Abstract
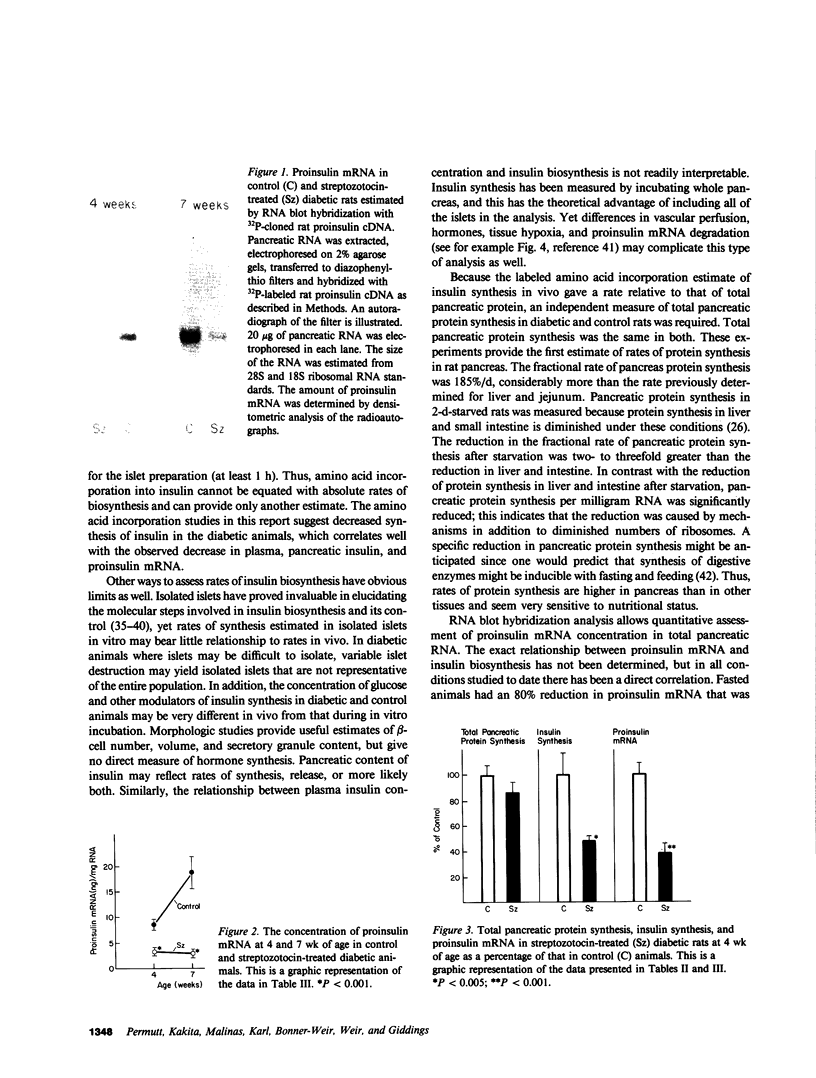
The purpose of these experiments was to estimate insulin biosynthesis in vivo in a rat model for non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Insulin biosynthesis rates were determined in 4-wk-old animals that had been injected with 90 mg/kg of streptozotocin 2 d postpartum. Control and diabetic animals did not differ in body weight or fasting plasma glucose. Fed plasma glucose was significantly elevated (186 +/- 13 micrograms/dl vs. 139 +/- 7 mg/dl, P less than 0.05) and pancreatic insulin content was reduced (41 +/- 2 micrograms/g vs. 63 +/- 8 micrograms/g, P less than 0.05) in the diabetic rats. Insulin biosynthesis was estimated in vivo by measuring and comparing [3H]leucine incorporation into proinsulin with that into total pancreatic protein 45 min after injection. Insulin biosynthesis was 0.391 +/- 0.07% of pancreas protein synthesized in control rats and 0.188 +/- 0.015% (P less than 0.05) in diabetic rats. In animals of the same age, the fractional and absolute rate of pancreatic protein synthesis were determined. Total pancreatic protein synthesis was not reduced in streptozotocin treated animals (185.5 +/- 14.1%/d vs. 158.6 +/- 14.9%/d, NS) but was markedly reduced in control rats after a 48-h fast (to 70.8 +/- 5.5%/d, P less than 0.01). Because total pancreatic protein synthesis was not decreased in the diabetic rats, the decrease in the fraction of radiolabel incorporated into insulin seems to represent an absolute decrease in the rate of insulin biosynthesis in this animal model for diabetes. Through RNA blot hybridization with 32P-labeled cloned rat insulin complementary DNA, proinsulin messenger RNA (mRNA) was estimated as the rate of insulin biosynthesis in control and diabetic animals. There was a 61% reduction in proinsulin mRNA at 4 wk and an 85% reduction at 7 wk (P less than 0.001) in the diabetic animals. After streptozotocin injection in neonatal rats, there is marked beta-cell damage and hyperglycemia. Beta-cell regeneration occurs with return to normoglycemia, but with age hyperglycemia develops. The reduction in insulin synthesis and proinsulin mRNA seemed disproportionate with the more modest reduction in beta-cell number. The importance of these observations is that, in this animal model, diabetes is associated with a limited ability to regenerate beta-cell mass and to synthesize insulin. The relationship between the defect in glucose-stimulated insulin release and impaired insulin biosynthesis has yet to be determined.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaucamp K., Walter H. E. Amino acid determination in the nanomole range by tRNA charging and isotope dilution technique. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 15;38(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80507-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone A. J., Howell S. L. Alterations in regulation of insulin biosynthesis in pregnancy and starvation studied in isolated rat islets of langerhans. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 15;166(3):501–507. doi: 10.1042/bj1660501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner-Weir S., Trent D. F., Honey R. N., Weir G. C. Responses of neonatal rat islets to streptozotocin: limited B-cell regeneration and hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 1981 Jan;30(1):64–69. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunstedt J., Chan S. J. Direct effect of glucose on the preproinsulin mRNA level in isolated pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1383–1389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell B., Diamond D., Smith S., Pünter J., Schöne H. H., Goodman H. M. Disproportionate expression of the two nonallelic rat insulin genes in a pancreatic tumor is due to translational control. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90309-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajans S. S., Cloutier M. C., Crowther R. L. The Banting Memorial Lecture 1978. Clinical and etiologic heterogeneity of idiopathic diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1978 Nov;27(11):1112–1125. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.11.1112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gepts W., Lecompte P. M. The pancreatic islets in diabetes. Am J Med. 1981 Jan;70(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90417-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Chirgwin J., Permutt M. A. Effects of glucose on proinsulin messenger RNA in rats in vivo. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):624–629. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.7.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Chirgwin J., Permutt M. A. The effects of fasting and feeding on preproinsulin messenger RNA in rats. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):952–960. doi: 10.1172/JCI110145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber A. L., Wood F. C., Jr, Williams R. H. Serum immunoreactive insulin response during prolonged glucose infusions in nondiabetic and diabetic humans. Diabetes. 1967 Mar;16(3):145–149. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.3.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halban P. A., Bonner-Weir S., Weir G. C. Elevated proinsulin biosynthesis in vitro from a rat model of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1983 Mar;32(3):277–283. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halter J. B., Graf R. J., Porte D., Jr Potentiation of insulin secretory responses by plasma glucose levels in man: evidence that hyperglycemia in diabetes compensates for imparied glucose potentiation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Jun;48(6):946–954. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-6-946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding J. D., Rutter W. J. Rat pancreatic amylase mRNA. Tissue specificity and accumulation during embryonic development. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8736–8740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakita K., Giddings S. J., Rotwein P. S., Permutt M. A. Insulin gene expression in the developing rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1983 Aug;32(8):691–696. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.8.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakita K., Giddings S., Permutt M. A. Biosynthesis of rat insulins I and II: evidence for differential expression of the two genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2803–2807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. L., Porte D., Jr Acute and steady-state insulin responses to glucose in nonobese diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1624–1631. doi: 10.1172/JCI106963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin B. J., Henderson M. J., Levine B. B., Nagy B. R., Nagy E. M. Effects of iodoacetate and fluoride on islate respiration and insulin biosynthesis. Horm Metab Res. 1976 Sep;8(5):353–358. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logothetopoulos J., Jain K. In vivo incorporation of [3H[ leucine and [3H] tryptophan into proinsulin-insulin and other islet cell proteins in normoglycemic, hyperglycemic, and hypoglycemic rats. Diabetes. 1980 Oct;29(10):801–805. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.10.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEAN N., OGILVIE R. F. Quantitative estimation of the pancreatic islet tissue in diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1955 Sep-Oct;4(5):367–376. doi: 10.2337/diab.4.5.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNurlan M. A., Tomkins A. M., Garlick P. J. The effect of starvation on the rate of protein synthesis in rat liver and small intestine. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):373–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1780373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. E., Korner A. RNA synthesis and the stimulation of insulin biosynthesis by glucose. FEBS Lett. 1970 Oct 5;10(3):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. E., Taylor J. M., Jefferson L. S. Correlation of albumin production rates and albumin mRNA levels in livers of normal, diabetic, and insulin-treated diabetic rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5879–5883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Permutt M. A., Kipnis D. M. Insulin biosynthesis. I. On the mechanism of glucose stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1194–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priestley J. T., Comfort M. W., Radcliffe J. Total Pancreatectomy for Hyperinsulinism Due to an Islet-Cell Adenoma: Survival and Cure at Sixteen MOnths after Operation Presentation of Metabolic Studies. Ann Surg. 1944 Feb;119(2):211–221. doi: 10.1097/00000658-194402000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E., Wright D., Mondon C. E., Solomon R., Ho H., Reaven G. M. Effect of age and diet on insulin secretion and insulin action in the rat. Diabetes. 1983 Feb;32(2):175–180. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J. I., Rimoin D. L. The genetics of the glucose intolerance disorders. Am J Med. 1981 Jan;70(1):116–126. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90418-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan W. G., Schwartz T. B., Nibbe A. F. Serum immunoreactive insulin levels during glucose tolerance and intensive islet stimulation. Diabetes. 1971 Jun;20(6):404–409. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.6.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. A., Fisher A. M. THE INSULIN AND THE ZINC CONTENT OF NORMAL AND DIABETIC PANCREAS. J Clin Invest. 1938 Nov;17(6):725–728. doi: 10.1172/JCI101000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. W., Reaven G. M., Farquhar J. W. Comparison of impedance to insulin-mediated glucose uptake in normal subjects and in subjects with latent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2151–2160. doi: 10.1172/JCI106433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Oyer P. E. The biosynthesis of insulin and a probable precursor of insulin by a human islet cell adenoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):473–480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjioe T. O., Bouman P. R. Effect of fasting on the incorporation of [3H]-L-phenylalanine into proinsulin-insulin and total protein in isolated rat pancreatic islets. Horm Metab Res. 1976 Jul;8(4):261–266. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRENSHALL G. A., BOGOCH A., RITCHIE R. C. Extractable insulin of pancreas; correlation with pathological and clinical findings in diabetic and nondiabetic cases. Diabetes. 1952 Mar-Apr;1(2):87–107. doi: 10.2337/diab.1.2.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. W., Braasch J. W., Thum C. W. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of carcinoma of the pancreas. Curr Probl Surg. 1968 Jun;:3–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir G. C., Clore E. T., Zmachinski C. J., Bonner-Weir S. Islet secretion in a new experimental model for non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1981 Jul;30(7):590–595. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.7.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker P., Logothetopoulos J. Persisting enhanced proinsulin-insulin and protein biosynthesis (3H-leucine incorporation) by pancreatic islets of the rat after glucose exposure. Diabetes. 1975 Feb;24(2):194–200. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.2.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




