in blood vessel walls. However, it is not known whether immune injury to endothelial cells is a part of this process. Therefore, we used a solid phase radioimmunoassay to study the ability of IgG from normal human sera and sera from patients with SLE to bind to endothelial cells. In this assay, cultured human umbilical venous endothelial cells were sequentially incubated with normal or SLE sera, goat anti-human IgG, and 125I-labeled staphylococcal protein A (*SPA). After exposure to normal sera, 2.5 +/- 0.5% (mean +/- SD) of the added *SPA bound to the cells, whereas after exposure to SLE sera 13.8 +/- 7.6% of the added *SPA bound to these cells. This difference in binding was highly significant (P less than 0.001). Binding was partially reduced when SLE sera were preincubated with B-lymphocytes or monocytes, but not after exposure to erythrocytes, platelets, or T lymphocytes. Incubation of endothelial cells with the 7S fraction of SLE sera or with the F(ab')2 fragment of SLE-IgG resulted in the deposition of greater than 80% as much IgG as was deposited on endothelial cells by whole serum. However, since higher molecular weight fractions (greater than 7S) of SLE sera were also active, we tested the capacity of endothelial cells to bind IgG complexes. Endothelial cells bound heat-aggregated IgG (HA-IgG) in a saturable manner at one log concentration below the binding of normal monomeric IgG. Binding of HA-IgG to endothelial cells was markedly enhanced by preincubation with a serum source of complement. Both HA-IgG and SLE-IgG also bound to freshly obtained endothelial cells in suspension, as detected by automated fluorescence flow cytometry. Binding of SLE-IgG and HA-IgG to endothelium initiated complement activation, deposition of the third component of complement, and disruption of the monolayer. In addition, SLE-IgG and HA-IgG caused endothelial cells to secrete prostacyclin and caused the adherence of platelets, confirmed by scanning electron microscopy. These studies demonstrate that IgG anti-endothelial antibodies are present in the sera of patients with active SLE. These sera may also contain IgG complexes that are capable of binding to endothelial cells. The association of IgG and complement with endothelial cells may initiate vascular injury in SLE and other human disorders.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. S., Shadforth M., Cunningham P., Davis J. S., 4th Demonstration of a C1q receptor on the surface of human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1075–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. S., Hoxie J. A., Leitman S. F., Vilaire G., Cines D. B. Inhibition of fibrinogen binding to stimulated human platelets by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2417–2421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F. M., Quarfoot A. J., Chediak J., Stemerman M. B., Maciag T. Characterization and properties of cultured human von Willebrand umbilical vein endothelial cells. Blood. 1981 Oct;58(4):788–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns E. R., Zucker-Franklin D. Pathologic effects of plasma from patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura on platelets and cultured vascular endothelial cells. Blood. 1982 Oct;60(4):1030–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerilli J., Brasile L. Endothelial cell alloantigens. Transplant Proc. 1980 Sep;12(3 Suppl 1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cines D. B., Lyss A. P., Bina M., Corkey R., Kefalides N. A., Friedman H. M. Fc and C3 receptors induced by herpes simplex virus on cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):123–128. doi: 10.1172/JCI110422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cines D. B., Schreiber A. D. Immune thrombocytopenia. Use of a Coombs antiglobulin test to detect IgG and C3 on platelets. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 18;300(3):106–111. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901183000302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G. Mechanisms involved in the deposition of immune complexes in tissues. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):75s–89s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czervionke R. L., Hoak J. C., Fry G. L. Effect of aspirin on thrombin-induced adherence of platelets to cultured cells from the blood vessel wall. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):847–856. doi: 10.1172/JCI109197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHoratius R. J., Tung K. S., Pincus T. Reduced T-lymphocyte subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus: effects of immune complexes and lymphocytotoxic antibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Oct;17(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Mihm M. C., Jr, Dvorak A. M., Barnes B. A., Manseau E. J., Galli S. J. Rejection of first-set skin allografts in man. the microvasculature is the critical target of the immune response. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):322–337. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Haynes B., Katz P. The spectrum of vasculitis: clinical, pathologic, immunologic and therapeutic considerations. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Nov;89(5 Pt 1):660–676. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-5-660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillit H. M., Jaffe E. A., Zabriskie J. B. In vitro correlates of endothelial injury and repair. Lab Invest. 1982 Jan;46(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Folkman J. Human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Growth and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1974 Mar;60(3):673–684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Björnheden T., Bylock A., Bondjers G. Fc-dependent binding of monocytes to areas with endothelial injury in the rabbit aorta. Exp Mol Pathol. 1981 Jun;34(3):264–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(81)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg H., Bergh O. J., Thorsby E. Antigen-presenting properties of human vascular endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2 Pt 2):249s–255s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg H., Moen T., Throsby E. Specific destruction of human endothelial cell monolayers by anti-DRw antisera. Transplantation. 1979 Aug;28(2):116–120. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197908000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip S. H., Rittershaus C. W., Struzziero C. C., Hoxie J. A., Hoffman R. A., Healey K. W., Lifter J. Evaluation of E-rosetting human lymphocytes with OKT11 and other monoclonal antibodies. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):795–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurlander R. J. Reversible and irreversible loss of Fc receptor function of human monocytes as a consequence of interaction with immunoglobulin G. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):773–781. doi: 10.1172/JCI109915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauterburg W., Ryffel B., Buerki H., Hess M. W., Cottier H., Stoner R. D. Increased lymphocyte load of postcapillary venules in regional lymph nodes following stimulation with antigen -- isologous antibody complexes as compared with antigen alone. Blood Cells. 1980;6(1):41–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder E. Binding of C1q and complement activation by vascular endothelium. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):648–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder E., Hormia M., Lehto V. P., Törnroth T. Identification of cytoskeletal intermediate filaments of vascular endothelial cells as targets for autoantibodies in patient sera. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Nov;21(2):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist K. J., Osterland C. K. Human antibodies to vascular endothelium. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Dec;9(6):753–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Cerundolo J., Ilsley S., Kelley P. R., Forand R. An endothelial cell growth factor from bovine hypothalamus: identification and partial characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5674–5678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moraes J. R., Stastny P. A new antigen system expressed in human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):449–454. doi: 10.1172/JCI108795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., WISSLER F. C., LIPMAN L. N., WOERNLEY D. L. Separation of univalent fragments from the bivalent rabbit antibody molecule by reduction of disulfide bonds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Aug;89:230–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez G., Ball E. J., Stastny P. Accessory cell function of human endothelial cells. I. A subpopulation of Ia positive cells is required for antigen presentation. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):666–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okudaira K., Searles R. P., Ceuppens J. L., Goodwin J. S., Williams R. C., Jr Anti-Ia reactivity in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):17–24. doi: 10.1172/JCI110428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul L. C., Carpenter C. B. Antibodies against renal endothelial alloantigens. Transplant Proc. 1980 Sep;12(3 Suppl 1):43–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul L. C., van Es L. A., Baldwin W. M., 3rd Antigens in human renal allografts. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 May;19(2):206–223. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S., Dierich M. P., Reisfeld R. A. Enhancement of sheep red blood cell human lymphocyte rosette formation by the sulfhydryl compound 2-amino ethylisothiouronium bromide. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Jan;3(3):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Reiss C. S., Burakoff S. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A. Ia expression by vascular endothelium is inducible by activated T cells and by human gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1983 Apr 1;157(4):1339–1353. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Expression of Ia-like antigens by human vascular endothelial cells is inducible in vitro: demonstration by monoclonal antibody binding and immunoprecipitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6641–6645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Del Vecchio P. J., Ryan J. W. Endothelial cells of bovine pulmonary artery lack receptors for C3b and for the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G. Science. 1980 May 16;208(4445):748–749. doi: 10.1126/science.7367890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Ruan J. W. Fc and C3b receptors on pulmonary endothelial cells: induction by injury. Science. 1981 Oct 30;214(4520):557–558. doi: 10.1126/science.6270789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Reeves J. P., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Complement-dependent immunoglobulin M anti-thymus-derived cell antibodies preferentially inactivate suppressor cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):954–965. doi: 10.1172/JCI109396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Brandtzaeg P., Hirschberg H., Solheim B. G., Thorsby E. Vascular and renal distribution of HLA--DR-like antigens. Tissue Antigens. 1981 Sep;18(3):195–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1981.tb01382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingu M., Hashimoto Y., Johnson A. R., Hurd E. R. The search for Fc receptors on human tissues and human endothelial cells in culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1981 Jun;167(2):147–155. doi: 10.3181/00379727-167-41140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingu M., Hurd E. R. Sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus reactive with human endothelial cells. J Rheumatol. 1981 Jul-Aug;8(4):581–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordat B., Hess M. W., Cottier H. IgG immunoglobulin in the wall of post-capillary venules: possible relationship to lymphocyte recirculation. Immunology. 1971 Jan;20(1):115–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkebaum G., Price T. H., Lee M. Y., Arend W. P. Autoimmune neutropenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jun;21(5):504–512. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens S. K., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. Differences in the migration of B and T lymphocytes: organ-selective localization in vivo and the role of lymphocyte-endothelial cell recognition. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):844–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr Antibodies in systemic lupus--diversity finally simplified. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Aug;100(2):161–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Rao P. E., Van Voorhis W. C., Craigmyle L. S., Iida K., Talle M. A., Westberg E. F., Goldstein G., Silverstein S. C. Identification of the C3bi receptor of human monocytes and macrophages by using monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5699–5703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B., Behnke O. Membrane structure of nonactivated and activated human blood platelets as revealed by freeze-fracture: evidence for particle redistribution during platelet contraction. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):209–218. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









