Abstract
We have tested the participation of endogenous opiate pathways in the negative feedback actions of gonadal steroids on pulsatile properties of luteinizing (LH) hormone release in normal men. To this end, sex steroid hormones were infused intravenously at dosages that under steady state conditions selectively suppressed either the frequency or the amplitude of the pulsatile LH signal. The properties of pulsatile LH secretion were assessed quantitatively by computerized analysis of LH series derived from serial blood sampling over 12 h of observation. When the pure (nonaromatizable) androgen, 5-alpha-dihydrotestosterone, was infused continuously for 108 h at the blood production rate of testosterone, we were able to achieve selective inhibition of LH pulse frequency akin to that observed in experimental animals after low-dosage androgen replacement. Under these conditions, serum concentrations of testosterone and estradiol-17 beta did not change significantly, but serum 5 alpha-dihydrotestosterone concentrations increased approximately two- to threefold, with a corresponding increase in levels of its major metabolite, 5 alpha-androstan-3 alpha, 17 beta-diol. In separate experiments, the infusion of estradiol-17 beta at its blood production rate over a 4.5-d interval selectively suppressed LH pulse amplitude without influencing LH pulse frequency. Estrogen infusion increased serum estradiol-17 beta levels approximately twofold without significantly altering blood androgen concentrations. We then used these schedules of selective androgen or estrogen infusion to investigate the participation of endogenous opiates in the individual inhibitory feedback actions of pure androgen or estrogen on pulsatile LH release by administering a potent and specific opiate-receptor antagonist, naltrexone, during the infusions. Our observations indicate that, despite the continuous infusion of a dosage of 5 alpha-dihydrotestosterone that significantly suppresses LH pulse frequency, co-administration of an opiate-receptor antagonist effectively reinstates LH pulse frequency to control levels. Moreover, during the infusion of a suppressive dose of estradiol-17 beta, opiate receptor blockade significantly augments LH pulse frequency and increases LH peak amplitude to control levels. Thus, the present studies in normal men demonstrate for the first time that the selective inhibitory action of a pure androgen on LH pulse frequency is effectively antagonized by opiate-receptor blockade. This pivotal observation indicates that opiatergic and androgen-dependent mechanisms specifically and coordinately control the hypothalamic pulse generator for gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Full text
PDF

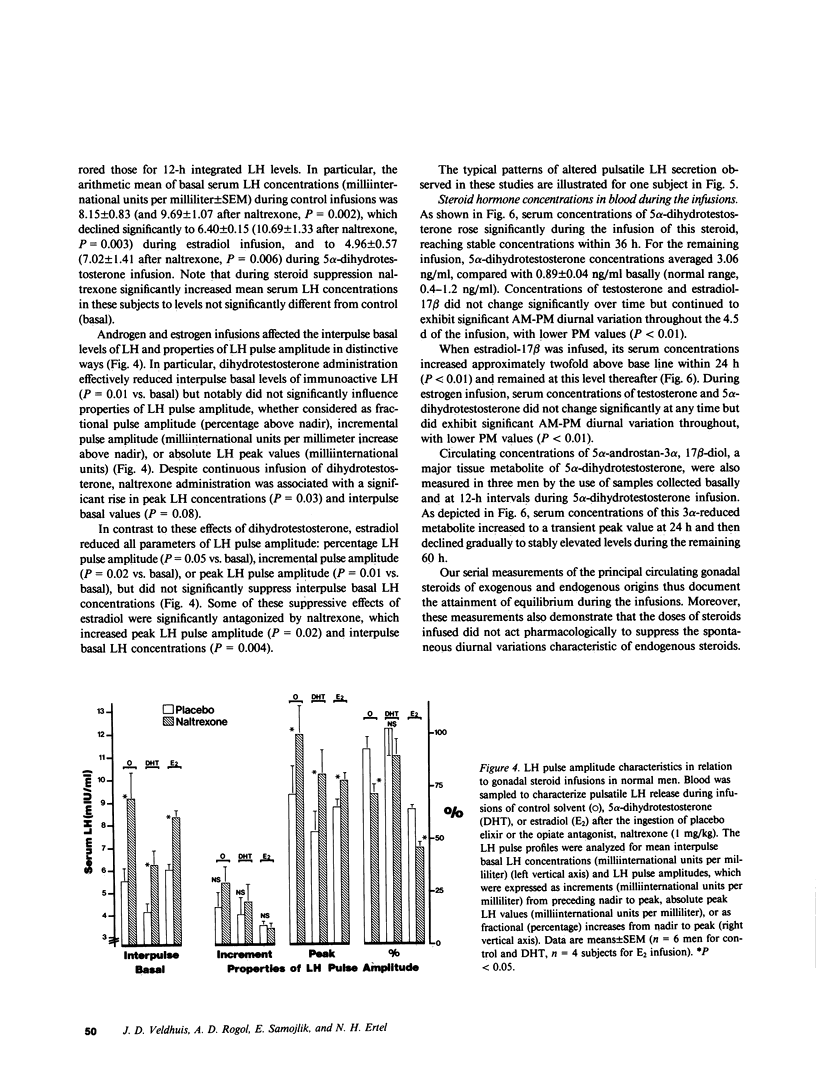
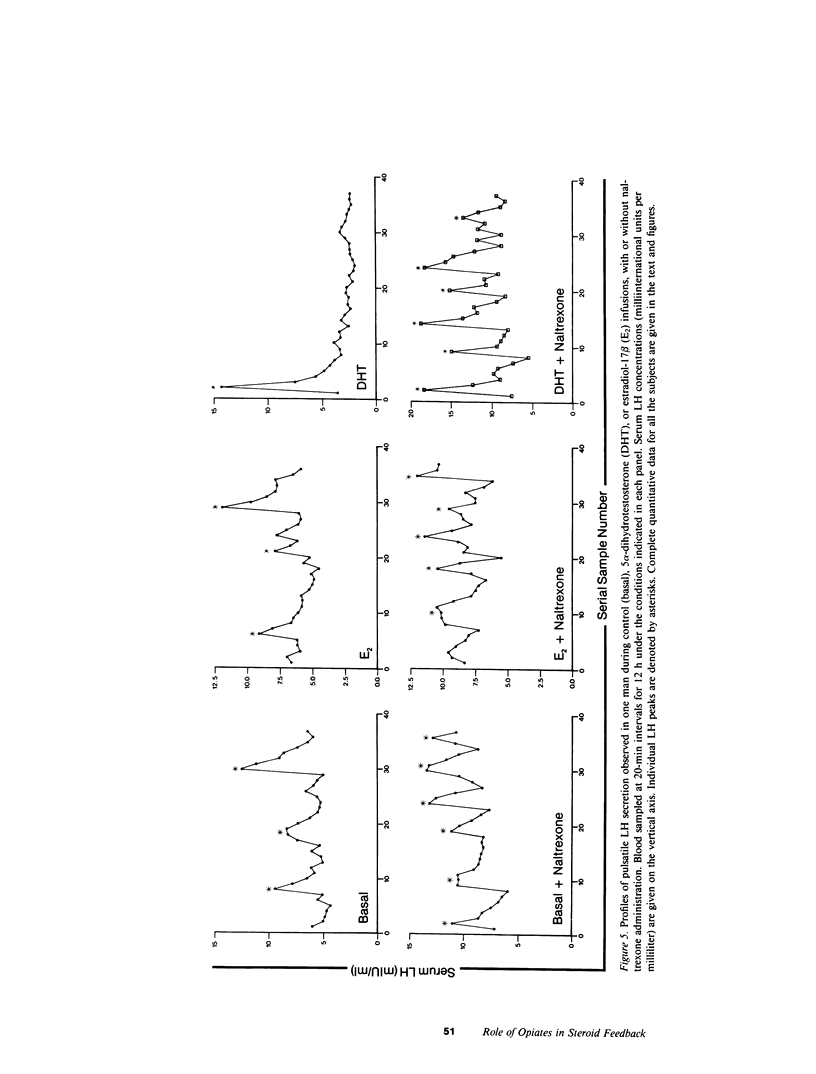
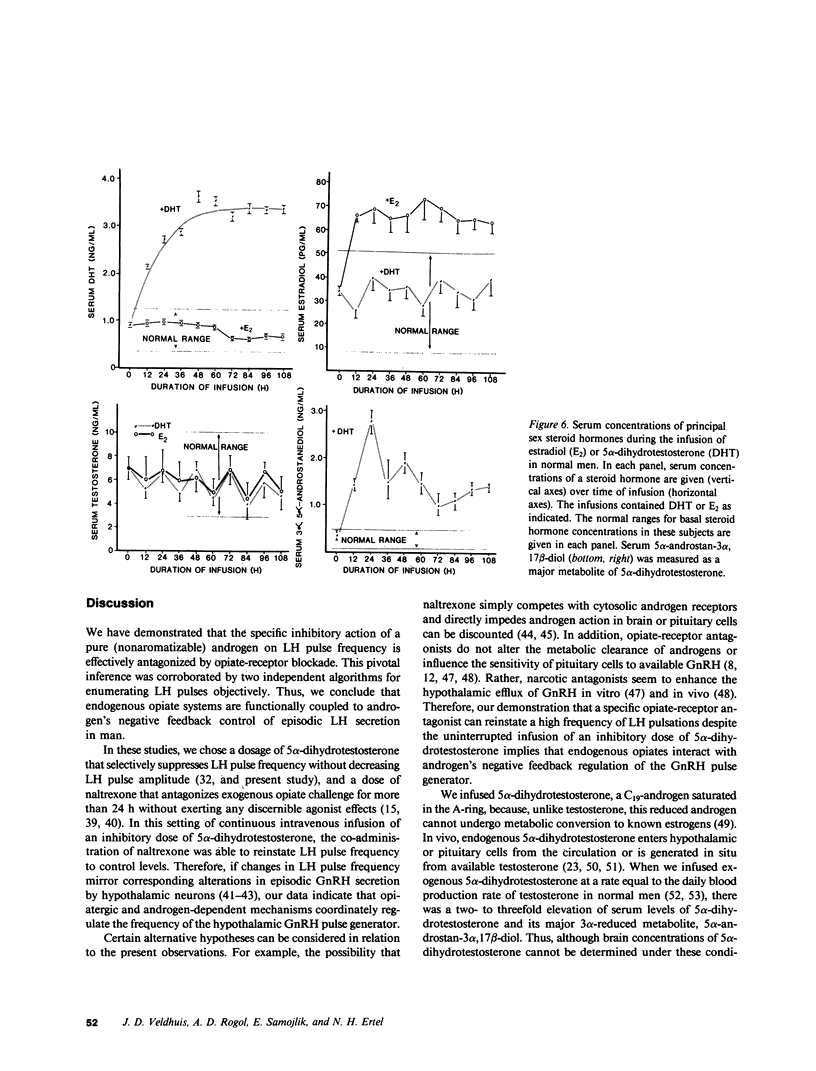



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andò S., Polosa P., D'Agata R. Further studies on the effects of dihydrotestosterone on gonadotrophin release induced by LH-RH in men. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1978 Dec;9(6):557–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1978.tb01514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azizi F., Vagenakis A. G., Longcope C., Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E. Decreased serum testosterone concentration in male heroin and methadone addicts. Steroids. 1973 Oct;22(4):467–472. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(73)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardin C. W., Lipsett M. B. Testosterone and androstenedione blood production rates in normal women and women with idiopathic hirsutism or polycystic ovaries. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):891–902. doi: 10.1172/JCI105588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyar R. M., Perlow M., Kapen S., Lefkowitz G., Weitzman E., Hellman L. The effect of clomiphene citrate on the 24-hour LH secretory pattern in normal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Mar;36(3):561–567. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-3-561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruni J. F., Van Vugt D., Marshall S., Meites J. Effects of naloxone, morphine and methionine enkephalin on serum prolactin, luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone and growth hormone. Life Sci. 1977 Aug 1;21(3):461–466. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicero T. J. Effects of exogenous and endogenous opiates on the hypothalamic--pituitary--gonadal axis in the male. Fed Proc. 1980 Jun;39(8):2551–2554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicero T. J., Meyer E. R., Bell R. D., Koch G. A. Effects of morphine and methadone on serum testosterone and luteinizing hormone levels and on the secondary sex organs of the male rat. Endocrinology. 1976 Feb;98(2):367–372. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-2-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicero T. J., Schainker B. A., Meyer E. R. Endogenous opioids participate in the regulation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-luteinizing hormone axis and testosterone's negative feedback control of luteinizing hormone. Endocrinology. 1979 May;104(5):1286–1291. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-5-1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicero T. J., Wilcox C. E., Bell R. D., Meyer E. R. Naloxone-induced increases in serum luteinizing hormone in the male: mechanisms of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Mar;212(3):573–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke I. J., Cummins J. T. The temporal relationship between gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) secretion in ovariectomized ewes. Endocrinology. 1982 Nov;111(5):1737–1739. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-5-1737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton D. K., Steiner R. A. Cycle detection: a technique for estimating the frequency and amplitude of episodic fluctuations in blood hormone and substrate concentrations. Endocrinology. 1983 Mar;112(3):1057–1064. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-3-1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Occhio M. J., Schanbacher B. D., Kinder J. E. Relationship between serum testosterone concentration and patterns of luteinizing hormone secretion in male sheep. Endocrinology. 1982 May;110(5):1547–1554. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-5-1547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Occhio M. J., Schanbacher B. D., Kinder J. E. Relationship between serum testosterone concentration and patterns of luteinizing hormone secretion in male sheep. Endocrinology. 1982 May;110(5):1547–1554. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-5-1547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delitala G., Devilla L., Arata L. Opiate receptors and anterior pituitary hormone secretion in man. Effect of naloxone infusion. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1981 Jun;97(2):150–156. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0970150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouva S. V., Epelbaum J., Tapia-Arancibia L., Laplante E., Kordon C. Opiate receptors modulate LHRH and SRIF release from mediobasal hypothalamic neurons. Neuroendocrinology. 1981 Mar;32(3):163–167. doi: 10.1159/000123150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgerton L. A., Baile C. A. Serum LH suppression by estradiol but not by testosterone or progesterone in wethers. J Anim Sci. 1977 Jan;44(1):78–83. doi: 10.2527/jas1977.4410078x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellingboe J., Veldhuis J. D., Mendelson J. H., Kuehnle J. C., Mello N. K. Effect of endogenous opioid blockade on the amplitude and frequency of pulsatile luteinizing hormone secretion in normal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Apr;54(4):854–857. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-4-854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. S., Rogol A. D., MacLeod R. M., Thorner M. O. Dopaminergic mechanisms and luteinizing hormone secretion. I. Acute administration of the dopamine agonist bromocriptine does not inhibit luteinizing hormone release in hyperprolactinemic women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jan;50(1):103–107. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. L., Karsch F. J. Pulsatile secretion of luteinizing hormone: differential suppression by ovarian steroids. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1286–1290. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A., Moult P. J., Gaillard R. C., Delitala G., Toff W. D., Rees L. H., Besser G. M. The opioid control of LH and FSH release: effects of a met-enkephalin analogue and naloxone. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1981 Jan;14(1):41–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1981.tb00363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORTON R., SHINSAKO J., FORSHAM P. H. TESTOSTERONE PRODUCTION AND METABOLIC CLEARANCE RATES WITH VOLUMES OF DISTRIBUTION IN NORMAL ADULT MEN AND WOMEN. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1965 Mar;48:446–458. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0480446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Horton R. The source of plasma dihydrotestosterone in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1621–1627. doi: 10.1172/JCI106650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalra P. S., Kalra S. P. Modulation of hypothalamic luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone levels by intracranial and subcutaneous implants of gonadal steroids in castrated rats: effects of androgen and estrogen antagonists. Endocrinology. 1980 Jan;106(1):390–397. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-1-390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. E., Pau K. Y., Ramirez V. D., Jackson G. L. Simultaneous measurement of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone and luteinizing hormone release in unanesthetized, ovariectomized sheep. Endocrinology. 1982 Nov;111(5):1449–1455. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-5-1449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. E., Ramirez V. D. Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone release during the rat estrous cycle and after ovariectomy, as estimated with push-pull cannulae. Endocrinology. 1982 Nov;111(5):1439–1448. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-5-1439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsett M. B. The role of testosterone and other hormones in regulation of LH. J Steroid Biochem. 1979 Jul;11(1B):659–661. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(79)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Karavolas H. J. Uptake and conversion of progesterone and testosterone to 5alpha-reduced products by enriched gonadotropic and chromophobic rat anterior pituitary cell fractions. Endocrinology. 1975 Sep;97(3):517–526. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-3-517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longcope C., Kato T., Horton R. Conversion of blood androgens to estrogens in normal adult men and women. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2191–2201. doi: 10.1172/JCI106185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massa R., Stupnicka E., Kniewald Z., Martini L. The transformation of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone by the brain and the anterior pituitary. J Steroid Biochem. 1972 Apr;3(3):385–399. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(72)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson J. H., Ellingboe J., Kuehnle J. C., Mello N. K. Heroin and naltrexone effects on pituitary-gonadal hormones in man: interaction of steroid feedback effects, tolerance and supersensitivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Sep;214(3):503–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merriam G. R., Wachter K. W. Algorithms for the study of episodic hormone secretion. Am J Physiol. 1982 Oct;243(4):E310–E318. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.4.E310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley J. E., Baranetsky N. G., Wingert T. D., Carlson H. E., Hershman J. M., Melmed S., Levin S. R., Jamison K. R., Weitzman R., Chang R. J. Endocrine effects of naloxone-induced opiate receptor blockade. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Feb;50(2):251–257. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naftolin F., Judd H. L., Yen S. S. Pulsatile patterns of gonadotropins and testosterone in man: the effects of clomiphene, with and without testosterone added. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Feb;36(2):285–288. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-2-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell W. D., Ross G. T., Rayford P. L. Radioimmunoassay for luteinizing hormone in human plasma or serum: physiological studies. J Clin Invest. 1967 Feb;46(2):248–255. doi: 10.1172/JCI105527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant T. M. Effects of orchidectomy and testosterone replacement treatment on pulsatile luteinizing hormone secretion in the adult rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Endocrinology. 1982 Jun;110(6):1905–1913. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-6-1905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen D. D., Liu J. H., Wolf P. L., Yen S. S. Endogenous opioid regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone release from the human fetal hypothalamus in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Nov;57(5):881–884. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-5-881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropert J. F., Quigley M. E., Yen S. S. Endogenous opiates modulate pulsatile luteinizing hormone release in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Mar;52(3):583–585. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samojlik E., Veldhuis J. D., Wells S. A., Santen R. J. Preservation of androgen secretion during estrogen suppression with aminoglutethimide in the treatment of metastatic breast carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):602–612. doi: 10.1172/JCI109705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
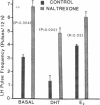
- Santen R. J., Bardin C. W. Episodic luteinizing hormone secretion in man. Pulse analysis, clinical interpretation, physiologic mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2617–2628. doi: 10.1172/JCI107454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santen R. J. Is aromatization of testosterone to estradiol required for inhibition of luteinizing hormone secretion in men? J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1555–1563. doi: 10.1172/JCI108237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santen R. J., Ruby E. B. Enhanced frequency and magnitude of episodic luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone discharge as a hypothalamic mechanism for increased luteinizing hormone secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Feb;48(2):315–319. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R., Wilhelm A., Pirke K. M., Gramsch C., Herz A. Beta-endorphin and dynorphin control serum luteinizing hormone level in immature female rats. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):757–759. doi: 10.1038/294757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
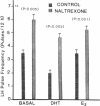
- Sheridan P. J., Buchanan J. M. The effects of opiates on androgen binding in the forebrain of the rat. Int J Fertil. 1980;25(1):36–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner R. A., Bremner W. J., Clifton D. K. Regulation of luteinizing hormone pulse frequency and amplitude by testosterone in the adult male rat. Endocrinology. 1982 Dec;111(6):2055–2061. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-6-2055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
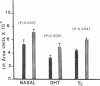
- Stewart-Bentley M., Odell W., Horton R. The feedback control of luteinizing hormone in normal adult men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Apr;38(4):545–553. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-4-545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs W. A., Delitala G., Jones A., Jeffcoate W. J., Edwards C. R., Ratter S. J., Besser G. M., Bloom S. R., Alberti K. G. Hormonal and metabolic responses to an enkephalin analogue in normal man. Lancet. 1978 Dec 9;2(8102):1225–1227. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester P. W., Van Vugt D. A., Aylsworth C. A., Hanson E. A., Meites J. Effects of morphine and naloxone on inhibition by ovarian hormones of pulsatile release of LH in ovariectomized rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1982 Apr;34(4):269–273. doi: 10.1159/000123311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vugt D. A., Meites J. Influence of endogenous opiates on anterior pituitary function. Fed Proc. 1980 Jun;39(8):2533–2538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vugt D. A., Sylvester P. W., Aylsworth C. F., Meites J. Counteraction of gonadal steroid inhibition of luteinizing hormone release by naloxone. Neuroendocrinology. 1982 Apr;34(4):274–278. doi: 10.1159/000123312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldhuis J. D., Rogol A. D., Johnson M. L. Endogenous opiates modulate the pulsatile secretion of biologically active luteinizing hormone in man. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):2031–2040. doi: 10.1172/JCI111168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldhuis J. D., Worgul T. J., Monsaert R., Hammond J. M. A possible role of endogenous opioids in the control of prolactin and luteinizing-hormone secretion in the human. J Endocrinol Invest. 1981 Jan-Mar;4(1):31–36. doi: 10.1007/BF03349410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verebey K., Volavka J., Mulé S. J., Resnick R. B. Naltrexone: disposition, metabolism, and effects after acute and chronic dosing. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Sep;20(3):315–328. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976203315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes M. M., Yen S. S. Augmentation by naloxone of efflux of LRF from superfused medial basal hypothalamus. Life Sci. 1981 May 21;28(21):2355–2359. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90500-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters S. J., Sherins R. J., Loriaux D. L. Studies on the role of sex steroids in the feedback control of gonadotropin concentrations in men. III. Androgen resistance in primary gonadal failure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Apr;48(4):553–558. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-4-553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Graffenried B., del Pozo E., Roubicek J., Krebs E., Poldinger W., Burmeister P., Kerp L. Effects of the synthetic enkephalin analogue FK 33-824 in man. Nature. 1978 Apr 20;272(5655):729–730. doi: 10.1038/272729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]