Abstract
Since elevated levels of circulating complexes have been noted to occur in the sera of patients with post-streptococcal sequelae, the possibility that these complexes contained streptococcal antigens within the complex was investigated. Sera from these patients were precipitated with polyethylene glycol to extract a fraction rich in these complexes, which was then injected into rabbits. The rabbit sera were then reacted with both cellular and extracellular fractions obtained from streptococcal strains associated with either acute post-streptococcal nephritis (APSGN) or acute rheumatic fever (ARF) by using immunoelectrophoresis and ELISA techniques. The data demonstrate that both ARF and APSGN complexes contain streptococcal antigens. However, APSGN complexes react uniquely to certain extracellular antigens present in those strains associated with nephritis, while ARF complexes react specifically to certain streptococcal extracellular antigens excreted by strains associated with rheumatic fever. Neither of the two groups of complexes appear to contain streptococcal antigens related to any cellular antigens derived from the group A streptococcus. Additionally, a rabbit serum immunized with streptococcal extracellular products reacted directly with complexes isolated from nephritis patients. Removal of the gamma globulin by absorption with an anti-human Fc serum resulted in the concomitant loss of reactivity with the anti-streptococcal serum, strongly suggesting an intimate association of the streptococcal antigen with these complexes. The presence of streptococcal antigens within the circulating immune complex of patients with APSGN coupled with their specific presence in those strains associated with post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis argues strongly for a causal role of these antigens in the disease process.
Full text
PDF



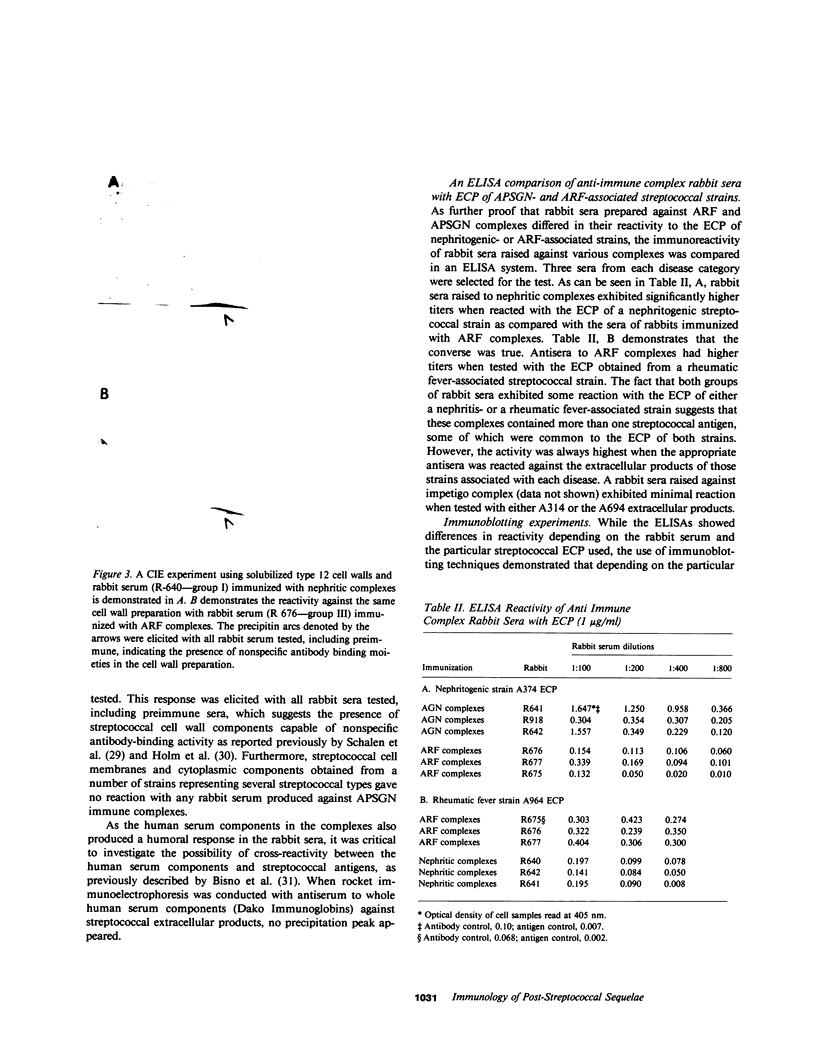
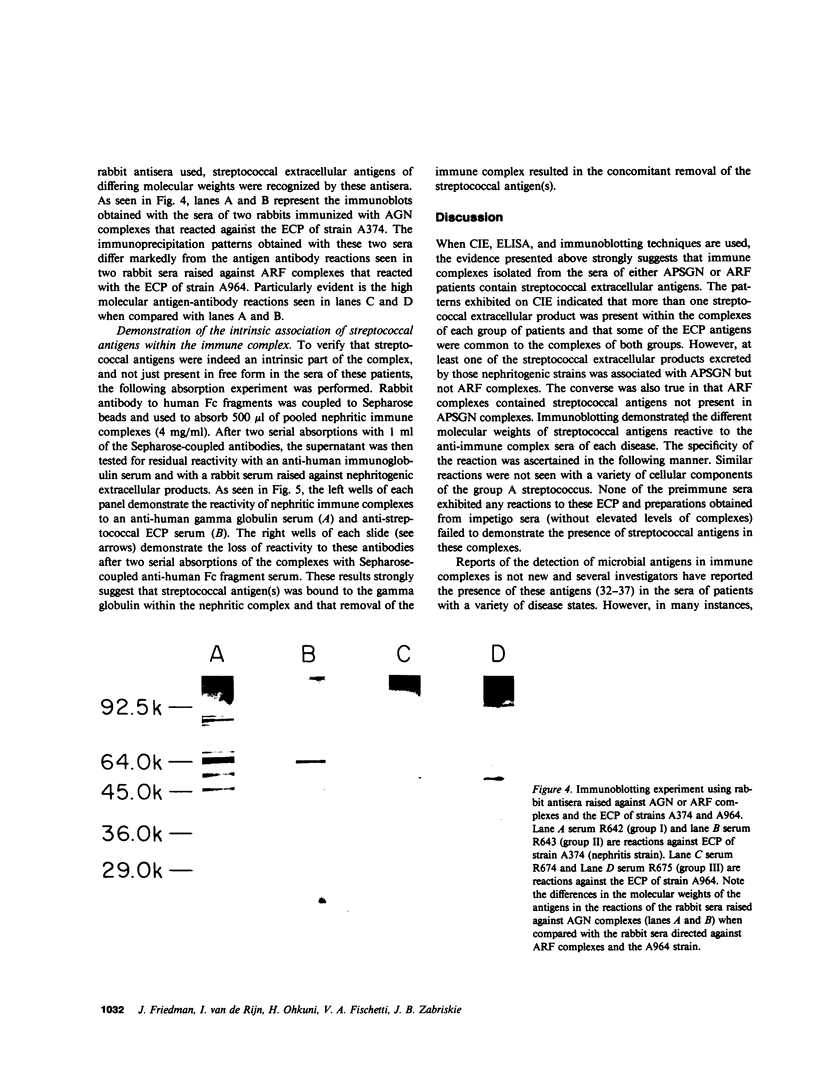


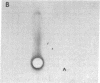
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anh-Tuan N., Novák E. Detection and quantitation of hepatitis-B surface antigen immune complexes (HBsAg-ICs) by an antigen-specific method. I. Detection and quantitation of in vitro prepared HBsAg-ICs. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(3):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLEIWEIS A. S., KARAKAWA W. W., KRAUSE R. M. IMPROVED TECHNIQUE FOR THE PREPARATION OF STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1198–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1198-1200.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisno A. L., Wood J. W., Lawson J., Roy S., Beachey E. H., Stollermann G. H. Antigens in urine of patients with glomerulonephritis and in normal human serum which cross-react with group A streptococci: identification and partial characterization. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Mar;91(3):500–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamp J. R., Hughes K. W., McPherson J. C. Glycoproteins from human spleen cell surfaces. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90455-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton W. D., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of antibodies and soluble antigen-antibody complexes by precipitation with polyethylene glycol. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1219–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHEL E. E. Immune reactions in human glomerulonephritis. J Chronic Dis. 1957 Jan;5(1):34–44. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(57)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. D., Mardiney M. R., Shuler S. E. Immunology and morphology of acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1966 Jan;15(1 Pt 2):283–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Gotschlich E. C., Bernheimer A. W. Purification and physical properties of group C streptococcal phage-associated lysin. J Exp Med. 1971 May 1;133(5):1105–1117. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.5.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. D., Redecha P. B., Knechtle S. J., Schned E. S., van de Rijn I., Christian C. L. Identification of bacterial antigens in circulating immune complexes of infective endocarditis. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):271–280. doi: 10.1172/JCI110614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUSE R. M., MCCARTY M. Studies on the chemical structure of the streptococcal cell wall. I. The identification of a mucopeptide in the cell walls of groups A and A-variant streptococci. J Exp Med. 1961 Jul 1;114:127–140. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., van de Rijn I. Quantitative immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Streptococcus pyogenes membrane. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):892–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.892-902.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Ahmed U., Kleinberger H., Treser G. A hitherto unknown streptococcal antigen and its probable relation to acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1976 May;5(5):207–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILGROM F., TUGGAC Z. M., CAMPBELL W. A. ANALYSIS OF ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEXES BY IMMUNOELECTROPHORESIS. Immunology. 1965 Apr;8:406–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey R. T. Evidence for immunologic mechanisms in several forms of human glomerular diseases. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1970 Oct;46(10):769–788. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey R. T., Vassalli P., Gallo G., Baldwin D. S. An immunofluorescent study of pathogenic mechanisms in glomerular diseases. N Engl J Med. 1966 Mar 31;274(13):695–701. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196603312741301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael A. F., Jr, Drummond K. N., Good R. A., Vernier R. L. Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis: immune deposit disease. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):237–248. doi: 10.1172/JCI105336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paganelli R., Levinsky R. J., Brostoff J., Wraith D. G. Immune complexes containing food proteins in normal and atopic subjects after oral challenge and effect of sodium cromoglycate on antigen absorption. Lancet. 1979 Jun 16;1(8129):1270–1272. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Iturbe B., Rabideau D., García R., Rubio L., McIntosh R. M. Characterization of the glomerular antibody in acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Apr;92(4):478–481. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-4-478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEEGAL B. C., ANDRES G. A., HSU K. C., ZABRISKIE J. B. STUDIES ON THE PATHOGENESIS OF ACUTE AND PROGRESSIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS IN MAN BY IMMUNOFLUORESCEIN AND IMMUNOFERRITIN TECHNIQUES. Fed Proc. 1965 Jan-Feb;24:100–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T. Refinement of the coomassie blue method of protein quantitation. A simple and linear spectrophotometric assay for less than or equal to 0.5 to 50 microgram of protein. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):142–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stass S. A., Phillips T. M., Weislow O. S., Perlin E., Schumacher H. R. Antigen--antibody complexes related to the baboon endogenous virus in humans with acute lymphoblastic leukemia--hand mirror variant (ALL-HMC). Blood. 1980 Oct;56(4):661–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treser G., Semar M., McVicar M., Franklin M., Ty A., Sagel I., Lange K. Antigenic streptococcal components in acute glomerulonephritis. Science. 1969 Feb 14;163(3868):676–677. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3868.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treser G., Semar M., Ty A., Agel I., Franklin M. A., Lange K. Partial characterization of antigenic streptococcal plasma membrane components in acute glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):762–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI106289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal H., Jr, Fischetti V. A., van de Rijn I., Zabriskie J. B. The occurrence of a protein in the extracellular products of streptococci isolated from patients with acute glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):459–472. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinoya S., Cox R. A., Pope R. M. Circulating immune complexes in coccidioidomycosis. Detection and characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):655–663. doi: 10.1172/JCI109901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B. The role of streptococci in human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):180s–192s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Fillit H., Brandeis W. E., Reid H., Poon-King T., McCarthy M., Day N. K., Zabriskie J. B. Serial studies on circulating immune complexes in post-streptococcal sequelae. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Dec;34(3):318–325. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Kessler R. E. Growth characteristics of group A streptococci in a new chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.444-448.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]