Abstract
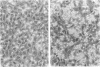
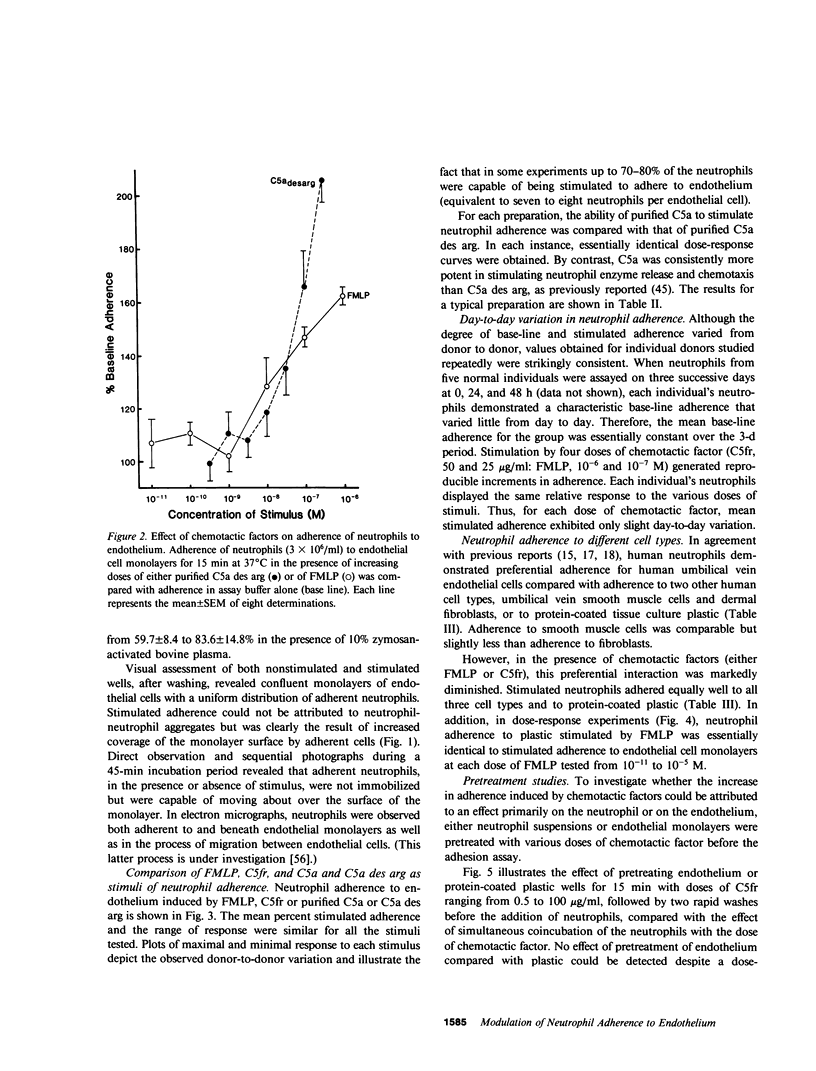
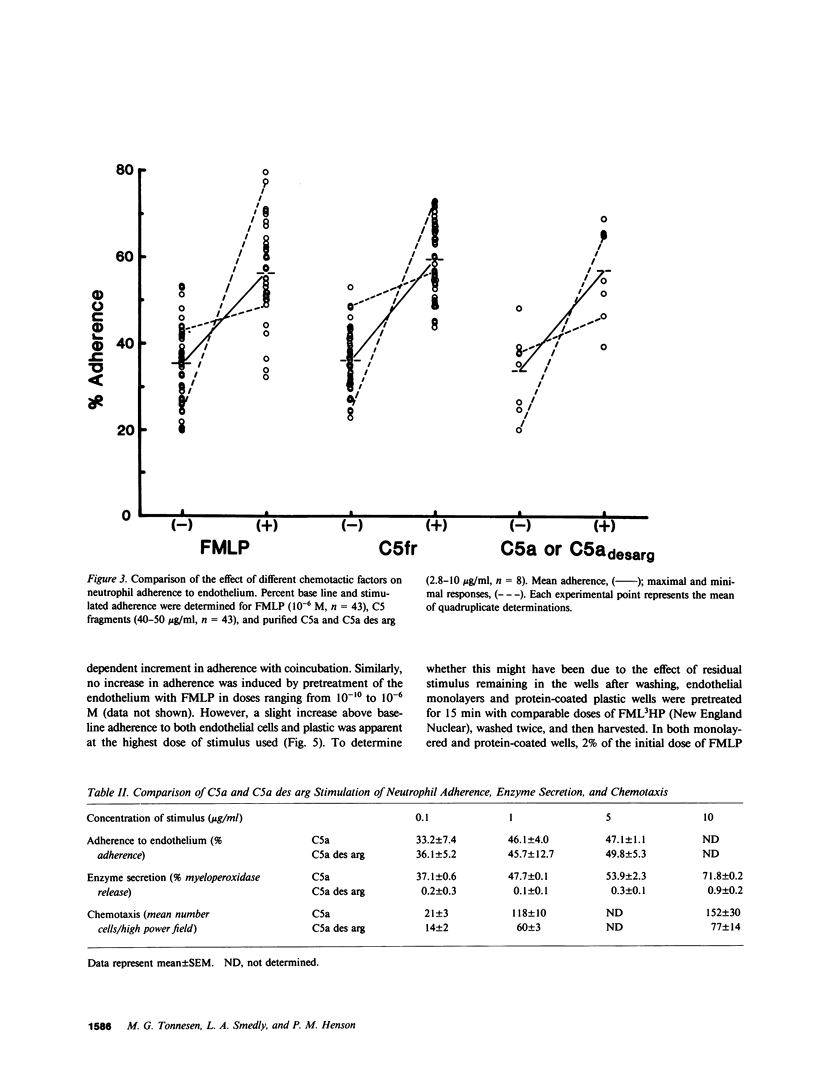
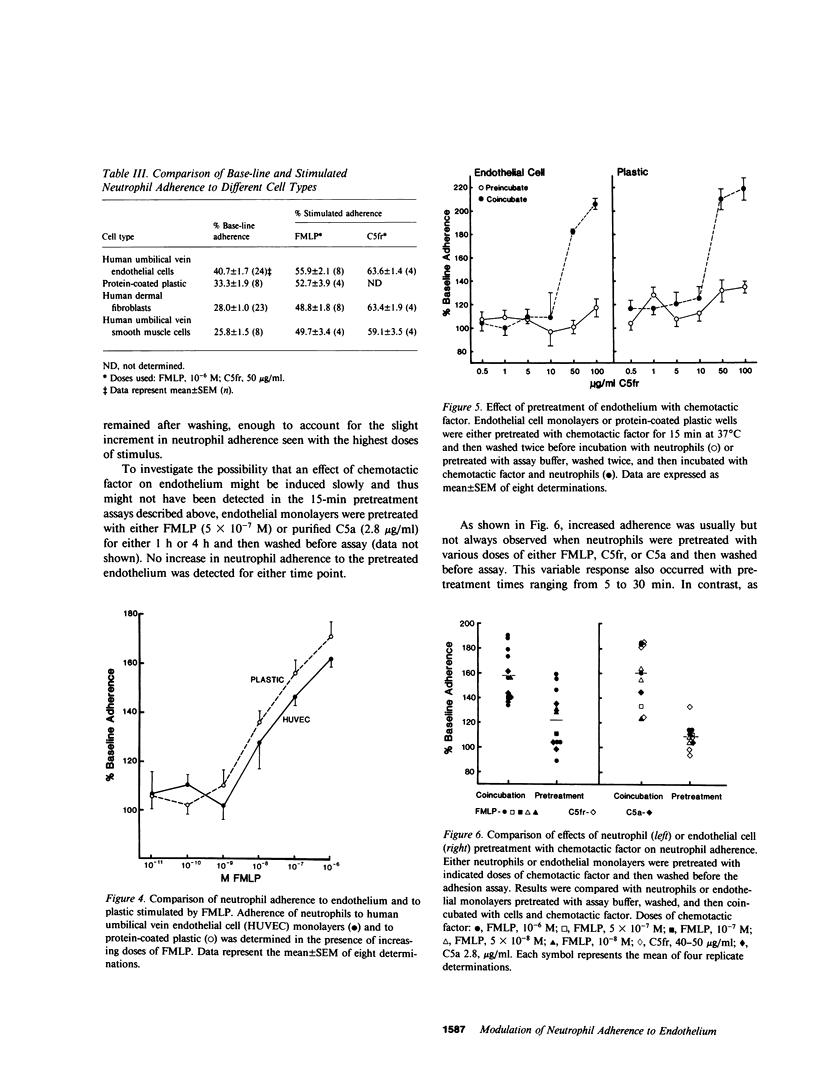
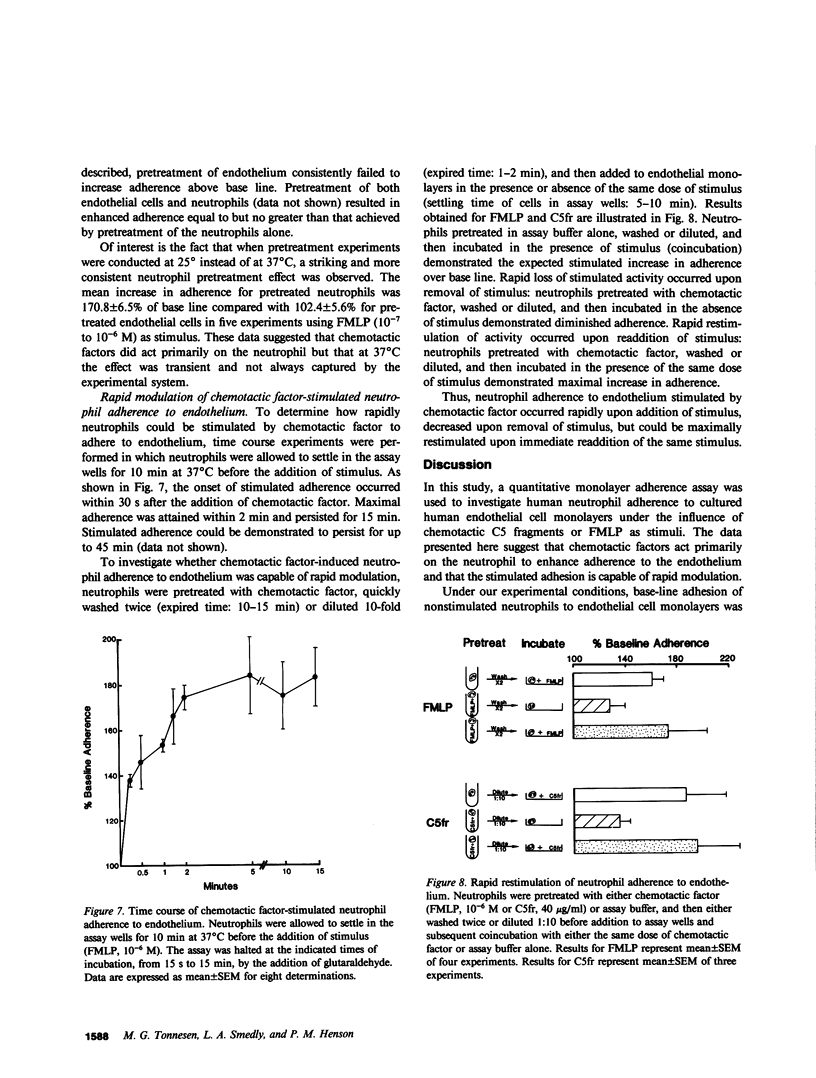
Neutrophil adherence to vascular endothelial cells is the initial event in the emigration of neutrophils through blood vessel walls to tissue sites of inflammation; this process is attributed to the generation of extravascular chemotactic factors. To investigate the effect of chemotactic factors on neutrophil adherence to endothelium, we developed a sensitive, reproducible in vitro microtiter adherence assay. Base-line nonstimulated adhesion of human neutrophils to cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cell monolayers was 35.2 +/- 0.9%, which is equivalent to three to four neutrophils per endothelial cell. Addition of either purified complement fragment C5a des arg, or formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP), in concentrations ranging from 10(-10) to 10(-6) M, increased neutrophil adherence to endothelium in a dose-dependent manner. Purified C5a and C5a des arg were essentially equal in their ability to enhance neutrophil adherence, in contrast to the previously described greater in vitro potency of C5a compared with C5a des arg in stimulating neutrophil chemotaxis and enzyme release. Nonstimulated neutrophils adhered preferentially to human endothelial cells compared with fibroblasts or smooth muscle cells, suggesting that endothelial cells may make a unique contribution to the base-line adhesive interaction. However, chemotactic factors appear to enhance neutrophil adherence to endothelium by exerting an effect primarily on the neutrophil. In the presence of chemotactic factor, neutrophils adhered equally well to different cell types or to protein-coated plastic. Pretreatment of endothelial cells with chemotactic factor for as long as 4 h failed to increase subsequent neutrophil adherence. In contrast, pretreatment of neutrophils with chemotactic factor increased adherence to endothelium. Chemotactic factor-stimulated neutrophil adherence to endothelium occurred rapidly (within 2 min), diminished upon removal of stimulus, but could be rapidly and maximally restimulated upon readdition of the original dose of chemotactic factor. Thus, adherence to endothelium stimulated by chemotactic factor would appear to be a dynamic neutrophil response capable of rapid modulation, possibly important to the ability of neutrophils to adhere to and then migrate through vessel walls to localize at sites of inflammation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON F., Jr, SMITH M. R., WOOD W. B., Jr Studies on the pathogenesis of acute inflammation. I. The inflammatory reaction to thermal injury as observed in the rabbit ear chamber. J Exp Med. 1955 Dec 1;102(6):655–668. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.6.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton A., Born G. V. Quantitative investigations of the adhesiveness of circulating polymorphonuclear leucocytes to blood vessel walls. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):447–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley J. E., Pearson J. D., Carleton J. S., Hutchings A., Gordon J. L. Interaction of leukocytes with vascular cells in culture. J Cell Sci. 1978 Oct;33:85–101. doi: 10.1242/jcs.33.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley J. E., Pearson J. D., Hutchings A., Carleton J. S., Gordon J. L. Granulocyte migration through endothelium in culture. J Cell Sci. 1979 Aug;38:237–248. doi: 10.1242/jcs.38.1.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan M. R., Vazquez M. J., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Arachidonic acid metabolism and the adhesion of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes to cultured vascular endothelial cells. Blood. 1983 Oct;62(4):889–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTWRIGHT G. E., ATHENS J. W., WINTROBE M. M. THE KINETICS OF GRANULOPOIESIS IN NORMAL MAN. Blood. 1964 Dec;24:780–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Quinn J. H., Winn H. J., Lanigan J. M., Dellepella P., Colvin R. B. Fibronectin is produced by blood vessels in response to injury. J Exp Med. 1982 Aug 1;156(2):646–651. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.2.646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Dalmasso A. P., Brighan K. L., Jacob H. S. Hemodialysis leukopenia. Pulmonary vascular leukostasis resulting from complement activation by dialyzer cellophane membranes. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):879–888. doi: 10.1172/JCI108710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D. E., Moldow C. F., Yamada O., Jacob H. S. Granulocyte aggregation as a manifestation of membrane interactions with complement: possible role in leukocyte margination, microvascular occlusion, and endothelial damage. Semin Hematol. 1979 Apr;16(2):140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D., White J. G., Dalmosso A. P., Jacob H. S. Complement (C5-a)-induced granulocyte aggregation in vitro. A possible mechanism of complement-mediated leukostasis and leukopenia. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):260–264. doi: 10.1172/JCI108763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curwen K. D., Kim H. Y., Vazquez M., Handin R. I., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Platelet adhesion to cultured vascular endothelial cells. A quantitative monolayer adhesion assay. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Sep;100(3):425–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahinden C., Galanos C., Fehr J. Granulocyte activation by endotoxin. I. Correlation between adherence and other granulocyte functions, and role of endotoxin structure on biologic activity. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):857–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOREY H. W., GRANT L. H. Leucocyte migration from small blood vessels stimulated with ultraviolet light: an electron-microscope study. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82:13–17. doi: 10.1002/path.1700820103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehr J., Jacob H. S. In vitro granulocyte adherence and in vivo margination: two associated complement-dependent functions. Studies based on the acute neutropenia of filtration leukophoresis. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):641–652. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Hugli T. E. Partial characterization of human C5a anaphylatoxin. I. Chemical description of the carbohydrate and polypeptide prtions of human C5a. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1688–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Wright D. G., Schiffmann E. Role of secretory events in modulating human neutrophil chemotaxis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1364–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI109257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Buchanan M. R. Interactions of platelets and leukocytes with vascular endothelium: in vitro studies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;401:171–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S. Human vascular smooth muscle in culture. Growth and ultrastructure. Lab Invest. 1975 Jul;33(1):16–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr Culture of vascular endothelium. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ham R. G. Dermal fibroblasts. Methods Cell Biol. 1980;21A:255–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt D. E., Bowers T. K., Lammi-Keefe C. J., Jacob H. S., Craddock P. R. Granulocyte aggregometry: a sensitive technique for the detection of C5a and complement activation. Blood. 1980 Jun;55(6):898–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt D. E., Craddock P. R., McCullough F., Kronenberg R. S., Dalmasso A. P., Jacob H. S. Complement activation and pulmonary leukotasis during nylon fiber filtration leukapheresis. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Larsen G. L., Webster R. O., Mitchell B. C., Goins A. J., Henson J. E. Pulmonary microvascular alterations and injury induced by complement fragments: synergistic effect of complement activation, neutrophil sequestration, and prostaglandins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;384:287–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb21379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Oades Z. G. Stimulation of human neutrophils by soluble and insoluble immunoglobulin aggregates. Secretion of granule constituents and increased oxidation of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):1053–1061. doi: 10.1172/JCI108152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Schwartzman N. A., Zanolari B. Intracellular control of human neutrophil secretion. II. Stimulus specificity of desensitization induced by six different soluble and particulate stimuli. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):754–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R. L., Briggs R. T., Karnovsky M. J. The adhesive interaction between polymorphonuclear leukocytes and endothelial cells in vitro. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):423–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R. L., Folger R., Haering W. A., Ware B. R., Karnovsky M. J. Adhesion of leukocytes to endothelium: roles of divalent cations, surface charge, chemotactic agents and substrate. J Cell Sci. 1980 Oct;45:73–86. doi: 10.1242/jcs.45.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh C. R., Jr, Kirkpatrick C. H. A microtiter assay for human monocyte activation by lymphokines. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Aug 3;72(1):207–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90449-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H. U., Gerber H., Hess M. W., Cottier H. Studies on the regulation of the neutrophil chemotactic response using a rapid and reliable method for measuring random migration and chemotaxis of neutrophil granulocytes. Agents Actions. 1976 Feb;6(1-3):326–339. doi: 10.1007/BF01972250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackie J. M. The aggregation of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN's): effects of agents which affect the acute inflammatory response and correlation with secretory activity. Inflammation. 1977 Mar;2(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00920870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackie J. M., de Bono D. Interactions of neutrophil granulocytes (PMNs) and endothelium in vitro. Microvasc Res. 1977 Jan;13(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(77)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen G. L., McCarthy K., Webster R. O., Henson J., Henson P. M. A differential effect of C5a and C5a des Arg in the induction of pulmonary inflammation. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jul;100(1):179–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHESI V. T., FLOREY H. W. Electron micrographic observations on the emigration of leucocytes. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1960 Oct;45:343–348. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1960.sp001489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Macarak E. J., Kefalides N. A. Comparative adherence of granulocytes to endothelial monolayers and nylon fiber. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):697–702. doi: 10.1172/JCI108981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall C. E., De Chatelet L. R., Brown D., Lachmann P. New biological activity following intravascular activation of the complement cascade. Nature. 1974 Jun 28;249(460):841–843. doi: 10.1038/249841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. L., Henson J. E., Henson P. M. Phagocytosis of senescent neutrophils by human monocyte-derived macrophages and rabbit inflammatory macrophages. J Exp Med. 1982 Aug 1;156(2):430–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Effect of intravascular complement activation on granulocyte adhesiveness and distribution. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):731–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Showell H. J., Vitkauskas G., Becker E. L., Ward P. A. Selective neutrophil desensitization to chemotactic factors. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):564–572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A. Chemotactic factor influences on the aggregation, swelling, and foreign surface adhesiveness of human leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1978 Mar;90(3):537–550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A. Neutrophil aggregation and swelling induced by chemotactic agents. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):232–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Showell H. J., Ward P. A. Influence of extracellular Ca2+ and Mg2+ on chemotactic factor-induced neutrophil aggregation. Inflammation. 1977 Dec;2(4):265–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00921006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Showell H. J., Ward P. A. Neutropenia induced by systemic infusion of chemotactic factors. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1586–1589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D., Carleton J. S., Beesley J. E., Hutchings A., Gordon J. L. Granulocyte adhesion to endothelium in culture. J Cell Sci. 1979 Aug;38:225–235. doi: 10.1242/jcs.38.1.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Mortara M., Whitaker C. Methods for microcarrier culture of bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells avoiding the use of enzymes. Tissue Cell. 1980;12(4):619–635. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(80)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. O., Henson P. M., Henson J., Webster R. O. Lung inflammation induced by complement-derived chemotactic fragments in the alveolus. Lab Invest. 1980 May;42(5):547–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. P., Lackie J. M., Wilkinson P. C. The effects of chemotactic factors on the adhesiveness of rabbit neutrophil granulocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Aug;122(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90571-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub N. C., Schultz E. L., Albertine K. H. Leucocytes and pulmonary microvascular injury. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;384:332–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb21382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonnesen M. G., Smedly L., Goins A., Henson P. M. The microvasculature in inflammation. Agents Actions Suppl. 1982;11:25–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther B. T., Ohman R., Roseman S. A quantitative assay for intercellular adhesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1569–1573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. O., Henson P. M. Rapid micromeasurement of neutrophil exocytosis. Inflammation. 1978 Jun;3(2):129–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00910734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. O., Hong S. R., Johnston R. B., Jr, Henson P. M. Biologial effects of the human complement fragments C5a and C5ades Arg on neutrophil function. Immunopharmacology. 1980 Jun;2(3):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(80)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]