Abstract
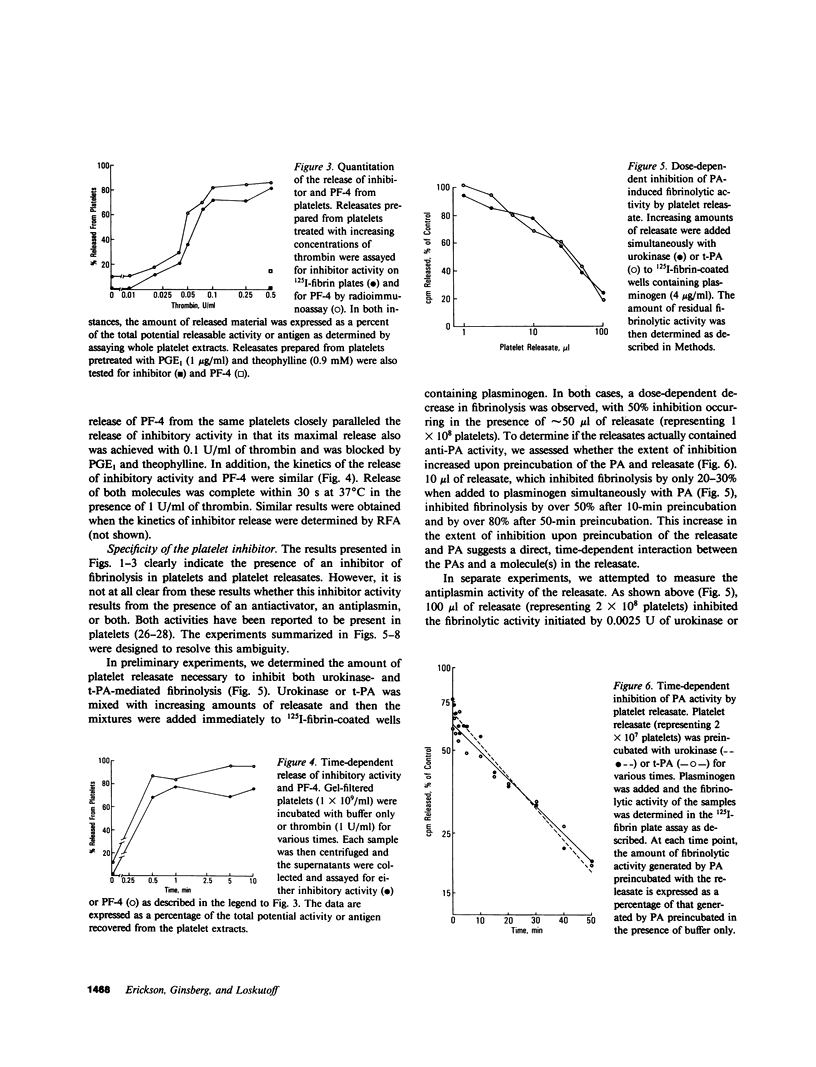
In this study, we demonstrate the presence of a previously undescribed fibrinolytic inhibitor in human serum. It has an apparent molecular weight of 50,000 and is not detected in serum derived from platelet-poor plasma, suggesting that it originates from platelets. This conclusion is supported by a number of observations. For example, extracts of washed, gel-filtered human platelets contain an inhibitor of similar activity and size, and physiological concentrations of thrombin induce its release from the platelets. Moreover, the kinetics and dose dependency of this release are similar to those observed for the release of platelet factor 4, and the release of both molecules is blocked by pretreating the platelets with prostaglandin E1 and theophylline. Mixing experiments, which were devised to investigate the specificity of the inhibitor, showed that the fibrinolytic activity initiated by both urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activator was blocked by platelet releasate in a dose-dependent manner. In both cases, the amount of inhibition increased when the releasates were preincubated with the purified activators, indicating a direct interaction between the activators and an inhibitor(s). The inhibitory activity was removed by preincubating the releasates with antiserum prepared against an antiactivator purified from cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. These results indicate that platelets contain an inhibitor which is released by thrombin, inhibits both urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activator, and is immunologically similar to an inhibitor produced by endothelial cells. This molecule may represent a new class of inhibitors, the antiactivators, which function together with alpha 2-antiplasmin to regulate the fibrinolytic system of the blood. Its release from platelets by thrombin may protect the growing thrombus against premature dissolution initiated by plasminogen activators released by the endothelium.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. B., Low D. A., Simmer R. L., Cunningham D. D. Protease-nexin: a cellular component that links thrombin and plasminogen activator and mediates their binding to cells. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Edward Kowalski Memorial Lecture. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson L. A., Lawrence D. A., Loskutoff D. J. Reverse fibrin autography: a method to detect and partially characterize protease inhibitors after sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1984 Mar;137(2):454–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Hoskins R., Sigrist P., Painter R. G. Purification of a heparin-neutralizing protein from rabbit platelets and its homology with human platelet Factor 4. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12365–12371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Taylor L., Painter R. G. The mechanism of thrombin-induced platelet factor 4 secretion. Blood. 1980 Apr;55(4):661–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoylaerts M., Rijken D. C., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the activation of plasminogen by human tissue plasminogen activator. Role of fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2912–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joist J. H., Niewiarowski S., Nath N., Mustard J. F. Platelet antiplasmin: its extrusion during the release reaction, subcellular localization, characterization, and relationship to antiheparin in pig platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Apr;87(4):659–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joist J. H. Platelets and fibrinolysis. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Dec 15;38(4):955–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korninger C., Collen D. Neutralization of human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in human plasma: no evidence for a specific inhibitor. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Oct;46(3):662–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Loskutoff D. J. Cultured bovine endothelial cells produce both urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activators. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):631–636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Interaction of plasminogen activators and inhibitors with plasminogen and fibrin. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1982 Jan;8(1):2–10. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Edgington T. E. Synthesis of a fibrinolytic activator and inhibitor by endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J. Effect of thrombin on the fibrinolytic activity of cultured bovine endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):329–332. doi: 10.1172/JCI109457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Mussoni L. Interactions between fibrin and the plasminogen activators produced by cultured endothelial cells. Blood. 1983 Jul;62(1):62–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., van Mourik J. A., Erickson L. A., Lawrence D. Detection of an unusually stable fibrinolytic inhibitor produced by bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo O., Rijken D. C., Collen D. Thrombolysis by human tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase in rabbits with experimental pulmonary embolus. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):590–591. doi: 10.1038/291590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S., Pepper D. S., Cash J. D. The isolation and characterisation of a platelet-specific beta-globulin (beta-thromboglobulin) and the detection of antiurokinase and antiplasmin released from thrombin-aggregated washed human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):360–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Collen D. The presence and release of alpha 2-antiplasmin from human platelets. Blood. 1981 Dec;58(6):1069–1074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Wijngaards G., Welbergen J. Immunological characterization of plasminogen activator activities in human tissues and body fluids. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Apr;97(4):477–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandbjerg Hansen M., Clemmensen I. Partial purification and characterization of a new fast-acting plasmin inhibitor from human platelets. Evidence for non-identity with the known plasma proteinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 1;187(1):173–180. doi: 10.1042/bj1870173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Tobia A., Ossowski L., Quigley J. P., Rifkin D. B., Reich E. An enzymatic function associated with transformation of fibroblasts by oncogenic viruses. I. Chick embryo fibroblast cultures transformed by avian RNA tumor viruses. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):85–111. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eijk H. G., Van Noort W. L. Isolation of rat transferrin using CNBr-activated sepharose 4B. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1976 Oct;14(10):475–478. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1976.14.1-12.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Gow L., Campbell D. M., Ogston D. The inhibition by plasma of urokinase and tissue activator-induced fibrinolysis in pregnancy and the puerperium. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Feb 28;49(1):21–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N., Gagnatelli G. Platelet antiheparin activity: storage site and release mechanism. Blood. 1974 Aug;44(2):157–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. Purification and characterization of human antiplasmin, the fast-acting plasmin inhibitor in plasma. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):19–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Mellbring G., Rånby M. Plasminogen activator release during venous stasis and exercise as determined by a new specific assay. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jan 24;127(2):279–288. doi: 10.1016/s0009-8981(83)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]