Abstract
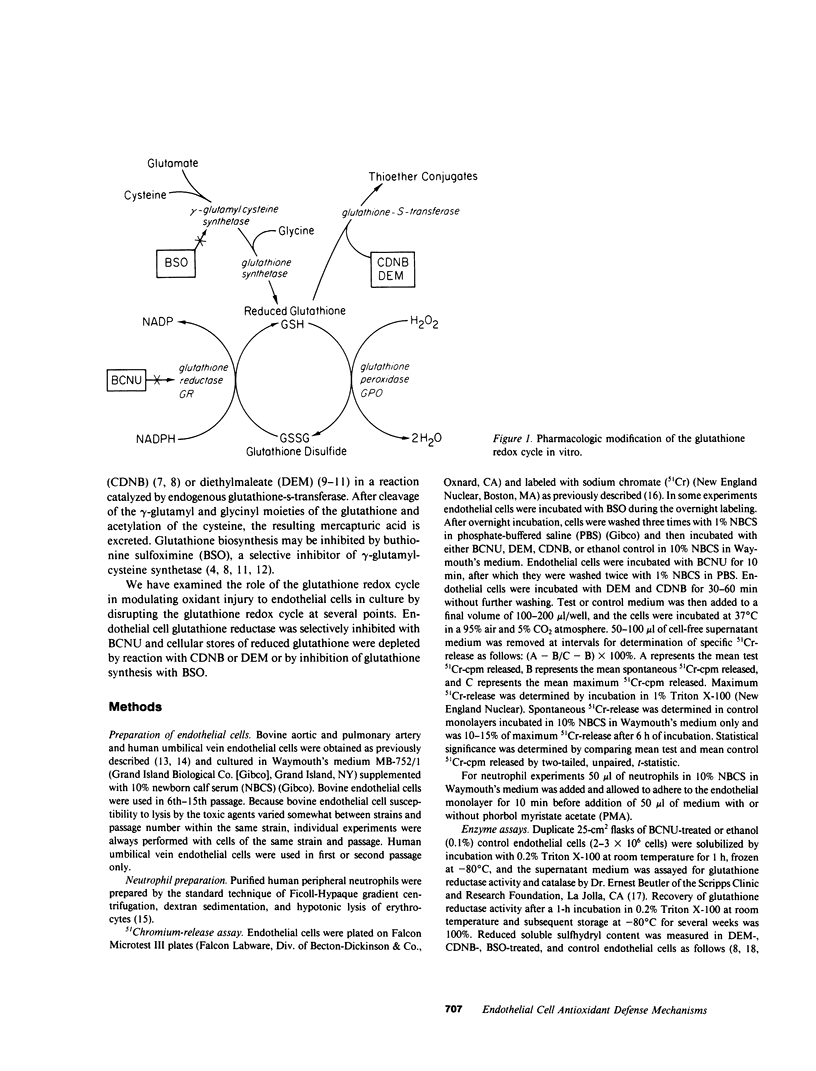
We have examined the role of the glutathione redox cycle as an antioxidant defense mechanism in cultured bovine and human endothelial cells by disrupting the glutathione redox cycle at several points. Endothelial glutathione reductase was selectively inhibited with 1,3-bis(chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea (BCNU). Cellular stores of reduced glutathione were depleted by reaction with diethylmaleate (DEM) or 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB) or by inhibition of glutathione synthesis with buthionine sulfoximine (BSO). Whereas several strains of untreated bovine and human endothelial cells were resistant to lysis by enzymatically generated hydrogen peroxide, BCNU-treated cells were readily lysed in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Glucose-glucose oxidase-mediated lysis of BCNU-treated bovine endothelial cells was catalase-inhibitable and directly related to BCNU concentration and endogenous glutathione reductase activity. Pretreatment of bovine endothelial cells with BCNU did not potentiate lysis by distilled water, calcium ionophore, lipopolysaccharide, or hypochlorous acid. Depletion of cellular reduced glutathione by reaction with DEM or CDNB or by inhibition of glutathione synthesis by BSO also potentiated endothelial lysis by enzymatically generated hydrogen peroxide. Inhibition of endothelial glutathione reductase by BCNU or depletion of reduced glutathione by BSO increased endothelial susceptibility to lysis by hydrogen peroxide generated by phorbol myristate acetate-activated neutrophils. We conclude that the glutathione redox cycle plays an important role as an endogenous antioxidant defense mechanism in cultured endothelial cells.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrick B. A., Nathan C. F., Griffith O. W., Cohn Z. A. Glutathione depletion sensitizes tumor cells to oxidative cytolysis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1231–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEUTLER E., DURON O., KELLY B. M. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 May;61:882–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babson J. R., Reed D. J. Inactivation of glutathione reductase by 2-chloroethyl nitrosourea-derived isocyanates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jul 28;83(2):754–762. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E. Abnormalities of the hexose monophosphate shunt. Semin Hematol. 1971 Oct;8(4):311–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasseaud L. F. The role of glutathione and glutathione S-transferases in the metabolism of chemical carcinogens and other electrophilic agents. Adv Cancer Res. 1979;29:175–274. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60848-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Summerville J., Massaro D. Potection from oxygen toxicity with endotoxin. Role of the endogenous antioxidant enzymes of the lung. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1104–1110. doi: 10.1172/JCI109763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischer H., Ahmad T. Severe generalized glutathione reductase deficiency after antitumor chemotherapy with BCNU" [1,3-bis(chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea]. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 May;89(5):1080–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Meister A. Potent and specific inhibition of glutathione synthesis by buthionine sulfoximine (S-n-butyl homocysteine sulfoximine). J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7558–7560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Killen P. D., Harker L. A., Striker G. E., Wright D. G. Neutrophil-mediated endothelial injury in vitro mechanisms of cell detachment. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1394–1403. doi: 10.1172/JCI110390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. E., Schultz J. Studies on the chlorinating activity of myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1371–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Oxygen metabolism and the toxic properties of phagocytes. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Sep;93(3):480–489. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-3-480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosower N. S., Kosower E. M. The glutathione status of cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;54:109–160. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A. Selective modification of glutathione metabolism. Science. 1983 Apr 29;220(4596):472–477. doi: 10.1126/science.6836290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson D. S., Metz E. N., Sagone A. L., Jr Effect of phagocytosis on the reduced soluble sulfhydryl content of human granulocytes. Blood. 1977 Dec;50(6):1023–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. B., Russo A., Kinsella T. J., Glatstein E. Glutathione elevation during thermotolerance induction and thermosensitization by glutathione depletion. Cancer Res. 1983 Mar;43(3):987–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Arrick B. A., Murray H. W., DeSantis N. M., Cohn Z. A. Tumor cell anti-oxidant defenses. Inhibition of the glutathione redox cycle enhances macrophage-mediated cytolysis. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):766–782. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Nehring R. E., Jr, Meister A. Inhibition of amino acid transport into lymphoid cells by the glutamine analog L-2-amino-4-oxo-5-chloropentanoate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4932–4935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos D., Weening R. S., Voetman A. A., van Schaik M. L., Bot A. A., Meerhof L. J., Loos J. A. Protection of phagocytic leukocytes by endogenous glutathione: studies in a family with glutathione reductase deficiency. Blood. 1979 May;53(5):851–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M. Selection and characterization of bovine aortic endothelial cells. In Vitro. 1978 Dec;14(12):966–980. doi: 10.1007/BF02616210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Simon L. M. Lung cell oxidant injury. Enhancement of polymorphonuclear leukocyte-mediated cytotoxicity in lung cells exposed to sustained in vitro hyperoxia. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):342–350. doi: 10.1172/JCI110623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt M. T., Thomas C., Vassallo C. L., Basford R. E., Gee J. B. Glutathione-dependent peroxidative metabolism in the alveolar macrophage. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):401–410. doi: 10.1172/JCI106507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R. T., Harker L. A., Quadracci L. J., Striker G. E. Factors influencing endothelial cell proliferation in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Aug;96(2):203–213. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040960209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedner H. J., Simchowitz L., Stenson W. F., Fischman C. M. Inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte function by 2-cyclohexene-1-one. A role for glutathione in cell activation. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):535–543. doi: 10.1172/JCI110285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Young J., LoBuglio A. F., Slivka A., Nimeh N. F. Role of hydrogen peroxide in neutrophil-mediated destruction of cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI110307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


