Abstract
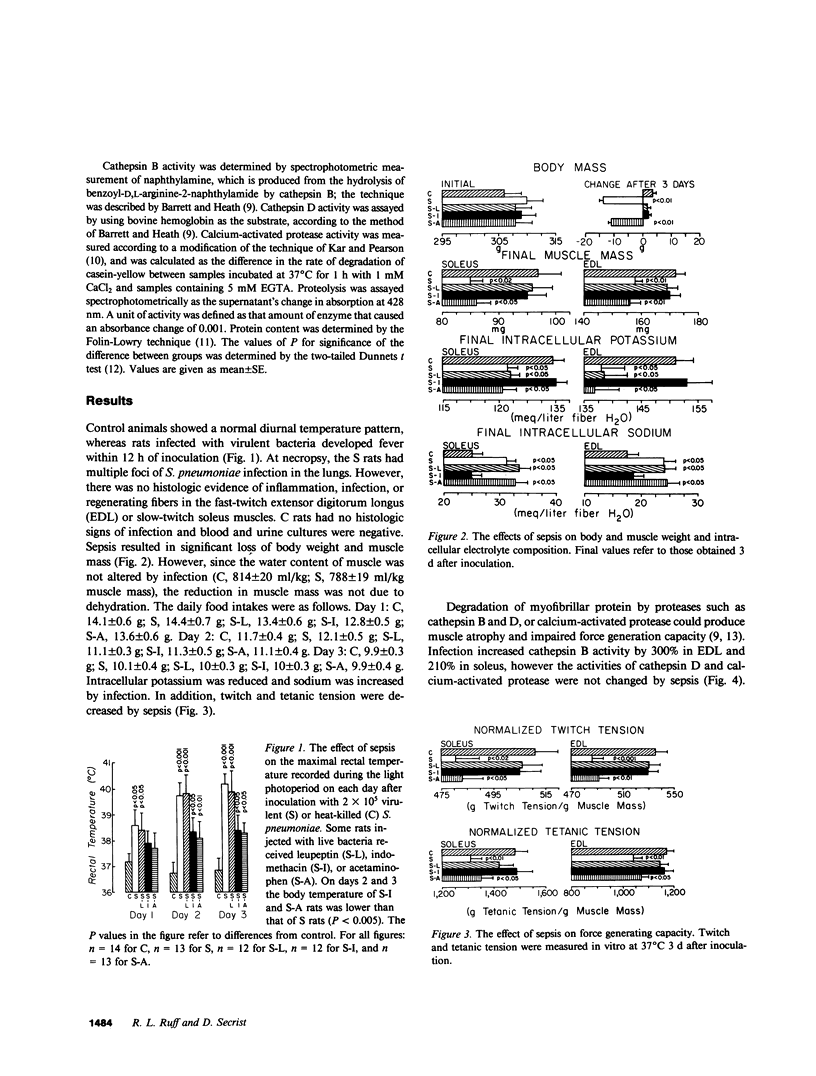
Systemic infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae produced atrophy, decreased twitch and tetanic tension, and altered intracellular electrolyte composition in rat skeletal muscle. Cathepsin B activity was selectively elevated early in the course of illness. Luepeptin, a cathepsin B inhibitor, and indomethacin, a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor, prevented muscle atrophy and impaired contractility. Indomethacin, but not leupeptin, prevented the intracellular electrolyte changes. Acetaminophen reduced fever but did not prevent muscle atrophy, impaired contractility, or altered intracellular electrolytes. Muscle wasting and impaired contractility associated with sepsis may involve selective prostaglandin stimulation of cathepsin B activity. Intracellular electrolyte changes may involve prostaglandin synthesis but do not require cathepsin B activation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baracos V., Rodemann H. P., Dinarello C. A., Goldberg A. L. Stimulation of muscle protein degradation and prostaglandin E2 release by leukocytic pyrogen (interleukin-1). A mechanism for the increased degradation of muscle proteins during fever. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 10;308(10):553–558. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303103081002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel W. R., Sawyer W. D., Ryll E. D., Crozier D. Metabolic effects of intracellular infections in man. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Oct;67(4):744–779. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-4-744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird J. W., Carter J. H., Triemer R. E., Brooks R. M., Spanier A. M. Proteinases in cardiac and skeletal muscle. Fed Proc. 1980 Jan;39(1):20–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes G. H., Jr, George B. C., Villee C. A., Jr, Saravis C. A. Muscle proteolysis induced by a circulating peptide in patients with sepsis or trauma. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 10;308(10):545–552. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303103081001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Wolff S. M. Pathogenesis of fever in man. N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 16;298(11):607–612. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803162981107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kar N. C., Pearson C. M. A calcium-activated neutral protease in normal and dystrophic human muscle. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Dec 1;73(2):293–297. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Goldberg A. L. Leupeptin, a protease inhibitor, decreases protein degradation in normal and diseased muscles. Science. 1978 Feb 3;199(4328):534–536. doi: 10.1126/science.622552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Anti-inflammatory agents as inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis in man. Med Clin North Am. 1981 Jul;65(4):713–757. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31495-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Vane J. R. Pharmacology and endogenous roles of prostaglandin endoperoxides, thromboxane A2, and prostacyclin. Pharmacol Rev. 1978 Sep;30(3):293–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodemann H. P., Goldberg A. L. Arachidonic acid, prostaglandin E2 and F2 alpha influence rates of protein turnover in skeletal and cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1632–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodemann H. P., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. The stimulation of protein degradation in muscle by Ca2+ is mediated by prostaglandin E2 and does not require the calcium-activated protease. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8716–8723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L., Martyn D., Gordon A. M. Glucocorticoid-induced atrophy is not due to impaired excitability of rat muscle. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):E512–E521. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.6.E512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


