Abstract
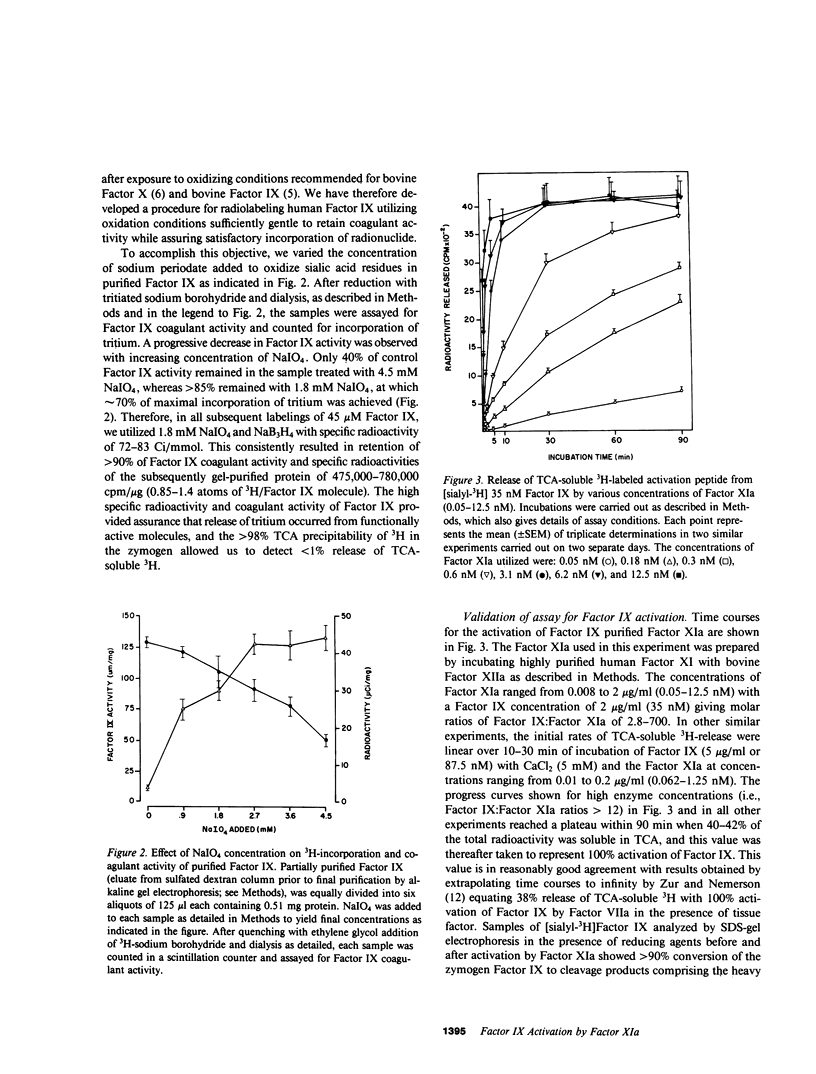
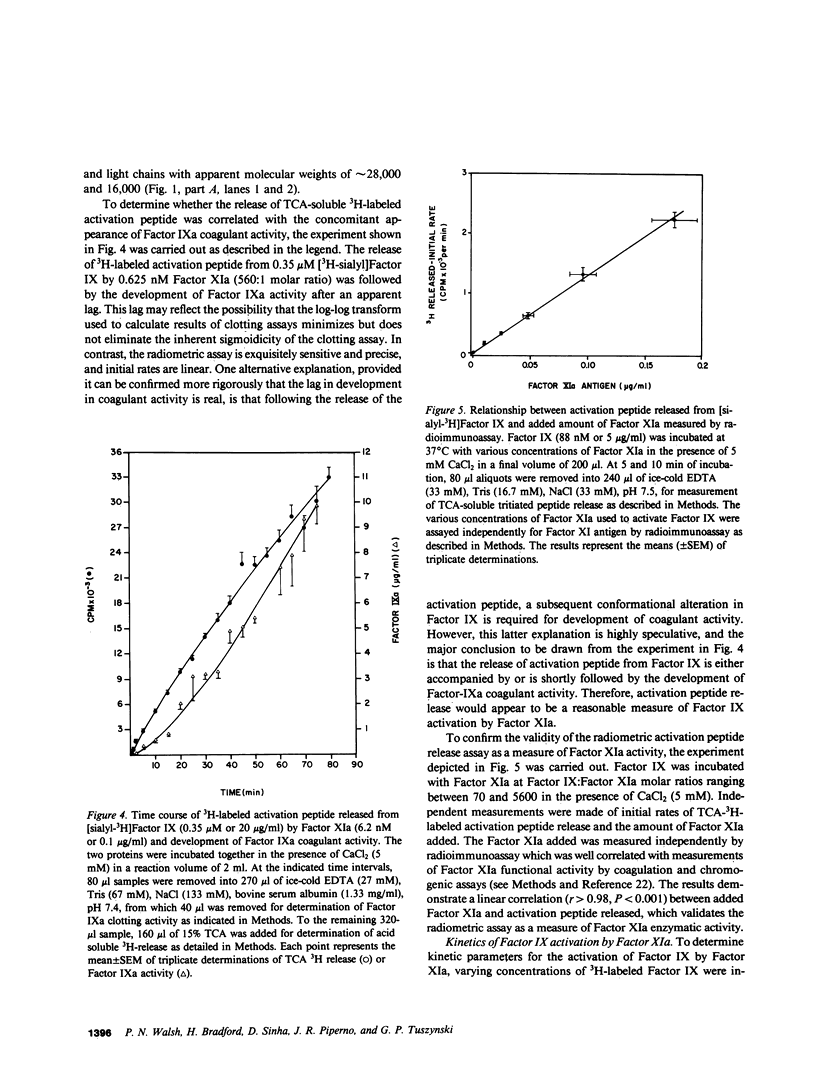
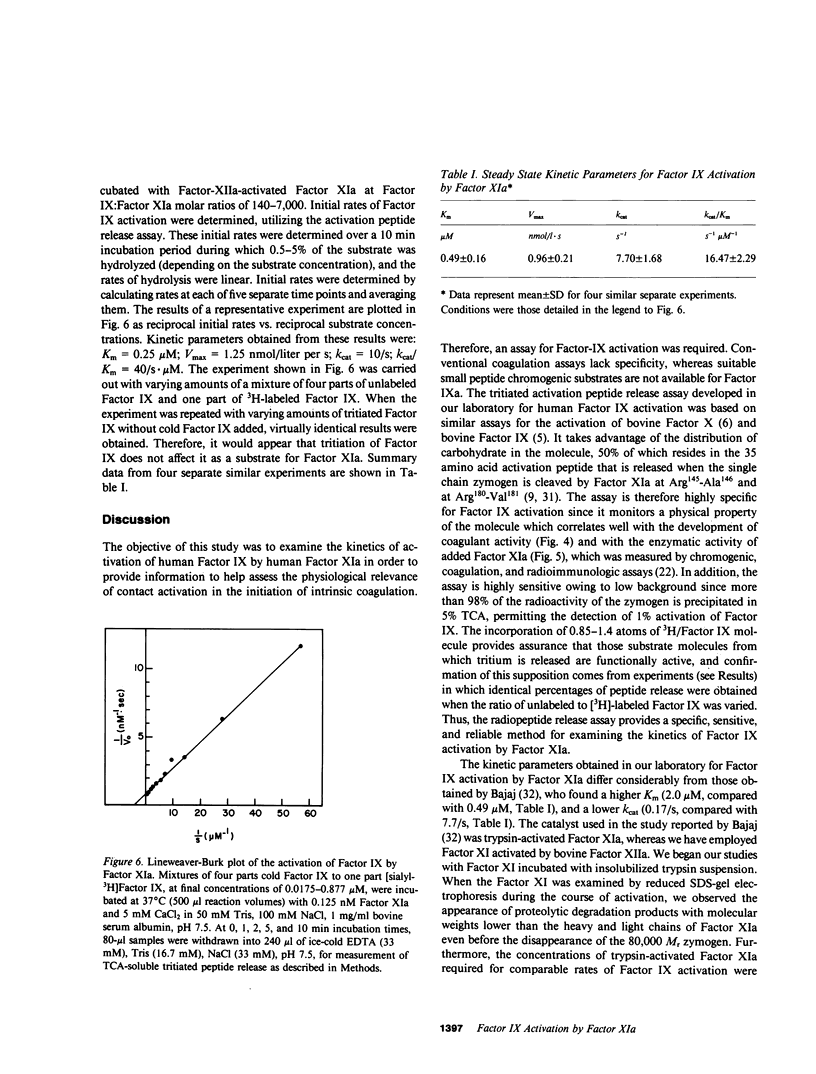
The kinetics of activation of human Factor IX by human Factor XIa was studied by measuring the release of a trichloroacetic acid-soluble tritium-labeled activation peptide from Factor IX by a modification of a method described for bovine Factor IX activation by Zur and Nemerson (Zur, M., and Y. Nemerson, 1980, J. Biol. Chem., 255:5703-5707). Initial rates of trichloroacetic acid-soluble 3H-release were linear over 10-30 min of incubation of Factor IX (88 nM) with CaCl2 (5 mM) and with pure (greater than 98%) Factor XIa (0.06-1.3 nM), which was prepared by incubating human Factor XI with bovine Factor XIIa. Release of 3H preceded the appearance of Factor IXa activity, and the percentage of 3H released remained constant when the mole fraction of 3H-labeled and unlabeled Factor IX was varied and the total Factor IX concentration remained constant. A linear correlation (r greater than 0.98, P less than 0.001) was observed between initial rates of 3H-release and the concentration of Factor XIa, measured by chromogenic assay and by radioimmunoassay and added at a Factor IX:Factor XIa molar ratio of 70-5,600. Kinetic parameters, determined by Lineweaver-Burk analysis, include Km (0.49 microM) of about five- to sixfold higher than the plasma Factor IX concentration, which could therefore regulate the reaction. The catalytic constant (kcat) (7.7/s) is approximately 20-50 times higher than that reported by Zur and Nemerson (Zur, M., and Y. Nemerson, 1980, J. Biol. Chem., 255:5703-5707) for Factor IX activation by Factor VIIa plus tissue factor. Therefore, depending on the relative amounts of Factor XIa and Factor VIIa generated in vivo and other factors which may influence reaction rates, these kinetic parameters provide part of the information required for assessing the relative contributions of the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways to Factor IX activation, and suggest that the Factor XIa catalyzed reaction is physiologically significant.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajaj S. P. Cooperative Ca2+ binding to human factor IX. Effects of Ca2+ on the kinetic parameters of the activation of factor IX by factor XIa. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4127–4132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz R. M., Nemerson Y. Quantification of contact system activation using a radiometric assay for activated factor IX. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):528–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Human blood coagulation factor XI. Purification, properties, and mechanism of activation by activated factor XII. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6432–6437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:1–32. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Hermodson M. A., Yates S. G., Davie E. W. A comparison of human prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), factor X (Stuart factor), and protein S. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):698–706. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Activation of human factor IX (Christmas factor). J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1528–1538. doi: 10.1172/JCI109073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Kato H., Davie E. W. The mechanism of activation of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor) by bovine factor XIa (activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent). Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 22;13(22):4508–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00719a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J., Silverberg S. A. Kinetics of the tissue factor-dependent activation of coagulation Factors IX and X in a bovine plasma system. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12337–12345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbiriou D. M., Griffin J. H. Human high molecular weight kininogen. Studies of structure-function relationships and of proteolysis of the molecule occurring during contact activation of plasma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12020–12027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6461–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist P. A., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W. Activation of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor) by factor XIa (activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent) and a protease from Russell's viper venom. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1902–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr, Majerus P. W. The synthesis of sulfated dextran beads for isolation of human plasma coagulation factors II, IX, and X. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):304–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Human blood coagulation factor IX. Purification, properties, and mechanism of activation by activated factor XI. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5946–5951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I. Activation of factor IX by the reaction product of tissue factor and factor VII: additional pathway for initiating blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5260–5264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCTOR R. R., RAPAPORT S. I. The partial thromboplastin time with kaolin. A simple screening test for first stage plasma clotting factor deficiencies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961 Sep;36:212–219. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. F., Sinha D., Seaman F. S., Walsh P. N., Colman R. W. Amidolytic assay of human factor XI in plasma: comparison with a coagulant assay and a new rapid radioimmunoassay. Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):42–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg S. A., Nemerson Y., Zur M. Kinetics of the activation of bovine coagulation factor X by components of the extrinsic pathway. Kinetic behavior of two-chain factor VII in the presence and absence of tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8481–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. R. Factor IX antigen by radioimmunoassay. Abnormal factor IX protein in patients on warfarin therapy and with hemophilia B. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):900–910. doi: 10.1172/JCI108712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuszynski G. P., Damsky C. H., Fuhrer J. P., Warren L. Recovery of concentrated protein samples from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90517-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuszynski G. P., Knight L., Piperno J. R., Walsh P. N. A rapid method for removal of [125I]iodide following iodination of protein solutions. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 15;106(1):118–122. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lenten L., Ashwell G. Studies on the chemical and enzymatic modification of glycoproteins. A general method for the tritiation of sialic acid-containing glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1889–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zur M., Nemerson Y. Kinetics of factor IX activation via the extrinsic pathway. Dependence of Km on tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5703–5707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Graaf F., Greengard J. S., Bouma B. N., Kerbiriou D. M., Griffin J. H. Isolation and functional characterization of the active light chain of activated human blood coagulation factor XI. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9669–9675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



